【翻译】Leapmotion-python开发官方文档(10)
相机图像
图像接口基础
图象畸变
图像方向
获得原始图像
获得校准映射矩阵
图像射线校准
使用Image.warp()校正
使用32位ARGB纹理编码畸变数据
Color encodeFloatRGBA(float input)
{
input = (input + 0.6)/2.3; //scale the input value to the range [0..1]
float r = input;
float g = input * 255;
float b = input * 255 * 255;
float a = input * 255 * 255 * 255;
r = r - (float)Math.floor(r);
g = g - (float)Math.floor(g);
b = b - (float)Math.floor(b);
a = a - (float)Math.floor(a);
return Color(r, g, b, a);
}为了重组在片断着色器中的值,你可以在纹理中查找对应值并进行倒数操作。为避免丢失太多精度,将x,y畸变值编码成独立的纹理。一旦失真指数从纹理中采样和解码,你能够在相机图像纹理中找到校正后的亮度值。(注:GLSL乱入中)
uniform sampler2D texture;
uniform sampler2D vDistortion;
uniform sampler2D hDistortion;
varying vec2 distortionLookup;
varying vec4 vertColor;
varying vec4 vertTexCoord;
const vec4 decoderCoefficients = vec4(1.0, 1.0/255.0, 1.0/(255.0*255.0), 1.0/(255.0*255.0*255.0));
void main() {
vec4 vEncoded = texture2D(vDistortion, vertTexCoord.st);
vec4 hEncoded = texture2D(hDistortion, vertTexCoord.st);
float vIndex = dot(vEncoded, decoderCoefficients) * 2.3 - 0.6;
float hIndex = dot(hEncoded, decoderCoefficients) * 2.3 - 0.6;
if(vIndex >= 0.0 && vIndex <= 1.0
&& hIndex >= 0.0 && hIndex <= 1.0)
{
gl_FragColor = texture2D(texture, vec2(hIndex, vIndex)) * vertColor;
} else {
gl_FragColor = vec4(1.0, 0, 0, 1.0); //show invalid pixels as red
}
}使用双线性插值校正
重新调用含有64X64网格元素的畸变映射矩阵,想象这些网格均匀的散布在你的目标图像中。(元素[0,0]在左下方角点同时[64,64]在右上方)。每一个元素包括水平座标与垂直坐标用于确定传感器图像数据中的图像数据,以找到目标图像中像素的记录亮度。为了寻找到畸变网格元素间的像素的亮度值,你应当利用该像素周围的4个网格点进行插值计算。
用于在目标图像中寻找给定像素的畸变修正亮度值的基本算法:
1.找到目标像素周围四个校正网格点。
2.计算基于目标点距离网格点的距离计算插值权重。
3.查找这四个网格点的每一个的水平值和垂直值(译者注:x坐标?y坐标?)
4.使用基于距离的权重因子计算水平值得双线性插值。
5.为纵向值重复插值计算。
6.拒绝那些横向坐标或纵向坐标不在[0,1]范围之内的。
7.反归一化这些值,使他们变成原始传感器数据中的像素坐标。
8.查找传感器值所计算的像素坐标。
9.在目标图像中为原始坐标设置亮度值。
在Python中遍历图像像素进行双线性插值是很慢的。你可以使用OpenCV提供的函数进行插值计算。第一将畸变数据转换成cv2.remap()函数能使用的数据格式:
import cv2, Leap, math, ctypes
import numpy as np
def convert_distortion_maps(image):
distortion_length = image.distortion_width * image.distortion_height
xmap = np.zeros(distortion_length/2, dtype=np.float32)
ymap = np.zeros(distortion_length/2, dtype=np.float32)
for i in range(0, distortion_length, 2):
xmap[distortion_length/2 - i/2 - 1] = image.distortion[i] * image.width
ymap[distortion_length/2 - i/2 - 1] = image.distortion[i + 1] * image.height
xmap = np.reshape(xmap, (image.distortion_height, image.distortion_width/2))
ymap = np.reshape(ymap, (image.distortion_height, image.distortion_width/2))
#resize the distortion map to equal desired destination image size
resized_xmap = cv2.resize(xmap,
(image.width, image.height),
0, 0,
cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
resized_ymap = cv2.resize(ymap,
(image.width, image.height),
0, 0,
cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
#Use faster fixed point maps
