自学很好的例子Spring AOP——Spring 中面向切面编程(一)
Spring AOP
- 一、Spring AOP
-
- 1.1 什么是 AOP
- 1.2 为什么要用AOP
- 1.3 AOP实现分类
- 二、 AOP体系与概念
-
- 2.1 一些概念详解:
- 2.2 Spring AOP 的特点
- 三、第一个小型实例(男女孩买东西)
-
- 3.0 Spring AOP依赖
- 3.1 男女孩买东西(初步需求)
-
- 3.1.1 首先创建一个接口 IBuy.java
- 3.1.2 Boy 和 Gril 两个类分别实现了这个接口
-
- 3.1.2.1 Boy.java
- 3.1.2.2 Girl.java
- 3.1.3 配置文件, AppConfig.java
- 3.1.4 测试类, AppTest.java
- 3.1.5 运行结果
- 3.2 更改需求
-
- 3.2.1 定义一个切面类,BuyAspectJ.java
-
- 3.2.1.1 这里讲一下@Pointcut
- 3.2.2 在配置文件中启用AOP切面功能
- 3.2.3 运行结果
- 四、 通过注解配置 Spring AOP,修改男女孩买东西
-
- 4.1 通过注解声明切点指示器
-
- 4.1.1 修改 BuyAspectJ.java
- 4.1.2 运行结果
- 4.2 通过注解声明 5 种通知类型
-
- 4.2.1 下面修改切面类
- 4.2.2 测试类AppTest类
- 4.2.3 运行结果
- 4.3 通过注解声明切点表达式
-
- 4.3.1 修改BuyAspectJ.java
- 4.3.2 运行结果
- 4.4 通过注解处理通知中的参数
-
- 4.4.1 修改 IBuy.java
- 4.4.2 Girl.java
- 4.4.3 Boy.java
- 4.4.4 BuyAspectJ 类
- 4.4.5 测试类:AppTest.java
- 4.4.6 运行结果
- 4.5 通过注解配置织入的方式
-
- 4.5.1 测试final(cglib 的动态代理)
-
- 4.5.1.1 修改AppConfig.java
- 4.5.1.2 修改Girl.java
- 4.5.1.3 运行结果
这些天一直都在百度和CSDN上自学AOP,真的一个头两个大,一搜一大堆,我这小白能看明白的就是那些汉字了,不断地寻找,不断的学习,我整理了一些东西,作为一个总结吧,我觉得我这也是初学,如果你也是,我希望能给你点启发吧!文章七七八八的从各处总结来的,今天先写一点,后边再总结。
一、Spring AOP
1.1 什么是 AOP
AOP(Aspect Oriented Programming),直译过来就是面向切面编程。通过预编译方式和运行期间动态代理实现程序功能的统一维护的一种技术。AOP是OOP的延续,是软件开发中的一个热点,也是Spring框架中的一个重要内容,是函数式编程的一种衍生范型。利用AOP可以对业务逻辑的各个部分进行隔离,从而使得业务逻辑各部分之间的耦合度降低,提高程序的可重用性,同时提高了开发的效率。是Spring的三大核心思想之一(两外两个:IOC-控制反转、DI-依赖注入)。
从《Spring实战(第4版)》图书中扒了一张图:
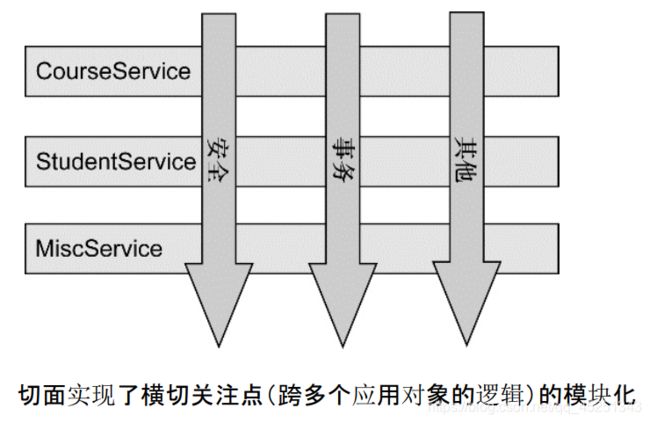
从该图可以很形象地看出,所谓切面,相当于应用对象间的横切点,我们可以将其单独抽象为单独的模块。
1.2 为什么要用AOP
