动手学深度学习之softmax实现
Softmax回归
回归VS分类
- 回归估计的是一个连续值
- 分类预测一个离散类别
从回归到多类分类
从回归到多类分类—均方损失
- 对类别进行一位有效编码:意思时一位代表一个类别。
$y=[y_1,y_2,…,y_n]^T $
y i = { 1 i f i = y 0 o t h e r w i s e y_i = \left\{\begin{matrix} 1 & if \quad i = y \\ 0& otherwise \end{matrix}\right. yi={10ifi=yotherwise - 使用均方损失训练
- 最大值为预测: y ^ = a r g m a x i o i \hat{y}=\underset{i}{argmax} o_i y^=iargmaxoi
- 需要更置信的识别正确类(大余量): o y − o i ≥ Δ ( y , i ) o_y-o_i \geq \Delta (y,i) oy−oi≥Δ(y,i),意思就是我们对正确类别的置信度特别大,使我们得到的正确类别的置信度 o y o_y oy远远大于其他非正确类别的 o i o_i oi
- 我们希望我们的输出是一个概率(这些概率非负并且和为1),这样我们引入了一个新的函数softmax,我们将softmax作用在o上,得到一个长为n的向量,这个向量具有的属性是:长为n,所有的元素非负且和为1。
y ^ = s o f t m a x ( o ) y i ^ = e x p ( o i ) Σ k e x p ( o k ) \qquad \hat{y}=softmax(o) \\ \qquad \hat{y_i} = \frac{exp(o_i)}{\Sigma _k exp(o_k)} y^=softmax(o)yi^=Σkexp(ok)exp(oi) - 使用y和 y ^ \hat{y} y^的区别作为损失
Softmax和交叉熵损失
- 交叉熵常用来衡量两个概率的区别: H ( p , q ) = ∑ i − p i l o g ( q i ) H(p,q)=\sum_{i} -p_ilog(q_i) H(p,q)=∑i−pilog(qi)
- 将它作为损失: l ( y , y ^ ) = − ∑ i y i l o g y i ^ = − l o g y y ^ l(y,\hat{y})=-\sum_i y_ilog\hat{y_i} = -log\hat{y_y} l(y,y^)=−∑iyilogyi^=−logyy^。式子中第二个等于的意思是对于正确类的交叉熵,对于分类问题我们不关心错误类别,只希望我们的到的正确类别的置信度要够大。
- 其梯度是真实概率和预测概率的区别:\partial_{o_i}l(y,\hat{y}) = softmax(o)_i - y_i。我们的目的就是不断的减小真实的值和我们预测的值之间的区别。
总结
- Softmax回归是一个多分类问题
- 使用softmax操作子得到的是每个类的置信度
- 使用交叉熵来衡量预测和标号的区别
损失函数
L2 Loss
- 均方损失
- l ( y , y ′ ) = 1 2 ( y − y ′ ) 2 l(y,y^{'})=\frac{1}{2}(y-y^{'})^2 l(y,y′)=21(y−y′)2
L1 Loss
- 绝对值损失函数
- l ( y , y ′ = ∣ y − y ′ ∣ l(y,y^{'}=|y-y^{'}| l(y,y′=∣y−y′∣
Huber’s Robust Loss
- 好处是当我们离真实值远的时候保持梯度为一个确定的值,当我们离真实值近的时候梯度回越来越小
- l ( y , y ′ ) = { ∣ y − y ′ ∣ − 1 2 i f ∣ y − y ′ ∣ > 1 1 2 ( y − y ′ ) 2 o t h e r w i s e l(y,y^{'})=\left\{\begin{matrix} |y-y^{'}|-\frac{1}{2} & \quad if|y-y^{'}| > 1 \\ \frac{1}{2}(y-y^{'})^2 & otherwise \end{matrix}\right. l(y,y′)={∣y−y′∣−2121(y−y′)2if∣y−y′∣>1otherwise
图像分类数据集
MNIST数据集是图像分类中广泛使用的数据集之一,但作为基准数据集国语简单。我们将使用类似但更复杂的Fashion-MNIST数据集
import torch
import torchvision
from torch.utils import data
from torchvision import transforms
from d2l import torch as d2l
# svg显示图片
d2l.use_svg_display()
通过框架中的内置函数将Fashion-MNIST数据集下载并读取到内存中
# 通过ToTensor实例将图像数据中PIL类型转变成为32位浮点数格式
# 并除以255使得所有像素的数值均在0到1之间
trans = transforms.ToTensor() # 将图片转换为pytorch的一个tensor
# 从datasets里面下载FashioMNIST这个数据集,root表示存放目录,train表示是否为训练数据集,transform=trans表示拿出来是一堆tensor而不是图片,download表示是否从网上下载
mnist_train = torchvision.datasets.FashionMNIST(root="../data", train=True, transform=trans, download=True)
mnist_test = torchvision.datasets.FashionMNIST(root="../data", train=False, transform=trans, download=True)
len(mnist_train), len(mnist_test)
(60000, 10000)
# 这里表示取出第1个example的第1张图片
mnist_train[0][0].shape # torch.Size([1, 28, 28]) 黑白图片,所以channl数等于1,长和宽都是28
torch.Size([1, 28, 28])
两个可视化数据集的函数
X, y = next(iter(data.DataLoader(mnist_train, batch_size=18)))
d2l.show_images(X.reshape(18, 28, 28), 2, 9, titles=d2l.get_fashion_mnist_labels(y))
array([,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
], dtype=object)
读取小批量数据,大小为batch_size
batch_size = 256
# DataLoader表示给丁数据集,批量大小,shuffle表示是否需要打乱顺序,num_workers表示使用多少进程
train_iter = data.DataLoader(mnist_train, batch_size, shuffle=True, num_workers=d2l.get_dataloader_workers())
# 下面代码的作用是看我们读去数据的速度
timer = d2l.Timer()
for X, y in train_iter:
continue
f'{timer.stop():.2f} sec'
'2.11 sec'
softmax回归从0开始实现
import torch
from IPython import display
from d2l import torch as d2l
# 批量大小,表示我们每次读去256张图片
batch_size = 256
# load_data_fashion_mnist的内部过程和上面一样,这里封装好了,返回的是训练集和测试集的迭代器
train_iter, test_iter = d2l.load_data_fashion_mnist(batch_size)
将展平每个图像,将它们视为长度为784(28*28)的向量。因为我们的数据集有10个类别,所以网络输出维度为10。这里将图像展平的原因是:softmax的输入是一个向量,所以我们需要输入一个向量。
num_inputs = 784
num_outputs = 10
# 这里定义权重,normal表示高斯分布,这里表示均值为0,方差为0.01,形状为(784*10)的矩阵,requires_grad=True表示需要保存梯度
W = torch.normal(0, 0.01, size=(num_inputs, num_outputs), requires_grad=True)
# 对于每一个输出我们都需要一个偏移,这样我们就是要一个长为10的向量
b = torch.zeros(num_outputs, requires_grad=True)
实现softmax
s o f t m a x ( X ) i j = e x p ( X i j ) ∑ k e x p ( X i k ) \qquad softmax(X)_{ij} = \frac{exp(X_{ij})}{\sum_k exp(X_{ik})} softmax(X)ij=∑kexp(Xik)exp(Xij)
def softmax(X):
# 这里的意思就是对每一个元素做指数计算
X_exp = torch.exp(X)
# 这里1表示按照维度为1来进行求和,也就是按行进行求和
partition = X_exp.sum(1, keepdim=True)
return X_exp / partition # 这里应用了广播机制
接下来我们来验证一下上面的softmax函数是否正确,这里我们将每个元素变成一个非负数。此外,根据原理每行的和为1
X = torch.normal(0, 1, (2, 5))
X_prob = softmax(X)
X_prob, X_prob.sum(1)
(tensor([[0.2509, 0.0402, 0.1908, 0.3485, 0.1696],
[0.1274, 0.1734, 0.0993, 0.1793, 0.4206]]),
tensor([1., 1.]))
