jupyter notebook 文件的调用(调用.py文件或.ipynb文件)
jupyter notebook 文件的调用(调用.py文件或.ipynb文件)
参考文献:
jupyter notebook的project管理——.ipynb中调用.py文件
在jupyter notebook中调用.ipynb文件
调用 .py文件
这两个文件在工程的同一个文件夹中
def hello():
print('say hello')
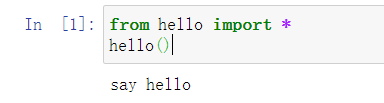
call_helper.ipynb中的代码:
from hello import *
hello()
这两个文件不在同一个文件夹中
如果这两个文件夹在同一个工程目录下
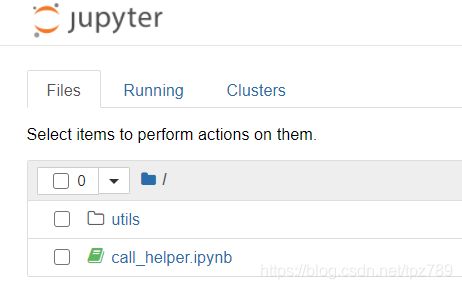
hello.py文件位于utils文件夹中,内容和上述的相同。
只需要将call_helper.ipynb中改为from utils.hello import hello
from utils.hello import *
hello()
如果这两个文件夹不在同一个工程目录下
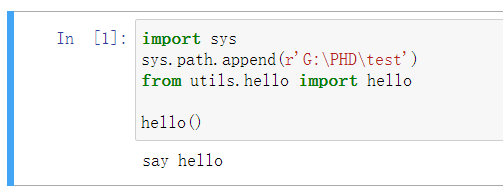
如call_helper.ipynb位于G:\PHD\jupyter,而hello.py位于G:\PHD\test\utils文件夹中。
则需要在call_helper.ipynb中使用sys将目录 G:\PHD\test\utils 添加。
import sys
sys.path.append(r'G:\PHD|test')
from utils.hello import *
hello()
调用.ipynb文件
两个文件在同一个文件夹中
添加jupyter notebook解析文件
首先,创建一个python文件,例如Ipynb_importer.py,代码如下:
注意是python文件,.py。
import io, os,sys,types
from IPython import get_ipython
from nbformat import read
from IPython.core.interactiveshell import InteractiveShell
class NotebookFinder(object):
"""Module finder that locates Jupyter Notebooks"""
def __init__(self):
self.loaders = {}
def find_module(self, fullname, path=None):
nb_path = find_notebook(fullname, path)
if not nb_path:
return
key = path
if path:
# lists aren't hashable
key = os.path.sep.join(path)
if key not in self.loaders:
self.loaders[key] = NotebookLoader(path)
return self.loaders[key]
def find_notebook(fullname, path=None):
"""find a notebook, given its fully qualified name and an optional path
This turns "foo.bar" into "foo/bar.ipynb"
and tries turning "Foo_Bar" into "Foo Bar" if Foo_Bar
does not exist.
"""
name = fullname.rsplit('.', 1)[-1]
if not path:
path = ['']
for d in path:
nb_path = os.path.join(d, name + ".ipynb")
if os.path.isfile(nb_path):
return nb_path
# let import Notebook_Name find "Notebook Name.ipynb"
nb_path = nb_path.replace("_", " ")
if os.path.isfile(nb_path):
return nb_path
class NotebookLoader(object):
"""Module Loader for Jupyter Notebooks"""
def __init__(self, path=None):