开发中在多个模块间有某段重复的代码,我们通常是怎么处理的?显然,没有人会靠“复制粘贴”吧。在传统的面向过程编程中,我们也会将这段代码,抽象成一个方法,然后在需要的地方分别调用这个方法,这样当这段代码需要修改时,我们只需要改变这个方法就可以了。然而需求总是变化的,有一天,新增了一个需求,需要再多出做修改,我们需要再抽象出一个方法,然后再在需要的地方分别调用这个方法,又或者我们不需要这个方法了,我们还是得删除掉每一处调用该方法的地方。实际上涉及到多个地方具有相同的修改的问题我们都可以通过 AOP 来解决。
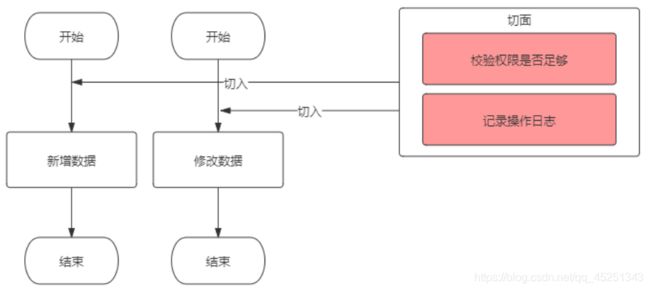
在我们的程序中,经常存在一些系统性的需求,比如权限校验、日志记录、统计等,这些代码会散落穿插在各个业务逻辑中,非常冗余且不利于维护。例如下面这个示意图:

有多少业务操作,就要写多少重复的校验和日志记录代码,这显然是无法接受的。当然,用面向对象的思想,我们可以把这些重复的代码抽离出来,写成公共方法,就是下面这样:

这样,代码冗余和可维护性的问题得到了解决,但每个业务方法中依然要依次手动调用这些公共方法,也是略显繁琐。有没有更好的方式呢?有的,那就是AOP,AOP将权限校验、日志记录等非业务代码完全提取出来,与业务代码分离,并寻找节点切入业务代码中:
1.3 AOP实现分类
AOP 要达到的效果是,保证开发者不修改源代码的前提下,去为系统中的业务组件添加某种通用功能。AOP 的本质是由 AOP 框架修改业务组件的多个方法的源代码,看到这其实应该明白了,AOP 其实代理模式的典型应用。
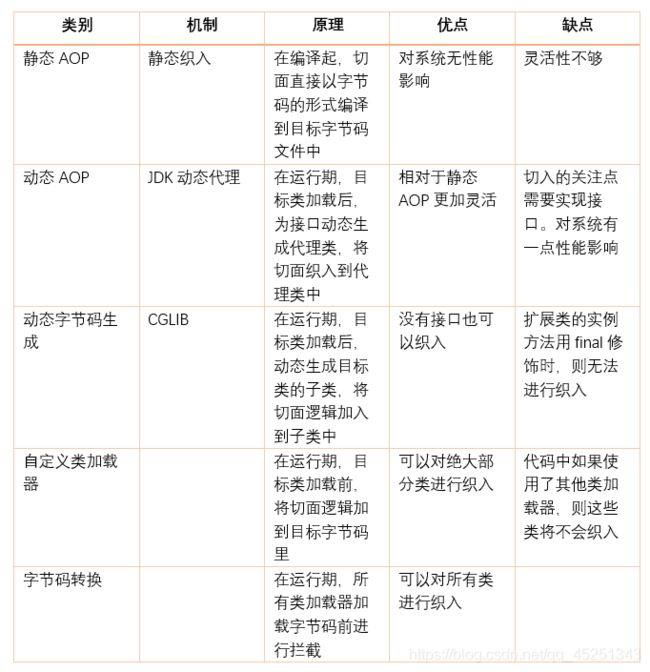
按照 AOP 框架修改源代码的时机,可以将其分为两类:
- 静态 AOP 实现
AOP 框架在编译阶段对程序源代码进行修改,生成了静态的 AOP 代理类(生成的 *.class 文件已经被改掉了,需要使用特定的编译器),比如 AspectJ。
- 动态 AOP 实现
AOP 框架在运行阶段对动态生成代理对象(在内存中以 JDK 动态代理,或 CGlib 动态地生成 AOP 代理类),如 SpringAOP。
下面给出常用 AOP 实现比较
二、 AOP体系与概念
简单地去理解,其实AOP要做三类事:
- 在哪里切入,也就是权限校验等非业务操作在哪些业务代码中执行。
- 在什么时候切入,是业务代码执行前还是执行后。
- 切入后做什么事,比如做权限校验、日志记录等。
2.1 一些概念详解:
- Pointcut:切点,决定处理如权限校验、日志记录等在何处切入业务代码中(即织入切面)。切点分为execution方式和annotation方式。前者可以用路径表达式指定哪些类织入切面,后者可以指定被哪些注解修饰的代码织入切面。
- Advice:处理,包括处理时机和处理内容。处理内容就是要做什么事,比如校验权限和记录日志。处理时机就是在什么时机执行处理内容,如下所示。
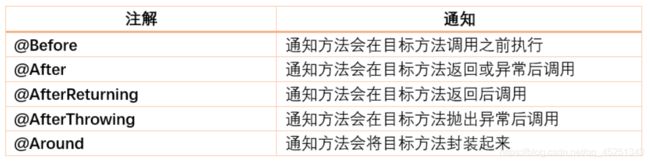
1.前置通知(Before Advice)
在某连接点(JoinPoint)之前执行的通知,但这个通知不能阻止连接点前的执行。例如,TestAspect 中的 doBefore 方法。
2.后置通知(After Advice)
当某连接点退出的时候执行的通知(不论是正常返回还是异常退出)。
例如,ServiceAspect 中的 returnAfter 方法,所以 Teser 中调用 UserService.delete 抛出异常时,returnAfter 方法仍然执行。
3.返回后通知(After Return Advice)
在某连接点正常完成后执行的通知,不包括抛出异常的情况。
