【3D 目标检测】2019 CVPR Learning 2D to 3D Lifting for Object Detection in 3D for Autonomous Vehicles
CVPR 2019
Learning 2D to 3D Lifting for Object Detection in 3D for Autonomous Vehicles
3D object detection
- 2D monocular images
- autonomous driving scenarios
Proposal
- lift the 2D images to 3D representations using learned neural network
3D representations using state-of-the-art GANs - leverage existing networks workding directly on 3D data to perform 3D object detection and localization
3D data for ground plane estimation using recent 3D networks
Results
-
highter results than many methods working on actual 3D inputs acquired from physical sensors
-
a late fusion of the output of the network trained on
- generated 3D image
- real 3D image
improve performance

Learning 2D to 3D Lifting for Object Detection in 3D for Autonomous Vehicles
- Introduction
- Related work
-
- Object Detection in 3D
- Inferring 3D using RGB images
- Generating 3D data from 2D
- Image to image translation
- Approach
-
- A. Generating BEV images from 2D images (BirdGAN)
- B. BirdNet 3D object detection
- C. MV3D as base architecture
- D. Ground plane estimation
- Experiments
-
-
- Dataset
- Training data for BirdGAN
- A. Quantitative results
- B. Qualitative Results
- C. Ablation Studies
-
- Conclusion
Introduction
Two approaches have been widespread for 3D object detection problems
-
to detect objects in 2D using monocular images and then infer in 3D
- [CVPR,2016] Monocular 3d object detection for autonomous driving
- [CVPR, 2018] Multi-level fusion based 3d object detection from monocular images
- [TPAMI, 2018] Deep supervision with intermediate concepts
-
to use 3D data (e.g. LiDAR(激光雷达)) to detect bounding boxes directly in 3D
- MV3D
[CVPR, 2017] Multi-view 3d object detection network for autonomous driving
- MV3D
-
Compare the two methods
-
the methods based on 2D monocular images significantly lag behind the the method use 3D data
- methods based on monocular images attempt at implicitly inferring 3D information from the input
- availability of depth information (derived or explicit)
greatly increases the performance of methods that use 3D data
-
a monocular image based 3D object detection method will be highly practical
- closing the gap in performance with the methods requiring explicit 3D data
- cheaper and lighter 2D cameras
- expensive and bulky 3D scanners
-
Our Results are of importance as
- (i) only using monocular images at inference
the efforts that are directed towards collecting high quality 3D data can help in scenarios where explicit 3D data cannot be acquired at test time. - (ii) the method can be used as a plug-and-play module
with any existing 3D method which works with BEV images, allowing operations with seamless switching between RGB and 3D scanners while leveraging the same underlying object detection platform.
This paper refers to the following methods
-
3D reconstruction from single images
-
MV3D
[CVPR, 2017] Multi-view 3d object detection network for autonomous driving -
[CVPR, 2017] A point set generation network for 3d object reconstruction from a single image
-
[NeurIPS, 2016] Perspective transformer nets: Learning single-view 3d object reconstruction without 3d supervision
-
-
depth estimation
- [CVPR,2016] Monocular 3d object detection for autonomous driving
- [CVPR, 2017] Unsupervised monocular depth estimation with left-right consistency
Related work
Object Detection in 3D
Images
-
3D data
- LiDAR
- Birdnet
[ITSC, 2018] Birdnet: A 3d object detection framework from lidar information - [CVPR, 2015] Data-driven 3d voxel patterns for object category recognition
- Birdnet
- stereo
- 3DVP
[TPAMI,2018] 3d object proposals using stereo imagery for accurate object class detection
- 3DVP
- LiDAR
-
monocular images
- [CVPR, 2015] Joint sfm and detection cues for monocular 3d localization in road scenes
The approaches for 3D object detection
-
proposing new neural network architectures
-
BirdNet
[ITSC, 2018] Birdnet: A 3d object detection framework from lidar information -
MV3D