coordinate_map, interpolation_coefficients = cv2.convertMaps(resized_xmap,
resized_ymap,
cv2.CV_32FC1,
nninterpolation = False)
return coordinate_map, interpolation_coefficients然后将这些map和相应的图像传给cv2.map()函数:
def undistort(image, coordinate_map, coefficient_map, width, height):
destination = np.empty((width, height), dtype = np.ubyte)
#wrap image data in numpy array
i_address = int(image.data_pointer)
ctype_array_def = ctypes.c_ubyte * image.height * image.width
# as ctypes array
as_ctype_array = ctype_array_def.from_address(i_address)
# as numpy array
as_numpy_array = np.ctypeslib.as_array(as_ctype_array)
img = np.reshape(as_numpy_array, (image.height, image.width))
#remap image to destination
destination = cv2.remap(img,
coordinate_map,
coefficient_map,
interpolation = cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
#resize output to desired destination size
destination = cv2.resize(destination,
(width, height),
0, 0,
cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
return destination注意你应当避免每一帧都转换畸变映射矩阵,只有当一个新的设备接入时、图像反转方向时(当手从相反的方向进入)或者设备被重新校准此矩阵才会发生改变。下面代码只会进行一次转换畸变映射矩阵(所以无法处理当畸变映射矩阵发生变化的情况)
def run(controller):
maps_initialized = False
while(True):
frame = controller.frame()
image = frame.images[0]
if image.is_valid:
if not maps_initialized:
left_coordinates, left_coefficients = convert_distortion_maps(frame.images[0])
right_coordinates, right_coefficients = convert_distortion_maps(frame.images[1])
maps_initialized = True
undistorted_left = undistort(image, left_coordinates, left_coefficients, 400, 400)
undistorted_right = undistort(image, right_coordinates, right_coefficients, 400, 400)
#display images
cv2.imshow('Left Camera', undistorted_left)
cv2.imshow('Right Camera', undistorted_right)
if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord('q'):
break
def main():
controller = Leap.Controller()
controller.set_policy_flags(Leap.Controller.POLICY_IMAGES)
try:
run(controller)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
sys.exit(0)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()在图像上画出追踪数据
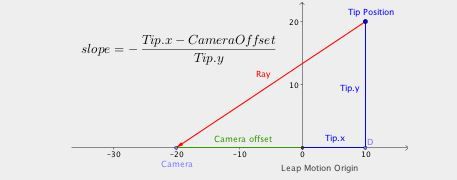
左相机的计算过程。加上偏移距离代替了减去右相机的对应值。
只要你知道光线的斜率,你就能通过调用warp()函数获得像素的坐标。
注意:偏移值可能因为LeapMotion控制器的不同形式的因素而不同,但是目前没有方法从API中获得这个值。
如果你显示了校正后的图像数据,那么将追踪数据与图像数据相关联取决于你显示图像的方式。对于3D视角,使用不变的缩放因子和纹理贴图的校正后的位置显示图像是有问题的。对于其他形式的显示,你必须根据你矫正图像的方式将代表LeapMotion中一个位置的光线斜率转换成目标图像像素坐标
计算图象特征的方向向量
使用Image.rectify()获得图像特征方向向量。Image.rectify()返回一个向量包含水平和竖直斜率(以相机原点定义)给出了在原始图像数据中的像素坐标。
如果你能以足够的精度辩认出图像中的相同的特征,你可以使用从两个摄像机获得的斜率值计算出3D位置/
头戴式显示模式
LeapMotion服务/守护程序提供了当LeapMotion附着于一个头戴式显示器上时优化跟踪数据的模式。在这个模式下LeapMotion软件会从上方而不是底部检测手。但是,手心是朝向LeapMotion传感器还是背离传感器是有二义性的,设置这个模式使得LeapMotion软件会初始化手部模型使得它默认手心是背向传感器的。这样有利于将LeapMotion设备安装在头戴式显示器的表面作为控制器。
为了在你的应用中开启这个模式,你需要开启优化HMD方法
controller.set_policy(Leap.Controller.POLICY_OPTIMIZE_HMD)对于那些不能安装在HMD上的硬件,这个方法是会被拒绝的,如那些嵌在笔记本上或者键盘上的设备。