numpy的N维数组对象ndarray
文章目录
-
-
- constructing arrays
- Internal memory layout of an ndarray
- Array attributes
-
-
- Memory Layout
- Data Type
- Other attributes
- Array Interface
-
- Array methods
-
-
- Array conversion
- Shape manipulation
- Item selection and manipulation
- Calculation
- Arithmetic, matrix multiplication, and comparison operations
-
-
The N-dimentional array 即 ndarray 对象,是用于存放同类型元素的多维数组,元素索引由0下标开始。
constructing arrays
创建一个 ndarray 只需调用 NumPy 的 array 函数即可:
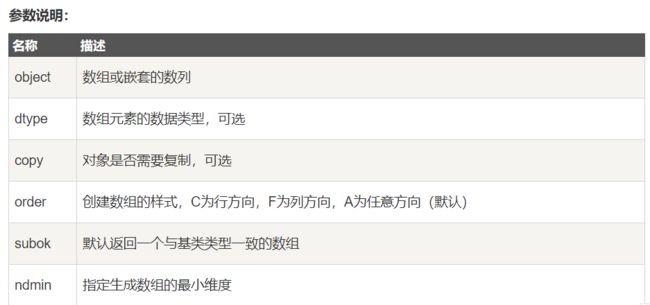
numpy.array(object, dtype = None, copy = True, order = None, subok = False, ndmin = 0)
Internal memory layout of an ndarray
ndarray 对象在计算机内存中由连续的一维的段(segment)组成,每个元素占用相同大小的存储区域(内存块),并且所有块的解释方式完全相同。结合索引(index),将每个元素映射到内存块中的一个位置(location of an item in the block),内存块以行顺序(C样式)或列顺序(F样式或MatLab风格) 保存元素(不同的方案,将N维数组的元素项安排在一维内存块中)。
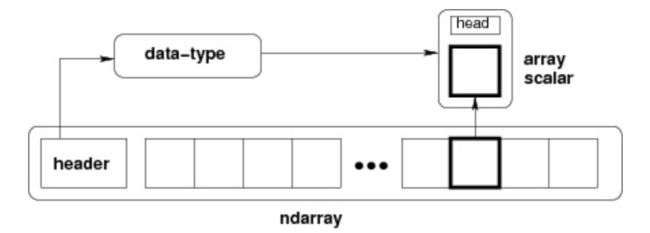
ndarray内部由以下内容组成:
[1] ndarray 本身,包括了数组的形状(指定了索引可以变化的范围)
[2] 指针(header),指向内存或内存映射文件中的一块数据
[3] 数据类型对象 (dtype),描述与数组元素相对应的固定大小的内存块中的字节。包括数据类型(ndarray数组元素是同一类型的,整型,浮点数,…),数据大小(占用字节数),数据字节顺序(big/little-endian)等。
Array attributes
数组属性反映了数组本身固有的信息。其中一部分可以被重置,而无需创建新的数组。
Memory Layout
ndarray.flags 有关数组的内存布局memory layout的信息。
ndarray.shape 数组维度的元组。
ndarray.ndim 数组的维数。
ndarray.size 数组中元素的数量。
ndarray.data 实际数组元素的缓冲区,指向数组数据的开头(数组内存地址是连续存放的)通常我们不需要使用这个属性,因为我们总是通过索引来使用数组中的元素。
ndarray.itemsize 数组一个元素的长度(以字节为单位)
ndarray.nbytes 数组元素消耗的总字节数
ndarray.base 基础对象,仅当内存来自其他对象的情况下出现
ndarray.strides 遍历数组 travering an array 时在每个维度上步进的字节数目的元组。
Example: an array of 32-bit integers (each 4 bytes)
x = np.array([[0, 1, 2, 3, 4],
[5, 6, 7, 8, 9]], dtype=np.int32)
32位整型数据占4字节 (bytes),因此 x 以40个字节的形式存储在连续的内存中。数组的步幅说明了要沿着某个轴移到下一个位置,我们必须在内存中跳过多少个字节。例如,我们必须跳过4个字节(1个值)才能移至下一列,但要跳过20个字节(5个值)才能移至下一行中的相同位置。因此,对于所述阵列的步幅X将是 (20,4)
同理,
>>> y = np.reshape(np.arange(2*3*4), (2,3,4))
>>> y
array([[[ 0, 1, 2, 3],
[ 4, 5, 6, 7],
[ 8, 9, 10, 11]],
[[12, 13, 14, 15],
[16, 17, 18, 19],
[20, 21, 22, 23]]])
>>> y.strides
(48, 16, 4)
>>> y[1,1,1]
17
Data Type
ndarray.dtype 数组元素的数据类型。
Other attributes
ndarray.T 转置数组。
ndarray.real 数组的实部。
ndarray.imag 数组的虚部。
ndarray.flat 数组上的一维迭代器。
ndarray.ctypes 一个用于简化数组与ctypes模块的交互的对象。
Array Interface
array_interface 数组接口的Python端
array_struct 数组接口的C端
ndarray.ctypes 一个用于简化数组与ctypes模块的交互的对象。
Array methods
An ndarray object has many methods which operate on or with the array in some fashion, typically returning an array result.
