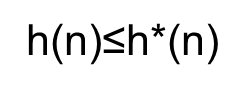搜索算法——深度优先搜索与广度优先搜索
搜索算法
前言:
我重新理了以下思路,并用代码实现了一下八数码问题的解决.
主要用的算法为2个: [深度优先搜索] (c语言描述)和 [广度优先搜索](java语言描述) 。
其他的搜索算法暂时没搞。。 先挖个坑有空再来填。
文章目录
- 搜索算法
-
-
- 前言:
- OPEN表和CLOSED表
- 八数码问题`
- 一、深度优先搜索 (c语言描述)
- 二、广度优先搜索 (java语言描述)
- 三、其他搜索(启发式搜索)
-
- 1.A算法
- 2.盲人登山法(局部优先搜索)
- 3.动态规划法
- 4.A*算法 (游戏中自动寻路的算法)
-
OPEN表和CLOSED表
搜索算法中设置两个表:OPEN和CLOSED.
OPEN中记录所有已经生成的未考察的结点,CLOSED表中记录已访问过的结点.
在搜索算法中根据估价函数重排OPEN表,每次只考察OPEN表中最优的结点.
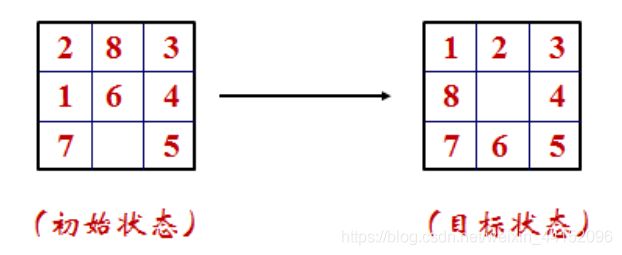
八数码问题`
从初始状态到目标状态,对于人来说还是很容易实现的.但是要交给计算机来执行,就要选择合适的算法.我们可以把每一次移动都当做是空格的移动.
以下就用几个算法来解决这个问题.
一、深度优先搜索 (c语言描述)
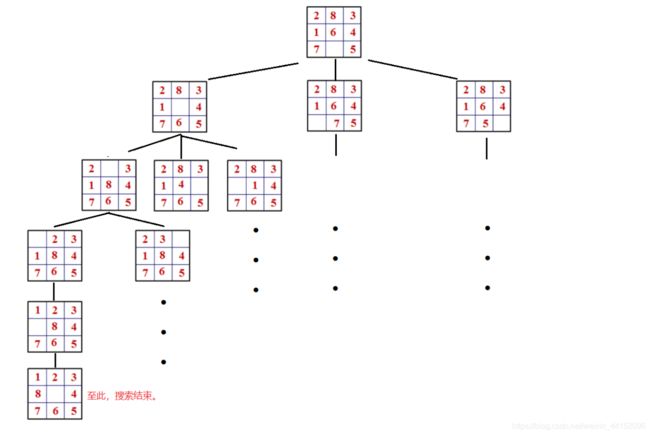
所谓深度优先搜索,就是在每次扩展一个结点时,选择到目前为止深度最深的结点优先扩展.(盲目搜索,不撞南墙不回头)
如图:
搜索结束,其他结点不再扩展.
#include命令行输出结果为5.
