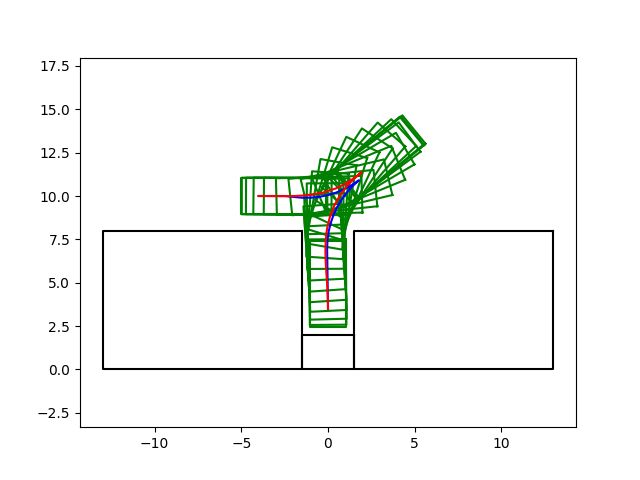
【局部规划】Hybird A*算法原理
HybridAstar是一种带有半径约束的路径平滑规划算法,算法思想来自A*算法,但A*是没有考虑平滑和半径约束的路径规划算法,且基于栅格地图的网格搜索算法,它们的目标代价函数是为了形成一条路径最短的无碰撞路径。而HybirdAstar是在二者的基础上加入半径约束,进行路径不同曲率方向采样,同时采用reedsheep曲线,进行目标点的衔接,来加速路径的生成效率。
1. A*算法原理
A*算法是基于网格的搜索算法。在算法中,路径的搜索主要考虑了两种代价,一个从起点到当前点路径长度代价g(n),另一个从当前点到目标点的预测代价h(n),二者之和构成栅格上目标搜索方向的判断的总代价f(n)。
因此,A*算法可以通过如下函数构建搜索方向上的栅格代价
其中,f(n)代表栅格节点n的总代价值,g(n) 代表栅格节点n距离起点的代价,h(n)是节点n距离终点的预测代价,也就是所谓的启发函数。
A*算法是通过openlist和closelist形成栅格的可行搜索解和封闭搜索解,算法实现如下:
初始化两个空的列表openlist和closelist,将起点加入openlist中,并设置代价值为0。
while(1)
{
if(openlist != null)
{
从openlist中选取代价值最小的节点n.
1. 如果节点n为终点,则从终点开始逐步追踪parent节点,一直达到起点,返回找到的结果路径,
跳出循环,算法结束,break;
2. 如果节点n不是终点,
2.1 将节点n从openlist中删除,加入到closelist中.
2.2 遍历节点n的8个相邻无碰撞节点
2.2.1 如果相邻节点在closelist或者openlist中,则跳过该节点,计算下一个节点。
2.2.2 如果相邻节点不在openlist中,则设置该节点父节点为n,通过f(n)计算该节点的
代价值,并将该节点放入openlist中。
}
else
break; //不能找到一条最优路径
}2. HybridAstar算法原理
HybridAstar算法主要分为两部分,一部分是最短路径的栅格代价值生成,有两种方式,一种是采用A*,另一种采用djkstra,但目标都一样,形成最短路径上的栅格代价值;另一部分是曲率采样,也就是所谓路径平滑,和A*的思想一样采用节点的方式产生树结构,在树结构中引入openlist和closelist两个列表,以此进行树的剪枝和回退操作。根据代价函数,将采样节点放到openlist中,同时根据最优代价从openlist中取出节点,并存放到closelist中,其操作过程和前面提到的A*算法过程一致。
代价函数g(n)同时考虑了路径长,转向、倒车等附加成本;启发函数考虑了最优的无碰撞路径,采用的是reedshepp曲线生成,满足了车辆的运动学约束;采用无碰撞的reedshepps曲线长度和运动学约束作为最终的启发函数代价项h(n)。以下是其实现的伪代码:
2.1 核心代码分析
下面以Apollo代码作为切入点来分析HybridAstar算法,主要分为四个部分:
- 栅格化规划区域内环境地图,采用djkstra或者A*算法生成当前位置到停车目标位置的栅格代价,也就是所谓的最优路径的栅格代价地图。
- 在车辆的世界坐标系下以一定的曲率采样间隔和步长,进行车辆的位姿采样,形成满足运动学约束的节点树。
- 计算采样的节点代价(会将前面计算的栅格代价也考虑进来),并存放到openlist中,从openlist中取出最优代价存放到closelist中,openlist和closelist的操作过程和前面讲到的A*算法原理一样。
- 在采样节点快要到达目标点时,反复采用reedshepps曲线将当前节点和目标点进行无碰撞连接,一旦reedshepps曲线连接成功,则标志着路径生成完成。
2.1.1 栅格代价地图生成
在Apollo代码中,有两种方式来生成栅格代价地图,一种是djkstra算法,另一种是A*算法,源代码在coarse_trajectorygenerator/http://grid_search.cc中,对应的函数分别为GenerateDpMap和GenerateAStarPath,Apollo提供的源码使用的是GenerateDpMap产生最短路径的栅格代价。
采用djkstra产生的栅格代价地图
bool GridSearch::GenerateDpMap(
const double ex, const double ey, const std::vector& XYbounds,
const std::vector>&
obstacles_linesegments_vec)
{
std::priority_queue,
std::vector>, cmp>
open_pq;
std::unordered_map> open_set;
dp_map_ = decltype(dp_map_)();
XYbounds_ = XYbounds;
// XYbounds with xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax
max_grid_y_ = std::round((XYbounds_[3] - XYbounds_[2]) / xy_grid_resolution_);
max_grid_x_ = std::round((XYbounds_[1] - XYbounds_[0]) / xy_grid_resolution_);
std::shared_ptr end_node =
std::make_shared(ex, ey, xy_grid_resolution_, XYbounds_);
// obstacles_linesegments_vec_ = obstacles_linesegments_vec;
open_set.insert(std::make_pair(end_node->GetIndex(), end_node));
open_pq.push(std::make_pair(end_node->GetIndex(), end_node->GetCost()));
// Grid a star begins
size_t explored_node_num = 0;
while (!open_pq.empty())
{
// std::cout<<"open_pq: "< current_node = open_set[current_id];
