数据结构入门
文章目录
- 栈
-
- AB1 【模板】栈
- 题解
- AB2 栈的压入、弹出序列
- 题解
- AB3 有效括号序列
- 题解
- AB4 逆波兰表达式求值
- 题解
- AB5 点击消除
- 题解
- *AB6 表达式求值
- 题解
- 队列
-
- AB7 【模板】队列
- 题解
- *AB8 【模板】循环队列
- 题解
- 链表
-
- *AB9 【模板】链表
- 题解
- AB10 反转链表
- 题解
- AB11 合并两个排序的链表
- AB12 删除链表的节点
- 题解
- 图论
-
- *AB13 【模板】拓扑排序
- 题解
- *AB14 最小生成树
- 题解
- *AB15 【模板】单源最短路2
- 题解
- 二叉树
-
- AB16 实现二叉树先序,中序和后序遍历
- 题解
- AB17 从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
- 题解
- 堆
-
- AB18 【模板】堆
- 题解
栈
AB1 【模板】栈
描述
请你实现一个栈。
操作:
push x:将 加x\x 入栈,保证 x\x 为 int 型整数。
pop:输出栈顶,并让栈顶出栈
top:输出栈顶,栈顶不出栈
输入描述:
第一行为一个正整数 n\n ,代表操作次数。(1 \leq n \leq 100000)(1≤n≤100000)
接下来的 n\n ,每行为一个字符串,代表一个操作。保证操作是题目描述中三种中的一种。
输出描述:
如果操作为push,则不输出任何东西。
如果为另外两种,若栈为空,则输出 "error“
否则按对应操作输出。
示例1
输入:
6
push 1
pop
top
push 2
push 3
pop
输出:
1
error
3
题解
#include
//gets(str);
fgets(str, 20, stdin);
int n = 0;
if (strncmp("push", str, 4) == 0) {
//cout << strlen(str) << "=" << "strlen(str)" << endl;
for (int i = 5; i < (strlen(str) - 1); i++) {
n = n * 10 + (str[i] - '0');
// cout << n << "="<< "n" << endl;
}
push[first++] = n;
} else if (strncmp("pop", str, 3) == 0) {
if (first == 0)
cout << "error" << endl;
else {
cout << push[first - 1] << endl;
first--;
}
} else if (strncmp("top", str, 3) == 0) {
if (first == 0)
cout << "error" << endl;
else
cout << push[first - 1] << endl;
}
}
}
AB2 栈的压入、弹出序列
描述
输入两个整数序列,第一个序列表示栈的压入顺序,请判断第二个序列是否可能为该栈的弹出顺序。假设压入栈的所有数字均不相等。例如序列1,2,3,4,5是某栈的压入顺序,序列4,5,3,2,1是该压栈序列对应的一个弹出序列,但4,3,5,1,2就不可能是该压栈序列的弹出序列。
- 0<=pushV.length == popV.length <=1000
- -1000<=pushV[i]<=1000
- pushV 的所有数字均不相同
示例1
输入:
[1,2,3,4,5],[4,5,3,2,1]
返回值:
true
说明:
可以通过push(1)=>push(2)=>push(3)=>push(4)=>pop()=>push(5)=>pop()=>pop()=>pop()=>pop()
这样的顺序得到[4,5,3,2,1]这个序列,返回true
示例2
输入:
[1,2,3,4,5],[4,3,5,1,2]
返回值:
false
说明:
由于是[1,2,3,4,5]的压入顺序,[4,3,5,1,2]的弹出顺序,要求4,3,5必须在1,2前压入,且1,2不能弹出,但是这样压入的顺序,1又不能在2之前弹出,所以无法形成的,返回false
题解
class Solution {
public:
bool IsPopOrder(vector<int> pushV,vector<int> popV) {
if(pushV.size()!=popV.size()||pushV.size()==0||popV.size()==0)
return false;
int len=0;
int n=pushV.size();
stack<int>s;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
s.push(pushV[i]);
while((!s.empty())&&(len<n)&&(s.top()==popV[len]))
{
s.pop();
len++;
}
}
return s.empty();
}
};
AB3 有效括号序列
描述
给出一个仅包含字符’(‘,’)‘,’{‘,’}‘,’[‘和’]',的字符串,判断给出的字符串是否是合法的括号序列
括号必须以正确的顺序关闭,"()“和”()[]{}“都是合法的括号序列,但”(]“和”([)]"不合法。
数据范围:字符串长度 0\le n \le 100000≤n≤10000
要求:空间复杂度 O(n)O(n),时间复杂度 O(n)O(n)
示例1
输入:
"["
返回值:
false
示例2
输入:
"[]"
返回值:
true
题解
class Solution {
public:
/**
*
* @param s string字符串
* @return bool布尔型
*/
bool isValid(string s) {
// write code here
if(s.size()==0) return false;
stack<char>st;
for(int i=0;i<s.size();i++)
{
if(s[i]=='(')
st.push(')');
else if(s[i]=='{')
st.push('}');
else if(s[i]=='[')
st.push(']');
else
{
if(st.empty()||(st.top()!=s[i]))
return false;
st.pop();
}
}
return st.empty();
}
};
AB4 逆波兰表达式求值
描述
给定一个逆波兰表达式,求表达式的值。
数据范围:表达式长度满足 1 \le n \le 10^4 \1≤n≤10
4 ,表达式中仅包含数字和 + ,- , * , / ,其中数字的大小满足 |val| \le 200 \∣val∣≤200 。
示例1
输入:
["2","1","+","4","*"]
返回值:
12
示例2
输入:
["2","0","+"]
返回值:
2
题解
class Solution {
public:
/**
* 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可
*
*
* @param tokens string字符串vector
* @return int整型
*/
int evalRPN(vector<string>& tokens) {
// write code here
stack<int>st;
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < tokens.size(); i++) {
if (tokens[i] == "+" || tokens[i] == "-" || tokens[i] == "*" ||
tokens[i] == "/") {
int a=st.top();
st.pop();
int b=st.top();
st.pop();
if(tokens[i]=="+")st.push(a+b);
if(tokens[i]=="-")st.push(b-a);
if(tokens[i]=="*")st.push(a*b);
if(tokens[i]=="/")st.push(b/a);
}
else
{
int n=stoi(tokens[i]);
st.push(n);
}}
return st.top();
}
};
AB5 点击消除
描述
牛牛拿到了一个字符串。
他每次“点击”,可以把字符串中相邻两个相同字母消除,例如,字符串"abbc"点击后可以生成"ac"。
但相同而不相邻、不相同的相邻字母都是不可以被消除的。
牛牛想把字符串变得尽可能短。他想知道,当他点击了足够多次之后,字符串的最终形态是什么?
输入描述:
一个字符串,仅由小写字母组成。(字符串长度不大于300000)
输出描述:
一个字符串,为“点击消除”后的最终形态。若最终的字符串为空串,则输出0。
示例1
输入:
abbc
输出:
ac
示例2
输入:
abba
输出:
0
示例3
输入:
bbbbb
输出:
b
题解
#include
for (int i = 0; i < str.size(); i++) {
if (st.empty())
st.push(str[i]);
else {
if (st.top() == str[i]) {
st.pop();
} else st.push(str[i]);
}
}
int n = st.size();
if (n == 0) cout << "0" << endl;
else {
char s[n + 1];
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
s[i] = st.top();
//printf("top=%c\n",st.top());
st.pop();
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (i != (n - 1))
printf("%c", s[i]);
else
printf("%c\n", s[i]);
}
}
}
*AB6 表达式求值
描述
请写一个整数计算器,支持加减乘三种运算和括号。
数据范围:0\le |s| \le 1000≤∣s∣≤100,保证计算结果始终在整型范围内
要求:空间复杂度: O(n)O(n),时间复杂度 O(n)O(n)
示例1
输入:
"1+2"
返回值:
3
示例2
输入:
"(2*(3-4))*5"
返回值:
-10
示例3
输入:
"3+2*3*4-1"
返回值:
26
题解
class Solution {
public:
/**
* 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可
* 返回表达式的值
* @param s string字符串 待计算的表达式
* @return int整型
*/
int priority(string op)
{
int priority;
if(op=="*"||op=="/") priority=2;
if(op=="+"||op=="-") priority=1;
if(op=="(") priority=0;
return priority;
}
int Trans(string s)
{
//符号栈
stack<string>sign;
//后缀表达式的栈
stack<string> postpression;
//将中缀表达式化为后缀表达式
for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++)
{
//判断是否遇到操作数
string ans;
if (s[i] >= '0' && s[i] <= '9')
{
ans=ans+s[i];
while (s[i+1] >= '0' && s[i+1] <= '9')
{
i++;
ans = ans + s[i];
// cout<<"**********"<
}
postpression.push(ans);
// cout << "ans=" << ans << endl;
}
//判断是否遇到操作数
// if (s[i] == '+' || s[i] == '-' || s[i] == '*')
else if (s[i] == '+' || s[i] == '-' || s[i] == '*' || s[i] == '(' || s[i] == ')') //不是字符
{
//首先判断栈是否为空
if (sign.empty())
{
string str1=string(1,s[i]);
sign.push(str1);
// cout<<"str1="<
}
//栈不为空 ,若左括号入栈
else if (s[i] == '(')
{
string str2 = string(1, s[i]);
sign.push(str2);
// cout << "str2=" << str2 << endl;
}
else if (s[i] == ')')
{
while (sign.top() != "(")
{
postpression.push(sign.top());
sign.pop();
}
sign.pop();
// cout<<")="<
}
else
{
string str = string(1, s[i]);
while (priority(str) <= priority(sign.top()))
{
postpression.push(sign.top());
// cout << "xiao=" << sign.top() <
sign.pop();
//栈为空,停止
if (sign.empty())
break;
}
string str3 = string(1, s[i]);
sign.push(str3);
// cout << "str3=" << str3 << endl;
}
}
}
while (!sign.empty())
{
postpression.push(sign.top());
sign.pop();
}
stack<string>str4;
while(!postpression.empty())
{
str4.push(postpression.top());
// cout << "postpression.top="<
postpression.pop();
}
stack<int> st;
while(!str4.empty())
{
if (str4.top() == "+" || str4.top() == "-" || str4.top() == "*")
{
int a = st.top();
st.pop();
int b = st.top();
st.pop();
if (str4.top() == "+")
st.push(a + b);
if (str4.top() == "-")
st.push(b - a);
if (str4.top() == "*")
st.push(a * b);
}
else
{
int n = stoi(str4.top());
st.push(n);
}
str4.pop();
}
// cout<<"st.empty="<
// cout << "st.top=" <
return st.top();
}
int solve(string s)
{
return Trans(s);
}
};
队列
AB7 【模板】队列
描述
请你实现一个队列。
操作:
push x:将 x\x 加入队尾,保证 x\x 为 int 型整数。
pop:输出队首,并让队首出队
front:输出队首:队首不出队
输入描述:
第一行为一个正整数 n\n ,代表操作次数。(1 \leq n \leq 100000)(1≤n≤100000)
接下来的 n\n ,每行为一个字符串,代表一个操作。保证操作是题目描述中三种中的一种。
输出描述:
如果操作为push,则不输出任何东西。
如果为另外两种,若队列为空,则输出 "error“
否则按对应操作输出。
示例1
输入:
6
push 1
pop
front
push 2
push 3
pop
输出:
1
error
2
题解
#include*AB8 【模板】循环队列
描述
请你实现一个循环队列,该循环队列可利用的空间大小等于nn个int型变量的大小。
操作:
push x:将xx加入到循环队列尾端。若循环队列已满,输出"full"(不含引号),否则不输出任何内容。保证xx为int型整数。
front:输出队首元素,队首不出队。若队列为空,输出"empty"(不含引号)。
pop:输出队首元素,且队首出队。若队列为空,输出"empty"(不含引号)。
输入描述:
第一行输入两个整数n,qn,q (1\le n,q \le 10^51≤n,q≤10
5
),表示循环队列可利用的空间大小和操作次数。
接下来的qq行,每行一个字符串,表示一个操作。保证操作是题目描述中的一种。
输出描述:
按对应操作要求输出。
示例1
输入:
3 10
push 1
push 2
front
push 3
push 4
pop
pop
pop
front
pop
输出:
1
full
1
2
3
empty
empty
题解
#include 链表
*AB9 【模板】链表
描述
请你实现一个链表。
操作:
insert x y:将yy加入链表,插入在第一个值为xx的结点之前。若链表中不存在值为xx的结点,则插入在链表末尾。保证xx,yy为int型整数。
delete x:删除链表中第一个值为xx的结点。若不存在值为xx的结点,则不删除。
输入描述:
第一行输入一个整数nn (1\le n \le 10^41≤n≤10
4 ),表示操作次数。接下来的nn行,每行一个字符串,表示一个操作。保证操作是题目描述中的一种。
输出描述:
输出一行,将链表中所有结点的值按顺序输出。若链表为空,输出"NULL"(不含引号)。
示例1
输入:
5
insert 0 1
insert 0 3
insert 1 2
insert 3 4
delete 4
输出:
2 1 3
题解
#includeAB10 反转链表
描述
给定一个单链表的头结点pHead(该头节点是有值的,比如在下图,它的val是1),长度为n,反转该链表后,返回新链表的表头。
数据范围: 0\leq n\leq10000≤n≤1000
要求:空间复杂度 O(1)O(1) ,时间复杂度 O(n)O(n) 。
如当输入链表{1,2,3}时,
经反转后,原链表变为{3,2,1},所以对应的输出为{3,2,1}。
示例1
输入:
{1,2,3}
返回值:
{3,2,1}
示例2
输入:
{}
返回值:
{}
说明:
空链表则输出空
题解
struct ListNode* ReverseList(struct ListNode* pHead ) {
// write code here
// write code here
int number[1002];
struct ListNode *Head=pHead;
int n=0;
struct ListNode *p=NULL;
struct ListNode *Last;
while(Head!=NULL)
{
number[n++]=Head->val;
Head=Head->next;
}
for(int i=n-1;i>=0;i--)
{
struct ListNode *temp = (struct ListNode *)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode ));
temp->val=number[i];
temp->next=NULL;
if (p == NULL)
{
p=temp;
}
else
{
Last->next=temp;
}
Last=temp;
}
return p;
}
AB11 合并两个排序的链表
描述
输入两个递增的链表,单个链表的长度为n,合并这两个链表并使新链表中的节点仍然是递增排序的。
数据范围: 0 \le n \le 10000≤n≤1000,-1000 \le 节点值 \le 1000−1000≤节点值≤1000
要求:空间复杂度 O(1)O(1),时间复杂度 O(n)O(n)
如输入{1,3,5},{2,4,6}时,合并后的链表为{1,2,3,4,5,6},所以对应的输出为{1,2,3,4,5,6}。
或输入{-1,2,4},{1,3,4}时,合并后的链表为{-1,1,2,3,4,4},所以对应的输出为{-1,1,2,3,4,4},转换过程如下图所示:
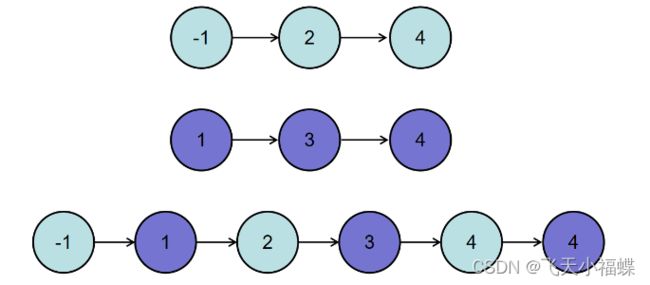
示例1
输入:
{1,3,5},{2,4,6}
返回值:
{1,2,3,4,5,6}
示例2
输入:
{},{}
返回值:
{}
示例3
输入:
{-1,2,4},{1,3,4}
返回值:
{-1,1,2,3,4,4}
void Insert(struct ListNode *Head, struct ListNode *Last,int data)
{
struct ListNode * p=(struct ListNode *)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
p->next=NULL;
p->val=data;
if(Head==NULL)
{
Head=p;
}
else
{
Last->next=p;
}
Last=p;
}
struct ListNode *Merge(struct ListNode *pHead1, struct ListNode *pHead2)
{
// write code here
struct ListNode *List1=pHead1;
struct ListNode *List2 = pHead2;
struct ListNode *Head = NULL;
struct ListNode *Last;
while(List1!=NULL && List2!=NULL)
{
if(List1->val<List2->val)
{
struct ListNode * p=(struct ListNode *)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
p->next=NULL;
p->val=List1->val;
if(Head==NULL)
{
Head=p;
}
else
{
Last->next=p;
}
Last=p;
List1=List1->next;
}
else
{
struct ListNode * p=(struct ListNode *)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
p->next=NULL;
p->val=List2->val;
if(Head==NULL)
{
Head=p;
}
else
{
Last->next=p;
}
Last=p;
List2 = List2->next;
}}
while(List1!=NULL)
{
struct ListNode * p=(struct ListNode *)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
p->next=NULL;
p->val=List1->val;
if(Head==NULL)
{
Head=p;
}
else
{
Last->next=p;
}
Last=p;
List1=List1->next;
}
while(List2!=NULL)
{
struct ListNode * p=(struct ListNode *)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