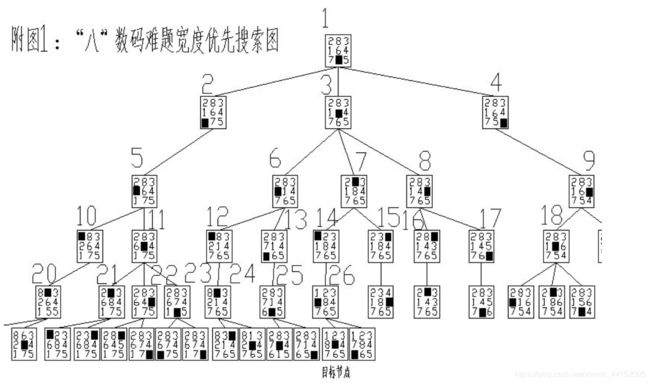
二、广度优先搜索 (java语言描述)
广度优先搜索与深度优先搜索相反,每次扩展结点时,选择到目前为止深度最浅的优先扩展.(盲目搜索,层层递进)
(图片来源:https://www.cnblogs.com/luoht/archive/2011/02/26/1965724.html )
public class Que {
int x;
int y;
int step;
int bx, by;
int curr[][] = { {2,8,3},
{1,6,4},
{7,0,5} };
int book[][] = new int[3][3];
public Que() {
int i,j;
for(i=0;i<3;i++) {
for(j=0;j<3;j++) {
book[i][j] = 0;
}
}
}
}
package com.bfs;
public class Bfs {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Bfs bfs = new Bfs();
}
int x = 2, y = 1;
int next[][] = { {-1,0},//up
{1,0},//down
{0,-1},//left
{0,1} //right
};
int tx,ty,k,temp;
int head = 1, tail = 1, flag = 0;
Que[] que = new Que[2000];
public Bfs() {
que[tail] = new Que();
que[tail].x = this.x;
que[tail].y = this.y;
que[tail].bx = this.x;
que[tail].by = this.y;
que[tail].step = 0;
tail++;
bfs();
}
public void bfs() {
while(head < tail) {
for(k=0;k<=3;k++) {
tx = que[head].x + next[k][0];
ty = que[head].y + next[k][1];
//判断是否越界
if(tx<0 || ty<0 || tx>2 || ty>2){
continue;
}
if(que[head].book[tx][ty] == 0) {
que[tail] = new Que();
//对新结点赋旧值----------------------------------
int i, j;
for(i=0;i<3;i++){
for(j=0;j<3;j++){
que[tail].curr[i][j] = que[head].curr[i][j];
}
}
que[tail].x = que[head].x;
que[tail].y = que[head].y;
//---------------------------------------------
//交换数值,相当于空格走一步.
que[tail].curr[ que[tail].x ][ que[tail].y ] = que[tail].curr[tx][ty];
que[tail].curr[tx][ty] = 0;
que[tail].step = que[head].step + 1;
que[tail].book[ que[tail].x][ que[tail].y] = 1;
que[tail].x = tx;
que[tail].y = ty;
tail++;
}
if( que[tail-1].curr[0][0] == 1 && que[tail-1].curr[0][1] == 2 && que[tail-1].curr[0][2] == 3
&& que[tail-1].curr[1][0] == 8 && que[tail-1].curr[1][1] == 0 && que[tail-1].curr[1][2] == 4
&& que[tail-1].curr[2][0] == 7 && que[tail-1].curr[2][1] == 6 && que[tail-1].curr[2][2] == 5 ) {
flag = 1;
break;
}
}//for
if(flag == 1) {
break;
}
head++;
}//while
System.out.println(que[tail-1].step);
}
}
控制台输出结果为5.
三、其他搜索(启发式搜索)
1.A算法
思路:定义一个评价函数 f,对当前的搜索状态进行评估,找出一个最有希望的结点来扩展.
评价函数 f(n)=g(n)+h(n),n为被评价的结点.
g*(n):表示从初始结点s到结点n的最短路径耗散值.
h*(n):表示从结点n到目标结点g的最短路径耗散值.
f*(n)=g*(n)+h*(n)
而f(n)、g(n)、h(n)则分别表示对 f*(n)、g*(n)、h*(n)三个函数值的估计值.
每次扩展结点时,总是选择当前f值最小的结点来优先扩展.
2.盲人登山法(局部优先搜索)
思路:设h(n)表示与山顶的高度差,则总是选择h(n)减小的方向进行.
这样在单峰的条件下,必能达到山顶,但是在多峰的情况下可能无法到达.(局部最优)