树莓派(四)adb命令控制手机打开APP并完成点击操作
打开界面-解决方案:
使用adb命令控制手机打开某app界面,通过模拟点击需要坐标点,完成相应功能
这里补充些adb命令:
- 安装应用
adb install C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\Root.apk- 卸载应用
adb uninstall com.baidu.map.location- 获取应用名称
adb shell dumpsys window | grep mCurrentFocus- 启动应用
adb shell am start -n com.test.provider/.MainActivity
- 停止应用
adb shell am force-stop com.ss.android.ugc.aweme更多可见 Android中常用的adb shell命令
例如:如何获取抖音的包名并打开? 首先获取app的包名以及当前页面的activity
adb shell dumpsys window windows | findstr "Current"
其中 “com.ss.android.ugc.aweme” 就是抖音的包名,后面的“com.ss.android.ugc.aweme.splash.SplashActivity” 就是抖音的页面activity
这样就可以直接使用adb打开抖音了
adb shell am start -n com.ss.android.ugc.aweme/com.ss.android.ugc.aweme.splash.SplashActivity
解析xml文件-解决方案:
获取app界面元素坐标的方法可见上一篇笔记,这里通过解析xml文件自动获取并点击
补充xml文件的内容和操作: xml处理模块
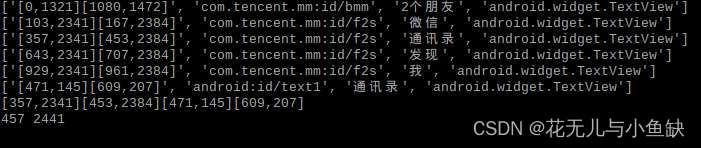
例如:获取微信通讯录界面的xml文件,并解析出“通讯录”元素的坐标位置
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
//获取xml文件
tree = ET.parse("/home/Desktop/window_dump.xml")
ls = []
m = []
for i in tree.iter(tag='node'):
//筛选text属性不为空的值
if i.attrib['text']:
//添加需要的属性信息并展示
ls.append([i.attrib['bounds'],i.attrib['resource-id'],i.attrib['text'], i.attrib['class']])
//筛选指定按钮位置
if i.attrib['text']=='公众号':
m.append(i.attrib['bounds'])
//换行查看信息
for e in ls:
print(e)
//转换列表为字符串
n = ''.join(m)
print(n)
//分别获取x、y坐标值
a = (n[1:n.index(',')])
b = (n[n.index(',')+1:n.index(']')])
print(a,b)结果输出如下,这样就可以通过adb命令模拟点击坐标位置了 'adb shell input tap %s %s'%(a,b)
补充python截取字符串指定内容的方法,有 a='123_abc':
- split()
a.split('_') # 结果 ['123','abc']
a.split('_')[0] # 结果 '123'- index()
ind = a.index('_') # 结果 3
a[:ind] # 结果 '123'
a[ind+1:] # 结果 'abc'
// index()相比于split()的优势在于,可以指定开始索引和结束索引,如a.index('_',0,5)- find()
ine = a.find('_') # 结果 3
a[:ine] # 结果 '123'
//find()相比于index()的优势是,若字符串中不包含'_',find()会返回-1,index()则会报错补充问题:
python报错:(No module named 'xml.etree'; 'xml' is not a package)
原因在于 import模块导入加载的顺序。
python首先查找当前路径、然后查找lib目录、site-packages目录(Python\Lib\site-packages)和环境变量PYTHONPATH设置的目录。
也就是若用户命名了一个文件名为xml.py时,import 模块会先加载我们写的xml.py文件,导致错误
所以解决办法是 xml.py重命名!不要xml直接作为文件名称!