[CVPR, 2017] Multi-view 3d object detection network for autonomous driving
-
-
novel object representations
- 3DVP
[TPAMI,2018] 3d object proposals using stereo imagery for accurate object class detection
- 3DVP
-
utilize other modalities along with 3D
-
corresponding 2D images
MV3D
[CVPR, 2017] Multi-view 3d object detection network for autonomous driving -
structure from motion
[CVPR, 2016] A continuous occlusion model for road scene understanding
-
-
follow the success of 2D object detection methods and are based on 3D proposal networks and classifying them
-
MV3D
[CVPR, 2017] Multi-view 3d object detection network for autonomous driving -
AVOD
[IROS, 2018] Joint 3d proposal generation and object detection from view aggregation
-
-
took multiview projections of the 3D data to use with 2D image networks followed by fusion mechanisms
[ICCV,2015] Multi-view convolutional neural networks for 3d shape recognition
Inferring 3D using RGB images
Methods
-
predicting 2D keypoint heat maps and 3D objects structure recovery
[ECCV,2016] Single image 3d interpreter network -
use single RGB image to obtain detailed 3D structure using MRFs on small homogeneous patches to predict plane parameters encoding 3D locations and orientations of the patches
[TPAMI, 2009] Make3d: Learning 3d scene structure from a single still image
-
learn to predict 3D human pose from single image using a fine discretization of the 3D space around the subject and predicting per voxel likelihoods for each joint, and using a coarse-to-fine scheme
[CVPR,2017] Coarse-tofine volumetric prediction for single-image 3d human pose
Generating 3D data from 2D
-
[NeurIPS, 2016] Learning a probabilistic latent space of object shapes via 3d generativeadversarial modeling
- use Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) to generate 3D objects
- using volumetric networks, extending the vanilla GAN and VAE GAN to 3D
-
[3DV, 2017] 3d shape induction from 2d views of multiple objects
PrGAN (propose projective generative adversarial networks)
for obtaining 3D structures from multiple 2D views -
[CVPR, 2017] Transformation-grounded image generation network for novel 3d view synthesis
synthesize novel views from a single image by inferring geometrical information followed by image completion, using a combination of adversarial and perceptual loss -
[NeurIPS, 2016] Learning single-view 3d object reconstruction without 3d supervision
propose Perspective Transformer Nets (PTNs), an encoder-decoder network with a novel projection loss using perspective transformation, for learning to use 2D observations without explicit 3D supervision -
[AAAI, 2018] Learning adversarial 3d model generation with 2d image enhancer
generate 3D models with an enhancer neural network extracting information from other corresponding domains (e.g. image) -
[ICCV, 2017] 3d object reconstruction from a single depth view with adversarial learning
uses a GAN to generate 3D objects from a single depth image, by combining autoencoders and conditional GAN -
[arXiv,2017] Improved adversarial systems for 3d object generation and reconstruction
uses a GAN to generate 3D from 2D images, and perform shape completion from occluded 2.5D views,using Wasserstein objective.
Image to image translation
Our work addresses the specific task of 3D object detection by translating RGB images to BEV
我们的工作是通过将RGB图像转换为BEV来解决三维目标检测的具体任务
近年来,图像翻译因其在风格转换中的应用而受到关注,如pix2pix① 或 ② 的最新成果。
虽然3D对象检测可能不如完整准确的3D场景生成具有挑战性,但是对于自动驾驶用例来说,3D对象检测仍然是一个非常具有挑战性和相关的任务。在这里,我们将生成3D数据作为中间步骤,但是我们并没有像 ①、 ② 那样关注生成的3D数据的质量,而是直接从单眼图像中设计和评估我们的方法。
① [CVPR, 2017] Image-to-image translation with conditional adversarial networks
② [NeurIPS, 2017] Toward multimodal image-to-image translation
Approach
A. Generating BEV images from 2D images (BirdGAN)
based on the GAN
- [CVPR, 2017] Image-to-image translation with conditional adversarial networks
BirdGAN
- Encoder
VGG-16 - generate the BEV image
DCGAN 对经过编码的向量进行条件处理
DCGAN [arXiv 2015] Unsupervised representation learning with deep convolutional generative adversarial networks
