【Few-Shot Segmentation论文阅读笔记】PANet: Few-Shot Image Semantic Segmentation with Prototype , ICCV, 2019
Abstract
Target Question: Few-shot Segmentation
本文主要工作:
基于metric-learning的思想,本文提出了PANet(Prototype Alignment network),能够更好地利用support set中包含的语义信息,实现小样本语义分割。
算法优点:
- segmentation阶段没有引入额外的learnable parameters, 减少了over-fitting的可能性
- Prototype embedding & prediction都是直接作用于feature maps,无需在网络结构中进行额外的信息传递
- 由于PAR只作用于训练阶段,因为不会影响inference cost.
Contributions:
- 本文提出了一个简单而有效的PANet框架,该模型使用metric learning over prototypes的方法,与之前的基于parametric classification的架构有明显区别
- PAR模块,使得query set和support set相互引导,充分利用率support set包含的信息,提高了性能
- 本文提出的PANet在weak annotations数据集上效果也很突出。
Comments: (引用于 https://blog.csdn.net/qq_36104364/article/details/106781918 )
- 创新点
- 采用基于原型网络的结构实现了小样本语义分割任务
- 设计了PAR方法,充分利用支持集图像信息,提高分割的准确性
- 算法评价:本文在很大程度上沿用了原型网络的思想,只不过将对一个图片的类别预测,改为了对每个像素的类别进行预测,设计的PAR方法非常有趣,有点类似于立体匹配中的左右一致性检测,由查询集的结果返回去预测支持集的结果,二者可以相互印证,的确是很有创新性的想法。本文还有一个进步,就是支持集中可以包含多个类别的图像,然后可以实现对查询集图像中多个类别物体的分割。我对本文存在的一点疑惑就是关于计算时间的问题,因为对每个像素都计算距离,并预测类别计算量可能会比较大,作者在文中并没有提及如何解决计算复杂度的问题。
代码: https://github.com/kaixin96/PANet
1. Method
计算过程:
- Step1: Feature Extraction: 对于每个Episode, 首先提取support and query features by a shared backbone network
- Step2: 计算Prototypes: 在support features上应用Masked Average Pooling, 计算每个类别的prototype:
本文采用了后混合掩码(late fusion mask)的方式,即:先提取特征图,再对特征图进行掩码。相对于先掩码(early fusion mask,即:就是先对输入图像进行掩码操作,然后再提取特征图)而言,能够保证输入到feature extractor的query和support input的一致性。得到掩码后的特征图,通过平均池化的方式计算得到每个类别对应的原型向量,计算过程如下:
- Step3: 生成预测结果:label each pixel of query images as the class of the nearest prototypes
- Calculate the distance between the query feature vector at each spatial location with each computed prototypes.
- Apply a softmax over the distances to produce a probability over semantic classes (including background)
- The final predicted result is then given by the max function
-
Step4:PAR (query-to-support):将predicted mask 和 query features 作为新的support set, 求取其对应的prototypes,再对原来的support set进行分割,从而获取反向信息。
想法:如果模型能够预测一个好的mask for query images,那么反过来用query images+predicted mask生成prototypes,也应该能够很好的分割support set。
==>使得query<==>support互相督促,学习更多有用的信息。
注意:该过程只应用于训练阶段。
具体实现发方法同步骤(2)和步骤(3),与之不同的仅在于用query features+predicted mask作为新的support set生成prototypes, 对原始的support set进行预测。
1.1 Generation to weaker annotations
PANet can work well by using only weak annotations, e.g, Scribbles + bounding box.
说明其具有如下优点:
- Easy to obtain weaker annotations than dense annotations
- By using late fusion strategy, it is also easy to be extended to images with weak annotations.
2. Experiments
数据集:
- PASCAL-5i [21]+ SBD [7]:20类分成4组,进行较差验证
- COCO 20i [8]:80类分成4组,进行较差验证
评估标准:
- Mean-IoU,[21, 28] ,本文关注
- Binary-IoU [16, 4, 8]
实现细节:
- VGG-16 pretrained on ILSVRC[19]
- 将图片resize为417*417
- 使用random horizontal flipping做Data Augmentation
- SGD,动量=0.9,30000次迭代;初始学习率为1e-3,每1W次减少0.1;weight decay是0.0005, batch size=1.
2.2 Comparison with SOTAs
PASCAL-5i
定量分析:
- Table 1:给出了1-way 1-shot & 5-shot的结果,mean-IoU作为指标
- Table 2:给出了1-way 1-shot & 5-shot的结果,binary-IoU作为指标
- Table 3:2-wau 1-shot & 5-shot
△ 表示5-shot相对于1-shot上性能的提升,可以看到本文算法提升很大,其他算法却不是很明显,说明了本文算法能够有效的获取support knowledge.
本文方法存在的问题:
- Tends to give segmentation results with unnatural patches,这可能是因为it predicts independently at each location,但是该问题可以被后处理解决。
- 模型不能区分chairs和tables, 由于他们具有相似的prototypes in embedding space.