4.环绕通知(Around Advice)
包围一个连接点的通知,类似 Web 中 Servlet 规范中的 Filter 的 doFilter 方法。可 以在方法的调用前后完成自定义的行为, 也可以选择不执行。
例如,ServiceAspect 中的 around 方法。
5.异常通知(After Throwing Advice)
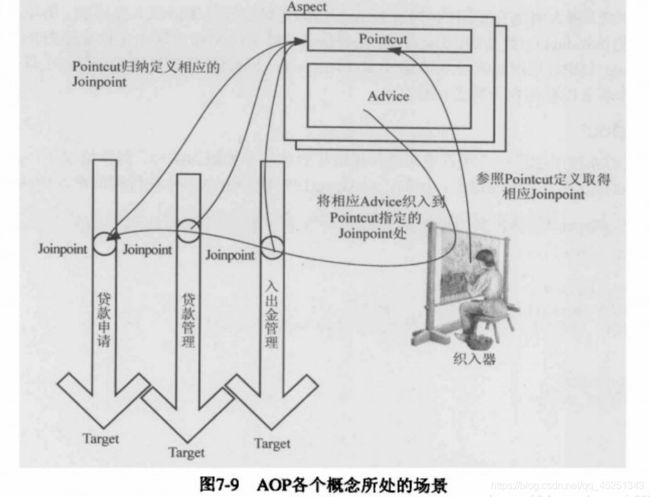
在 方 法 抛 出 异 常 退 出 时 执 行 的 通 知 。 - Aspect:切面,即Pointcut和Advice。通知和切点的结合。它既包括了横切逻辑的定义,也包括了连接点的定义,SpringAOP就是将切面所定义的横切逻辑织入到切面所制定的连接点中。
- Joint point:连接点,是程序执行的一个点。例如,一个方法的执行或者一个异常的处理。在 Spring AOP 中,一个连接点总是代表一个方法执行。
- Target Object:目标对象,被一个或者多个切面所通知的对象。例如,AServcieImpl 和 BServiceImpl,当然在实际运行时,Spring AOP 采用代理实现,实际 AOP 操作的是 TargetObject 的代理对象。
- Weaving:织入,就是通过动态代理,在目标对象方法中执行处理内容的过程。
- Proxy:代理类,一个类被AOP织入增强后,就产生了一个代理类。
网络上有张图,我觉得非常传神,贴在这里供大家观详:
2.2 Spring AOP 的特点
AOP 框架有很多种,Spring 中的 AOP 是通过动态代理实现的。不同的 AOP 框架支持的连接点也有所区别,例如,AspectJ 和 JBoss,除了支持方法切点,它们还支持字段和构造器的连接点。而 Spring AOP 不能拦截对对象字段的修改,也不支持构造器连接点,我们无法在 Bean 创建时应用通知。
三、第一个小型实例(男女孩买东西)
3.0 Spring AOP依赖
在pom.xml中配置,意思加入依赖,以下所有都需要有这个包
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframeworkgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-aspectsartifactId>
<version>4.3.7.RELEASEversion>
dependency>
3.1 男女孩买东西(初步需求)
上代码,对着代码说比较好说
3.1.1 首先创建一个接口 IBuy.java
package com.mystep.step.test;
/**
* @author step
* @date 2021年07月17日 15:01
*/
public interface IBuy {
String buy();
}
3.1.2 Boy 和 Gril 两个类分别实现了这个接口
3.1.2.1 Boy.java
package com.mystep.step.test;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* @author step
* @date 2021年07月17日 15:01
*/
@Component
public class Boy implements IBuy {
@Override
public String buy() {
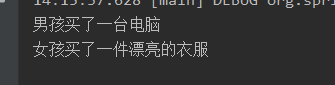
