如何利用DGL官方库中的rgcn链接预测代码跑自己的数据集(如何在DGL库的链接预测数据集模块定义自己的数据集类)
最近在忙我的省创,是有关于知识图谱的,其中有一个内容是使用rgcn的链接预测方法跑自己的数据集,我是用的dgl库中给出的在pytorch环境下实现rgcn的链接预测的代码,相关链接贴在这里:
dgl库中关于rgcn的介绍文档
dgl库中在pytorch环境下实现rgcn的链接预测的代码
这个代码给的示例就是使用FB15k237数据集,调用方法是这样的:
from dgl.data.knowledge_graph import FB15k237Dataset
data = FB15k237Dataset(reverse=False)
graph = data[0]
print("graph",graph)
这里就调用了FB15k237数据集,返回的的data[0]就是使用dgl库使用该数据集构建的图g。
我一开始想用自己的数据构图,然后使用rgcn的代码跑我自己的数据集,但是我不知道它的构图是如何实现的,于是我修改了rgcn的代码,实现了自己的构图方式如下,就是使用入结点出节点和边的编号列表构图:
g = dgl.graph((src, dst), num_nodes=num_nodes)
g.edata[dgl.ETYPE] = rel
鉴于rgcn示例里使用的FB15k237数据集的图的属性有'train_mask'和'test_mask'等属性,我就把rgcn代码里有关构图的部分全改成我自己的了,修改过后的完整可运行rgcn代码如下。
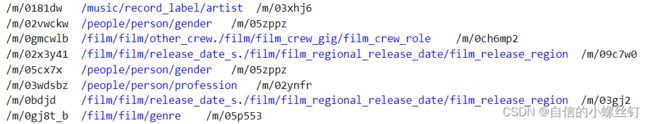
这个代码需要自己提供entity.txt,relation.txt,train.txt,valid.txt,test.txt五个文件,entity.txt和relation.txt分别代表实体编号到实体描述的映射,关系编号到关系描述的映射,类似这样:

train.txt,valid.txt,test.txt这三个文件就代表训练集,验证集和测试集的已经被映射为编号的(h,r,t)格式的三元组,类似这样:

在代码中写入对应的自己的数据集已经处理好的这五个文件的地址,运行下面的文件就可以运行完整的rgcn代码了:
import numpy as np
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import scipy as sp
import torch.nn.functional as F
import dgl
from dgl.data.knowledge_graph import FB15k237Dataset
from dgl.data.knowledge_graph import FB15kDataset
from dgl.dataloading import GraphDataLoader
from dgl.nn.pytorch import RelGraphConv
import tqdm
# for building training/testing graphs
def get_subset_g(g, mask, num_rels, bidirected=False):
src, dst = g.edges()
sub_src = src[mask]
sub_dst = dst[mask]
sub_rel = g.edata['etype'][mask]
if bidirected:
sub_src, sub_dst = torch.cat([sub_src, sub_dst]), torch.cat([sub_dst, sub_src])
sub_rel = torch.cat([sub_rel, sub_rel + num_rels])
sub_g = dgl.graph((sub_src, sub_dst), num_nodes=g.num_nodes())
sub_g.edata[dgl.ETYPE] = sub_rel
return sub_g
class GlobalUniform:
def __init__(self, g, sample_size):
self.sample_size = sample_size
self.eids = np.arange(g.num_edges(),dtype='int64')
def sample(self):
return torch.from_numpy(np.random.choice(self.eids, self.sample_size))
class NegativeSampler:
def __init__(self, k=10): # negative sampling rate = 10
self.k = k
def sample(self, pos_samples, num_nodes):
batch_size = len(pos_samples)
neg_batch_size = batch_size * self.k
neg_samples = np.tile(pos_samples, (self.k, 1))
values = np.random.randint(num_nodes, size=neg_batch_size)
choices = np.random.uniform(size=neg_batch_size)
subj = choices > 0.5
obj = choices <= 0.5
neg_samples[subj, 0] = values[subj]
neg_samples[obj, 2] = values[obj]
samples = np.concatenate((pos_samples, neg_samples))
# binary labels indicating positive and negative samples
labels = np.zeros(batch_size * (self.k + 1), dtype=np.float32)
labels[:batch_size] = 1
return torch.from_numpy(samples), torch.from_numpy(labels)
class SubgraphIterator:
def __init__(self, g, num_rels, sample_size=30000, num_epochs=6000):
self.g = g
self.num_rels = num_rels
self.sample_size = sample_size
self.num_epochs = num_epochs
self.pos_sampler = GlobalUniform(g, sample_size)
self.neg_sampler = NegativeSampler()
def __len__(self):
return self.num_epochs
def __getitem__(self, i):
eids = self.pos_sampler.sample()
src, dst = self.g.find_edges(eids)
src, dst = src.numpy(), dst.numpy()