用于训练GAN的数据质量对最终性能有很大影响,提出并实验了两种训练GAN生成BEV图像的方法
- take all the objects in the scene
- take only the ‘well defined’ objects in the scene
motivated by the fact that the point clouds become relatively noisy, and possibly uninformative for object detection, as the distance increases due to very small objects and occlusions

RGB —— only shows the front view
the top mounted LiDAR point cloud —— front、back and sides view
我们适当地裁剪激光雷达点云,只剩下两种模式中的对应信息。还删除了远处的BEV点,因为它们在RGB图像中高度遮挡(如红色箭头对象)
B. BirdNet 3D object detection
- Input
extracted from the full LIDAR point cloud- 3 channel BEV image consisting of height , density , intensity of the point
- ground plane estimation for determining the height of the 3D bounding boxes
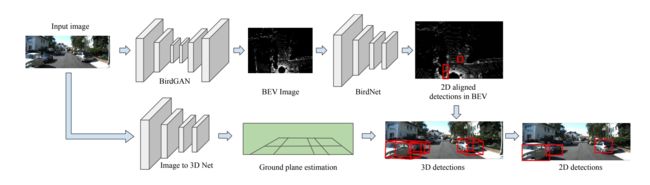
Proposed pipeline with BirdNet
-
BirdGAN
translated the 2D RGB images into 3 channel BEV image
3 channel BEV are height , density , intensity of the point -
Image to 3D network
like the [NeurIPS, 2016] Learning single-view 3d object reconstruction without 3d supervision- input
3 channel RGB - generate either the point clouds or their voxelized version as the 3D model
- 3D model used to obtain the ground planes estimation
for constructing the 3D bounding boxes around the detected objects
- input
-
The BEV detections are then converted to 3D detections using the ground plane estimation
C. MV3D as base architecture

Proposed pipeline with MV3D
-
BirdGANs
- input
2D RGB image - translate to
(m+2) channel BEV images
- input
-
Image to Depth Net
- input
2D RGB image - to obtain the corresponding depth image
- use the depth map image to obtain the 3D point cloud
- generate LiDAR FV (Front View) image
- input
-
MV3D
- input
RGB , FV , BEV images - obtain 3D detection
- input
The difference between MV3D and BirdNet
-
the format of BEV
-
BirdNet
takes a 3 channel BEV image ( i.e. height, intensity, density )
-
MV3D
pre-processes the height channel to encode more detailed height information
-
divides the point cloud into M M M slice
-
compute a height map for each slice
-
giving a BEV image of M + 2 M+2 M+2 channels
-
use multiple independently trained BirdGANs to generate the M height channels of the BEV image is better than directly generating the M + 2 channel BEV image
-
-
D. Ground plane estimation
The ground plane estimation
-
BirdNet
uses the ground plane,
i.e. the bottom-most points, to estimate the height of the object for constructing the 3D bounding boxes -
MV3D
obtains the 3D localizations by projecting the 3D bounding boxes to the ground plane.
The ground plane estimation is an important step here, especially for MV3D, as it governs the size of the projected objects on the BEV impacting the quality of 3D object localization.
Two ways to obtain the ground plane
-
by reconstructing a 3D model from a single RGB image
-
Perspective Transformer Network
[NeurIPS, 2016] Learning single-view 3d object reconstruction without 3d supervision -
Point Set generation
[CVPR, 2017] Unsupervised monocular depth estimation with left-right consistency -
depth estimation
[ITSC, 2018] Birdnet: A 3d object detection framework from lidar information
-
-
using the image to directly estimate the ground plane without transforming the image to 3D
requires explicit presence of strong 2D object proposals or texture/color pattern- [CVPR, 2015] Joint sfm and detection cues for monocular 3d localization in road scenes
- [ICRA, 2009] Accurate 3d ground plane estimation from a single image
- [IVS, 2014] Color-based road detection and its evaluation on the kitti road benchmark
Methods of this paper
-
choose the former paradigm with PTN and reconstruct the 3D object/scene
-
The ground plane is then estimated by fitting a plane using RANSAC [31].
RANSAC [ICCAS,2014] Robust ground plane detection from 3d point clouds
Experiments
Dataset
KITTI
training : 7, 481 images
testing : 7, 518 images
validation
- like [NeurIPS,2015] 3d object proposals for accurate object class detection split the KITTI training set into train and validation sets (each containing half of the images).
We ensure that our training and validation set do not come from the same video sequences, and evaluate the performance of our bounding box proposals on the validation set
Training data for BirdGAN
training BirdGAN on two types of training data
-
w/o clipping
use the data in the field of view of RGB images i.e. 90° in the front view -
clipping
In KITTI dataset, the objects that are far, are difficult to detect mostly due to occlusion
using only the nearby objects for training the GANs, i.e. we remove the BEV image data corresponding to points which are more than 25 meters away and use these modified BEV images to train the GAN based translation model
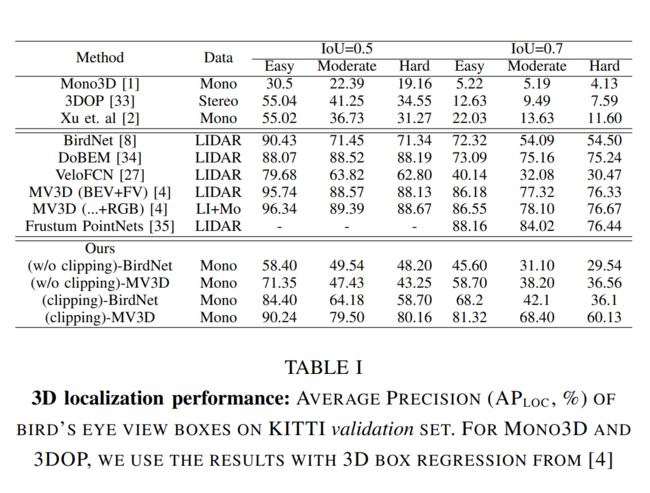
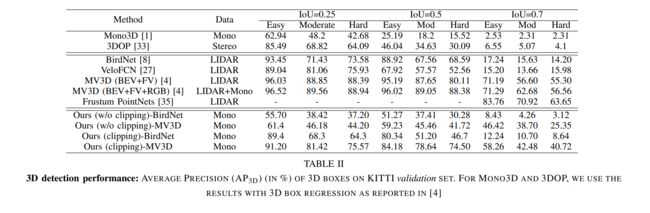
A. Quantitative results
BEV Object Detection
- MV3D在真实数据和生成数据的情况下都优于BirdNet
- 剪切数据方法比不剪切数据训练的相应网络的性能提高了10- 25%
低噪声训练通过学习更好的质量BEV生成器来提高测试时的性能
3D Object Detection
Generalization Ability
2D Object Detection

It can be observed that even with entirely generated data the method also performs close to the base networks for 2D object detection
B. Qualitative Results
-
actual BEV images for compared methods
(first three columns) -
generated BEV images for the proposed methods

-
从第一和第二列都可以看出来 outs MV3D 能够使用生成的BEVs的图像检测结果与用真实的BEV图像的MV3D结果非常接近
-
第二列可以看出 ours BirdNet 对遮挡高度敏感(杆子影响了车的检测)
C. Ablation Studies
the impact of various channels within BEV on 3D object detection and localization
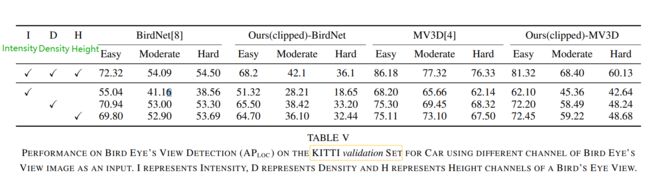
分析生成的数据是否可以通过增加真实数据来提高检测和定位性能
-
首先尝试将地面真实训练图像和生成的BEV图像合并成一个公共数据集去训练
性能下降了这可能是由于网络无法优化合并的数据集。对同一图像,一个是真实的,另一个是生成的。他们会有不同的统计数据,在一起训练时可能会混淆检测器
-
分别训练两个独立的网络
将它们的输出与一个连接操作(如拼接或平均值)相结合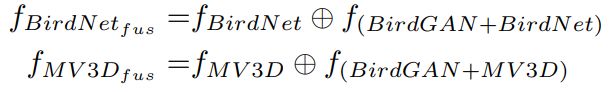
性能提高了,hard drops(可能是因为图片包含严重的遮挡,generated BEVs 降低性能)

Conclusion
- 使用GANs从2D图像生成3D数据可以使性能接近最先进的3D对象检测器
- 提出了两种生成机制,以配合两种不同的最新三维目标检测体系结构,并提出了训练策略,有较好的检测性能
- 分别用真实和生成的3D数据训练的网络的后期融合,可以提高他们各自的性能
