非梯度类启发式搜索算法:Nelder Mead
算法介绍
Hello,今天给大家介绍一种不基于梯度的优化算法 Nelder Mead。
Nelder Mead 算法通常是用来求解非线性(nonlinear)、导函数未知情况下目标函数的最大值或者最小值。学过梯度下降的同学应该知道,梯度下降类算法的每一步都需要计算当前位置的梯度,从而更新当前解使得最终逐渐逼近最优解。但在某一些情况下,目标函数的梯度难以求得或是函数值离散的情况下,这时候便无法直接使用梯度类算法来求解了。
Nelder Mead 算法的思想十分简单,它本质上是受空间中 Simplex 各个顶点之间关系所启发而迭代优化的一类算法。在经过多次迭代后,算法逐渐收敛到最优解。Nelder Mead 是说,我既然不使用梯度,那么能不能在空间中模拟出一个梯度,算法使用 n+1n+1 个点来构造出一个 nn 维搜索空间下的 Simplex。例如在二维空间下使用三个点构成一个 Simplex,此时是一个三角形。然后在每个 iteration 中,对这个 Simplex 进行移动、收缩或者是扩张,以使该 Simplex 往好的方向变化。
(注意:文中所说的最优解并非解析形式的最优解,基于梯度和不基于梯度的这些优化方法都是为了解决难以求得解析解而使用其他办法来逼近的一类方法)
在详细介绍算法流程之前,给大家先看几张图,直观的理解一下 Nelder Mead 算法。(图片均来源于 Wikipedia)
算法流程
我们以二维空间下寻找最优解为例,在二维空间下,一般我们会选取 2+12+1 个点构成一个 Simplex。
然后开始一个 iteration,每一次 iteration 可能遇到不同的情况,接下来我们一一讲解。
reflection
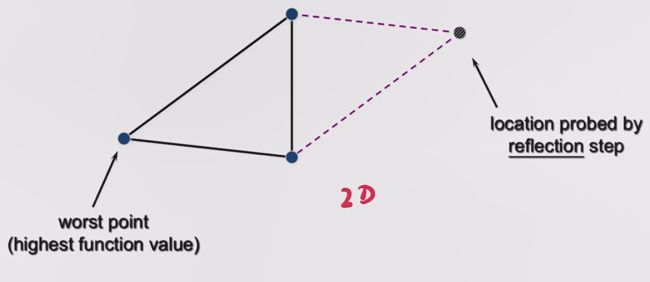
如下图所示,我们可以根据目标函数计算得到 Simplex 各个顶点的好坏,假设最左边的点是 worst point。
一个朴素的思想是,从一个差的点往好的点的方向走,那是否可能会找到一个潜在好的点。
在 reflection 操作中,我们会试探 worst point 关于另外两点连线中点的 reflection point 怎么样,将该点记为 location probed by reflection step。
expansion
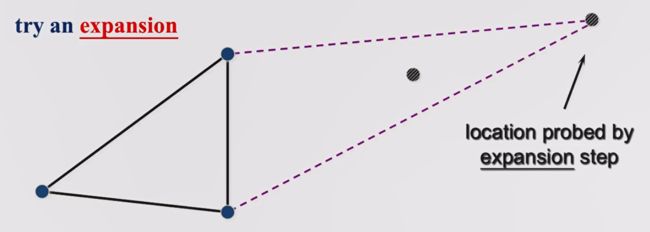
假设经过一次 reflection 得到的结果比原先好,那我想更好是不是可以沿着这个方向再走一点呢?这就是 expansion,我们将 expansion 后的点记为 location probed by expansion step。
最终,如果 expansion 操作的结果比单纯 reflection 更好,此时接受 location probed by expansion step,否则接受 location probed by reflection step,接受的新点与原先的 nn 个好点共同组成新的 Simplex。
为了更清晰一点理解,假设 worst point 距离 Simplex 中另外两个好点连线的中点距离为 stepstep,那么 location probed by reflection step 距离 worst point 为 2×step2×step,而 location probed by expansion step 距离 worst point 为 3×step3×step。
contraction
假设经过一次 reflection 得到的结果比原先差,那可能说明我沿着 reflection 的方向走的太远了,但我认为这个方向应该没有多大问题。于是尝试缩小步长,此时的步长为 0.5×step0.5×step,我们记该点为 location probed by contraction step,这就是 contraction 操作。如果 contraction 以后得到的点比 worst point 更好,那么我们接受这个点,并与原先的好点组成新的 Simplex。
shrink
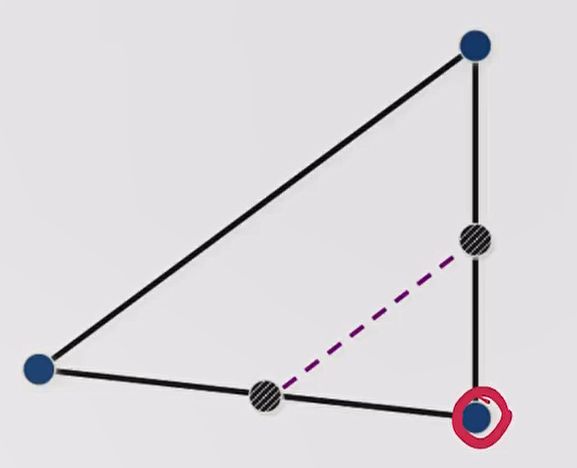
还有一种情况是,即使我执行了 contraction 操作,得到的点依然不好。那此时说明我们的 Simplex 可能太大了,执行 shrink 操作将所有非最优点全部往最优点(图中画圈的点)靠近其之间距离的一半,此时由 nn 个新点与旧的最优点组成新的 Simplex。
restart
在 Nelder-Mead 算法中,随着迭代的进行,Simplex 可能会变得越来越小,且每次更新的幅度都非常小,此时程序陷入一个假死的状态,为了解决该问题,我们引入了 restart 的概念。
restart 即如果程序触发我们预先设定的阈值,则重置当前的 Simplex。