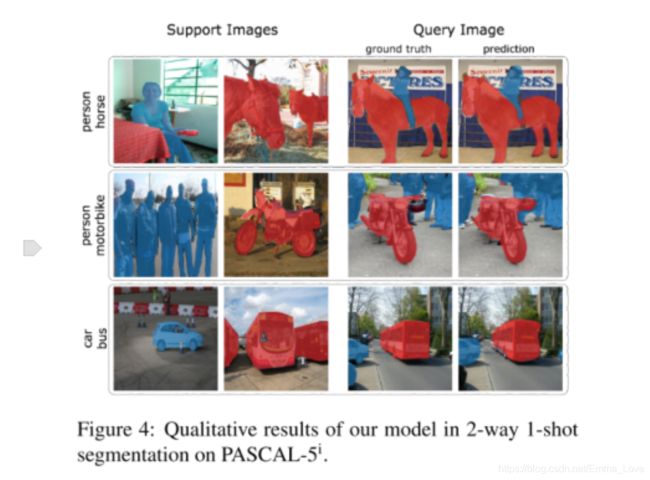
定性分析:
MSCOCO-20i
- Table 4: 1-way 1-shot & 5-shot
2.3 Analysis PAR
- Aligning embedding prototypes: 消融实验
- 证明PAR是有效的(表格5),且能帮助更快的收敛(图5)
2.4 Test with weak annotations
- Scribble + bounding box annotation (Table 6 + Figure 6)
在测试阶段,将pixel-level annotation换成scribble和bounding box annotation.
实验结果:在1-shot上,bbox优于scribble;而在5-shot上scribble优于bbox,原因可能是由于bbox会涵盖更多的噪声

3. Related Work
问题1:基于DL的语义分割需要大量的有标签数据,但是获取这类标签是耗时耗力的。
于是有了semi-/weakly-supervised learning methods:
- [26] Yunchao Wei, Jiashi Feng, Xiaodan Liang, Ming-Ming Cheng, Yao Zhao, and Shuicheng Yan. Object region mining with adversarial erasing: A simple classification to semantic segmentation approach. In Proceedings of the IEEE con- ference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pages 1568–1576, 2017
- [3] Jifeng Dai, Kaiming He, and Jian Sun. Boxsup: Exploit- ing bounding boxes to supervise convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Inter- national Conference on Computer Vision, pages 1635–1643, 2015.
- [9] Di Lin, Jifeng Dai, Jiaya Jia, Kaiming He, and Jian Sun. Scribblesup: Scribble-supervised convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Con- ference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 3159–3167, 2016.
- [15] George Papandreou, Liang-Chieh Chen, Kevin P Murphy, and Alan L Yuille. Weakly-and semi-supervised learning of a deep convolutional network for semantic image segmenta- tion. In Proceedings ofthe IEEE international conference on computer vision, pages 1742–1750, 2015.
但是weakly和semi-supervised方法只能解决部分问题,但是仍需要大量的weakly annotations training images.
问题2:传统的基于DL的语义分割,Poor generation to unseen classes.
为了解决问题1+问题2==> Few-Shot Segmentation
Related Work:
- Few-shot Classification:
- Metric-learning based methods: [23, 24, 25]
- Optimization based methods: [18, 6]
- Graph-based methods: [20, 12, 14]
- Few-Shot Segmentation: (To Read)
- [21] Amirreza Shaban, Shray Bansal, Zhen Liu, Irfan Essa, and Byron Boots. One-shot learning for semantic segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1709.03410, 2017.
- [17] Kate Rakelly, Evan Shelhamer, Trevor Darrell, Alexei A Efros, and Sergey Levine. Few-shot segmentation propagation with guided networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:1806.07373, 2018
- [4] Nanqing Dong and Eric P Xing. Few-shot semantic segmen- tation with prototype learning. In BMVC, volume 3, page 4, 2018.
- [28] Xiaolin Zhang, Yunchao Wei, Yi Yang, and Thomas Huang. Sg-one: Similarity guidance network for one-shot semantic segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1810.09091, 2018.
- [8] Tao Hu, Pengwan, Chiliang Zhang, Gang Yu, Yadong Mu, and Cees G. M. Snoek. Attention-based multi-context guid- ing for few-shot semantic segmentation. 2018.
- [16] Kate Rakelly, Evan Shelhamer, Trevor Darrell, Alyosha Efros, and Sergey Levine. Conditional networks for few-shot semantic segmentation. 2018.
- Segmentation:
- [13, 10, 1, 29, 2]
- [13, 27, 2]
注意:
- 本文follow structure of FCN[13] + adopt dilated convolutions to enjoy a large receptive field.
- 本文follow [23] (prototypical network)的思想,并采用late fusion [17]策略 to incorporate the annotation masks, making it easier to generalize to cases with sparse or updating annotations.
4. Conclusion
本文提出了一种基于metric-learnng的PANet模型用于few-shot segmentation问题。PANet不仅能够提取鲁棒性的prototypes from the support set, 还能是由无参数的距离计算实现语义分割。在两个数据集上均取得更好的效果。