p->next=NULL;
p->val=List2->val;
if(Head==NULL)
{
Head=p;
}
else
{
Last->next=p;
}
Last=p;
List2 = List2->next;
}
return Head;
}
AB12 删除链表的节点
描述
给定单向链表的头指针和一个要删除的节点的值,定义一个函数删除该节点。返回删除后的链表的头节点。
1.此题对比原题有改动
2.题目保证链表中节点的值互不相同
3.该题只会输出返回的链表和结果做对比,所以若使用 C 或 C++ 语言,你不需要 free 或 delete 被删除的节点
数据范围:
0<=链表节点值<=10000
0<=链表长度<=10000
示例1
输入:
{2,5,1,9},5
返回值:
{2,1,9}
说明:
给定你链表中值为 5 的第二个节点,那么在调用了你的函数之后,该链表应变为 2 -> 1 -> 9
示例2
输入:
{2,5,1,9},1
返回值:
{2,5,9}
说明:
给定你链表中值为 1 的第三个节点,那么在调用了你的函数之后,该链表应变为 2 -> 5 -> 9
题解
struct ListNode *deleteNode(struct ListNode *head, int val)
{
// write code here
struct ListNode *p=head;
if(head->val==val)
{
head=head->next;
return head;
}
while(head->next!=NULL)
{
if(head->next->val==val)
{
head->next=head->next->next;
}
head=head->next;
}
return p;
}
图论
*AB13 【模板】拓扑排序
描述
给定一个包含nn个点mm条边的有向无环图,求出该图的拓扑序。若图的拓扑序不唯一,输出任意合法的拓扑序即可。若该图不能拓扑排序,输出-1−1。
输入描述:
第一行输入两个整数n,mn,m ( 1\le n,m \le 2\cdot 10^51≤n,m≤2⋅10 5 ),表示点的个数和边的条数。
接下来的mm行,每行输入两个整数u_i,v_iu i ,v i(1\le u,v \le n1≤u,v≤n),表示u_iu i 到v_ivi之间有一条有向边。
输出描述:
若图存在拓扑序,输出一行nn个整数,表示拓扑序。否则输出-1。
示例1
输入:
5 4
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
输出:
1 2 3 4 5
题解
#include *AB14 最小生成树
描述
一个有 n 户人家的村庄,有 m 条路相互连接着。村里现在要修路,每条路都有一个成本价格,现在请你帮忙计算下,最少需要花费多少钱,就能让这 n 户人家连接起来。
costcost 为一个二维数组,每个元素是一个长度为 3 的一维数组 aa , a[0]a[0] 和 a[1]a[1] 表示村庄 a[0]a[0] 和村庄 a[1]a[1] 有一条路,修这条路的成本价格为 a[2]a[2] 。
每户之间可能有多条道路连接,但不可能自己与自己相连。
进阶: 时间复杂度 O(n+mlogm)O(n+mlogm) , 空间复杂度 O(n)O(n)
示例1
输入:
3,3,[[1,3,3],[1,2,1],[2,3,1]]
返回值:
2
示例2
输入:
2,1,[[1,2,1]]
返回值:
1
题解
class Solution {
public:
/**
* 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可
*
* 返回最小的花费代价使得这n户人家连接起来
* @param n int n户人家的村庄
* @param m int m条路
* @param cost intvector> 一维3个参数,表示连接1个村庄到另外1个村庄的花费的代价
* @return int
*/
static bool cmp(vector<int>&x,vector<int>&y)
{
return x[2]<y[2];
}
int find(vector<int>&parent,int x)
{
if(x!=parent[x])
{
parent[x]=find(parent,parent[x]);
}
return parent[x];
}
int miniSpanningTree(int n, int m, vector<vector<int> >& cost) {
// write code here
vector<int>parent(n+1);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
parent[i]=i;
sort(cost.begin(),cost.end(),cmp);
int sum=0;
for(int i=0;i<cost.size();i++)
{
int u=cost[i][0];
int v=cost[i][1];
int w=cost[i][2];
int pu=find(parent,u);
int pv=find(parent,v);
if(pv!=pu)
{
sum+=w;
parent[pu]=pv;
}
}
return sum;
}
};
*AB15 【模板】单源最短路2
描述
给你一个无向图,图中包含 5000 个点 m 个边,任意两个点之间的距离是 w ,无重边或自环。请求出1号点到n号点的最短距离。
注意:图中可能存在孤立点,即存在点与任意点都没有边相连。如果1号点不能到达n号点,输出-1。
输入描述:
第一行两个整数n和m,表示图的点和边数。
接下来m行,每行三个整数u,v, w,表示u到v有一条无向边, 长度为w。
输出描述:
输出一行,表示1到n的最短路,如不存在,输出-1.
示例1
输入:
4 4
1 2 3
2 4 7
3 4 5
3 1 3
输出:
8
示例2
输入:
4 3
1 2 5
2 3 3
3 1 3
输出:
-1
题解
#include 二叉树
AB16 实现二叉树先序,中序和后序遍历
描述
给定一棵二叉树,分别按照二叉树先序,中序和后序打印所有的节点。
要求:空间复杂度 O(n)O(n),时间复杂度 O(n)O(n)
示例1
输入:
{1,2,3}
返回值:
[[1,2,3],[2,1,3],[2,3,1]]
示例2
输入:
{}
返回值:
[[],[],[]]
题解
class Solution {
public:
/**
*
* @param root TreeNode类 the root of binary tree
* @return int整型vector>
*/
vector<int>pre;
vector<int>mid;
vector<int>post;
vector<vector<int> > threeOrders(TreeNode* root) {
// write code here
if(root!=nullptr)
{
Preorder(root);
Midorder(root);
Postorder(root);
}
vector<vector<int> > tree={pre,mid,post};
return tree;
}
void Preorder(TreeNode *root)//跟左右
{
if(root==NULL) return;
pre.push_back(root->val);
Preorder(root->left);
Preorder(root->right);
}
void Midorder(TreeNode *root)//左根右
{
if(root==NULL) return;
Midorder(root->left);
mid.push_back(root->val);
Midorder(root->right);
}
void Postorder(TreeNode *root)//左右根
{
if(root==NULL) return;
Postorder(root->left);
Postorder(root->right);
post.push_back(root->val);
}
};
AB17 从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
描述
给定一个二叉树的中序与后序遍历结果,请你根据两个序列构造符合这两个序列的二叉树。
例如输入[2,1,4,3,5],[2,4,5,3,1]时,
根据中序遍历的结果[2,1,4,3,5]和后序遍历的结果[2,4,5,3,1]可构造出二叉树{1,2,3,#,#,4,5}。
示例1
输入:
[1],[1]
返回值:
{1}
示例2
输入:
[2,1,4,3,5],[2,4,5,3,1]
返回值:
{1,2,3,#,#,4,5}
题解
class Solution {
public:
/**
* 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可
*
*
* @param inorder int整型vector 中序遍历序列
* @param postorder int整型vector 后序遍历序列
* @return TreeNode类
*/
unordered_map<int, int>pos;
TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& inorder, vector<int>& postorder) {
// write code here
int n=inorder.size();
for(int i=0;i<n;i++) pos[inorder[i]]=i;
return build(inorder,postorder,0,n-1,0,n-1);
}
TreeNode *build(vector<int>& inorder, vector<int>& postorder,int il,int ir,int pl,int pr)
{
if(il>ir||pl>pr) return nullptr;
TreeNode * root=new TreeNode(postorder[pr]);
int k=pos[postorder[pr]]-il;
root->left=build(inorder, postorder, il, il+k-1, pl, pl+k-1);
root->right=build(inorder, postorder, il+k+1, ir, pl+k, pr-1);
return root;
}
};
堆
AB18 【模板】堆
描述
请你实现一个堆(大根堆)。
操作:
push x:将xx加入堆。保证xx为int型整数。不输出任何内容。
top:输出堆顶元素。若堆为空,输出"empty"(不含引号)。
pop:输出堆顶元素,且弹出堆顶。若堆为空,输出"empty"(不含引号)。
输入描述:
第一行输入一个整数nn (1\le n \le 10^51≤n≤10 5 ),表示操作次数。接下来的nn行,每行一个字符串,表示一个操作。保证操作是题目描述中的一种。
输出描述:
按对应操作要求输出。
示例1
输入:
11
push 1
top
push 3
top
push 2
top
pop
pop
pop
top
pop
输出:
1
3
3
3
2
1
empty
empty
题解
#include