【人脸识别】arcface-pytorch代码解析
参考:
https://github.com/ronghuaiyang/arcface-pytorch
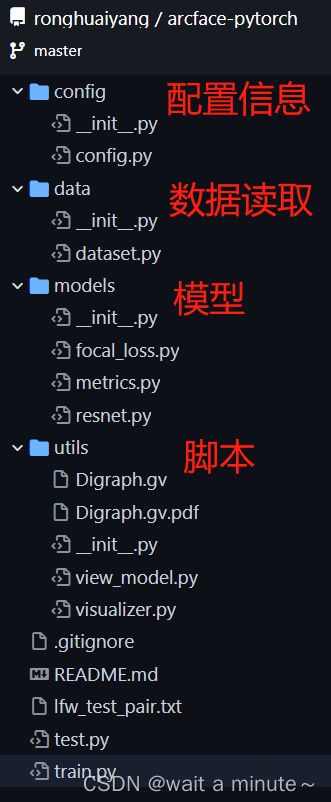
1.代码结构
目录结构如下:
配置信息:包含许多训练或者测试的一些信息配置,比如backbone选用的模型结构等;
数据读取:里面是一个pytorch的Dataloder,我们可以自定义,其中__getitem__用于迭代时输出图像与label数据对;
模型:这里面含有backbone结构,loss损失函数等结构;
脚本:这里面放了一些其他的用于后续处理的脚本。
test:测试脚本
train:训练脚本
2.关键脚本解析
2.1 config/config.py文件
这里是使用一个类设置初始变量配置信息。在调用的使用只需要实例化这个类,然后用这个对象名称加上.env(里面的参数名,就可以调用了)
class Config(object):
env = 'default'
backbone = 'resnet18'
classify = 'softmax'
num_classes = 13938
metric = 'arc_margin'
easy_margin = False
use_se = False
loss = 'focal_loss'
display = False
finetune = False
train_root = '/data/Datasets/webface/CASIA-maxpy-clean-crop-144/'
train_list = '/data/Datasets/webface/train_data_13938.txt'
val_list = '/data/Datasets/webface/val_data_13938.txt'
test_root = '/data1/Datasets/anti-spoofing/test/data_align_256'
test_list = 'test.txt'
lfw_root = '/data/Datasets/lfw/lfw-align-128'
lfw_test_list = '/data/Datasets/lfw/lfw_test_pair.txt'
checkpoints_path = 'checkpoints'
load_model_path = 'models/resnet18.pth'
test_model_path = 'checkpoints/resnet18_110.pth'
save_interval = 10
train_batch_size = 16 # batch size
test_batch_size = 60
input_shape = (1, 128, 128)
optimizer = 'sgd'
use_gpu = True # use GPU or not
gpu_id = '0, 1'
num_workers = 4 # how many workers for loading data
print_freq = 100 # print info every N batch
debug_file = '/tmp/debug' # if os.path.exists(debug_file): enter ipdb
result_file = 'result.csv'
max_epoch = 50
lr = 1e-1 # initial learning rate
lr_step = 10
lr_decay = 0.95 # when val_loss increase, lr = lr*lr_decay
weight_decay = 5e-4
2.2 data/dataset.py文件
参考此处:【从DataLoader到Model(一)】三步法写自定义Torch的DataLoader - 知乎
我们会发现下面的dataloader是一个标准的dataloader格式,包含__init__,__getitem__,__len__,这几个方法。其中__init__中定义了图像从文件目录中读取到一个list中,以及train模式下与其他模式下要进行的一些tranforms的一些数据增强操作。__getitem__会读取图像,并进行初始化过程中的一些transforms操作,并返回图像与labels。__len__返回图像的总数目。通过main函数中,前面几行就可以按批次迭代地调用数据了。
import os
from PIL import Image
import torch
from torch.utils import data
import numpy as np
from torchvision import transforms as T
import torchvision
import cv2
import sys
class Dataset(data.Dataset):
def __init__(self, root, data_list_file, phase='train', input_shape=(1, 128, 128)):
self.phase = phase
self.input_shape = input_shape
with open(os.path.join(data_list_file), 'r') as fd:
imgs = fd.readlines()
imgs = [os.path.join(root, img[:-1]) for img in imgs]
self.imgs = np.random.permutation(imgs)
# normalize = T.Normalize(mean=[0.5, 0.5, 0.5],
# std=[0.5, 0.5, 0.5])
normalize = T.Normalize(mean=[0.5], std=[0.5])
if self.phase == 'train':
self.transforms = T.Compose([
T.RandomCrop(self.input_shape[1:]),
T.RandomHorizontalFlip(),
T.ToTensor(),
normalize
])
else:
self.transforms = T.Compose([
T.CenterCrop(self.input_shape[1:]),
T.ToTensor(),
normalize
])
def __getitem__(self, index):
sample = self.imgs[index]
splits = sample.split()
img_path = splits[0]
data = Image.open(img_path)
data = data.convert('L')
data = self.transforms(data)
label = np.int32(splits[1])
return data.float(), label
def __len__(self):
return len(self.imgs)
if __name__ == '__main__':
dataset = Dataset(root='/data/Datasets/fv/dataset_v1.1/dataset_mix_aligned_v1.1',
data_list_file='/data/Datasets/fv/dataset_v1.1/mix_20w.txt',
phase='test',
input_shape=(1, 128, 128))
trainloader = data.DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=10)
for i, (data, label) in enumerate(trainloader):
# imgs, labels = data
# print imgs.numpy().shape
# print data.cpu().numpy()
# if i == 0:
img = torchvision.utils.make_grid(data).numpy()
# print img.shape
# print label.shape
# chw -> hwc
img = np.transpose(img, (1, 2, 0))
# img *= np.array([0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
# img += np.array([0.485, 0.456, 0.406])
img += np.array([1, 1, 1])
img *= 127.5
img = img.astype(np.uint8)
img = img[:, :, [2, 1, 0]]
cv2.imshow('img', img)
cv2.waitKey()
# break
# dst.decode_segmap(labels.numpy()[0], plot=True)2.3 models/resnet.py
下面的结构应该是在resnet基础上修改的,包含resnetface。
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on 18-5-21 下午5:26
@author: ronghuaiyang
"""