System.out.println("男孩买了一台电脑");
return "电脑";
}
}
3.1.2.2 Girl.java
package com.mystep.step.test;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* @author step
* @date 2021年07月17日 15:01
*/
@Component
public class Girl implements IBuy {
@Override
public String buy() {
System.out.println("女孩买了一件漂亮的衣服");
return "衣服";
}
}
3.1.3 配置文件, AppConfig.java
package com.mystep.step.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
/**
* @author setp
* @date 2021年07月17日 15:32
*/
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackageClasses = {com.mystep.step.test.IBuy.class})
public class AppConfig {
}
3.1.4 测试类, AppTest.java
package com.mystep.step.aopdemo;
import com.mystep.step.test.Boy;
import com.mystep.step.test.Girl;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
/**
* @author step
* @date 2021年07月17日 15:05
*/
public class AppTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context =
new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(com.mystep.step.config.AppConfig.class);
Boy boy = context.getBean("boy",Boy.class);
Girl girl = (Girl) context.getBean("girl");
boy.buy();
girl.buy();
}
}
3.1.5 运行结果
3.2 更改需求
这里运用SpringIOC里的自动部署。现在需求改变了,我们需要在男孩和女孩的 buy 方法之前,需要打印出“男孩女孩都买了自己喜欢的东西”。用 Spring AOP 来实现这个需求只需下面几个步骤:
3.2.1 定义一个切面类,BuyAspectJ.java
package com.mystep.step.test;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* @author step
* @date 2021年07月17日 15:29
*/
@Aspect
//@Aspect 表示它是一个切面
@Component
//@Component 表明它将作为一个Spring Bean 被装配
public class BuyAspectJ {
@Before("execution(* com.mystep.step.test.IBuy.buy(..))")
//@Before 这个注解,表示他将在方法执行之前执行
//参数("execution(* * com.mystep.step.test.IBuy.buy(..))") 声明了切点,
// 表明在该切面的切点是com.mystep.step.test.IBuy这个接口中的buy方法
public void haha(){
System.out.println("男孩女孩都买自己喜欢的东西");
}
}
这个类,我们使用了注解 @Component 表明它将作为一个Spring Bean 被装配,该类交给 Spring 来管理。
使用注解 @Aspect 表示它是一个切面。
类中只有一个方法 haha 我们使用 @Before 这个注解,表示他将在方法执行之前执行。
参数**(“execution(* com.mystep.step.test.IBuy.buy(…))”)** 声明了切点,表明在该切面的切点是com.mystep.step.test.IBuy这个接口中的buy方法。
3.2.1.1 这里讲一下@Pointcut
@Pointcut 注解指定一个切点,定义需要拦截的东西,这里介绍两个常用的表达式:一个是使用 execution(),另一个是使用 annotation()。
execution表达式:
以 execution(* com.mutest.controller….(…))) 表达式为例:
- 第一个 * 号的位置:表示返回值类型,* 表示所有类型。
- 包名:表示需要拦截的包名,后面的两个句点表示当前包和当前包的所有子包,在本例中指
com.mutest.controller包、子包下所有类的方法。 - 第二个 * 号的位置:表示类名,* 表示所有类。
- (…):这个星号表示方法名, 表示所有的方法,后面括弧里面表示方法的参数,两个句点表示任何参数。
annotation() 表达式:
annotation() 方式是针对某个注解来定义切点,比如我们对具有 @PostMapping 注解的方法做切面,可以如下定义切面:
@Pointcut("@annotation(org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping)")
public void annotationPointcut() {}
然后使用该切面的话,就会切入注解是 @PostMapping 的所有方法。这种方式很适合处理 @GetMapping、@PostMapping、@DeleteMapping不同注解有各种特定处理逻辑的场景。
3.2.2 在配置文件中启用AOP切面功能
package com.mystep.step.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.EnableAspectJAutoProxy;
/**
* @author step
* @date 2021年07月17日 15:32
*/
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackageClasses = {com.mystep.step.test.IBuy.class})
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy(proxyTargetClass = true)
//@EnableAspectJAutoProxy注解,启用了 AOP 功能,参数proxyTargetClass的值设为了 true,默认为false
public class AppConfig {
}
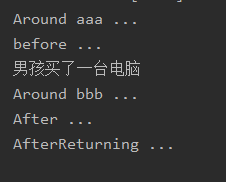
3.2.3 运行结果
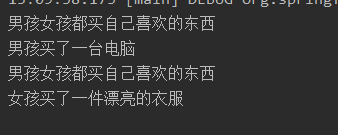
我们看到,结果与我们需求一致,我们并没有修改 Boy 和 Girl 类的 Buy 方法,也没有修改测试类的代码,几乎是完全无侵入式地实现了需求。这就是 AOP 的“神奇”之处。
四、 通过注解配置 Spring AOP,修改男女孩买东西
4.1 通过注解声明切点指示器
Spring AOP 所支持的 AspectJ 切点指示器
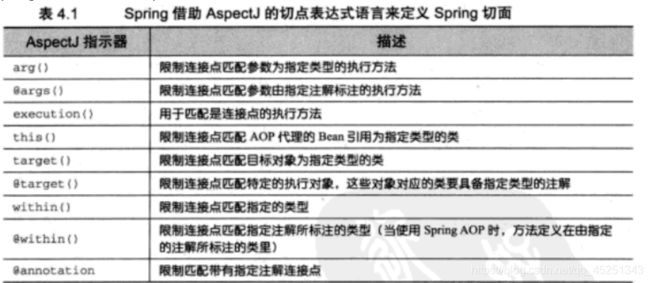
在spring中尝试使用AspectJ其他指示器时,将会抛出IllegalArgumentException异常。
当我们查看上面展示的这些spring支持的指示器时,注意只有execution指示器是唯一的执行匹配,而其他的指示器都是用于限制匹配的。这说明execution指示器是我们在编写切点定义时最主要使用的指示器,在此基础上,我们使用其他指示器来限制所匹配的切点。
execution(* com.mystep.step.test.IBuy.buy(..))

