Hive——Hive常用内置函数总结
✅作者简介:最近接触到大数据方向的程序员,刚入行的小白一枚
作者博客主页:皮皮皮皮皮皮皮卡乒的博客
当前专栏:Hive学习进阶之旅
研究方向:大数据方向,数据汇聚,数据治理
上一篇博文:Hive——详细总结Hive中各大查询语法
文章目录
- 1. 基础函数
-
- 1.1 NVL函数
- 1.2 CASE WHEN THEN ELSE END函数
- 1.3 行转列CONCAT[列合并]
- 1.4 列转行EXPLODE(炸裂函数)
- 2. 开窗函数OVER()
-
- 2.1 开窗函数介绍
- 2.2 开创函数实际应用
- 2.3 开窗函数官方文档
- 3. Rank函数,以及函数分类
-
- 3.1 RANK函数
- 3.2 RANK()函数使用
- 3.3 函数类别
1. 基础函数
1.1 NVL函数
- 函数说明
- NVL:给值为 NULL 的数据赋值,它的格式是 NVL( value ,default_value)。
- 函数功能
- 如果 value 为 NUL则 NVL ,函数返回 default_value 的值,否则返回 value 的值,如果两个参数 都为 NULL ,则返回 NULL。
使用样例:
下列场景说明:有两个表,员工表和部门表,有这样不规则一组数据,虽有有这个部门但是部门没有员工,所以再求满外连接的时候,需要使用NVL函数
select
e.empno,
e.ename,
nvl(e.deptno,d.deptno),
d.dname
from emp e
full join dept d
on e.deptno = d.deptno;
1.2 CASE WHEN THEN ELSE END函数
- 函数说明
- 这组函数类似于C语言中的case语句,case 变量 when ‘变量值1’ then ‘表达式1’ when ‘变量值2’ then ‘表达式2’ else ‘表达式3’ end 【中间还可以继续嵌入when then】
- 函数功能
- 用于处理有判断字段值需求的查询语句,例如:在同时求不同部门男生以及女生总数的查询时,显示不能简单地使用SUM函数+GROUP BY 子句进行查询,因为有两个分组需求,一个是部门,一个是性别,所以需要借助CASE WHEN函数,在GROUP 分组之后,在SUM函数内部做出性别分组
上述样例实现
select
dept_id,
sum(case sex when '男 ' then 1 else 0 end) male_count,
sum(case sex when '女 ' then 1 else 0 end) female_count
from emp_sex
group by dept_id;
1.3 行转列CONCAT[列合并]
说明:
COLLECT_SET(),会将传入的数值进行去重处理
COLLECT_LIST(),不会将传入的数值进行去重处理
函数测试:
创建表以及加载数据
create table person_info(
name string,
constellation string,
blood_type string)
row format delimited fields terminated by "\t";
load data local inpath "/opt/module/hive/data/person_info.txt"
into table person_info;
查询语句:
select
con_blo,concat_ws('|',collect_set(name))
from
(select
concat(constellation,',',blood_type) con_blo,name
from person_info)t1
group by con_blo);
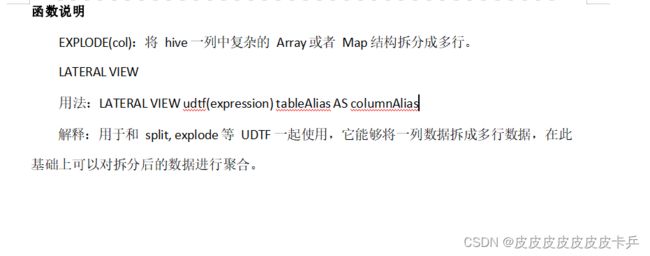
1.4 列转行EXPLODE(炸裂函数)
- EXPLODE函数:
- 功能:可以将一个具有多个数据地字段拆开,变成多行显示
- LATERAL_VIEW函数
- 功能:可以将炸裂出来的字段跟原表的字段保留出来原有的关联
create table movie_info(
movie string, category string)
row format delimited fields terminated by "\t";
load data local inpath "/opt/module/data/movie.txt"
into table movie_info;
select movie ,category_name from movie_info
LATERAL VIEW explode(split(category,",")) cate_gory_tmp AS category_name;
2. 开窗函数OVER()
2.1 开窗函数介绍
深入理解何为开窗?