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import math
import torch.utils.model_zoo as model_zoo
import torch.nn.utils.weight_norm as weight_norm
import torch.nn.functional as F
# __all__ = ['ResNet', 'resnet18', 'resnet34', 'resnet50', 'resnet101',
# 'resnet152']
model_urls = {
'resnet18': 'https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnet18-5c106cde.pth',
'resnet34': 'https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnet34-333f7ec4.pth',
'resnet50': 'https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnet50-19c8e357.pth',
'resnet101': 'https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnet101-5d3b4d8f.pth',
'resnet152': 'https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnet152-b121ed2d.pth',
}
def conv3x3(in_planes, out_planes, stride=1):
"""3x3 convolution with padding"""
return nn.Conv2d(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=3, stride=stride,
padding=1, bias=False)
class BasicBlock(nn.Module):
expansion = 1
def __init__(self, inplanes, planes, stride=1, downsample=None):
super(BasicBlock, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = conv3x3(inplanes, planes, stride)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.conv2 = conv3x3(planes, planes)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)
self.downsample = downsample
self.stride = stride
def forward(self, x):
residual = x
out = self.conv1(x)
out = self.bn1(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv2(out)
out = self.bn2(out)
if self.downsample is not None:
residual = self.downsample(x)
out += residual
out = self.relu(out)
return out
class IRBlock(nn.Module):
expansion = 1
def __init__(self, inplanes, planes, stride=1, downsample=None, use_se=True):
super(IRBlock, self).__init__()
self.bn0 = nn.BatchNorm2d(inplanes)
self.conv1 = conv3x3(inplanes, inplanes)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(inplanes)
self.prelu = nn.PReLU()
self.conv2 = conv3x3(inplanes, planes, stride)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)
self.downsample = downsample
self.stride = stride
self.use_se = use_se
if self.use_se:
self.se = SEBlock(planes)
def forward(self, x):
residual = x
out = self.bn0(x)
out = self.conv1(out)
out = self.bn1(out)
out = self.prelu(out)
out = self.conv2(out)
out = self.bn2(out)
if self.use_se:
out = self.se(out)
if self.downsample is not None:
residual = self.downsample(x)
out += residual
out = self.prelu(out)
return out
class Bottleneck(nn.Module):
expansion = 4
def __init__(self, inplanes, planes, stride=1, downsample=None):
super(Bottleneck, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(inplanes, planes, kernel_size=1, bias=False)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(planes, planes, kernel_size=3, stride=stride,
padding=1, bias=False)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)
self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(planes, planes * self.expansion, kernel_size=1, bias=False)
self.bn3 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes * self.expansion)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.downsample = downsample
self.stride = stride
def forward(self, x):
residual = x
out = self.conv1(x)
out = self.bn1(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv2(out)
out = self.bn2(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv3(out)
out = self.bn3(out)
if self.downsample is not None:
residual = self.downsample(x)
out += residual
out = self.relu(out)
return out
class SEBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, channel, reduction=16):
super(SEBlock, self).__init__()
self.avg_pool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1)
self.fc = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(channel, channel // reduction),
nn.PReLU(),
nn.Linear(channel // reduction, channel),
nn.Sigmoid()
)
def forward(self, x):
b, c, _, _ = x.size()
y = self.avg_pool(x).view(b, c)
y = self.fc(y).view(b, c, 1, 1)
return x * y
class ResNetFace(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, block, layers, use_se=True):
self.inplanes = 64
self.use_se = use_se
super(ResNetFace, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 64, kernel_size=3, padding=1, bias=False)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(64)
self.prelu = nn.PReLU()
self.maxpool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2)
self.layer1 = self._make_layer(block, 64, layers[0])
self.layer2 = self._make_layer(block, 128, layers[1], stride=2)
self.layer3 = self._make_layer(block, 256, layers[2], stride=2)
self.layer4 = self._make_layer(block, 512, layers[3], stride=2)
self.bn4 = nn.BatchNorm2d(512)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout()
self.fc5 = nn.Linear(512 * 8 * 8, 512)
self.bn5 = nn.BatchNorm1d(512)
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
nn.init.xavier_normal_(m.weight)
elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d) or isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm1d):
nn.init.constant_(m.weight, 1)
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
elif isinstance(m, nn.Linear):
nn.init.xavier_normal_(m.weight)
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
def _make_layer(self, block, planes, blocks, stride=1):
downsample = None
if stride != 1 or self.inplanes != planes * block.expansion:
downsample = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(self.inplanes, planes * block.expansion,
kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(planes * block.expansion),
)
layers = []
layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes, stride, downsample, use_se=self.use_se))
self.inplanes = planes
for i in range(1, blocks):
layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes, use_se=self.use_se))
return nn.Sequential(*layers)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.bn1(x)
x = self.prelu(x)
x = self.maxpool(x)
x = self.layer1(x)
x = self.layer2(x)
x = self.layer3(x)
x = self.layer4(x)
x = self.bn4(x)
x = self.dropout(x)
x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)
x = self.fc5(x)
x = self.bn5(x)
return x
class ResNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, block, layers):
self.inplanes = 64
super(ResNet, self).__init__()
# self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=7, stride=2, padding=3,
# bias=False)
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 64, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1,
bias=False)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(64)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
# self.maxpool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1)
self.layer1 = self._make_layer(block, 64, layers[0], stride=2)
self.layer2 = self._make_layer(block, 128, layers[1], stride=2)
self.layer3 = self._make_layer(block, 256, layers[2], stride=2)
self.layer4 = self._make_layer(block, 512, layers[3], stride=2)
# self.avgpool = nn.AvgPool2d(8, stride=1)
# self.fc = nn.Linear(512 * block.expansion, num_classes)
self.fc5 = nn.Linear(512 * 8 * 8, 512)
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out', nonlinearity='relu')
elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):
nn.init.constant_(m.weight, 1)
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
def _make_layer(self, block, planes, blocks, stride=1):
downsample = None
if stride != 1 or self.inplanes != planes * block.expansion:
downsample = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(self.inplanes, planes * block.expansion,
kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(planes * block.expansion),
)
layers = []
layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes, stride, downsample))
self.inplanes = planes * block.expansion
for i in range(1, blocks):
layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes))
return nn.Sequential(*layers)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.bn1(x)
x = self.relu(x)
# x = self.maxpool(x)
x = self.layer1(x)
x = self.layer2(x)
x = self.layer3(x)
x = self.layer4(x)
# x = nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size=x.size()[2:])(x)
# x = self.avgpool(x)
x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)
x = self.fc5(x)
return x
def resnet18(pretrained=False, **kwargs):
"""Constructs a ResNet-18 model.
