1.课后习题



import numpy as np
import time
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
from pylab import mpl
mpl.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['Microsoft YaHei']
class LogisticRegression:
def __init__(self, learn_rate=0.1, max_iter=10000, tol=1e-2):
self.learn_rate = learn_rate
self.max_iter = max_iter
self.tol = tol
self.w = None
def preprocessing(self, X):
"""将原始X末尾加上一列,该列数值全部为1"""
row = X.shape[0]
y = np.ones(row).reshape(row, 1)
X_prepro = np.hstack((X, y))
return X_prepro
def sigmod(self, x):
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))
def fit(self, X_train, y_train):
X = self.preprocessing(X_train)
y = y_train.T
self.w = np.array([[0] * X.shape[1]], dtype=np.float)
k = 0
for loop in range(self.max_iter):
z = np.dot(X, self.w.T)
grad = X * (y - self.sigmod(z))
grad = grad.sum(axis=0)
if (np.abs(grad) <= self.tol).all():
break
else:
self.w += self.learn_rate * grad
k += 1
print("迭代次数:{}次".format(k))
print("最终梯度:{}".format(grad))
print("最终权重:{}".format(self.w[0]))
def predict(self, x):
p = self.sigmod(np.dot(self.preprocessing(x), self.w.T))
print("Y=1的概率被估计为:{:.2%}".format(p[0][0]))
p[np.where(p > 0.5)] = 1
p[np.where(p < 0.5)] = 0
return p
def score(self, X, y):
y_c = self.predict(X)
error_rate = np.sum(np.abs(y_c - y.T)) / y_c.shape[0]
return 1 - error_rate
def draw(self, X, y):
y = y[0]
X_po = X[np.where(y == 1)]
X_ne = X[np.where(y == 0)]
ax = plt.axes(projection='3d')
x_1 = X_po[0, :]
y_1 = X_po[1, :]
z_1 = X_po[2, :]
x_2 = X_ne[0, :]
y_2 = X_ne[1, :]
z_2 = X_ne[2, :]
ax.scatter(x_1, y_1, z_1, c="r", label="正实例")
ax.scatter(x_2, y_2, z_2, c="b", label="负实例")
ax.legend(loc='best')
x = np.linspace(-3, 3, 3)
y = np.linspace(-3, 3, 3)
x_3, y_3 = np.meshgrid(x, y)
a, b, c, d = self.w[0]
z_3 = -(a * x_3 + b * y_3 + d) / c
ax.plot_surface(x_3, y_3, z_3, alpha=0.5)
plt.show()
X_train = np.array([[3, 3, 3], [4, 3, 2], [2, 1, 2], [1, 1, 1], [-1, 0, 1], [2, -2, 1]])
y_train = np.array([[1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0]])
clf = LogisticRegression()
clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
clf.draw(X_train, y_train)
迭代次数:3232次
最终梯度:[ 0.00144779 0.00046133 0.00490279 -0.00999848]
最终权重:[ 2.96908597 1.60115396 5.04477438 -13.43744079]
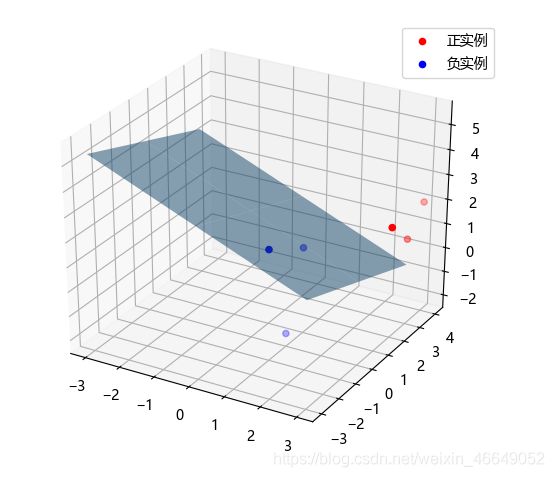

链接3
2.视频课后习题

"""逻辑斯蒂回归算法实现-使用梯度下降"""
import numpy as np
import time
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
import matplotlib as mpl
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei']
