Python调用C++/CUDA
CUDA的核函数可以指定GPU来计算调用,这在深度学习网络模型计算等方面十分有用,CUDA编程中核函数需要写在.cu文件中。
这里介绍如何编写一个核函数.cu,通过.cpp调用该核函数,并将cpp通过pybind11打包成python可调用的.pyd文件。
一、示例代码
本文的示例代码来源于:https://github.com/torstem/demo-cuda-pybind11,共有4个文件:

使用代码时需要对gpu_library.cu和CMakeLists.txt进行一点修改:
gpu_library.cu的头需要插入:
#include CMakeLists.txt中需要设置PythonLib的路径,故txt中第3行被替换为:
set(PythonLibs required PATHS "C:\\Python27\\ArcGIS10.7\\libs")
懒得下载的可以复制以下代码制作示例文件:
gpu_library.cu
#include gpu_library.cpp
#include CMakeLists.txt
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.8)
find_package(CUDA)
set(PythonLibs required PATHS "C:\\Python27\\ArcGIS10.7\\libs")
include_directories(${PYTHON_INCLUDE_DIRS})
set(CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS "${CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS} -std=c++11")
cuda_add_library(gpu_library SHARED
gpu_library.cpp
gpu_library.cu)
target_link_libraries(gpu_library
${PYTHON_LIBRARIES}
cudart)
set_target_properties(gpu_library PROPERTIES PREFIX "")
二、CMake编译
编译之前需要:(1)创建编译文件夹“build”;(2)拷贝pybind11文件夹。
编译依旧使用CMake-gui,平台按照自己电脑选,这里是x64的:

输入源目录、编译目录,然后依次点“Configure”和"Generate"

这样就编译成功了,然后打开编译好的VS工程(“Open Project”)

三、VS生成
1、VS配置
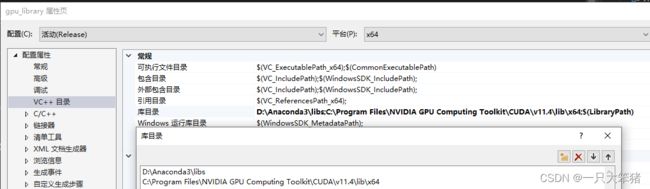
配置库目录:要把CUDA的lib目录、python的lib目录都放进去
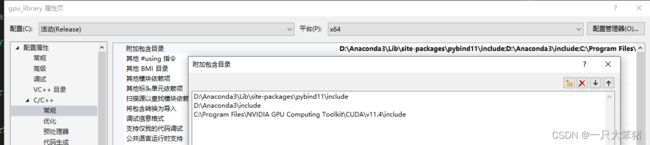
配置附加包含目录:把python的include、CUDA的include和pybind11的include目录都放进去
2、生成
配置完成之后直接:“生成”-“生成gpu_library”
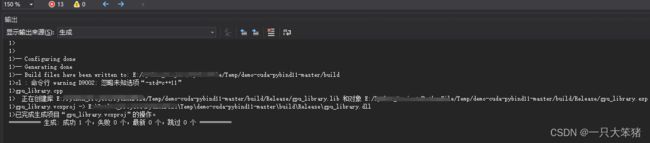
有一个Warning,应该是CMakeLists.txt中set(CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS “${CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS} -std=c++11”)写的有问题,但是问题不大,成功生成了gpu_library.dll。
3、import测试
要在python中import成功,首先需要是.pyd文件,并且放在python直接可以找到的路径下,所以将生成的.dll文件拷贝到“D:\Anaconda3\Lib\site-packages”里面,并且修改后缀名为.pyd(没错,直接重命名修改)。
运行一下“test.py”:
import gpu_library
import numpy
vec = numpy.linspace(0,1,10)
print("before: ", vec)
gpu_library.multiply_with_scalar(vec, 10)
print("after: ", vec)