Args:
pretrained (bool): If True, returns a model pre-trained on ImageNet
"""
model = ResNet(BasicBlock, [2, 2, 2, 2], **kwargs)
if pretrained:
model.load_state_dict(model_zoo.load_url(model_urls['resnet18']))
return model
def resnet34(pretrained=False, **kwargs):
"""Constructs a ResNet-34 model.
Args:
pretrained (bool): If True, returns a model pre-trained on ImageNet
"""
model = ResNet(BasicBlock, [3, 4, 6, 3], **kwargs)
if pretrained:
model.load_state_dict(model_zoo.load_url(model_urls['resnet34']))
return model
def resnet50(pretrained=False, **kwargs):
"""Constructs a ResNet-50 model.
Args:
pretrained (bool): If True, returns a model pre-trained on ImageNet
"""
model = ResNet(Bottleneck, [3, 4, 6, 3], **kwargs)
if pretrained:
model.load_state_dict(model_zoo.load_url(model_urls['resnet50']))
return model
def resnet101(pretrained=False, **kwargs):
"""Constructs a ResNet-101 model.
Args:
pretrained (bool): If True, returns a model pre-trained on ImageNet
"""
model = ResNet(Bottleneck, [3, 4, 23, 3], **kwargs)
if pretrained:
model.load_state_dict(model_zoo.load_url(model_urls['resnet101']))
return model
def resnet152(pretrained=False, **kwargs):
"""Constructs a ResNet-152 model.
Args:
pretrained (bool): If True, returns a model pre-trained on ImageNet
"""
model = ResNet(Bottleneck, [3, 8, 36, 3], **kwargs)
if pretrained:
model.load_state_dict(model_zoo.load_url(model_urls['resnet152']))
return model
def resnet_face18(use_se=True, **kwargs):
model = ResNetFace(IRBlock, [2, 2, 2, 2], use_se=use_se, **kwargs)
return model2.4 models/metrics.py
这里应该是度量学习的一些指标,最后一层的特征表示成什么样,具体后续补充。
from __future__ import print_function
from __future__ import division
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
from torch.nn import Parameter
import math
class ArcMarginProduct(nn.Module):
r"""Implement of large margin arc distance: :
Args:
in_features: size of each input sample
out_features: size of each output sample
s: norm of input feature
m: margin
cos(theta + m)
"""
def __init__(self, in_features, out_features, s=30.0, m=0.50, easy_margin=False):
super(ArcMarginProduct, self).__init__()
self.in_features = in_features
self.out_features = out_features
self.s = s
self.m = m
self.weight = Parameter(torch.FloatTensor(out_features, in_features))
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(self.weight)
self.easy_margin = easy_margin
self.cos_m = math.cos(m)
self.sin_m = math.sin(m)
self.th = math.cos(math.pi - m)
self.mm = math.sin(math.pi - m) * m
def forward(self, input, label):
# --------------------------- cos(theta) & phi(theta) ---------------------------
cosine = F.linear(F.normalize(input), F.normalize(self.weight))
sine = torch.sqrt((1.0 - torch.pow(cosine, 2)).clamp(0, 1))
phi = cosine * self.cos_m - sine * self.sin_m
if self.easy_margin:
phi = torch.where(cosine > 0, phi, cosine)
else:
phi = torch.where(cosine > self.th, phi, cosine - self.mm)
# --------------------------- convert label to one-hot ---------------------------
# one_hot = torch.zeros(cosine.size(), requires_grad=True, device='cuda')
one_hot = torch.zeros(cosine.size(), device='cuda')
one_hot.scatter_(1, label.view(-1, 1).long(), 1)
# -------------torch.where(out_i = {x_i if condition_i else y_i) -------------
output = (one_hot * phi) + ((1.0 - one_hot) * cosine) # you can use torch.where if your torch.__version__ is 0.4
output *= self.s
# print(output)
return output
class AddMarginProduct(nn.Module):
r"""Implement of large margin cosine distance: :
Args:
in_features: size of each input sample
out_features: size of each output sample
s: norm of input feature
m: margin
cos(theta) - m
"""
def __init__(self, in_features, out_features, s=30.0, m=0.40):
super(AddMarginProduct, self).__init__()
self.in_features = in_features
self.out_features = out_features
self.s = s
self.m = m
self.weight = Parameter(torch.FloatTensor(out_features, in_features))
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(self.weight)
def forward(self, input, label):
# --------------------------- cos(theta) & phi(theta) ---------------------------
cosine = F.linear(F.normalize(input), F.normalize(self.weight))
phi = cosine - self.m
# --------------------------- convert label to one-hot ---------------------------
one_hot = torch.zeros(cosine.size(), device='cuda')
# one_hot = one_hot.cuda() if cosine.is_cuda else one_hot
one_hot.scatter_(1, label.view(-1, 1).long(), 1)
# -------------torch.where(out_i = {x_i if condition_i else y_i) -------------
output = (one_hot * phi) + ((1.0 - one_hot) * cosine) # you can use torch.where if your torch.__version__ is 0.4
output *= self.s
# print(output)
return output
def __repr__(self):
return self.__class__.__name__ + '(' \
+ 'in_features=' + str(self.in_features) \
+ ', out_features=' + str(self.out_features) \
+ ', s=' + str(self.s) \
+ ', m=' + str(self.m) + ')'
class SphereProduct(nn.Module):
r"""Implement of large margin cosine distance: :
Args:
in_features: size of each input sample
out_features: size of each output sample
m: margin
cos(m*theta)
"""
def __init__(self, in_features, out_features, m=4):
super(SphereProduct, self).__init__()
self.in_features = in_features
self.out_features = out_features
self.m = m
self.base = 1000.0
self.gamma = 0.12
self.power = 1
self.LambdaMin = 5.0
self.iter = 0
self.weight = Parameter(torch.FloatTensor(out_features, in_features))
nn.init.xavier_uniform(self.weight)
# duplication formula
self.mlambda = [
lambda x: x ** 0,
lambda x: x ** 1,
lambda x: 2 * x ** 2 - 1,
lambda x: 4 * x ** 3 - 3 * x,
lambda x: 8 * x ** 4 - 8 * x ** 2 + 1,
lambda x: 16 * x ** 5 - 20 * x ** 3 + 5 * x
]
def forward(self, input, label):
# lambda = max(lambda_min,base*(1+gamma*iteration)^(-power))
self.iter += 1
self.lamb = max(self.LambdaMin, self.base * (1 + self.gamma * self.iter) ** (-1 * self.power))
# --------------------------- cos(theta) & phi(theta) ---------------------------
cos_theta = F.linear(F.normalize(input), F.normalize(self.weight))
cos_theta = cos_theta.clamp(-1, 1)
cos_m_theta = self.mlambda[self.m](cos_theta)
theta = cos_theta.data.acos()
k = (self.m * theta / 3.14159265).floor()
phi_theta = ((-1.0) ** k) * cos_m_theta - 2 * k
NormOfFeature = torch.norm(input, 2, 1)
# --------------------------- convert label to one-hot ---------------------------
one_hot = torch.zeros(cos_theta.size())
one_hot = one_hot.cuda() if cos_theta.is_cuda else one_hot
one_hot.scatter_(1, label.view(-1, 1), 1)
# --------------------------- Calculate output ---------------------------
output = (one_hot * (phi_theta - cos_theta) / (1 + self.lamb)) + cos_theta
output *= NormOfFeature.view(-1, 1)
return output
def __repr__(self):
return self.__class__.__name__ + '(' \
+ 'in_features=' + str(self.in_features) \
+ ', out_features=' + str(self.out_features) \
+ ', m=' + str(self.m) + ')'
2.5 utils/view_model.py
大概是输出模型每层的参数量的一个函数。
import torch
from torch.autograd import Variable
import torch.nn as nn
from graphviz import Digraph
__all__ = ['view_model']
class CNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(CNN, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=1, out_channels=16, kernel_size=5, stride=1, padding=2),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2)
