数字图像处理---低高通滤波实验(MATLAB实现)
数字图像处理—低高通滤波实验(MATLAB实现)
【实验目的】
1. 了解图像傅里叶变换的意义和手段;
2. 熟悉理想低通滤波器、巴特沃斯低通滤波器、高斯低通滤波器的基本原理和性质;
3. 熟悉理想高通滤波器、巴特沃斯高通滤波器、高斯高通滤波器的基本原理和性质;
4. 掌握MATLAB编程实现数字图像的低高通滤波器的变换,并分析各参数对于实验结果的影响。
【实验原理】
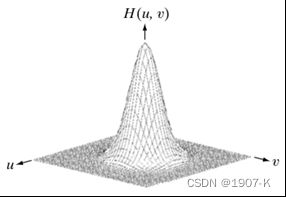
1. 理想低通滤波器
低通滤波是要保留图像中的低频分量而除去高频分量。图像中的边缘和噪声都对应图像傅里叶频谱中的高频部分,所以低通滤波可以除去或削弱噪声的影响并模糊边缘轮廓。理想低通滤波器具有传递函数:

其中,D0表示通带半径,D(u,v)是到频谱中心的距离(欧式距离),计算公式如下:
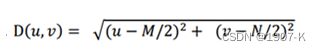
M和N表示频谱图像的大小,(M/2,N/2)即为频谱中心。
理想低通滤波器在数学上定义得很清楚,在计算机模拟中也可实现,但在截断频率处直上直下的理想低通滤波器是不能用实际的电子器件实现的。理想的高通滤波器与此相反,1减去低通滤波模板即可。
2. 巴特沃斯低/高通滤波器
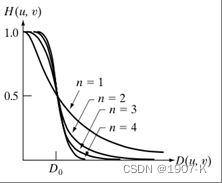
巴特沃斯低通滤波器函数为

从函数图上看,更圆滑,用幂系数n可以改变滤波器的形状。n越大,则该滤波器越接近于理想滤波器。巴特沃斯低通滤波器的处理结果比理想滤波器的要好,但阶数增高时振铃便成为一个重要因素。

3. 高斯低/高通滤波器
因为噪声主要集中在高频段,所以通过高斯低通滤波器可以滤除噪声信息、平滑图像,但与此同时会滤除图像的细节信息,使图像变得模糊。
高斯低通滤波器函数为:

