【Detectron2】代码库学习-5.标注格式- 矩形框, 旋转框,关键点, mask, 实例标注,IOU计算, 旋转框IOU计算,
文章目录
-
- Detectron2 内置的标注格式
- BoxMode 表示方式
- 实用API
- RotatedBoxes
- Instances 实例标注
- Keypoints
- Masks
- 结语
Detectron2 内置的标注格式
- Boxes
- RotatedBoxes
- BitMasks
- PolygonMasks
- ROIMasks
- Keypoints
- Instances
- ImageList
BoxMode 表示方式
- XYXY_ABS
- XYWH_ABS
- XYXY_REL # 相对模式
- XYWH_REL # 相对模式
- XYWHA_ABS # 带角度的旋转框 xc, yc 中心点坐标; A, 逆时针度数
实用API
成对Boxes 交集计算
def pairwise_intersection(boxes1: Boxes, boxes2: Boxes) -> torch.Tensor:
"""
Given two lists of boxes of size N and M,
compute the intersection area between __all__ N x M pairs of boxes.
The box order must be (xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax)
Args:
boxes1,boxes2 (Boxes): two `Boxes`. Contains N & M boxes, respectively.
Returns:
Tensor: intersection, sized [N,M].
"""
boxes1, boxes2 = boxes1.tensor, boxes2.tensor
width_height = torch.min(boxes1[:, None, 2:], boxes2[:, 2:]) - torch.max(
boxes1[:, None, :2], boxes2[:, :2]
) # [N,M,2]
width_height.clamp_(min=0) # [N,M,2]
intersection = width_height.prod(dim=2) # [N,M]
return intersection
```
成对Boxes IOU 计算
```python
def pairwise_iou(boxes1: Boxes, boxes2: Boxes) -> torch.Tensor:
"""
Given two lists of boxes of size N and M, compute the IoU
(intersection over union) between **all** N x M pairs of boxes.
The box order must be (xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax).
Args:
boxes1,boxes2 (Boxes): two `Boxes`. Contains N & M boxes, respectively.
Returns:
Tensor: IoU, sized [N,M].
"""
area1 = boxes1.area() # [N]
area2 = boxes2.area() # [M]
inter = pairwise_intersection(boxes1, boxes2)
# handle empty boxes
iou = torch.where(
inter > 0,
inter / (area1[:, None] + area2 - inter),
torch.zeros(1, dtype=inter.dtype, device=inter.device),
)
return iou
RotatedBoxes
旋转框 表示 N x 5, N个 框, cx, cy, w,h, angle 。 旋转框角度 无范围限制, 推荐 在 [-180, 180)
旋转角表示法:


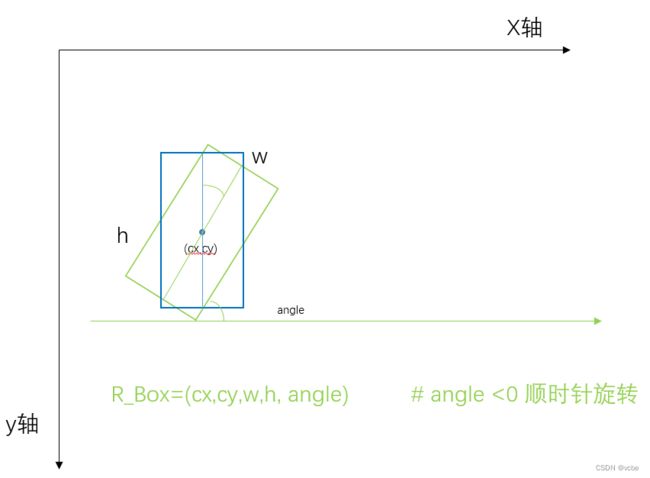
def inside_box(self, box_size: Tuple[int, int], boundary_threshold: int = 0) -> torch.Tensor:
支持旋转框尺度放缩,
def scale(self, scale_x: float, scale_y: float) -> None:
"""
Scale the rotated box with horizontal and vertical scaling factors
Note: when scale_factor_x != scale_factor_y,
the rotated box does not preserve the rectangular shape when the angle
is not a multiple of 90 degrees under resize transformation.
Instead, the shape is a parallelogram (that has skew)
Here we make an approximation by fitting a rotated rectangle to the parallelogram.
"""
self.tensor[:, 0] *= scale_x
self.tensor[:, 1] *= scale_y
theta = self.tensor[:, 4] * math.pi / 180.0
c = torch.cos(theta)
s = torch.sin(theta)
# In image space, y is top->down and x is left->right
# Consider the local coordintate system for the rotated box,
# where the box center is located at (0, 0), and the four vertices ABCD are
# A(-w / 2, -h / 2), B(w / 2, -h / 2), C(w / 2, h / 2), D(-w / 2, h / 2)
# the midpoint of the left edge AD of the rotated box E is:
# E = (A+D)/2 = (-w / 2, 0)
# the midpoint of the top edge AB of the rotated box F is:
# F(0, -h / 2)
# To get the old coordinates in the global system, apply the rotation transformation
# (Note: the right-handed coordinate system for image space is yOx):
# (old_x, old_y) = (s * y + c * x, c * y - s * x)
# E(old) = (s * 0 + c * (-w/2), c * 0 - s * (-w/2)) = (-c * w / 2, s * w / 2)
# F(old) = (s * (-h / 2) + c * 0, c * (-h / 2) - s * 0) = (-s * h / 2, -c * h / 2)
# After applying the scaling factor (sfx, sfy):
# E(new) = (-sfx * c * w / 2, sfy * s * w / 2)
# F(new) = (-sfx * s * h / 2, -sfy * c * h / 2)
# The new width after scaling tranformation becomes:
# w(new) = |E(new) - O| * 2
# = sqrt[(sfx * c * w / 2)^2 + (sfy * s * w / 2)^2] * 2
# = sqrt[(sfx * c)^2 + (sfy * s)^2] * w
# i.e., scale_factor_w = sqrt[(sfx * c)^2 + (sfy * s)^2]
#
# For example,
# when angle = 0 or 180, |c| = 1, s = 0, scale_factor_w == scale_factor_x;
# when |angle| = 90, c = 0, |s| = 1, scale_factor_w == scale_factor_y
self.tensor[:, 2] *= torch.sqrt((scale_x * c) ** 2 + (scale_y * s) ** 2)
# h(new) = |F(new) - O| * 2
# = sqrt[(sfx * s * h / 2)^2 + (sfy * c * h / 2)^2] * 2
# = sqrt[(sfx * s)^2 + (sfy * c)^2] * h
# i.e., scale_factor_h = sqrt[(sfx * s)^2 + (sfy * c)^2]
#
# For example,
# when angle = 0 or 180, |c| = 1, s = 0, scale_factor_h == scale_factor_y;
# when |angle| = 90, c = 0, |s| = 1, scale_factor_h == scale_factor_x
self.tensor[:, 3] *= torch.sqrt((scale_x * s) ** 2 + (scale_y * c) ** 2)
# The angle is the rotation angle from y-axis in image space to the height
# vector (top->down in the box's local coordinate system) of the box in CCW.
#
# angle(new) = angle_yOx(O - F(new))
# = angle_yOx( (sfx * s * h / 2, sfy * c * h / 2) )
# = atan2(sfx * s * h / 2, sfy * c * h / 2)
# = atan2(sfx * s, sfy * c)
#
# For example,
# when sfx == sfy, angle(new) == atan2(s, c) == angle(old)
self.tensor[:, 4] = torch.atan2(scale_x * s, scale_y * c) * 180 / math.pi
支持计算成对旋转框 IOU 计算,
def pairwise_iou(boxes1: RotatedBoxes, boxes2: RotatedBoxes) -> None:
"""
Given two lists of rotated boxes of size N and M,
compute the IoU (intersection over union)
between **all** N x M pairs of boxes.
The box order must be (x_center, y_center, width, height, angle).
Args:
boxes1, boxes2 (RotatedBoxes):
two `RotatedBoxes`. Contains N & M rotated boxes, respectively.
Returns:
Tensor: IoU, sized [N,M].
"""
return pairwise_iou_rotated(boxes1.tensor, boxes2.tensor)
Instances 实例标注
Instances数据结构包含一个图像的所有实例,如Boxes, Masks,可通过域操作设置和获取值。所有属性对应的实例数量许保持一致。
instances=Instances((640,640), ...)
instances.gt_boxes= Boxes(...)
pred_boxes=instances.pred_masks
可以通过python 语法判断是否包含特定结果。
assert "gt_mask" in instances
可以通过len获取实例个数
print(len(instances))
可以通过 index 获取特定实例
# 获取得分大于0.9 的 实例
confident_detections = instances[instances.scores > 0.9]
Keypoints
存储关键点标注数据,
gt_points= keypoints.gt_keypoints # (N, K,3)
# N 个实例,每个实例K 个点, 每个点 x,y, visible
可将 keypoint 转为 方形heatmap 格式。
heatmaps= keypoints.to_heatmap(boxes, heatmap_size)
可将预测heatmap 转换为 keypoint 格式
Masks
通过COCO API 将多边形转为 Masks
def polygons_to_bitmask(polygons: List[np.ndarray], height: int, width: int) -> np.ndarray:
"""
Args:
polygons (list[ndarray]): each array has shape (Nx2,)
height, width (int)
Returns:
ndarray: a bool mask of shape (height, width)
"""
if len(polygons) == 0:
# COCOAPI does not support empty polygons
return np.zeros((height, width)).astype(np.bool)
rles = mask_util.frPyObjects(polygons, height, width)
rle = mask_util.merge(rles)
return mask_util.decode(rle).astype(np.bool)
BitMasks 标注
PolygonMasks
ROI Masks
均支持 get_bounding box 和 计算面积。
结语
detectron2 提供了多种标注类型的标准数据结构和丰富多样的API, 方便直接使用或者在其他项目中使用。