我们使用execution指示器选择IBuy的play方法,方法表达式以 * 号开始,标识我们不关心方法的返回值类型。然后我们指定了全限定类名和方法名。对于方法参数列表,我们使用 … 标识切点选择任意的play方法,无论该方法的入参是什么。 多个匹配之间我们可以使用链接符 &&、||、!来表示 “且”、“或”、“非”的关系。但是在使用 XML 文件配置时,这些符号有特殊的含义,所以我们使用 “and”、“or”、“not”来表示。
举例:
限定该切点仅匹配的包是com.mystep.step.test,可以使用
execution(* com.mystep.step.test.IBuy.buy(…)) && within(com.mystep.step.test.*)
在切点中选择 bean,可以使用
execution(* com.mystep.step.test.IBuy.buy(..)) && bean(girl)
4.1.1 修改 BuyAspectJ.java
package com.mystep.step.test;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* @author step
* @date 2021年07月17日 15:29
*/
@Aspect
//@Aspect 表示它是一个切面
@Component
//@Component 表明它将作为一个Spring Bean 被装配
public class BuyAspectJ {
@Before("execution(* com.mystep.step.test.IBuy.buy(..)) && within(com.mystep.step.test.*) && bean(girl)")
public void hehe(){
System.out.println("男孩女孩都买自己喜欢的东西");
}
}
4.1.2 运行结果
此时,切面只会对 Girl.java 这个类生效,执行结果:
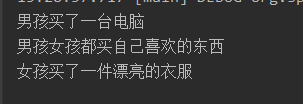
细心的你,可能发现了,切面中的方法名,已经被我悄悄地从haha改成了hehe,丝毫没有影响结果,说明方法名没有影响。和 Spring IOC 中用 java 配置文件装配 Bean 时,用@Bean 注解修饰的方法名一样,没有影响。
4.2 通过注解声明 5 种通知类型
Spring AOP 中有 5 中通知类型,上文2.1中我们提到过,我们再做一遍简述,分别如下:
4.2.1 下面修改切面类
package com.mystep.step.test;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* @author step
* @date 2021年07月17日 15:29
*/
@Aspect
//@Aspect 表示它是一个切面
@Component
//@Component 表明它将作为一个Spring Bean 被装配
public class BuyAspectJ {
@Before("execution(* com.mystep.step.test.IBuy.buy(..))")
public void hehe() {
System.out.println("before ...");
}
@After("execution(* com.mystep.step.test.IBuy.buy(..))")
public void haha() {
System.out.println("After ...");
}
@AfterReturning("execution(* com.mystep.step.test.IBuy.buy(..))")
public void xixi() {
System.out.println("AfterReturning ...");
}
@Around("execution(* com.mystep.step.test.IBuy.buy(..))")