rel = self.g.edata[dgl.ETYPE][eids].numpy()
# relabel nodes to have consecutive node IDs
uniq_v, edges = np.unique((src, dst), return_inverse=True)
num_nodes = len(uniq_v)
# edges is the concatenation of src, dst with relabeled ID
src, dst = np.reshape(edges, (2, -1))
relabeled_data = np.stack((src, rel, dst)).transpose()
samples, labels = self.neg_sampler.sample(relabeled_data, num_nodes)
# use only half of the positive edges
chosen_ids = np.random.choice(np.arange(self.sample_size),
size=int(self.sample_size / 2),
replace=False)
src = src[chosen_ids]
dst = dst[chosen_ids]
rel = rel[chosen_ids]
src, dst = np.concatenate((src, dst)), np.concatenate((dst, src))
rel = np.concatenate((rel, rel + self.num_rels))
sub_g = dgl.graph((src, dst), num_nodes=num_nodes)
sub_g.edata[dgl.ETYPE] = torch.from_numpy(rel)
sub_g.edata['norm'] = dgl.norm_by_dst(sub_g).unsqueeze(-1)
uniq_v = torch.from_numpy(uniq_v).view(-1).long()
return sub_g, uniq_v, samples, labels
class RGCN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_nodes, h_dim, num_rels):
super().__init__()
# two-layer RGCN
self.emb = nn.Embedding(num_nodes, h_dim)
self.conv1 = RelGraphConv(h_dim, h_dim, num_rels, regularizer='bdd',
num_bases=100, self_loop=True)
self.conv2 = RelGraphConv(h_dim, h_dim, num_rels, regularizer='bdd',
num_bases=100, self_loop=True)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(0.2)
def forward(self, g, nids):
x = self.emb(nids)
h = F.relu(self.conv1(g, x, g.edata[dgl.ETYPE], g.edata['norm']))
h = self.dropout(h)
h = self.conv2(g, h, g.edata[dgl.ETYPE], g.edata['norm'])
return self.dropout(h)
class LinkPredict(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_nodes, num_rels, h_dim = 500, reg_param=0.01):
super().__init__()
self.rgcn = RGCN(num_nodes, h_dim, num_rels * 2)
self.reg_param = reg_param
self.w_relation = nn.Parameter(torch.Tensor(num_rels, h_dim))
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(self.w_relation,
gain=nn.init.calculate_gain('relu'))
def calc_score(self, embedding, triplets):
s = embedding[triplets[:,0]]
r = self.w_relation[triplets[:,1]]
o = embedding[triplets[:,2]]
score = torch.sum(s * r * o, dim=1)
return score
def forward(self, g, nids):
return self.rgcn(g, nids)
def regularization_loss(self, embedding):
return torch.mean(embedding.pow(2)) + torch.mean(self.w_relation.pow(2))
def get_loss(self, embed, triplets, labels):
# each row in the triplets is a 3-tuple of (source, relation, destination)
score = self.calc_score(embed, triplets)
predict_loss = F.binary_cross_entropy_with_logits(score, labels)
reg_loss = self.regularization_loss(embed)
return predict_loss + self.reg_param * reg_loss
def filter(triplets_to_filter, target_s, target_r, target_o, num_nodes, filter_o=True):
"""Get candidate heads or tails to score"""
target_s, target_r, target_o = int(target_s), int(target_r), int(target_o)
# Add the ground truth node first
if filter_o:
candidate_nodes = [target_o]
else:
candidate_nodes = [target_s]
for e in range(num_nodes):
triplet = (target_s, target_r, e) if filter_o else (e, target_r, target_o)
# Do not consider a node if it leads to a real triplet
if triplet not in triplets_to_filter:
candidate_nodes.append(e)