dp_map_.insert(std::make_pair(current_node->GetIndex(), current_node));
Box2d node_box = GetNodeExpandRange(current_node->GetGridX(),current_node->GetGridY());
obstacles_linesegments_vec_.clear();
for(const auto& obstacle : obstacles_linesegments_vec)
{
for(const auto& linesegment : obstacle)
if(node_box.HasOverlap(linesegment))
{
obstacles_linesegments_vec_.emplace_back(obstacle);
break;
}
}
std::vector> next_nodes =
std::move(GenerateNextNodes(current_node));
for (auto& next_node : next_nodes)
{
if (!CheckConstraints(next_node))
{
continue;
}
if (dp_map_.find(next_node->GetIndex()) != dp_map_.end())
{
continue;
}
if (open_set.find(next_node->GetIndex()) == open_set.end())
{
++explored_node_num;
next_node->SetPreNode(current_node);
open_set.insert(std::make_pair(next_node->GetIndex(), next_node));
open_pq.push(
std::make_pair(next_node->GetIndex(), next_node->GetCost()));
}
else
{
if (open_set[next_node->GetIndex()]->GetCost() > next_node->GetCost())
{
open_set[next_node->GetIndex()]->SetCost(next_node->GetCost());
open_set[next_node->GetIndex()]->SetPreNode(current_node);
}
}
}
}
ADEBUG << "explored node num is " << explored_node_num;
// std::cout<<"explored node num is " < 采用A*算法产生的栅格代价地图:
bool GridSearch::GenerateAStarPath(
const double sx, const double sy, const double ex, const double ey,
const std::vector& XYbounds,
const std::vector>&
obstacles_linesegments_vec,
GridAStartResult* result) {
std::priority_queue,
std::vector>, cmp>
open_pq;
std::unordered_map> open_set;
std::unordered_map> close_set;
XYbounds_ = XYbounds;
std::shared_ptr start_node =
std::make_shared(sx, sy, xy_grid_resolution_, XYbounds_);
std::shared_ptr end_node =
std::make_shared(ex, ey, xy_grid_resolution_, XYbounds_);
std::shared_ptr final_node_ = nullptr;
obstacles_linesegments_vec_ = obstacles_linesegments_vec;
open_set.insert(std::make_pair(start_node->GetIndex(), start_node));
open_pq.push(std::make_pair(start_node->GetIndex(), start_node->GetCost()));
// Grid a star begins
size_t explored_node_num = 0;
while (!open_pq.empty()) {
std::string current_id = open_pq.top().first;
open_pq.pop();
std::shared_ptr current_node = open_set[current_id];
// Check destination
if (*(current_node) == *(end_node)) {
final_node_ = current_node;
break;
}
close_set.emplace(current_node->GetIndex(), current_node);
std::vector> next_nodes =
std::move(GenerateNextNodes(current_node));
for (auto& next_node : next_nodes) {
if (!CheckConstraints(next_node)) {
continue;
}
if (close_set.find(next_node->GetIndex()) != close_set.end()) {
continue;
}
if (open_set.find(next_node->GetIndex()) == open_set.end()) {
++explored_node_num;
next_node->SetHeuristic(
EuclidDistance(next_node->GetGridX(), next_node->GetGridY(),
end_node->GetGridX(), end_node->GetGridY()));
next_node->SetPreNode(current_node);