在我的实验中,设定了两种阈值与不同的重置方法:
- 假如最优点与最差点之间经过目标函数得到的差异小于 epseps,则保留最优点随机初始化其他点
- 假如最优点保持了 maxAllowRepeatmaxAllowRepeat 次迭代且没有变化,则重置 Simplex 所有点
实验中,我所设定的 eps=0.001eps=0.001,maxAllowRepeat=1000maxAllowRepeat=1000
实验展示
Ellipsoid Problem
问题定义:
minf(x)=∑i=1dix2ix∈[−5.12,5.12],i=1,…,dminf(x)=∑i=1dixi2x∈[−5.12,5.12],i=1,…,d
效果展示:(其中红色的点为第一类 restart,绿色点为第二类 restart)
Global best value: 0.0000
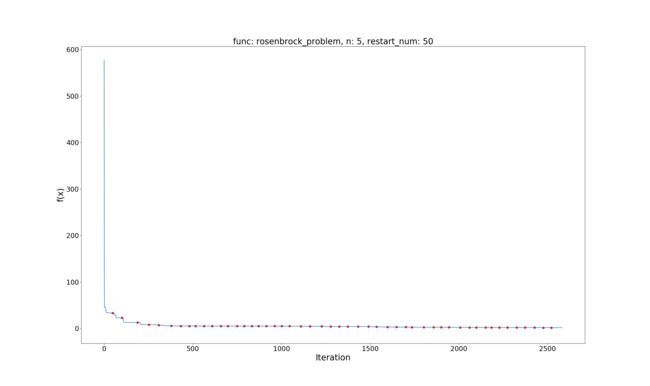
Rosenbrock Problem
问题定义:
minf(x)=∑i=1d(100(xi+1–x2i)2+(1−xi)2)x∈[−2.048,2.048],i=1,…,dminf(x)=∑i=1d(100(xi+1–xi2)2+(1−xi)2)x∈[−2.048,2.048],i=1,…,d
效果展示:
Global best value: 1.2414
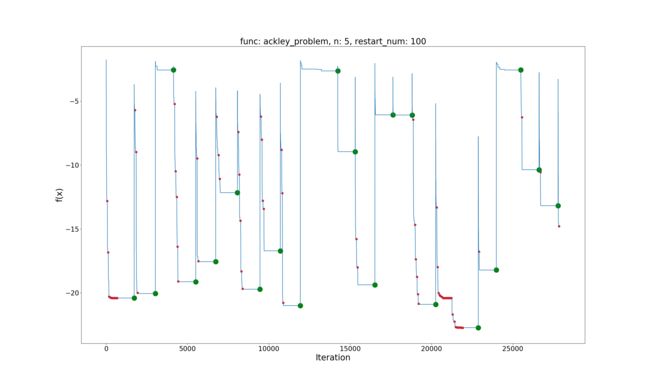
Ackley Problem
问题定义:
minf(x)=−20e−0.21d∑di=1x2i√−e1d∑di=1cos(2πxi)x∈[−32.768,32.768],i=1,…,dminf(x)=−20e−0.21d∑i=1dxi2−e1d∑i=1dcos(2πxi)x∈[−32.768,32.768],i=1,…,d
效果展示:
Global best value: -22.7164
Griewank Problem
问题定义:
minf(x)=1+∑i=1dx2i4000−∏i=1dcos(xii√)x∈[−600,600],i=1,…,dminf(x)=1+∑i=1dxi24000−∏i=1dcos(xii)x∈[−600,600],i=1,…,d
Global best value: 0.0302
Python 实现
尚未解决的问题:每一次反射等操作后没有检查每个点是否还在设定范围内,不过感觉问题不大。
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from typing import Callable, Tuple, NoReturn
def ellipsoid_problem(x: np.ndarray) -> np.ndarray:
res = np.array(0.0)
for di, xi in enumerate(x):
res = res + (di + 1) * xi * xi
return res
def rosenbrock_problem(x: np.ndarray) -> np.ndarray:
res = np.array(0.0)
d = len(x)
for i in range(d - 1):
res = res + 100 * ((x[i + 1] - x[i] * x[i]) ** 2) + (1 - x[i]) ** 2
res = res + 100 * ((-x[d - 1] * x[d - 1]) ** 2) + (1 - x[d - 1]) ** 2
return res
def ackley_problem(x: np.ndarray) -> np.ndarray:
d = len(x)
tmp1, tmp2 = 0.0, 0.0
for i in range(d):
tmp1 += x[i] * x[i] * 1.0 / d
tmp2 += np.cos(2.0 * np.pi * x[i])
tmp1 = -0.2 * np.sqrt(tmp1)
tmp2 = tmp2 * 1.0 / d
res = -20.0 * np.exp(tmp1) - np.exp(tmp2)
return res
def griewank_problem(x: np.ndarray) -> np.ndarray:
d = len(x)
tmp1, tmp2 = 0.0, 1.0
for i in range(d):
tmp1 = tmp1 + x[i] * x[i] / 4000.0
tmp2 = tmp2 * np.cos(x[i] / np.sqrt(i + 1))
res = 1 + tmp1 - tmp2
return res
def sampling(n: int, d: int, low: float, high: float) -> np.ndarray:
"""
生成 n 个随机点,且每个点有 d 维,其各个坐标在 [low, high) 之间
"""
return np.random.rand(n, d) * (high - low) + low
def restart(x: np.array, low: float, high: float, is_reset: bool, f: Callable[[np.ndarray], np.ndarray]) -> Tuple[
np.ndarray, np.ndarray]:
"""
restart, is_reset 控制是否完全重置,否则保留最优值重置其他位置
"""
tmp_x = sampling(n=x.shape[0], d=x.shape[1], low=low, high=high)
if not is_reset:
f_value = f(x.T)
best_idx = f_value.argmin()
tmp_x[best_idx] = x[best_idx]
tmp_f_value = f(tmp_x.T)
return tmp_x, tmp_f_value
def downhill_simplex_method(n: int, low: float, high: float, restart_num: int,
f: Callable[[np.ndarray], np.ndarray]) -> NoReturn:
"""
n 维空间需要初始化 n+1 个点,逼近函数最小值
"""
x = sampling(n=n + 1, d=n, low=low, high=high)
f_value = f(x.T)
vertice_min_list = [] # 存储每一次迭代所产生的最优值
vertice_min_point = []
vertice_restart_reset = [] # 记录当前位置是否经历过 restart,以及 reset
eps, max_allow_repeat = 1e-3, 1000 # restart 的条件,以及最大允许同一个最优值持续的轮数
restart_idx = 0
while True:
# 找出最差的点 bad_idx
bad_idx = f_value.argmax()
# 求反射的 step,为差点到好点所有向量之和的一半
step = (x.sum(axis=0) - x[bad_idx] * x.shape[0]) / 2.0
reflection_point = x[bad_idx] + 2 * step
reflection_value = f(reflection_point)
if (reflection_value < f_value[bad_idx]):
x[bad_idx] = reflection_point
f_value[bad_idx] = reflection_value
# 反射一次效果变好了,尝试再扩展一步
expansion_point = reflection_point + step
expansion_value = f(expansion_point)
if (expansion_value < reflection_value):
# 如果扩展以后效果更好,则保留这一个点,否则继续使用 reflection point
x[bad_idx] = expansion_point
f_value[bad_idx] = expansion_value
else:
# 反射不好,尝试收缩
contraction_point = x[bad_idx] + step / 2.0
contraction_value = f(contraction_point)
if (contraction_value < f_value[bad_idx]):
# 效果变好,接受
x[bad_idx] = contraction_point
f_value[bad_idx] = contraction_value
else:
# shrink
best_idx = f_value.argmin()
shrink_step = (x[best_idx] - x) / 2.0
x = x + shrink_step
f_value = f(x.T)
f_value_min = np.min(f_value)
f_value_max = np.max(f_value)
vertice_min_list.append(f_value_min)
vertice_min_point.append(x[f_value.argmin()])
vertice_restart_reset.append(0)
value_span = f_value_max - f_value_min
if value_span < eps or (