return torch.LongTensor(candidate_nodes)
def perturb_and_get_filtered_rank(emb, w, s, r, o, test_size, triplets_to_filter, filter_o=True):
"""Perturb subject or object in the triplets"""
num_nodes = emb.shape[0]
ranks = []
for idx in tqdm.tqdm(range(test_size), desc="Evaluate"):
target_s = s[idx]
target_r = r[idx]
target_o = o[idx]
candidate_nodes = filter(triplets_to_filter, target_s, target_r,
target_o, num_nodes, filter_o=filter_o)
if filter_o:
emb_s = emb[target_s]
emb_o = emb[candidate_nodes]
else:
emb_s = emb[candidate_nodes]
emb_o = emb[target_o]
target_idx = 0
emb_r = w[target_r]
emb_triplet = emb_s * emb_r * emb_o
scores = torch.sigmoid(torch.sum(emb_triplet, dim=1))
_, indices = torch.sort(scores, descending=True)
rank = int((indices == target_idx).nonzero())
ranks.append(rank)
return torch.LongTensor(ranks)
def calc_mrr(emb, w, triplets_to_filter, batch_size=100, filter=True):
with torch.no_grad():
test_triplets = triplets_to_filter
s, r, o = test_triplets[:,0], test_triplets[:,1], test_triplets[:,2]
test_size = len(s)
triplets_to_filter = {tuple(triplet) for triplet in triplets_to_filter.tolist()}
ranks_s = perturb_and_get_filtered_rank(emb, w, s, r, o, test_size,
triplets_to_filter, filter_o=False)
ranks_o = perturb_and_get_filtered_rank(emb, w, s, r, o,
test_size, triplets_to_filter)
ranks = torch.cat([ranks_s, ranks_o])
ranks += 1 # change to 1-indexed
mrr = torch.mean(1.0 / ranks.float()).item()
mr = torch.mean(ranks.float()).item()
print("MRR (filtered): {:.6f}".format(mrr))
print("MR (filtered): {:.6f}".format(mr))
hits=[1,3,10]
for hit in hits:
avg_count = torch.mean((ranks <= hit).float())
print("Hits (filtered) @ {}: {:.6f}".format(hit, avg_count.item()))
return mrr
def train(dataloader, test_g, test_nids, triplets, device, model_state_file, model):
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=1e-2)
best_mrr = 0
for epoch, batch_data in enumerate(dataloader): # single graph batch
model.train()
g, train_nids, edges, labels = batch_data
g = g.to(device)
train_nids = train_nids.to(device)
edges = edges.to(device)
labels = labels.to(device)
embed = model(g, train_nids)
loss = model.get_loss(embed, edges, labels)
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
nn.utils.clip_grad_norm_(model.parameters(), max_norm=1.0) # clip gradients
optimizer.step()
print("Epoch {:04d} | Loss {:.4f} | Best MRR {:.4f}".format(epoch, loss.item(), best_mrr))
if (epoch + 1) % 500 == 0:
# perform validation on CPU because full graph is too large
model = model.cpu()
model.eval()
embed = model(test_g, test_nids)
mrr = calc_mrr(embed, model.w_relation, triplets,
batch_size=500)
# save best model
if best_mrr < mrr:
best_mrr = mrr
torch.save({'state_dict': model.state_dict(), 'epoch': epoch}, model_state_file)
model = model.to(device)
if __name__ == '__main__':
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
print(f'Training with DGL built-in RGCN module')
# load and preprocess dataset
# data = FB15k237Dataset(reverse=False)
# data = FB15kDataset(reverse=False)
entityfile=r'data/entity.txt'
relationfile=r'data/relation.txt'
f1 = open(entityfile, 'r')
f2 = open(relationfile, 'r')
entity=[]
relation=[]
for line in f1:
l=line.strip().split("\t")
entity.append(int(l[0]))
for line in f2:
l=line.strip().split("\t")
relation.append(int(l[0]))
num_nodes=len(entity)
num_rels=len(relation)
n_entities=num_nodes
print("# entities:",num_nodes)
print("# relations:",num_rels)
trainfile=r'data/train.txt'
f3 = open(trainfile, 'r')
src_train=[]
rel_train=[]
dst_train=[]
for line in f3:
l=line.strip().split("\t")
h=int(l[0])
r=int(l[1])
t=int(l[2])
src_train.append(h)
rel_train.append(r)
dst_train.append(t)
print("# training edges: ",len(src_train))
src_train=torch.LongTensor(src_train)
rel_train=torch.LongTensor(rel_train)
dst_train=torch.LongTensor(dst_train)
train_g = dgl.graph((src_train, dst_train), num_nodes=num_nodes)
train_g.edata[dgl.ETYPE] = rel_train
src_test, dst_test = torch.cat([src_train, dst_train]), torch.cat([dst_train,src_train])
rel_test = torch.cat([rel_train, rel_train + num_rels])
test_g = dgl.graph((src_test, dst_test), num_nodes=num_nodes)
test_g.edata[dgl.ETYPE] = rel_test
test_g.edata['norm'] = dgl.norm_by_dst(test_g).unsqueeze(-1)
test_nids = torch.arange(0, num_nodes)
subg_iter = SubgraphIterator(train_g, num_rels) # uniform edge sampling
dataloader = GraphDataLoader(subg_iter, batch_size=1, collate_fn=lambda x: x[0])
validfile=r'data/valid.txt'
f4 = open(validfile, 'r')
num_valid=0
for line in f4:
num_valid+=1
print("# validation edges: ",num_valid)
# Prepare data for metric computation
testfile=r'data/test.txt'
f5 = open(testfile, 'r')
src=[]
rel=[]
dst=[]
for line in f5:
l=line.strip().split("\t")
h=int(l[0])
r=int(l[1])
t=int(l[2])
src.append(h)
rel.append(r)
dst.append(t)
print("# testing edges: ",len(src))
src=torch.LongTensor(src)
rel=torch.LongTensor(rel)
dst=torch.LongTensor(dst)
triplets_test = torch.stack([src,rel, dst], dim=1)
# create RGCN model
model = LinkPredict(num_nodes, num_rels).to(device)
# train
model_state_file = 'model_state.pth'
train(dataloader, test_g, test_nids, triplets_test, device, model_state_file, model)
# testing
print("Testing...")
checkpoint = torch.load(model_state_file)
model = model.cpu() # test on CPU
model.eval()
model.load_state_dict(checkpoint['state_dict'])
embed = model(test_g, test_nids)
best_mrr = calc_mrr(embed, model.w_relation,triplets_test,
batch_size=500)
print("Best MRR {:.4f} achieved using the epoch {:04d}".format(best_mrr, checkpoint['epoch']))
但是,这个代码的效果并不太好,贴在这里只是做个过程记录,同样的数据集,为什么这样简单的构图效果就没有dgl库里自己构图的效果好呢?说实话我也不知道(°ー°〃)我也看了dgl库里处理数据然后构图的代码,确实要精细很多,我就认为是预处理数据的方式不一样导致效果的差别吧。因此下面要说的就是如何在如何在DGL库的链接预测数据集模块定义自己的数据集类,将自己的数据集输入,使用dgl库中处理数据的方法处理我们的数据,再像刚刚调用FB15k237数据集那样调用自己的数据集。
- step 1 :
找到你的dgl.data.knowledge_graph.py文件,(我这里使用的版本是dgl 0.9.0),在这个文件中,定义了FB15k237Dataset,FB15Dataset和WN18Dataset三个常用的知识图谱数据集类,我们添加一个自己的数据集类MyDataset(其实就是copy了一下别的类(°ー°〃))
class MyDataset(KnowledgeGraphDataset):
def __init__(self, reverse=True, raw_dir=None, force_reload=False,
verbose=True, transform=None):
name = 'mydata'
super(MyDataset, self).__init__(name, reverse, raw_dir,
force_reload, verbose, transform)
def __getitem__(self, idx):
r"""Gets the graph object """
return super(MyDataset, self).__getitem__(idx)
def __len__(self):
r"""The number of graphs in the dataset."""