open_set.insert(std::make_pair(next_node->GetIndex(), next_node));
open_pq.push(
std::make_pair(next_node->GetIndex(), next_node->GetCost()));
}
}
}
if (final_node_ == nullptr) {
AERROR << "Grid A searching return null ptr(open_set ran out)";
return false;
}
LoadGridAStarResult(result);
ADEBUG << "explored node num is " << explored_node_num;
return true;
} 最终在HybirdAstar通过调用CheckDpMap(const double sx, const double sy)获取栅格代价。
2.1.2 HybirdAstar路径搜索
该部分代码在coarse_trajectorygenerator/http://hybrid_a_star.cc中。节点采样采用了半径约束,是在世界坐标系下进行的,节点搜索借鉴的是A*的思想。
bool HybridAStar::Plan(
double sx, double sy, double sphi,double sv, double ex, double ey, double ephi,double ev,
const std::vector& XYbounds,
const std::vector>& obstacles_vertices_vec,
HybridAStartResult* result) //HybridAstar路径规划主函数
{
// clear containers
open_set_.clear(); //前面A*中提到的openlist
close_set_.clear(); //前面A*中提到的closelist
open_pq_ = decltype(open_pq_)();
final_node_ = nullptr;
obstacles_linesegments_vec_.clear();
for (const auto& obstacle_vertices : obstacles_vertices_vec) //感知活动的障碍物边界信息,以直线段的形式存储
{
size_t vertices_num = obstacle_vertices.size();
std::vector obstacle_linesegments;
for (size_t i = 0; i < vertices_num - 1; ++i)
{
common::math::LineSegment2d line_segment = common::math::LineSegment2d(
obstacle_vertices[i], obstacle_vertices[i + 1]);
obstacle_linesegments.emplace_back(line_segment);
// printf("linesegment:%f,%f-%f,%f\n",line_segment.start().x(),line_segment.start().y(),line_segment.end().x(),line_segment.end().y());
}
obstacles_linesegments_vec_.emplace_back(obstacle_linesegments);
}
// obstacles_linesegments_vec_ = std::move(obstacles_linesegments_vec);
obstacles_linesegments_vec_local_ = obstacles_linesegments_vec_;
// load XYbounds
XYbounds_ = XYbounds;
// load nodes and obstacles
start_node_.reset(
new Node3d({sx}, {sy}, {sphi}, XYbounds_, planner_open_space_config_));
end_node_.reset(
new Node3d({ex}, {ey}, {ephi}, XYbounds_, planner_open_space_config_));
if (!ValidityCheck(start_node_)) //检查起点是否发生碰撞,是否有效
{
AINFO << "start_node in collision with obstacles";
return false;
}
if (!ValidityCheck(end_node_)) //检查终点是否发生碰撞,是否有效
{
AINFO << "end_node in collision with obstacles";
return false;
}
double map_start = Clock::NowInSeconds();
grid_a_star_heuristic_generator_->GenerateDpMap(ex, ey, XYbounds_,
obstacles_linesegments_vec_); //栅格路径搜索,主要用于产生栅格路径势场,也就是栅格最短路径的代价值
double map_time = Clock::NowInSeconds() - map_start;
ADEBUG << "map time " << map_time;
// load open set, pq
open_set_.insert(std::make_pair(start_node_->GetIndex(), start_node_));
open_pq_.push(
std::make_pair(start_node_->GetIndex(), start_node_->GetCost()));
// Hybrid A* begins
size_t explored_node_num = 0;
double astar_start_time = Clock::NowInSeconds();
double heuristic_time = 0.0;
double rs_time = 0.0;
double start_time = 0.0;
double end_time = 0.0;
unsigned int node_cnt = 0;