len(vertice_min_list) > max_allow_repeat
and vertice_min_list[-max_allow_repeat] == f_value_min):
if restart_idx < restart_num:
print('restart... ', restart_idx + 1)
restart_idx = restart_idx + 1
is_reset = False if value_span < eps else True
vertice_restart_reset[-1] = 1 + int(is_reset)
x, f_value = restart(x=x,
low=low,
high=high,
is_reset=is_reset,
f=f)
else:
break
# print('{:.4f} {:.4f}'.format(value_span, f_value.min()))
last_best_idx = f_value.argmin()
global_best_ids = np.argmin(vertice_min_list).item()
print('last best point: ', x[last_best_idx])
print('last best value: {:.4f}'.format(f_value[last_best_idx]))
print('global best point: ', vertice_min_point[global_best_ids])
print('global best value: {:.4f}'.format(
vertice_min_list[global_best_ids]))
# plot show
plt.title('func: {}, n: {}, restart_num: {}'.format(
getattr(f, '__name__'), n, restart_num), fontsize=25)
plt.xticks(fontsize=20)
plt.yticks(fontsize=20)
plt.xlabel('Iteration', fontsize=25)
plt.ylabel('f(x)', fontsize=25)
plt_x = np.arange(len(vertice_min_list))
plt_y = np.array(vertice_min_list)
plt.plot(plt_x, plt_y) # 画最优值曲线
restart_point_x = plt_x[np.array(vertice_restart_reset) == 1]
plt.scatter(restart_point_x, plt_y[restart_point_x], c='r') # 描 restart 点
restart_point_x = plt_x[np.array(vertice_restart_reset) == 2]
plt.scatter(restart_point_x,
plt_y[restart_point_x],
c='green',
linewidths=10) # 描 reset 点
plt.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
n = 5
low, high = -5.12, 5.12
restart_num = 50
downhill_simplex_method(n=n,
low=low,
high=high,
restart_num=restart_num,
f=ellipsoid_problem)
# n = 5
# low, high = -2.048, 2.048
# restart_num = 50
# downhill_simplex_method(n=n,
# low=low,
# high=high,
# restart_num=restart_num,
# f=rosenbrock_problem)
# n = 5
# low, high = -32.768, 32.768
# restart_num = 100
# downhill_simplex_method(n=n,
# low=low,
# high=high,
# restart_num=restart_num,
# f=ackley_problem)
# n = 5
# low, high = -600.0, 600.0
# restart_num = 100
# downhill_simplex_method(n=n,
# low=low,
# high=high,
# restart_num=restart_num,
# f=griewank_problem)
pass