1减去低通滤波模板即可得到高通滤波模板

【实验内容】
- 对数字图象进行低通滤波处理
- 对数字图象进行高通滤波处理
- 比较和分析所得到的结果。
【实验结果分析】
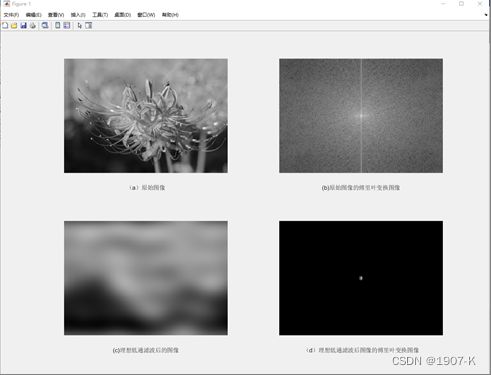
- 理想低通滤波器:低通滤波器的特性使得低于设定临界值频率的信号能正常通过,而高于设定临界值频率(d0)的信号则被阻隔和衰减。理想低通滤波器当截止频率d0较低时,细节信息缺失,导致图像变得模糊不清。当截止频率d0较高时,图像比较清晰。
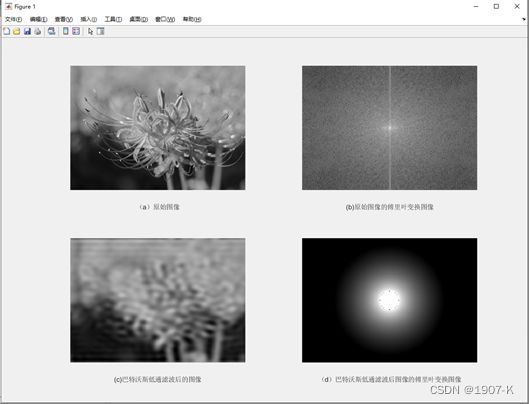
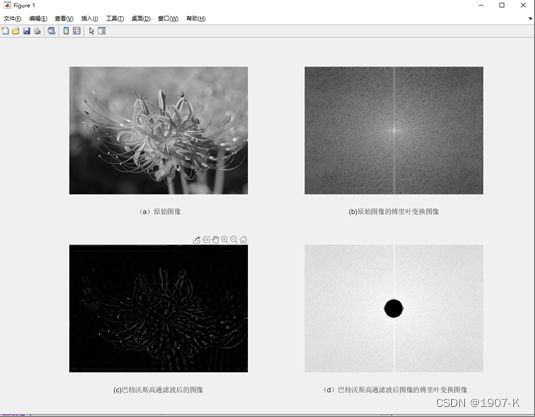
- 巴特沃斯低通滤波器:在截止频率(d0)前较为平坦,这个平坦也保证了信号的原始值,不会因为滤波被衰减。巴特沃斯低通滤波器的通频带最大扁平效应使通频带的增益得到扁平优化.。n趋近于无穷,增益变为一个矩形函数,其幅频响应就越逼近理想情况。
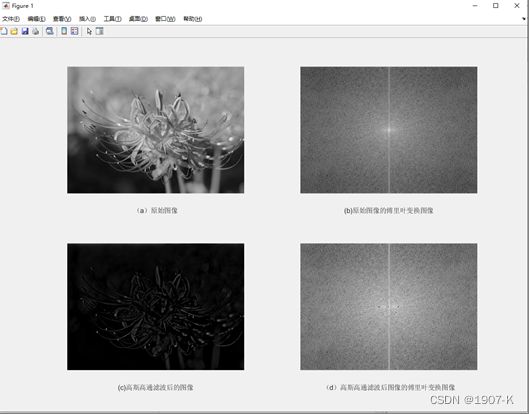
- 高斯低通滤波器:高斯低通滤波器其低频信息保留,高频细节被滤除。当截止频率较低时,滤波后图像虽然比原图像平滑,由于许多细节信息缺失,导致图像变得模糊不清。当截止频率d0较高时,图像比较清晰。高斯高通滤波器可以增强细节信息,提升图像的高频分量,减少低频分量,对微小物体和细线条也能很好地增强显示。
理想低高通滤波器结果如下:
巴特沃斯低高通滤波器结果如下:
高斯低高通滤波器结果如下:
【实验代码】
一、 理想低通滤波器
clc;
I1=imread('15.jpg');
I1=rgb2gray(I1);
subplot(221),imshow(I1);
xlabel('(a)原始图像');
f=double(I1);
g=fftshift(fft2(I1));
F2=log(abs(g));
subplot(222),imshow(F2,[],'InitialMagnification','fit');
xlabel('(b)原始图像的傅里叶变换图像');
[a,b]=size(g);
a0=round(a/2);
b0=round(b/2);
d0=20;
for i=1:a
for j=1:b
dis=sqrt((i-a0)^2+(j-b0)^2);
if dis<=d0
h=1;
else
h=0;
end
result(i,j)=h*g(i,j);
end
end
F3=log(abs(result));
subplot(224),imshow(F3,[],'InitialMagnification','fit');
xlabel('(d)理想低通滤波后图像的傅里叶变换图像');
result=ifftshift(result);
result=ifft2(result);
X2=uint8(real(result));
subplot(223),imshow(X2);
xlabel('(c)理想低通滤波后的图像');
二、 巴特沃斯低通滤波器
clc;
I1=imread('15.jpg');
I1=rgb2gray(I1);
subplot(221),imshow(I1);
xlabel('(a)原始图像');
f=double(I1);
g=fftshift(fft2(I1));
F2=log(abs(g));
subplot(222),imshow(F2,[],'InitialMagnification','fit');
xlabel('(b)原始图像的傅里叶变换图像');
[a,b]=size(g);
a0=round(a/2);
b0=round(b/2);
n=200;
d0=20;%%使用不同参数对其进行分析
for i=1:a
for j=1:b
dis=sqrt((i-a0)^2+(j-b0)^2);
if dis==d0
h=0;
else
h=1/(1+(dis/d0)^(2*n));
h=1-h;
end
result(i,j)=h*g(i,j);
end
end
F3=log(abs(result));
subplot(224),imshow(F3,[],'InitialMagnification','fit');
xlabel('(d)巴特沃斯高通滤波后图像的傅里叶变换图像');
result=ifftshift(result);
result=ifft2(result);
X2=uint8(real(result));
subplot(223),imshow(X2);
xlabel('(c)巴特沃斯高通滤波后的图像');
三、 高斯低通滤波器
clc;
I1=imread('15.jpg');
I1=rgb2gray(I1);
subplot(221),imshow(I1);
xlabel('(a)原始图像');
f=double(I1);
g=fftshift(fft2(I1));
F2=log(abs(g));
subplot(222),imshow(F2,[],'InitialMagnification','fit');
xlabel('(b)原始图像的傅里叶变换图像');
[a,b]=size(g);
a0=round(a/2);
b0=round(b/2);
d0=20;
for i=1:a
for j=1:b
dis=sqrt((i-a0)^2+(j-b0)^2);
if dis==d0
h=0;
else
h=exp(-dis/d0);
%h=1-h;
end
result(i,j)=h*g(i,j);
end
end
F3=log(abs(result));
subplot(224),imshow(F3,[],'InitialMagnification','fit');
xlabel('(d)高斯高通滤波后图像的傅里叶变换图像');
result=ifftshift(result);
result=ifft2(result);
X2=uint8(real(result));
subplot(223),imshow(X2);
xlabel('(c)高斯高通滤波后的图像');