public void xxx(ProceedingJoinPoint pj) {
try {
System.out.println("Around aaa ...");
pj.proceed();
System.out.println("Around bbb ...");
} catch (Throwable throwable) {
throwable.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
4.2.2 测试类AppTest类
为了方便看效果,我们测试类中,只要 Boy 类:
package com.mystep.step.aopdemo;
import com.mystep.step.config.AppConfig;
import com.mystep.step.test.Boy;
import com.mystep.step.test.Girl;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
/**
* @author step
* @date 2021年07月17日 15:05
*/
public class AppTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
Boy boy = context.getBean("boy",Boy.class);
Girl girl = (Girl) context.getBean("girl");
boy.buy();
// girl.buy();
}
}
4.2.3 运行结果
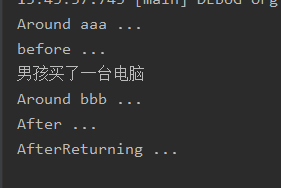
结果显而易见。指的注意的是 @Around 修饰的环绕通知类型,是将整个目标方法封装起来了,在使用时,我们传入了 ProceedingJoinPoint 类型的参数,这个对象是必须要有的,并且需要调用 ProceedingJoinPoint 的 proceed() 方法。 如果没有调用 该方法,用法如下对照自测

执行结果为 :
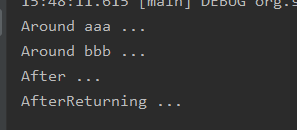
可见,如果不调用该对象的 proceed() 方法,表示原目标方法被阻塞调用,当然也有可能你的实际需求就是这样。
4.3 通过注解声明切点表达式
如你看到的,上面我们写的多个通知使用了相同的切点表达式,对于像这样频繁出现的相同的表达式,我们可以使用 @Pointcut注解声明切点表达式,然后使用表达式,修改代码如下:
4.3.1 修改BuyAspectJ.java
package com.mystep.step.test;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* @author step
* @date 2021年07月17日 15:29
*/
@Aspect
//@Aspect 表示它是一个切面
@Component
//@Component 表明它将作为一个Spring Bean 被装配
public class BuyAspectJ {
@Pointcut("execution(* com.mystep.step.test.IBuy.buy(..))")
public void point() {
}
@Before("point()")
public void hehe() {
System.out.println("before ...");
}
@After("point()")
public void haha() {
System.out.println("After ...");
}
@AfterReturning("point()")
public void xixi() {
System.out.println("AfterReturning ...");
}
@Around("point()")
public void xxx(ProceedingJoinPoint pj) {
try {
System.out.println("Around aaa ...");
pj.proceed();
System.out.println("Around bbb ...");
} catch (Throwable throwable) {
throwable.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
程序运行结果没有变化。
这里,我们使用
@Pointcut("execution(* com.mystep.step.test.IBuy.buy(..))")
public void point() {
}
4.3.2 运行结果
4.4 通过注解处理通知中的参数
上面的例子,我们要进行增强处理的目标方法没有参数,下面我们来说说有参数的情况,并且在增强处理中使用该参数。
下面我们给接口增加一个参数,表示购买所花的金钱。通过AOP 增强处理,如果女孩买衣服超过了 99 元,就可以赠送一双袜子。
更改代码如下:
4.4.1 修改 IBuy.java
package com.mystep.step.test;
/**
* @author step
* @date 2021年07月17日 15:01
*/
public interface IBuy {
String buy(double price);
}
4.4.2 Girl.java
package com.mystep.step.test;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* @author zxj
* @date 2021年07月17日 15:01
*/
@Component
public class Girl implements IBuy {
@Override
public String buy(double price) {
System.out.println(String.format("女孩花了%s元买了一件漂亮的衣服", price));
return "衣服";
}
}
4.4.3 Boy.java
package com.mystep.step.test;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* @author step
* @date 2021年07月17日 15:01
*/
@Component
public class Boy implements IBuy {
@Override
public String buy(double price) {
System.out.println(String.format("男孩花了%s元买了一台电脑", price));