)
self.conv2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=16, out_channels=32, kernel_size=5, stride=1, padding=2),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2)
)
self.out = nn.Linear(32*7*7, 10)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.conv2(x)
x = x.view(x.size(0), -1) # (batch, 32*7*7)
out = self.out(x)
return out
def make_dot(var, params=None):
""" Produces Graphviz representation of PyTorch autograd graph
Blue nodes are the Variables that require grad, orange are Tensors
saved for backward in torch.autograd.Function
Args:
var: output Variable
params: dict of (name, Variable) to add names to node that
require grad (TODO: make optional)
"""
if params is not None:
assert isinstance(params.values()[0], Variable)
param_map = {id(v): k for k, v in params.items()}
node_attr = dict(style='filled',
shape='box',
align='left',
fontsize='12',
ranksep='0.1',
height='0.2')
dot = Digraph(node_attr=node_attr, graph_attr=dict(size="12,12"))
seen = set()
def size_to_str(size):
return '('+(', ').join(['%d' % v for v in size])+')'
def add_nodes(var):
if var not in seen:
if torch.is_tensor(var):
dot.node(str(id(var)), size_to_str(var.size()), fillcolor='orange')
elif hasattr(var, 'variable'):
u = var.variable
name = param_map[id(u)] if params is not None else ''
node_name = '%s\n %s' % (name, size_to_str(u.size()))
dot.node(str(id(var)), node_name, fillcolor='lightblue')
else:
dot.node(str(id(var)), str(type(var).__name__))
seen.add(var)
if hasattr(var, 'next_functions'):
for u in var.next_functions:
if u[0] is not None:
dot.edge(str(id(u[0])), str(id(var)))
add_nodes(u[0])
if hasattr(var, 'saved_tensors'):
for t in var.saved_tensors:
dot.edge(str(id(t)), str(id(var)))
add_nodes(t)
add_nodes(var.grad_fn)
return dot
def view_model(net, input_shape):
x = Variable(torch.randn(1, *input_shape))
y = net(x)
g = make_dot(y)
g.view()
params = list(net.parameters())
k = 0
for i in params:
l = 1
print("layer parameters size:" + str(list(i.size())))
for j in i.size():
l *= j
print("layer parameters:" + str(l))
k = k + l
print("total parameters:" + str(k))
if __name__ == '__main__':
net = CNN()
view_model(net)
# x = Variable(torch.randn(1, 1, 28, 28))
# y = net(x)
# g = make_dot(y)
# g.view()
#
# params = list(net.parameters())
# k = 0
# for i in params:
# l = 1
# print("layer parameters:" + str(list(i.size())))
# for j in i.size():
# l *= j
# print("layer parameters:" + str(l))
# k = k + l
# print("total parameters:" + str(k))2.6 utils/visualizer.py
下面这个脚本,主要通过visdom在线画图。其中有两个方法,display_current_results方法会根据输入的xy坐标画图,display_roc会根据y_true, y_pred计算roc曲线的横纵坐标fpr, tpr,然后画图。
import visdom
import time
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from sklearn.metrics import roc_curve
class Visualizer(object):
def __init__(self, env='default', **kwargs):
self.vis = visdom.Visdom(env=env, **kwargs)
self.vis.close()
self.iters = {}
self.lines = {}
def display_current_results(self, iters, x, name='train_loss'):
if name not in self.iters:
self.iters[name] = []
if name not in self.lines:
self.lines[name] = []
self.iters[name].append(iters)
self.lines[name].append(x)
self.vis.line(X=np.array(self.iters[name]),
Y=np.array(self.lines[name]),
win=name,
opts=dict(legend=[name], title=name))
def display_roc(self, y_true, y_pred):
fpr, tpr, ths = roc_curve(y_true, y_pred)
self.vis.line(X=fpr,
Y=tpr,
# win='roc',
opts=dict(legend=['roc'],
title='roc'))
2.7 train.py
包含以下几个步骤:
(1)初始化数据读取dataloader(训练与测试集)
(2)初始化backbone模型
(3)初始化衡量的metric
(4)初始化优化器与学习率
(5)模型训练
(6)可视化训练过程
(7)模型测试
(8)可视化测试过程
from __future__ import print_function
import os