如下仅包括已用到过的,查找 戳这里
Array conversion
ndarray.astype(dtype [, order, casting, …]) Copy of the array, cast to a specified type. 数组的副本,强制转换数据类型。
ndarray.copy([order]) Return a copy of the array.
ndarray.view([dtype, type]) New view of array with the same data.
ndarray.fill(value) Fill the array with a scalar value.
Shape manipulation
For reshape, resize, and transpose, the single tuple argument may be replaced with n integers which will be interpreted as an n-tuple.
ndarray.reshape(shape[, order]) Returns an array containing the same data with a new shape.
ndarray.resize(new_shape[, refcheck]) Change shape and size of array in-place.
ndarray.transpose(*axes) Returns a view of the array with axes transposed.
ndarray.swapaxes(axis1, axis2) Return a view of the array with axis1 and axis2 interchanged.
ndarray.flatten([order]) Return a copy of the array collapsed into one dimension. 返回折叠成一维的数组副本。
ndarray.ravel([order]) Return a flattened array.返回一个展平的数组。
ndarray.squeeze([axis]) Remove single-dimensional entries from the shape of a.
Item selection and manipulation
For array methods that take an axis keyword, it defaults to None. If axis is None, then the array is treated as a 1-D array. Any other value for axis represents the dimension along which the operation should proceed.
对于采用axis关键字的数组方法,默认为 None。如果axis为None,则将该数组视为一维数组。轴的任何其他值都表示应该进行操作的尺寸。
ndarray.sort([axis, kind, order]) 就地排序数组Sort an array in-place.
ndarray.argsort([axis, kind, order]) 返回数组排序后的索引 Returns the indices that would sort this array.
ndarray.partition(kth[, axis, kind, order]) Rearranges the elements in the array in such a way that the value of the element in kth position is in the position it would be in a sorted array.
重新排列数组中的元素,使第k个位置的元素的值处于排序数组中的位置。所有小于第k个元素的元素都将在该元素之前移动,所有等于或大于第k个元素的元素都将移动到其后面。两个分区中元素的顺序未定义。
ndarray.argpartition(kth[, axis, kind, order]) 返回分区后的索引 Returns the indices that would partition this array.
ndarray.searchsorted(v[, side, sorter]) 查找应将v的元素插入到a中以保持顺序的索引。
ndarray.nonzero() 返回非零元素的索引。
ndarray.compress(condition[, axis, out]) 沿给定轴返回此数组的选定切片
Calculation
这些方法很多都采用axis参数。在这种情况下:
[1] 如果axis为None(默认值),则将该数组视为一维数组,并在整个数组上执行该操作。如果self是0维数组或数组标量,则此行为也是默认行为。(数组标量是类型/类float32,float64等的实例,而0维数组是仅包含一个数组标量的ndarray实例。)
[2] 如果axis是整数,将在给定的轴上进行操作(沿给定轴创建多个1-D子数组)。
Example of the axis argument
A 3-dimensional array of size 3 x 3 x 3, summed over each of its three axes
>>> x
array([[[ 0, 1, 2],
[ 3, 4, 5],
[ 6, 7, 8]],
[[ 9, 10, 11],
[12, 13, 14],
[15, 16, 17]],
[[18, 19, 20],
[21, 22, 23],
[24, 25, 26]]])
>>> x.sum(axis=0)
array([[27, 30, 33],
[36, 39, 42],
[45, 48, 51]])
>>> # for sum, axis is the first keyword, so we may omit it,
>>> # specifying only its value
>>> x.sum(0), x.sum(1), x.sum(2)
(array([[27, 30, 33],
[36, 39, 42],
[45, 48, 51]]),
array([[ 9, 12, 15],
[36, 39, 42],
[63, 66, 69]]),
array([[ 3, 12, 21],
[30, 39, 48],
[57, 66, 75]]))
参数dtype指定了进行运算操作后生成的(如求和)的数据类型。默认生成的数据类型与self的数据类型相同。为避免溢出,一般使用较大的数据类型执行操作。
对于其中几种方法,还可以提供可选的out参数,并将结果放入给定的输出数组中。该参数必须是具有相同数目元素的ndarray。它可以具有不同的数据类型,在这种情况下将执行强制转换。
(沿给定轴)求最大/小值(以及索引),限制最大最小值的数组切片,累加和,对角线的和,复数共轭,平均值,方差,标准差,元素乘积,评估是否为True
Arithmetic, matrix multiplication, and comparison operations
ndarray 的算术和比较运算被定义为按元素运算,并且通常将 ndarray对象作为结果。每个算术运算(的+,-,*,/,//, %,divmod(),**或pow(),<<,>>,&, ^,|,~)和比较(==,<,>, <=,>=,!=)等效于Numpy中相应的通用功能(简称ufunc)