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
class LogisticRegression:
def __init__(self, learn_rate=0.01, max_iter=10000, tol=1e-2):
self.learn_rate = learn_rate
self.max_iter = max_iter
self.tol = tol
self.w = None
def preprocessing(self, X):
"""将原始X末尾加上一列,该列数值全部为1"""
row = X.shape[0]
y = np.ones(row).reshape(row, 1)
X_prepro = np.hstack((X, y))
return X_prepro
def sigmod(self, x):
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))
def fit(self, X_train, y_train):
X = self.preprocessing(X_train)
y = y_train.T
self.w = np.array([[0] * X.shape[1]], dtype=np.float)
k = 0
for loop in range(self.max_iter):
z = np.dot(X, self.w.T)
grad = X * (y - self.sigmod(z))
grad = grad.sum(axis=0)
if (np.abs(grad) <= self.tol).all():
break
else:
self.w += self.learn_rate * grad
k += 1
print("迭代次数:{}次".format(k))
print("最终梯度:{}".format(grad))
print("最终权重:{}".format(self.w[0]))
def predict(self, x):
p = self.sigmod(np.dot(self.preprocessing(x), self.w.T))
print("Y=1的概率被估计为:{:.2%}".format(p[0][0]))
p[np.where(p > 0.5)] = 1
p[np.where(p < 0.5)] = 0
return p
def score(self, X, y):
y_c = self.predict(X)
error_rate = np.sum(np.abs(y_c - y.T)) / y_c.shape[0]
return 1 - error_rate
def draw(self, X, y):
y = y[0]
X_po = X[np.where(y == 1)]
X_ne = X[np.where(y == 0)]
ax = plt.axes(projection='3d')
x_1 = X_po[0, :]
y_1 = X_po[1, :]
z_1 = X_po[2, :]
x_2 = X_ne[0, :]
y_2 = X_ne[1, :]
z_2 = X_ne[2, :]
ax.scatter(x_1, y_1, z_1, c="r", label="正实例")
ax.scatter(x_2, y_2, z_2, c="b", label="负实例")
ax.legend(loc='best')
x = np.linspace(-3, 3, 3)
y = np.linspace(-3, 3, 3)
x_3, y_3 = np.meshgrid(x, y)
a, b, c, d = self.w[0]
z_3 = -(a * x_3 + b * y_3 + d) / c
ax.plot_surface(x_3, y_3, z_3, alpha=0.5)
plt.show()
def main():
star = time.time()
X_train = np.array([[3, 3, 3], [4, 3, 2], [2, 1, 2], [1, 1, 1], [-1, 0, 1], [2, -2, 1]])
y_train = np.array([[1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0]])
clf = LogisticRegression()
clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
X_new = np.array([[1, 2, -2]])
y_predict = clf.predict(X_new)
print("{}被分类为:{}".format(X_new[0], y_predict[0]))
clf.draw(X_train, y_train)
X_test=X_train
y_test=y_train
correct_rate=clf.score(X_test,y_test)
print("共测试{}组数据,正确率:{:.2%}".format(X_test.shape[0],correct_rate))
end = time.time()
print("用时:{:.3f}s".format(end - star))
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
迭代次数:10000次
最终梯度:[ 0.00483138 0.00138275 0.01561255 -0.03217626]
最终权重:[ 2.40550339 1.42893511 3.19459105 -9.63604478]
Y=1的概率被估计为:0.00%
[ 1 2 -2]被分类为:[0.]