实现softmax回归模型
def net(X):
# 这里就是将X给reshape,-1表示让机器自己算,也就是总元素除以给出的维度中的元素个数。例如:2*5的矩阵我们(-1, 1)之后就是一个10*1的矩阵
# 这里代码的意思就是将X,reshape,然后乘以权重加上偏差
return softmax(torch.matmul(X.reshape((-1, W.shape[0])), W) + b)
**补充:**创建一个数据y_hat,其中包含2个样本在3个类别的预测概率,使用y作为y_hat中概率的索引
y = torch.tensor([0, 2])
y_hat = torch.tensor([[0.1, 0.3, 0.6], [0.3, 0.2, 0.5]])
y_hat[[0, 1], y]
tensor([0.1000, 0.5000])
实现交叉熵损失函数
def cross_entropy(y_hat, y):
return -torch.log(y_hat[range(len(y_hat)), y])
cross_entropy(y_hat, y)
tensor([2.3026, 0.6931])
将预测类别与真实y元素进行比较
def accuracy(y_hat, y):
"""计算预测正确的数量"""
if len(y_hat.shape) > 1 and y_hat.shape[1] > 1:
# 取出每一行元素值最大的下标
y_hat = y_hat.argmax(axis=1)
cmp = y_hat.type(y.dtype) == y
return float(cmp.type(y.dtype).sum())
accuracy(y_hat, y) / len(y)
0.5
我们可以评估在任意模型net的准确率
def evaluate_accuracy(net, data_iter):
"""计算在指定数据集上模型的精度。"""
if isinstance(net, torch.nn.Module):
net.eval() # 将模型设置为评估模式
# 正确预测数,预测总数
metric = d2l.Accumulator(2) # Accumulator表示一个含有两个元素的累加器
for X, y in data_iter:
# 这里是将我们所有预测正确的样本数和样本总数放到累加器里面
metric.add(accuracy(net(X), y), y.numel()) # numel函数的作用是返回tensor中总元素数目。
return metric[0] / metric[1]
evaluate_accuracy(net, test_iter)
0.1264
def train_epoch_ch3(net, train_iter, loss, updater): #@save
"""训练模型一个迭代周期(定义见第3章)。"""
# 将模型设置为训练模式
if isinstance(net, torch.nn.Module):
net.train()
# 训练损失总和、训练准确度总和、样本数
metric = d2l.Accumulator(3)
for X, y in train_iter:
# 计算梯度并更新参数
y_hat = net(X)
l = loss(y_hat, y)
if isinstance(updater, torch.optim.Optimizer):
# 使用PyTorch内置的优化器和损失函数
updater.zero_grad()
l.backward()
updater.step()
metric.add(
float(l) * len(y), accuracy(y_hat, y),
y.size().numel())
else:
# 使用定制的优化器和损失函数
l.sum().backward()
updater(X.shape[0])
metric.add(float(l.sum()), accuracy(y_hat, y), y.numel())
# 返回训练损失和训练准确率
return metric[0] / metric[2], metric[1] / metric[2]
定义一个在动画中绘制数据的实用程序类
class Animator: #@save
"""在动画中绘制数据。"""
def __init__(self, xlabel=None, ylabel=None, legend=None, xlim=None,
ylim=None, xscale='linear', yscale='linear',
fmts=('-', 'm--', 'g-.', 'r:'), nrows=1, ncols=1,
figsize=(3.5, 2.5)):
# 增量地绘制多条线
if legend is None:
legend = []
d2l.use_svg_display()
self.fig, self.axes = d2l.plt.subplots(nrows, ncols, figsize=figsize)
if nrows * ncols == 1:
self.axes = [self.axes,]
# 使用lambda函数捕获参数
self.config_axes = lambda: d2l.set_axes(self.axes[
0], xlabel, ylabel, xlim, ylim, xscale, yscale, legend)
self.X, self.Y, self.fmts = None, None, fmts
def add(self, x, y):
# 向图表中添加多个数据点
if not hasattr(y, "__len__"):
y = [y]
n = len(y)
if not hasattr(x, "__len__"):
x = [x] * n
if not self.X:
self.X = [[] for _ in range(n)]
if not self.Y:
self.Y = [[] for _ in range(n)]
for i, (a, b) in enumerate(zip(x, y)):
if a is not None and b is not None:
self.X[i].append(a)
self.Y[i].append(b)
self.axes[0].cla()
for x, y, fmt in zip(self.X, self.Y, self.fmts):
self.axes[0].plot(x, y, fmt)
self.config_axes()
display.display(self.fig)
display.clear_output(wait=True)
训练函数
def train_ch3(net, train_iter, test_iter, loss, num_epochs, updater): #@save
"""训练模型(定义见第3章)。"""
animator = Animator(xlabel='epoch', xlim=[1, num_epochs], ylim=[0.3, 0.9],
legend=['train loss', 'train acc', 'test acc'])
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
train_metrics = train_epoch_ch3(net, train_iter, loss, updater)
test_acc = evaluate_accuracy(net, test_iter)
animator.add(epoch + 1, train_metrics + (test_acc,))
train_loss, train_acc = train_metrics
assert train_loss < 0.5, train_loss
assert train_acc <= 1 and train_acc > 0.7, train_acc
assert test_acc <= 1 and test_acc > 0.7, test_acc
小批量随机梯度下降来优化模型的损失函数
lr = 0.1
def updater(batch_size):
return d2l.sgd([W, b], lr, batch_size)
num_epochs = 5
train_ch3(net, train_iter, test_iter, cross_entropy, num_epochs, updater)
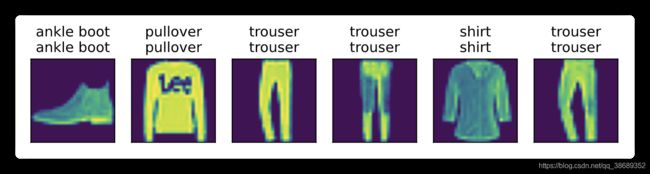
def predict_ch3(net, test_iter, n=6): #@save
"""预测标签(定义见第3章)。"""
for X, y in test_iter:
break
trues = d2l.get_fashion_mnist_labels(y)
preds = d2l.get_fashion_mnist_labels(net(X).argmax(axis=1))
titles = [true + '\n' + pred for true, pred in zip(trues, preds)]
d2l.show_images(X[0:n].reshape((n, 28, 28)), 1, n, titles=titles[0:n])
predict_ch3(net, test_iter)
softmax回归的简洁实现
通过深度学习框架的高级API能够使实现softmax回归变得更加容易
import torch
from torch import nn
from d2l import torch as d2l
batch_size = 256
train_iter, test_iter = d2l.load_data_fashion_mnist(batch_size)
Softmax回归的输出层是一个全连接层
# PyTorch不会隐式地调整输入的形状
# 因此,我们定义了展平层(flatten)在线性层前调整网络输入形状
# nn.Flatten的作用就是将任意维度的tensor拉成一个一维的,其中第0维度保留。Linear的作用是定义一个线性层输入是784输出是10
# 然后我们将这两个串在一起放在Sequential中,就可以拿到一个network
net = nn.Sequential(nn.Flatten(), nn.Linear(784, 10))
# m表示一个layer,这个函数的作用就是:当m是一个线性层的话我们就将它的weights初始化为一个均值为0,默认为0,方差为0.01的随机值
def init_weights(m):
if type(m) == nn.Linear:
nn.init.normal_(m.weight, std=0.01)
# 这里是将每一层应用一下初始化函数
net.apply(init_weights);
在交叉熵损失函数中传递未归一化的预测,并同时计算softmax及其对数
loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
使用学习率为0.1的小批量随机梯度下降作为优化算法
trainer = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=0.1)
调用之前定义的训练函数来训练模型
num_epochs = 10
train_ch3(net, train_iter, test_iter, loss, num_epochs, trainer)