self.shell = InteractiveShell.instance()
self.path = path
def load_module(self, fullname):
"""import a notebook as a module"""
path = find_notebook(fullname, self.path)
print ("importing Jupyter notebook from %s" % path)
# load the notebook object
with io.open(path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
nb = read(f, 4)
# create the module and add it to sys.modules
# if name in sys.modules:
# return sys.modules[name]
mod = types.ModuleType(fullname)
mod.__file__ = path
mod.__loader__ = self
mod.__dict__['get_ipython'] = get_ipython
sys.modules[fullname] = mod
# extra work to ensure that magics that would affect the user_ns
# actually affect the notebook module's ns
save_user_ns = self.shell.user_ns
self.shell.user_ns = mod.__dict__
try:
for cell in nb.cells:
if cell.cell_type == 'code':
# transform the input to executable Python
code = self.shell.input_transformer_manager.transform_cell(cell.source)
# run the code in themodule
exec(code, mod.__dict__)
finally:
self.shell.user_ns = save_user_ns
return mod
sys.meta_path.append(NotebookFinder())
def hello():
print('say hello')
call_helper.ipynb
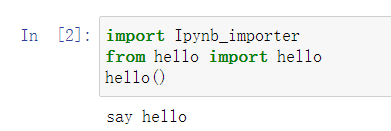
import Ipynb_importer
from hello import hello
hello()
两个文件不在同一个文件夹中
如果这两个文件夹在同一个工程目录下:
如果将hello.ipynb移入到utils文件夹。
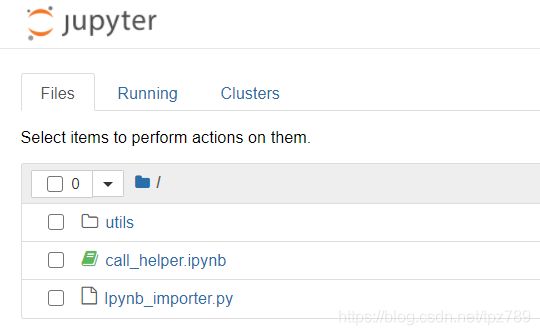
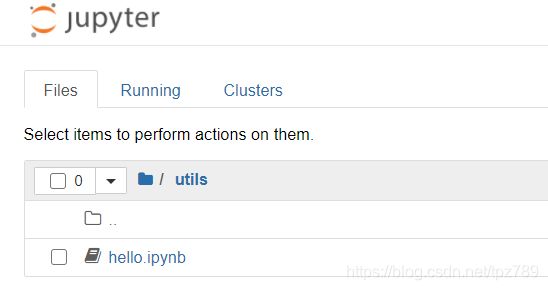
call_helper.ipynb:
import Ipynb_importer
from utils.hello import hello
hello()
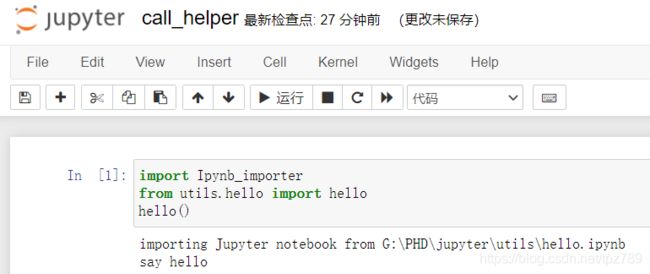
如果将hello.ipynb和Ipynb_importer.py都移入到utils文件夹。
call_helper.ipynb:
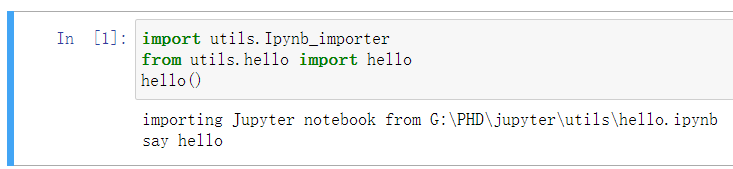
import utils.Ipynb_importer
from utils.hello import hello
hello()
如果这两个文件夹不在同一个工程目录下
call_helper.ipynb:
import sys
import Ipynb_importer
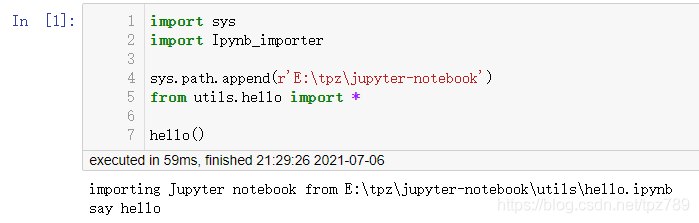
sys.path.append(r'E:\tpz\jupyter-notebook')
from utils.hello import *
hello()
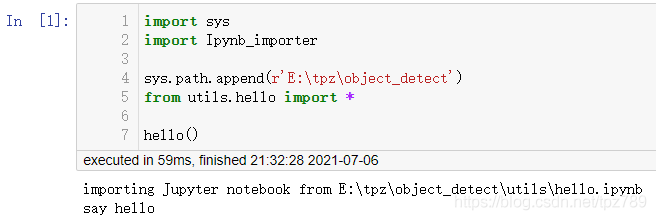
如果hello.ipynb放在更远的地方
import sys
import Ipynb_importer
sys.path.append(r'E:\tpz\object_detect')
from utils.hello import *
hello()