return super(MyDataset, self).__len__()
- step 2:
找到你的dgl.data.dgl_dataset.py文件,找到下图对应的代码位置,加入框框内的代码:
(至于为什么要这样呢,,,,自己看代码吧,虽然我也很想做记录,方便自己下次看懂,但是感觉要讲的话将不太清楚,打半天字解释不如自己看看代码咋写的 ┭┮﹏┭┮)
if self.name=='mydata':
return os.path.join(self.raw_dir)
- step 3:
在rgcn的链接预测代码里调用一下自己的数据就好啦,下面是一个简单的demo,这样就可以调用自己的数据集类了。
from dgl.data.knowledge_graph import MyDataset
dataset = MyDataset(raw_dir=r'你自己装数据集的文件夹位置',reverse=False)
还有十分重要的一点就是,数据集的格式,我是把自己的数据集都设成了和它调用的FB15k237数据集一样的格式,因为step 3中要写入的文件夹地址内要包含的文件有5个:entities.dict,relations.dict,train.txt,valid.txt,test.txt。
entities.dict和relations.dict分别代表实体编号到实体描述的映射,关系编号到关系描述的映射,类似这样:
train.txt,valid.txt,test.txt这三个文件代表训练集,验证集和测试集的还没有被映射为编号的(h,r,t)格式的三元组,类似这样:(它们中间的间隔均是'\t')
把我改过的最终的rgcn代码贴在下面,做个记录,其中我对calc_mrr函数做了修改的,它原本的代码里只有mrr一个评估指标,我增加了mr,hist@1,hist@3,hist@10这几个指标,在代码里看吧:
import numpy as np
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import dgl
from dgl.data.knowledge_graph import FB15k237Dataset
from dgl.data.knowledge_graph import FB15kDataset
from dgl.data.knowledge_graph import MyDataset
from dgl.dataloading import GraphDataLoader
from dgl.nn.pytorch import RelGraphConv
import tqdm
# for building training/testing graphs
def get_subset_g(g, mask, num_rels, bidirected=False):
src, dst = g.edges()
sub_src = src[mask]
sub_dst = dst[mask]
sub_rel = g.edata['etype'][mask]
if bidirected:
sub_src, sub_dst = torch.cat([sub_src, sub_dst]), torch.cat([sub_dst, sub_src])
sub_rel = torch.cat([sub_rel, sub_rel + num_rels])
sub_g = dgl.graph((sub_src, sub_dst), num_nodes=g.num_nodes())
sub_g.edata[dgl.ETYPE] = sub_rel
return sub_g
class GlobalUniform:
def __init__(self, g, sample_size):
self.sample_size = sample_size
self.eids = np.arange(g.num_edges())
def sample(self):
return torch.from_numpy(np.random.choice(self.eids, self.sample_size))
class NegativeSampler:
def __init__(self, k=10): # negative sampling rate = 10
self.k = k
def sample(self, pos_samples, num_nodes):
batch_size = len(pos_samples)
neg_batch_size = batch_size * self.k
neg_samples = np.tile(pos_samples, (self.k, 1))
values = np.random.randint(num_nodes, size=neg_batch_size)
choices = np.random.uniform(size=neg_batch_size)
subj = choices > 0.5
obj = choices <= 0.5
neg_samples[subj, 0] = values[subj]
neg_samples[obj, 2] = values[obj]
samples = np.concatenate((pos_samples, neg_samples))
# binary labels indicating positive and negative samples
labels = np.zeros(batch_size * (self.k + 1), dtype=np.float32)
labels[:batch_size] = 1
return torch.from_numpy(samples), torch.from_numpy(labels)
class SubgraphIterator:
def __init__(self, g, num_rels, sample_size=30000, num_epochs=6000):
self.g = g
self.num_rels = num_rels
self.sample_size = sample_size
self.num_epochs = num_epochs
self.pos_sampler = GlobalUniform(g, sample_size)
self.neg_sampler = NegativeSampler()
def __len__(self):
return self.num_epochs
def __getitem__(self, i):
eids = self.pos_sampler.sample()
src, dst = self.g.find_edges(eids)
src, dst = src.numpy(), dst.numpy()
rel = self.g.edata[dgl.ETYPE][eids].numpy()
# relabel nodes to have consecutive node IDs
uniq_v, edges = np.unique((src, dst), return_inverse=True)
num_nodes = len(uniq_v)
# edges is the concatenation of src, dst with relabeled ID
src, dst = np.reshape(edges, (2, -1))
relabeled_data = np.stack((src, rel, dst)).transpose()
samples, labels = self.neg_sampler.sample(relabeled_data, num_nodes)
# use only half of the positive edges
chosen_ids = np.random.choice(np.arange(self.sample_size),
size=int(self.sample_size / 2),
replace=False)
