Pytorch实现ResNet-50(pycharm实现)
使用的数据是吴恩达第四课第二周中的手势图片识别,网址下载(https://pan.baidu.com/s/1dsTsaaykje6dNpwIcP0A-w&shfl=sharepset)提取码:hb3y
我是使用pycharm实现(亲测可用)
代码实现:
import math
import numpy as np
import h5py
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import scipy
from PIL import Image
from scipy import ndimage
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from cnn_utils import *
from torch import nn, optim
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader, Dataset
from torchvision import transforms
#% matplotlib
#inline
np.random.seed(1)
torch.manual_seed(1)
batch_size = 24
learning_rate = 0.009
num_epocher = 100
X_train_orig, Y_train_orig, X_test_orig, Y_test_orig, classes = load_dataset()
X_train = X_train_orig / 255.
X_test = X_test_orig / 255.
class MyData(Dataset): # 继承Dataset
def __init__(self, data, y, transform=None): # __init__是初始化该类的一些基础参数
self.transform = transform # 变换
self.data = data
self.y = y
def __len__(self): # 返回整个数据集的大小
return len(self.data)
def __getitem__(self, index): # 根据索引index返回dataset[index]
sample = self.data[index]
if self.transform:
sample = self.transform(sample) # 对样本进行变换
return sample, self.y[index] # 返回该样本
train_dataset = MyData(X_train, Y_train_orig[0],
transform=transforms.ToTensor())
test_dataset = MyData(X_test, Y_test_orig[0],
transform=transforms.ToTensor())
train_loader = DataLoader(train_dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True)
test_loader = DataLoader(test_dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=False)
#实现ResNet
class ConvBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channel, f, filters, s):
super(ConvBlock, self).__init__()
F1, F2, F3 = filters
self.stage = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channel, F1, 1, stride=s, padding=0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(F1),
nn.ReLU(True),
nn.Conv2d(F1, F2, f, stride=1, padding=True, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(F2),
nn.ReLU(True),
nn.Conv2d(F2, F3, 1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(F3),
)
self.shortcut_1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channel, F3, 1, stride=s, padding=0, bias=False)
self.batch_1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(F3)
self.relu_1 = nn.ReLU(True)
def forward(self, X):
X_shortcut = self.shortcut_1(X)
X_shortcut = self.batch_1(X_shortcut)
X = self.stage(X)
X = X + X_shortcut
X = self.relu_1(X)
return X
class IndentityBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channel, f, filters):
super(IndentityBlock, self).__init__()
F1, F2, F3 = filters
self.stage = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channel, F1, 1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(F1),
nn.ReLU(True),
nn.Conv2d(F1, F2, f, stride=1, padding=True, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(F2),
nn.ReLU(True),
nn.Conv2d(F2, F3, 1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(F3),
)
self.relu_1 = nn.ReLU(True)
def forward(self, X):
X_shortcut = X
X = self.stage(X)
X = X + X_shortcut
X = self.relu_1(X)
return X
class ResModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, n_class):
super(ResModel, self).__init__()
self.stage1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(3, 64, 7, stride=2, padding=3, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(64),
nn.ReLU(True),
nn.MaxPool2d(3, 2, padding=1),
)
self.stage2 = nn.Sequential(
ConvBlock(64, f=3, filters=[64, 64, 256], s=1),
IndentityBlock(256, 3, [64, 64, 256]),
IndentityBlock(256, 3, [64, 64, 256]),
)
self.stage3 = nn.Sequential(
ConvBlock(256, f=3, filters=[128, 128, 512], s=2),
IndentityBlock(512, 3, [128, 128, 512]),
IndentityBlock(512, 3, [128, 128, 512]),
IndentityBlock(512, 3, [128, 128, 512]),
)
self.stage4 = nn.Sequential(
ConvBlock(512, f=3, filters=[256, 256, 1024], s=2),
IndentityBlock(1024, 3, [256, 256, 1024]),
IndentityBlock(1024, 3, [256, 256, 1024]),
IndentityBlock(1024, 3, [256, 256, 1024]),
IndentityBlock(1024, 3, [256, 256, 1024]),
IndentityBlock(1024, 3, [256, 256, 1024]),
)
self.stage5 = nn.Sequential(
ConvBlock(1024, f=3, filters=[512, 512, 2048], s=2),
IndentityBlock(2048, 3, [512, 512, 2048]),
IndentityBlock(2048, 3, [512, 512, 2048]),
)
self.pool = nn.AvgPool2d(2, 2, padding=1)
self.fc = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(8192, n_class)
)
def forward(self, X):
out = self.stage1(X)
out = self.stage2(out)
out = self.stage3(out)
out = self.stage4(out)
out = self.stage5(out)
out = self.pool(out)
out = out.view(out.size(0), 8192)
out = self.fc(out)
return out
#训练和预测
device = 'cuda'
def test():
model.eval() # 需要说明是否模型测试
eval_loss = 0
eval_acc = 0
for data in test_loader:
img, label = data
img = img.float().to(device)
label = label.long().to(device)
out = model(img) # 前向算法
loss = criterion(out, label) # 计算loss
eval_loss += loss.item() * label.size(0) # total loss
_, pred = torch.max(out, 1) # 预测结果
num_correct = (pred == label).sum() # 正确结果
eval_acc += num_correct.item() # 正确结果总数
print('Test Loss:{:.6f},Acc: {:.6f}'
.format(eval_loss / (len(test_dataset)), eval_acc * 1.0 / (len(test_dataset))))
model = ResModel(6)
model = model.to(device)
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=learning_rate, momentum=0.8)
# 开始训练
for epoch in range(num_epocher):
model.train()
running_loss = 0.0
running_acc = 0.0
for i, data in enumerate(train_loader, 1):
img, label = data
img = img.float().to(device)
label = label.long().to(device)
# 前向传播
out = model(img)
loss = criterion(out, label) # loss
running_loss += loss.item() * label.size(0)
_, pred = torch.max(out, 1) # 预测结果
num_correct = (pred == label).sum() # 正确结果的数量
running_acc += num_correct.item() # 正确结果的总数
optimizer.zero_grad() # 梯度清零
loss.backward() # 后向传播计算梯度
optimizer.step() # 利用梯度更新W,b参数
# 打印一个循环后,训练集合上的loss和正确率
if (epoch + 1) % 1 == 0:
print('Train{} epoch, Loss: {:.6f},Acc: {:.6f}'.format(epoch + 1, running_loss / (len(train_dataset)),
running_acc / (len(train_dataset))))
test()
运行结果:
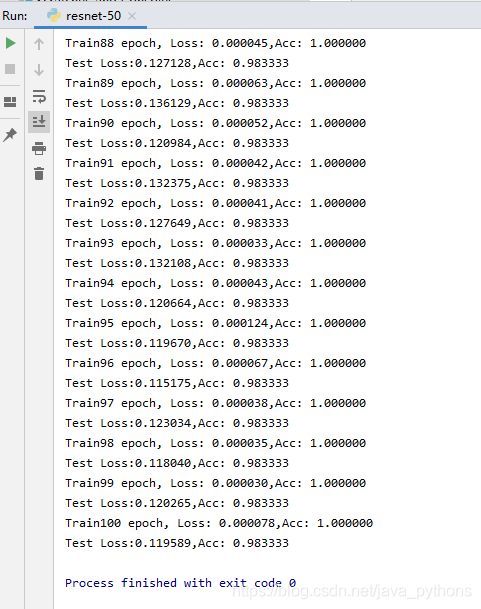
若提示 缺少cnn_utils这个模块,就自己在你的项目中添加这一模块
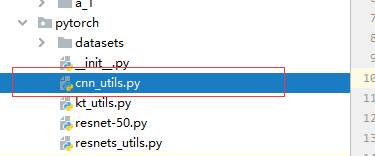

以下为cnn_utils模块代码:
import math
import numpy as np
import h5py
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.python.framework import ops
def load_dataset():
train_dataset = h5py.File('datasets/train_signs.h5', "r")
train_set_x_orig = np.array(train_dataset["train_set_x"][:]) # your train set features
train_set_y_orig = np.array(train_dataset["train_set_y"][:]) # your train set labels
test_dataset = h5py.File('datasets/test_signs.h5', "r")
test_set_x_orig = np.array(test_dataset["test_set_x"][:]) # your test set features
test_set_y_orig = np.array(test_dataset["test_set_y"][:]) # your test set labels
classes = np.array(test_dataset["list_classes"][:]) # the list of classes
train_set_y_orig = train_set_y_orig.reshape((1, train_set_y_orig.shape[0]))
test_set_y_orig = test_set_y_orig.reshape((1, test_set_y_orig.shape[0]))
return train_set_x_orig, train_set_y_orig, test_set_x_orig, test_set_y_orig, classes
def random_mini_batches(X, Y, mini_batch_size=64, seed=0):
"""
Creates a list of random minibatches from (X, Y)
Arguments:
X -- input data, of shape (input size, number of examples) (m, Hi, Wi, Ci)
Y -- true "label" vector (containing 0 if cat, 1 if non-cat), of shape (1, number of examples) (m, n_y)
mini_batch_size - size of the mini-batches, integer
seed -- this is only for the purpose of grading, so that you're "random minibatches are the same as ours.
Returns:
mini_batches -- list of synchronous (mini_batch_X, mini_batch_Y)
"""
m = X.shape[0] # number of training examples
mini_batches = []
np.random.seed(seed)
# Step 1: Shuffle (X, Y)
permutation = list(np.random.permutation(m))
shuffled_X = X[permutation, :, :, :]
shuffled_Y = Y[permutation, :]
# Step 2: Partition (shuffled_X, shuffled_Y). Minus the end case.
num_complete_minibatches = math.floor(
m / mini_batch_size) # number of mini batches of size mini_batch_size in your partitionning
for k in range(0, num_complete_minibatches):
mini_batch_X = shuffled_X[k * mini_batch_size: k * mini_batch_size + mini_batch_size, :, :, :]
mini_batch_Y = shuffled_Y[k * mini_batch_size: k * mini_batch_size + mini_batch_size, :]
mini_batch = (mini_batch_X, mini_batch_Y)
mini_batches.append(mini_batch)
# Handling the end case (last mini-batch < mini_batch_size)
if m % mini_batch_size != 0:
mini_batch_X = shuffled_X[num_complete_minibatches * mini_batch_size: m, :, :, :]
mini_batch_Y = shuffled_Y[num_complete_minibatches * mini_batch_size: m, :]
mini_batch = (mini_batch_X, mini_batch_Y)
mini_batches.append(mini_batch)
return mini_batches
def convert_to_one_hot(Y, C):
Y = np.eye(C)[Y.reshape(-1)].T
return Y
def forward_propagation_for_predict(X, parameters):
"""
Implements the forward propagation for the model: LINEAR -> RELU -> LINEAR -> RELU -> LINEAR -> SOFTMAX
Arguments:
X -- input dataset placeholder, of shape (input size, number of examples)
parameters -- python dictionary containing your parameters "W1", "b1", "W2", "b2", "W3", "b3"
the shapes are given in initialize_parameters
Returns:
Z3 -- the output of the last LINEAR unit
"""
# Retrieve the parameters from the dictionary "parameters"
W1 = parameters['W1']
b1 = parameters['b1']
W2 = parameters['W2']
b2 = parameters['b2']
W3 = parameters['W3']
b3 = parameters['b3']
# Numpy Equivalents:
Z1 = tf.add(tf.matmul(W1, X), b1) # Z1 = np.dot(W1, X) + b1
A1 = tf.nn.relu(Z1) # A1 = relu(Z1)
Z2 = tf.add(tf.matmul(W2, A1), b2) # Z2 = np.dot(W2, a1) + b2
A2 = tf.nn.relu(Z2) # A2 = relu(Z2)
Z3 = tf.add(tf.matmul(W3, A2), b3) # Z3 = np.dot(W3,Z2) + b3
return Z3
def predict(X, parameters):
W1 = tf.convert_to_tensor(parameters["W1"])
b1 = tf.convert_to_tensor(parameters["b1"])
W2 = tf.convert_to_tensor(parameters["W2"])
b2 = tf.convert_to_tensor(parameters["b2"])
W3 = tf.convert_to_tensor(parameters["W3"])
b3 = tf.convert_to_tensor(parameters["b3"])
params = {"W1": W1,
"b1": b1,
"W2": W2,
"b2": b2,
"W3": W3,
"b3": b3}
x = tf.placeholder("float", [12288, 1])
z3 = forward_propagation_for_predict(x, params)
p = tf.argmax(z3)
sess = tf.Session()
prediction = sess.run(p, feed_dict={x: X})
return prediction
# def predict(X, parameters):
#
# W1 = tf.convert_to_tensor(parameters["W1"])
# b1 = tf.convert_to_tensor(parameters["b1"])
# W2 = tf.convert_to_tensor(parameters["W2"])
# b2 = tf.convert_to_tensor(parameters["b2"])
## W3 = tf.convert_to_tensor(parameters["W3"])
## b3 = tf.convert_to_tensor(parameters["b3"])
#
## params = {"W1": W1,
## "b1": b1,
## "W2": W2,
## "b2": b2,
## "W3": W3,
## "b3": b3}
#
# params = {"W1": W1,
# "b1": b1,
# "W2": W2,
# "b2": b2}
#
# x = tf.placeholder("float", [12288, 1])
#
# z3 = forward_propagation(x, params)
# p = tf.argmax(z3)
#
# with tf.Session() as sess:
# prediction = sess.run(p, feed_dict = {x: X})
#
# return prediction