return "电脑";
}
}
4.4.4 BuyAspectJ 类
我们将之前的通知都注释掉。我这里注释掉的就不展示了,我们用一个环绕通知来实现这个功能:
package com.mystep.step.test;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* @author step
* @date 2021年07月17日 15:29
*/
@Aspect
//@Aspect 表示它是一个切面
@Component
//@Component 表明它将作为一个Spring Bean 被装配
public class BuyAspectJ {
@Pointcut("execution(String com.mystep.step.test.IBuy.buy(double)) && args(price) && bean(girl)")
public void gif(double price) {
}
@Around("gif(price)")
public String hehe(ProceedingJoinPoint pj, double price){
try {
pj.proceed();
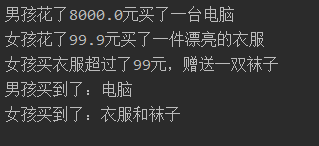
if (price > 99) {
System.out.println("女孩买衣服超过了99元,赠送一双袜子");
return "衣服和袜子";
}
} catch (Throwable throwable) {
throwable.printStackTrace();
}
return "衣服";
}
}
前文提到,当不关心方法返回值的时候,我们在编写切点指示器的时候使用了 * , 当不关心方法参数的时候,我们使用了 …。现在如果我们需要传入参数,并且有返回值的时候,则需要使用对应的类型。在编写通知的时候,我们也需要声明对应的返回值类型和参数类型。具体就是看文章4.4.4 和4.3.1
4.4.5 测试类:AppTest.java
package com.mystep.step.aopdemo;
import com.mystep.step.config.AppConfig;
import com.mystep.step.test.Boy;
import com.mystep.step.test.Girl;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
/**
* @author step
* @date 2021年07月17日 15:05
*/
public class AppTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
Boy boy = context.getBean("boy",Boy.class);
Girl girl = (Girl) context.getBean("girl");
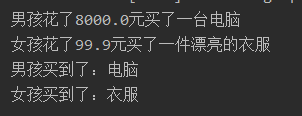
String boyBought = boy.buy(8000);
String girlBought = girl.buy(99.9);
System.out.println("男孩买到了:" + boyBought);
System.out.println("女孩买到了:" + girlBought);
}
}
4.4.6 运行结果
4.5 通过注解配置织入的方式
前面还有一个遗留问题,在配置文件中,我们用注解 @EnableAspectJAutoProxy() 启用Spring AOP 的时候,我们给参数 proxyTargetClass 赋值为 true,如果我们不写参数,默认为 false。这个时候运行程序,程序抛出异常

配置文件内容
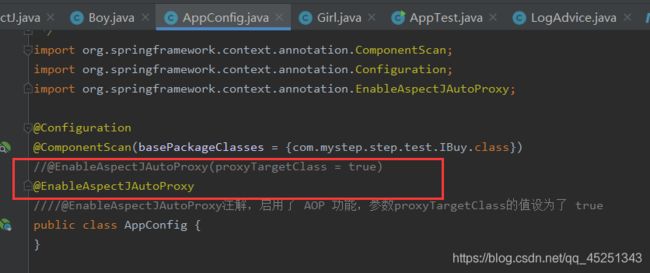
这是一个强制类型转换异常。为什么会抛出这个异常呢?或许已经能够想到,这跟Spring AOP 动态代理的机制有关,这个 proxyTargetClass 参数决定了代理的机制。
当这个参数为 false 时:
通过jdk的基于接口的方式进行织入,这时候代理生成的是一个接口对象,将这个接口对象强制转换为实现该接口的一个类,自然就抛出了上述类型转换异常。
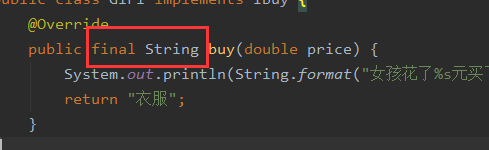
反之,proxyTargetClass 为 true,则会使用 cglib 的动态代理方式。这种方式的缺点是拓展类的方法被final修饰时,无法进行织入。
4.5.1 测试final(cglib 的动态代理)
我们将 proxyTargetClass 参数设为 true,同时将 Girl.java 的 Buy 方法用 final 修饰:
4.5.1.1 修改AppConfig.java
package com.mystep.step.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.EnableAspectJAutoProxy;
/**
* @author step
* @date 2021年07月17日 15:32
*/
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackageClasses = {com.mystep.step.test.IBuy.class})
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy(proxyTargetClass = true)
//@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy注解,启用了 AOP 功能,参数proxyTargetClass的值设为了 true
public class AppConfig {
}
4.5.1.2 修改Girl.java
package com.mystep.step.test;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* @author step
* @date 2021年07月17日 15:01
*/
@Component
public class Girl implements IBuy {
@Override
public final String buy(double price) {
System.out.println(String.format("女孩花了%s元买了一件漂亮的衣服", price));
return "衣服";
}
}