src = src[chosen_ids]
dst = dst[chosen_ids]
rel = rel[chosen_ids]
src, dst = np.concatenate((src, dst)), np.concatenate((dst, src))
rel = np.concatenate((rel, rel + self.num_rels))
sub_g = dgl.graph((src, dst), num_nodes=num_nodes)
sub_g.edata[dgl.ETYPE] = torch.from_numpy(rel)
sub_g.edata['norm'] = dgl.norm_by_dst(sub_g).unsqueeze(-1)
uniq_v = torch.from_numpy(uniq_v).view(-1).long()
return sub_g, uniq_v, samples, labels
class RGCN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_nodes, h_dim, num_rels):
super().__init__()
# two-layer RGCN
self.emb = nn.Embedding(num_nodes, h_dim)
self.conv1 = RelGraphConv(h_dim, h_dim, num_rels, regularizer='bdd',
num_bases=100, self_loop=True)
self.conv2 = RelGraphConv(h_dim, h_dim, num_rels, regularizer='bdd',
num_bases=100, self_loop=True)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(0.2)
def forward(self, g, nids):
x = self.emb(nids)
h = F.relu(self.conv1(g, x, g.edata[dgl.ETYPE], g.edata['norm']))
h = self.dropout(h)
h = self.conv2(g, h, g.edata[dgl.ETYPE], g.edata['norm'])
return self.dropout(h)
class LinkPredict(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_nodes, num_rels, h_dim = 500, reg_param=0.01):
super().__init__()
self.rgcn = RGCN(num_nodes, h_dim, num_rels * 2)
self.reg_param = reg_param
self.w_relation = nn.Parameter(torch.Tensor(num_rels, h_dim))
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(self.w_relation,
gain=nn.init.calculate_gain('relu'))
def calc_score(self, embedding, triplets):
s = embedding[triplets[:,0]]
r = self.w_relation[triplets[:,1]]
o = embedding[triplets[:,2]]
score = torch.sum(s * r * o, dim=1)
return score
def forward(self, g, nids):
return self.rgcn(g, nids)
def regularization_loss(self, embedding):
return torch.mean(embedding.pow(2)) + torch.mean(self.w_relation.pow(2))
def get_loss(self, embed, triplets, labels):
# each row in the triplets is a 3-tuple of (source, relation, destination)
score = self.calc_score(embed, triplets)
predict_loss = F.binary_cross_entropy_with_logits(score, labels)
reg_loss = self.regularization_loss(embed)
return predict_loss + self.reg_param * reg_loss
def filter(triplets_to_filter, target_s, target_r, target_o, num_nodes, filter_o=True):
"""Get candidate heads or tails to score"""
target_s, target_r, target_o = int(target_s), int(target_r), int(target_o)
# Add the ground truth node first
if filter_o:
candidate_nodes = [target_o]
else:
candidate_nodes = [target_s]
for e in range(num_nodes):
triplet = (target_s, target_r, e) if filter_o else (e, target_r, target_o)
# Do not consider a node if it leads to a real triplet
if triplet not in triplets_to_filter:
candidate_nodes.append(e)
return torch.LongTensor(candidate_nodes)
def perturb_and_get_filtered_rank(emb, w, s, r, o, test_size, triplets_to_filter, filter_o=True):
"""Perturb subject or object in the triplets"""
num_nodes = emb.shape[0]
ranks = []
for idx in tqdm.tqdm(range(test_size), desc="Evaluate"):
target_s = s[idx]
target_r = r[idx]
target_o = o[idx]
candidate_nodes = filter(triplets_to_filter, target_s, target_r,
target_o, num_nodes, filter_o=filter_o)
if filter_o:
emb_s = emb[target_s]
emb_o = emb[candidate_nodes]
else:
emb_s = emb[candidate_nodes]
emb_o = emb[target_o]
target_idx = 0
emb_r = w[target_r]
emb_triplet = emb_s * emb_r * emb_o
scores = torch.sigmoid(torch.sum(emb_triplet, dim=1))
_, indices = torch.sort(scores, descending=True)
rank = int((indices == target_idx).nonzero())
ranks.append(rank)
return torch.LongTensor(ranks)