from data import Dataset
import torch
from torch.utils import data
import torch.nn.functional as F
from models import *
import torchvision
from utils import Visualizer, view_model
import torchVisualizer
import numpy as np
import random
import time
from config import Config
from torch.nn import DataParallel
from torch.optim.lr_scheduler import StepLR
from test import *
def save_model(model, save_path, name, iter_cnt)Visualizer:
save_name = os.path.join(save_path, name + '_' + str(iter_cnt) + '.pth')
torch.save(model.state_dict(), save_name)
return save_name
if __name__ == '__main__':
opt = Config()
if opt.display:
visualizer = Visualizer()
device = torch.device("cuda")
train_dataset = Dataset(opt.train_root, opt.train_list, phase='train', input_shape=opt.input_shape)
trainloader = data.DataLoader(train_dataset,
batch_size=opt.train_batch_size,
shuffle=True,
num_workers=opt.num_workers)
identity_list = get_lfw_list(opt.lfw_test_list)
img_paths = [os.path.join(opt.lfw_root, each) for each in identity_list]
print('{} train iters per epoch:'.format(len(trainloader)))
if opt.loss == 'focal_loss':
criterion = FocalLoss(gamma=2)
else:
criterion = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
if opt.backbone == 'resnet18':
model = resnet_face18(use_se=opt.use_se)
elif opt.backbone == 'resnet34':
model = resnet34()
elif opt.backbone == 'resnet50':
model = resnet50()
if opt.metric == 'add_margin':
metric_fc = AddMarginProduct(512, opt.num_classes, s=30, m=0.35)
elif opt.metric == 'arc_margin':
metric_fc = ArcMarginProduct(512, opt.num_classes, s=30, m=0.5, easy_margin=opt.easy_margin)
elif opt.metric == 'sphere':
metric_fc = SphereProduct(512, opt.num_classes, m=4)
else:
metric_fc = nn.Linear(512, opt.num_classes)
# view_model(model, opt.input_shape)
print(model)
model.to(device)
model = DataParallel(model)
metric_fc.to(device)
metric_fc = DataParallel(metric_fc)
if opt.optimizer == 'sgd':
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD([{'params': model.parameters()}, {'params': metric_fc.parameters()}],
lr=opt.lr, weight_decay=opt.weight_decay)
else:
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam([{'params': model.parameters()}, {'params': metric_fc.parameters()}],
lr=opt.lr, weight_decay=opt.weight_decay)
scheduler = StepLR(optimizer, step_size=opt.lr_step, gamma=0.1)
start = time.time()
for i in range(opt.max_epoch):
scheduler.step()
model.train()
for ii, data in enumerate(trainloader):
data_input, label = data
data_input = data_input.to(device)
label = label.to(device).long()
feature = model(data_input)
output = metric_fc(feature, label)
loss = criterion(output, label)
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
iters = i * len(trainloader) + ii
if iters % opt.print_freq == 0:
output = output.data.cpu().numpy()
output = np.argmax(output, axis=1)
label = label.data.cpu().numpy()
# print(output)
# print(label)
acc = np.mean((output == label).astype(int))
speed = opt.print_freq / (time.time() - start)
time_str = time.asctime(time.localtime(time.time()))
print('{} train epoch {} iter {} {} iters/s loss {} acc {}'.format(time_str, i, ii, speed, loss.item(), acc))
if opt.display:
visualizer.display_current_results(iters, loss.item(), name='train_loss')
visualizer.display_current_results(iters, acc, name='train_acc')
start = time.time()
if i % opt.save_interval == 0 or i == opt.max_epoch:
save_model(model, opt.checkpoints_path, opt.backbone, i)
model.eval()
acc = lfw_test(model, img_paths, identity_list, opt.lfw_test_list, opt.test_batch_size)
if opt.display:
visualizer.display_current_results(iters, acc, name='test_acc')