import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import matplotlib as mpl
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
hidden_size = 30
num_layers = 2
timestep = 10
train_step = 10000
batch_size = 32
training_examples = 10000
test_examples = 1000
sample_gap = 0.01
def generate_data(seq):
X = []
Y = []
for i in range(len(seq) - timestep):
X.append([seq[i:i+timestep]])
Y.append([seq[i + timestep]])
return np.array(X,dtype=np.float32),np.array(Y,dtype=np.float32)
def lstm_model(X,y,is_train):
cell = tf.nn.rnn_cell.MultiRNNCell([tf.nn.rnn_cell.BasicLSTMCell(hidden_size) for _ in range(num_layers)])
outputs,_ = tf.nn.dynamic_rnn(cell,X,dtype=tf.float32)
outputs = outputs[:,-1,:]
predictions = tf.contrib.layers.fully_connected(outputs,1,activation_fn=None)
if not is_train:
return predictions,None,None
loss = tf.losses.mean_squared_error(labels=y,predictions=predictions)
train_op = tf.contrib.layers.optimize_loss(loss,tf.train.get_global_step(),optimizer="Adagrad",learning_rate=0.01)
return predictions,loss,train_op
def train(sess,train_X,train_Y):
ds = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((train_X,train_Y))
ds = ds.repeat().shuffle(10000).batch(batch_size)
X,y = ds.make_one_shot_iterator().get_next()
with tf.variable_scope("model",reuse=tf.AUTO_REUSE):
predicttion,loss,train_op = lstm_model(X,y,True)
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
saver = tf.train.Saver()
for i in range(train_step):
_,l = sess.run([train_op,loss])
if i % 100 == 0:
print("train step: " + str(i) + ",loss: "+ str(l))
saver.save(sess,"model_basic_RNN/model.ckpt")
def run_eval(sess,test_X,test_Y):
ds = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((test_X,test_Y))
ds = ds.batch(1)
X,y = ds.make_one_shot_iterator().get_next()
with tf.variable_scope("model",reuse=True):
prediction,_,_ = lstm_model(X,[0.0],False)
predictions = []
labels = []
for i in range(test_examples):
p,l = sess.run([prediction,y])
predictions.append(p)
labels.append(l)
predictions = np.array(predictions).squeeze()
labels = np.array(labels).squeeze()
rmse = np.sqrt(((predictions - labels) ** 2).mean(axis =0 ))
print("RMSE",rmse)
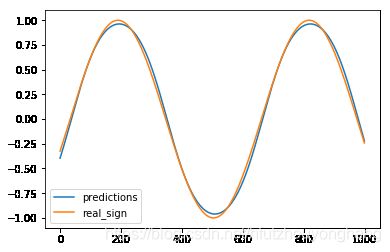
plt.figure()
plt.plot(predictions,label='predictions')
plt.plot(labels,label='real_sign')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
print("ok")
return predictions,labels
test_start = (training_examples + timestep) * sample_gap
test_end = test_start + (test_examples + timestep) * sample_gap
train_X,train_Y = generate_data(np.sin(np.linspace(0,test_start,training_examples+timestep,dtype=np.float32)))
test_X,test_Y = generate_data(np.sin(np.linspace(test_start,test_end,test_examples+timestep,dtype=np.float32)))
with tf.Session() as sess:
train(sess,train_X,train_Y)
p,l = run_eval(sess,test_X,test_Y)