while (!open_pq_.empty())
{
//timeout check
if(Clock::NowInSeconds() - astar_start_time > 3.0)
{
std::cout <<"timeout in 3 s,return" << std::endl;
return false;
}
// take out the lowest cost neighboring node
const std::string current_id = open_pq_.top().first;
open_pq_.pop();
std::shared_ptr current_node = open_set_[current_id];
// check if an analystic curve could be connected from current
// configuration to the end configuration without collision. if so, search
// ends.:Plan(
node_cnt++;
double current_heuristic = grid_a_star_heuristic_generator_->CheckDpMap(current_node->GetX(),
current_node->GetY()); //grid_search中djkstra栅格搜索的栅格代价值(可以理解最优路径花费)
unsigned int N= static_cast(0.1*current_heuristic); //用于加速hybridastar搜索速度,
if(node_cnt >= N+1)
{
node_cnt =0;
start_time = Clock::NowInSeconds();
if (AnalyticExpansion(current_node)) //是否可以生成到目标点的无碰撞的reedshepp曲线,加速搜索,直接连接规划终点。
{
break;
}
end_time = Clock::NowInSeconds();
rs_time += end_time - start_time;
}
close_set_.insert(std::make_pair(current_node->GetIndex(), current_node)); //将最优代价值节点放入到closelist中。
Box2d node_box = GetNodeExpandRange(current_node->GetX(),current_node->GetY(),current_node->GetPhi()); //节点footprint
obstacles_linesegments_vec_local_.clear();
for(const auto& obstacle : obstacles_linesegments_vec_) //感知获得的障碍物边界信息以直线段的形式存储
{
for(const auto& linesegment : obstacle)
if(node_box.HasOverlap(linesegment))
{
obstacles_linesegments_vec_local_.emplace_back(obstacle);
break;
}
}
for (size_t i = 0; i < next_node_num_; ++i)
{
std::shared_ptr next_node = Next_node_generator(current_node, i); //以不同曲率产生下一个相邻节点
// boundary check failure handle
if (next_node == nullptr)
{
continue;
}
// check if the node is already in the close set
if (close_set_.find(next_node->GetIndex()) != close_set_.end()) //检查下一个采样节点是否在closelist中
{
continue;
}
// collision check
if (!ValidityCheck(next_node)) //检查下一个采样节点是否发生碰撞
{
continue;
}
if (open_set_.find(next_node->GetIndex()) == open_set_.end()) //下一个节点也不在openlist中
{
explored_node_num++;
start_time = Clock::NowInSeconds();
CalculateNodeCost(current_node, next_node); //计算当前采样节点的代价值
end_time = Clock::NowInSeconds();
heuristic_time += end_time - start_time;
open_set_.emplace(next_node->GetIndex(), next_node);
open_pq_.emplace(next_node->GetIndex(), next_node->GetCost()); //将当前节点放入到closelist中,, //将当前节点放入到closelist中, cost = traj_cost_ + heuristic_cost_
}
}
}
if (final_node_ == nullptr)
{
ADEBUG << "Hybrid A searching return null ptr(open_set ran out)";
return false;
}
if (!GetResult(result,sv,ev)) //将前面获得的搜寻节点信息按顺序提取为特定格式的路径数据
{
ADEBUG << "GetResult failed";
return false;
}
double astar_end_time = Clock::NowInSeconds() - astar_start_time;
double total_plan = Clock::NowInSeconds()-map_start;
ADEBUG << "explored node num is " << explored_node_num;
ADEBUG << "heuristic time is " << heuristic_time;