def calc_mrr(emb, w, test_mask, triplets_to_filter, batch_size=100, filter=True):
with torch.no_grad():
test_triplets = triplets_to_filter[test_mask]
s, r, o = test_triplets[:,0], test_triplets[:,1], test_triplets[:,2]
test_size = len(s)
triplets_to_filter = {tuple(triplet) for triplet in triplets_to_filter.tolist()}
ranks_s = perturb_and_get_filtered_rank(emb, w, s, r, o, test_size,
triplets_to_filter, filter_o=False)
ranks_o = perturb_and_get_filtered_rank(emb, w, s, r, o,
test_size, triplets_to_filter)
ranks = torch.cat([ranks_s, ranks_o])
ranks += 1 # change to 1-indexed
mrr = torch.mean(1.0 / ranks.float()).item()
mr = torch.mean(ranks.float()).item()
print("MRR (filtered): {:.6f}".format(mrr))
print("MR (filtered): {:.6f}".format(mr))
hits=[1,3,10]
for hit in hits:
avg_count = torch.mean((ranks <= hit).float())
print("Hits (filtered) @ {}: {:.6f}".format(hit, avg_count.item()))
return mrr
def train(dataloader, test_g, test_nids, test_mask, triplets, device, model_state_file, model):
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=1e-2)
best_mrr = 0
for epoch, batch_data in enumerate(dataloader): # single graph batch
model.train()
g, train_nids, edges, labels = batch_data
g = g.to(device)
train_nids = train_nids.to(device)
edges = edges.to(device)
labels = labels.to(device)
embed = model(g, train_nids)
loss = model.get_loss(embed, edges, labels)
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
nn.utils.clip_grad_norm_(model.parameters(), max_norm=1.0) # clip gradients
optimizer.step()
print("Epoch {:04d} | Loss {:.4f} | Best MRR {:.4f}".format(epoch, loss.item(), best_mrr))
if (epoch + 1) % 500 == 0:
# perform validation on CPU because full graph is too large
model = model.cpu()
model.eval()
embed = model(test_g, test_nids)
mrr = calc_mrr(embed, model.w_relation, test_mask, triplets,
batch_size=500)
# save best model
if best_mrr < mrr:
best_mrr = mrr
torch.save({'state_dict': model.state_dict(), 'epoch': epoch}, model_state_file)
model = model.to(device)
if __name__ == '__main__':
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
print(f'Training with DGL built-in RGCN module')
# load and preprocess dataset
# data = FB15k237Dataset(reverse=False)
data = MyDataset(raw_dir=r'data/FB15k237',reverse=False)
g = data[0]
num_nodes = g.num_nodes()
num_rels = data.num_rels
train_g = get_subset_g(g, g.edata['train_mask'], num_rels)
test_g = get_subset_g(g, g.edata['train_mask'], num_rels, bidirected=True)
test_g.edata['norm'] = dgl.norm_by_dst(test_g).unsqueeze(-1)
test_nids = torch.arange(0, num_nodes)
test_mask = g.edata['test_mask']
subg_iter = SubgraphIterator(train_g, num_rels) # uniform edge sampling
dataloader = GraphDataLoader(subg_iter, batch_size=1, collate_fn=lambda x: x[0])
# Prepare data for metric computation
src, dst = g.edges()
triplets = torch.stack([src, g.edata['etype'], dst], dim=1)
# create RGCN model
model = LinkPredict(num_nodes, num_rels).to(device)
# train
model_state_file = 'model_state.pth'
train(dataloader, test_g, test_nids, test_mask, triplets, device, model_state_file, model)
# testing
print("Testing...")
checkpoint = torch.load(model_state_file)
model = model.cpu() # test on CPU
model.eval()
model.load_state_dict(checkpoint['state_dict'])
embed = model(test_g, test_nids)
best_mrr = calc_mrr(embed, model.w_relation, test_mask, triplets,
batch_size=500)
print("Best MRR {:.4f} achieved using the epoch {:04d}".format(best_mrr, checkpoint['epoch']))
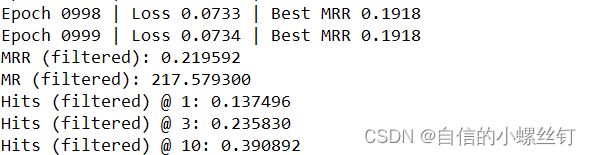
跑代码的输出图如下:
,over!