Y=1的概率被估计为:100.00%
共测试6组数据,正确率:100.00%
用时:0.324s
"""逻辑斯蒂回归算法实现-使用随机梯度下降"""
import numpy as np
import time
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei']
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
class LogisticRegression:
def __init__(self, learn_rate=0.01, max_iter=10000, tol=1e-3):
self.learn_rate = learn_rate
self.max_iter = max_iter
self.tol = tol
self.w = None
def preprocessing(self, X):
"""将原始X末尾加上一列,该列数值全部为1"""
row = X.shape[0]
y = np.ones(row).reshape(row, 1)
X_prepro = np.hstack((X, y))
return X_prepro
def sigmod(self, x):
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))
def fit(self, X_train, y_train):
X = self.preprocessing(X_train)
y = y_train.T
self.w = np.array([[0] * X.shape[1]], dtype=np.float)
i = 0
k = 0
for loop in range(self.max_iter):
z = np.dot(X[i], self.w.T)
grad = X[i] * (y[i] - self.sigmod(z))
if (np.abs(grad) <= self.tol).all():
break
else:
self.w += self.learn_rate * grad
k += 1
i = (i + 1) % X.shape[0]
print("迭代次数:{}次".format(k))
print("最终梯度:{}".format(grad))
print("最终权重:{}".format(self.w[0]))
def predict(self, x):
p = self.sigmod(np.dot(self.preprocessing(x), self.w.T))
print("Y=1的概率被估计为:{:.2%}".format(p[0][0]))
p[np.where(p > 0.5)] = 1
p[np.where(p < 0.5)] = 0
print('p=', p)
return p
def score(self, X, y):
y_c = self.predict(X)
error_rate = np.sum(np.abs(y_c - y.T)) / y_c.shape[0]
return 1 - error_rate
def draw(self, X, y):
y = y[0]
X_po = X[np.where(y == 1)]
X_ne = X[np.where(y == 0)]
ax = plt.axes(projection='3d')
x_1 = X_po[0, :]
y_1 = X_po[1, :]
z_1 = X_po[2, :]
x_2 = X_ne[0, :]
y_2 = X_ne[1, :]
z_2 = X_ne[2, :]
ax.scatter(x_1, y_1, z_1, c="r", label="正实例")
ax.scatter(x_2, y_2, z_2, c="b", label="负实例")
ax.legend(loc='best')
x = np.linspace(-3, 3, 3)
y = np.linspace(-3, 3, 3)
x_3, y_3 = np.meshgrid(x, y)
a, b, c, d = self.w[0]
z_3 = -(a * x_3 + b * y_3 + d) / c
ax.plot_surface(x_3, y_3, z_3, alpha=0.5)
plt.show()
def main():
star = time.time()
X_train = np.array([[3, 3, 3], [4, 3, 2], [2, 1, 2], [1, 1, 1], [-1, 0, 1], [2, -2, 1]])
y_train = np.array([[1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0]])
clf = LogisticRegression()
clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
X_new = np.array([[1, 2, -2],[4, 3, 2]])
y_predict = clf.predict(X_new)
print("{}被分类为:{}".format(X_new[0], y_predict[0]))
clf.draw(X_train, y_train)
end = time.time()
print("用时:{:.3f}s".format(end - star))
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
迭代次数:10000次
最终梯度:[-0.29285292 -0.29285292 -0.29285292 -0.29285292]
最终权重:[ 1.53586681 1.23393345 0.75978189 -4.42286443]
Y=1的概率被估计为:12.58%
p= [[0.]
[1.]]
[ 1 2 -2]被分类为:[0.]
用时:0.271s
"""逻辑斯蒂回归算法实现-调用sklearn模块"""
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
import numpy as np
def main():
X_train=np.array([[3,3,3],[4,3,2],[2,1,2],[1,1,1],[-1,0,1],[2,-2,1]])
y_train=np.array([1,1,1,0,0,0])
methodes=["liblinear","newton-cg","lbfgs","sag","saga"]
res=[]
X_new = np.array([[1, 2, -2]])
for method in methodes:
clf=LogisticRegression(solver=method,intercept_scaling=2,max_iter=1000)
clf.fit(X_train,y_train)
y_predict=clf.predict(X_new)
X_test=X_train
y_test=y_train
correct_rate=clf.score(X_test,y_test)
res.append((y_predict,correct_rate))
methodes=["liblinear","newton-cg","lbfgs ","sag ","saga "]
print("solver选择: {}".format(" ".join(method for method in methodes)))
print("{}被分类为: {}".format(X_new[0]," ".join(str(re[0]) for re in res)))
print("测试{}组数据,正确率: {}".format(X_train.shape[0]," ".join(str(round(re[1],1)) for re in res)))
if __name__=="__main__":
main()
solver选择: liblinear newton-cg lbfgs sag saga
[ 1 2 -2]被分类为: [0] [0] [0] [0] [0]
测试6组数据,正确率: 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0