ADEBUG << "reed shepp time is " << rs_time;
ADEBUG << "hybrid astar total time is "
<< astar_end_time;
std::cout <<"map time is " << map_time << std::endl;
std::cout <<"explored node num is " << explored_node_num << std::endl;
std::cout <<"heuristic time is " << heuristic_time << std::endl;
std::cout <<"reed shepp time is " << rs_time << std::endl;
std::cout <<"hybrid astar run time is " << astar_end_time << std::endl;
std::cout <<"total plan time is " << total_plan << std::endl;
return true;
} 2.1.3 HybirdAstar的代价值计算
该部分代码在coarse_trajectorygenerator/http://hybrid_a_star.cc中。代码实现如下:
//路径搜索的总花费计算
void HybridAStar::CalculateNodeCost(std::shared_ptr current_node,
std::shared_ptr next_node)
{
next_node->SetTrajCost(current_node->GetTrajCost() +
TrajCost(current_node, next_node)); //节点搜索的代价值
// evaluate heuristic cost
double optimal_path_cost = 0.0;
optimal_path_cost += HoloObstacleHeuristic(next_node); //栅格搜索的路径代价值,最短栅格路径
next_node->SetHeuCost(optimal_path_cost); //将栅格搜索的最短路径花费合并到节点搜索的花费中
}
//HybirdAstar路径搜索花费
double HybridAStar::TrajCost(std::shared_ptr current_node,
std::shared_ptr next_node)
{
// evaluate cost on the trajectory and add current cost
double piecewise_cost = 0.0;
if (next_node->GetDirec())
{
piecewise_cost += static_cast(next_node->GetStepSize() - 1) *
step_size_ * traj_forward_penalty_; //路径长度正向花费
}
else
{
piecewise_cost += static_cast(next_node->GetStepSize() - 1) *
step_size_ * traj_back_penalty_; //路径反向长度花费 倒车路径
}
if (current_node->GetDirec() != next_node->GetDirec())
{
piecewise_cost += traj_gear_switch_penalty_; //反向花费
}
piecewise_cost += traj_steer_penalty_ * std::abs(next_node->GetSteer()); //节点转向角花费
piecewise_cost += traj_steer_change_penalty_ *
std::abs(next_node->GetSteer() - current_node->GetSteer()); //节点转向角变化率花费
return piecewise_cost;
}
//栅格搜索的最短路径花费
double HybridAStar::HoloObstacleHeuristic(std::shared_ptr next_node)
{
return grid_a_star_heuristic_generator_->CheckDpMap(next_node->GetX(),
next_node->GetY()); //栅格搜索的最短路径花费
} 代价函数的计算项:
cost = traj_cost_ + heuristic_cost_;
traj_cost_ = kfp* step_cnt * step_size + kbp*dir + ksvp*steer + ksap*dsteer ;
cost = kfp* step_cnt * step_size + kbp*dir + ksvp*steer + ksap*dsteer + heuristic_cost_; 其中, kfp代表hybridstar路径搜索的路径长度代价项权重。
kbp代表hybridstar路径搜索倒车时的代价项权重。
ksvp代表hybridastar路径搜索转向角的代价权重。
ksap代表hybridastar路径搜索的转向角变化率的权重。
heuristic_cost_代表grid_search中的最短栅格路径代价值。
2.1.4 ReedSheep曲线
ReedShepp曲线由Reeds和Shepp二人在1990年的论文《
Optimal paths for a car that goes both forwards and backwardssector3.imm.uran.ru/shepp/Reeds_Shepp_trunk.pdf
》中提出,ReedShepp曲线由几段半径固定的圆弧和一段直线段拼接组成,而且圆弧的半径就是汽车的最小转弯半径。前原理类似于Dubin曲线,不过在Dubin曲线的基础上考虑了倒车的情景,因此在无人驾驶领域的引用非常普遍。
ReedShepps曲线从起点到终点路径是通过车辆最小转弯半径的圆弧和直线拼接组成,曲线类型有48种,所有类型的组合如下表所示:
表中的form代表按圆弧和直线的组合分类,可以分为9大类,"C"代表了圆弧,"S" 代表了直线,"|"表示车辆运动朝向由正向转为反向或者由反向转为正向。
在Baseword下又可以分为很多的基元类型,由![]() ,
,![]() ,
,![]() ,
,![]() ,
,![]() ,
,![]() 这六种元素组成,其中
这六种元素组成,其中![]() 表示车辆左转前进;
表示车辆左转前进;![]() 表示车辆左转后退;
表示车辆左转后退;![]() 表示车辆右转前进;
表示车辆右转前进;![]() 表示车辆右转后退;
表示车辆右转后退;![]() 表示车辆直行前进;
表示车辆直行前进;![]() 表示车辆直行后退。更加详细内容,请参考论文《Optimal paths for a car that goes both forwards and backwards》,上图图表亦来自论文。
表示车辆直行后退。更加详细内容,请参考论文《Optimal paths for a car that goes both forwards and backwards》,上图图表亦来自论文。
ReedShepp曲线部分的代码在coarse_trajectorygenerator/http://reeds_shepp_path.cc中。
bool ReedShepp::ShortestRSP(const std::shared_ptr start_node,
const std::shared_ptr end_node,
std::shared_ptr optimal_path) {
std::vector all_possible_paths;
if (!GenerateRSPs(start_node, end_node, &all_possible_paths)) //产生所有类型的reedshepp曲线
{
ADEBUG << "Fail to generate different combination of Reed Shepp "
"paths";
return false;
}
double optimal_path_length = std::numeric_limits::infinity();
size_t optimal_path_index = 0;
size_t paths_size = all_possible_paths.size();
for (size_t i = 0; i < paths_size; ++i)
{
if (all_possible_paths.at(i).total_length > 0 &&
all_possible_paths.at(i).total_length < optimal_path_length) {
optimal_path_index = i;
optimal_path_length = all_possible_paths.at(i).total_length; //寻找最短的reedshepp曲线参数
}
}
if (!GenerateLocalConfigurations(start_node, end_node,
&(all_possible_paths[optimal_path_index]))) //根据曲线参数插值reedshepp曲线
{
ADEBUG << "Fail to generate local configurations(x, y, phi) in SetRSP";
return false;
}
//检验是否精确插值到目标点
if (std::abs(all_possible_paths[optimal_path_index].x.back() -
end_node->GetX()) > 1e-3 ||
std::abs(all_possible_paths[optimal_path_index].y.back() -
end_node->GetY()) > 1e-3 ||
std::abs(all_possible_paths[optimal_path_index].phi.back() -
end_node->GetPhi()) > 1e-3)
{
ADEBUG << "RSP end position not right";
for (size_t i = 0;
i < all_possible_paths[optimal_path_index].segs_types.size(); ++i)
{
ADEBUG << "types are "
<< all_possible_paths[optimal_path_index].segs_types[i];
}
ADEBUG << "x, y, phi are: "
<< all_possible_paths[optimal_path_index].x.back() << ", "
<< all_possible_paths[optimal_path_index].y.back() << ", "
<< all_possible_paths[optimal_path_index].phi.back();
ADEBUG << "end x, y, phi are: " << end_node->GetX() << ", "
<< end_node->GetY() << ", " << end_node->GetPhi();
return false;
}
(*optimal_path).x = all_possible_paths[optimal_path_index].x;
(*optimal_path).y = all_possible_paths[optimal_path_index].y;
(*optimal_path).phi = all_possible_paths[optimal_path_index].phi;
(*optimal_path).gear = all_possible_paths[optimal_path_index].gear;
(*optimal_path).total_length =
all_possible_paths[optimal_path_index].total_length;
(*optimal_path).segs_types =
all_possible_paths[optimal_path_index].segs_types;
(*optimal_path).segs_lengths =
all_possible_paths[optimal_path_index].segs_lengths;
return true;
} reedshepp曲线起点start_node到终点end_node最短路径ShortestRSP一定是上表类型中的一个,且其曲线路径是所有reedshepp曲线中最短的。