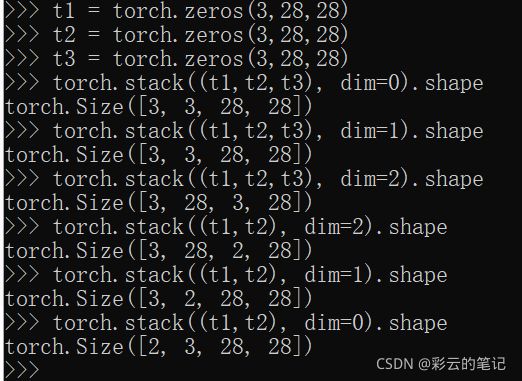
pytorch (四)F.softmax cross_entropy confusion_matrix stack
import numpy as np
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch
>>> F.softmax(x, dim=0)
tensor([[0.3333, 0.3333, 0.3333, 0.3333, 0.3333],
[0.3333, 0.3333, 0.3333, 0.3333, 0.3333],
[0.3333, 0.3333, 0.3333, 0.3333, 0.3333]])
>>> x
tensor([[1., 2., 3., 4., 5.],
[1., 2., 3., 4., 5.],
[1., 2., 3., 4., 5.]])
>>> F.softmax(x, dim=1)
tensor([[0.0117, 0.0317, 0.0861, 0.2341, 0.6364],
[0.0117, 0.0317, 0.0861, 0.2341, 0.6364],
[0.0117, 0.0317, 0.0861, 0.2341, 0.6364]])
>>> sum([0.0117, 0.0317, 0.0861, 0.2341, 0.6364])
1.0
>>>
softmax功能是把一组数归一为和为1.
如v = [a , b , c ,d ],, s = sum(v) softmax变成[a/ s, b/s, c/s,d/s]
>>> from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
>>> confusion_matrix([1, 2, 1, 3,3,3,4],[1,3,1,4,3,3,4])
array([[2, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 2, 1],
[0, 0, 0, 1]], dtype=int64)
import numpy as np
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch
x = np.array([[1, 2,3,4,5],
[1, 2,3,4,5],
[1, 2,3,4,5]]).astype(np.float32)
y = np.array([1, 1, 0])
x = torch.from_numpy(x)
y = torch.from_numpy(y).long()
soft_out = F.softmax(x,dim=1)
log_soft_out = torch.log(soft_out)
loss = F.nll_loss(log_soft_out, y)
print(soft_out)
print(log_soft_out)
print(loss)
loss = F.cross_entropy(x, y)
print(loss)Example::
>>> # input is of size N x C = 3 x 5
>>> input = torch.randn(3, 5, requires_grad=True)
>>> # each element in target has to have 0 <= value < C
>>> target = torch.tensor([1, 0, 4])
>>> output = F.nll_loss(F.log_softmax(input), target)
>>> output.backward()