开窗,可以理解为窗口的大小,这个窗口是对当前查询情景而言的,例如:在一个用户的年度商品购买记录表中,需要计算6月份花销总额,那么窗口的大小就是6月1号到6月30号,如果求第二季度的花销,那么窗口就从4月1号到6月30号
2.2 开创函数实际应用
数据准备
第一列为用户名,第二列为用户购买商品时间,第三列为购买金额
jack,2017-01-01,10
tony,2017-01-02,15
jack,2017-02-03,23
tony,2017-01-04,29
jack,2017-01-05,46
jack,2017-04-06,42
tony,2017-01-07,50
jack,2017-01-08,55
mart,2017-04-08,62
mart,2017-04-09,68
neil,2017-05-10,12
mart,2017-04-11,75
neil,2017-06-12,80
mart,2017-04-13,94
需求
(1) 查询在 2017 年 4 月份购买过的顾客及总人数
窗口大小:所有被’2017-04’过滤出来的数据
select
name,
count(*) over()
from business
where substring(orderdate,0,7) = '2017-04'
group by name;
(2)查询顾客的购买明细及购买总额
窗口大小:限制为相同的姓名
select
name,
orderdate,
cost,
sum(cost) over(partition by name) per_cost_sum
from
business;
(3)查询顾客的购买明细以及每一个顾客每一个月购买总额
窗口大小:每一个顾客的每一个月,因此尽量两个分区
select
name,
orderdate,
cost,
sum(cost) over(partition by name ,month(orderdate)) per_cost_sum
from
business;
(4) 将每个顾客的 cost 按照日期进行累加
窗口大小:每一个顾客,规则:按照日期对用户的购买记录排序
select
name,
orderdate,
cost,
sum(cost) over(partition by name order by orderdate)
from business;
注意:使用order by 默认在后面进行行限制rows bewtween UNBOUNDED PRECEDING and CURRENT ROW
以下为测试
CURRENT ROW:当前行
n PRECEDING:往前 n 行数据
n FOLLOWING:往后 n 行数据
UNBOUNDED :起点,
UNBOUNDED PRECEDING 表示从前面的起点,
UNBOUNDED FOLLOWING 表示到后面的终点
- 随便玩,只需要修改BETWEEN AND里面的范围即可
Ⅰ:将每个顾客的 cost 加上当前行,前一行和后一行进行累加
select
name,
orderdate,
cost,sum(cost) over(partition by name order by orderdate
rows between 1 preceding and 1 following)
from business;
Ⅱ:将每个顾客的 cost 加上没有边界的地方开始加,加到前一行
select
name,
orderdate,
cost,
sum(cost) over(partition by name order by orderdate
rows between unbounded preceding and 1 preceded)
from business;
Ⅲ:将每个顾客的 cost 加上当前行到最后一行进行累加
select
name,
orderdate,
cost,sum(cost) over(partition by name order by orderdate
rows between current row and unbounded following)
from business;
LAG()函数测试
lag(参数名称,向前几行,如果为null,显示的值)
测试:显示每一个用户的上一次购买商品的时间
select
name,orderdate,
lag(orderdate,1,orderdate)over(group by name order by orderdate)
from business;
- 实际应用场景:
- 求用户页面的转发率,A->B A->C B->C,
ntile()
查询前 20%时间的订单信息
select
name,orderdate,cost,sorted
from
(select name,orderdate,cost,
ntile(5) over(order by orderdate) sorted
from business)t1
where sorted =1;
2.3 开窗函数官方文档
3. Rank函数,以及函数分类
3.1 RANK函数
RANK()函数在使用时,因为他有窗口的限制,也需要结合OVER来使用。
- 在进行排序时,通常会伴随着排名,而且可能是多种类型的排名,场景:公司排名–》部门排名—》小组排名,因此也需要设置窗口。
3.2 RANK()函数使用
数据准备:
创建表以及加载数据
create table score(
name string,
subject string,
score int)
row format delimited fields terminated by "\t";
load data local inpath '/opt/module/data/score.txt' into table score;
Ⅰ:根据学科进行排名
select *,rank()over(partition by subject order by score)
from score;
Ⅱ:取每一个学科前三名
select
name,subject,score,rank_id
from
(select *,rank()over(partition by subject order by score desc) rank_id
from score)t1
where rank_id <=3;
3.3 函数类别
函数分三类: