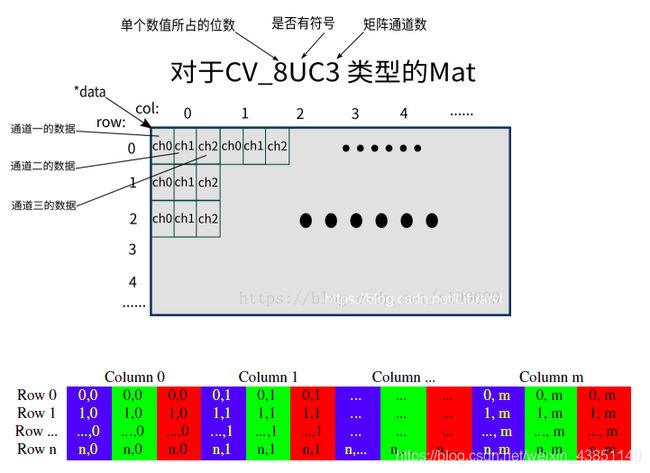
Opencv 常用变量类型(Mat详解)
1.常用变量类型
1.1 基本变量
Basic data types are those that are assembled directly from C++ primitives ( int , float , etc.)
1.2 几何概念
Simple geometric concepts like points, rectangles, sizes, and the like
1.2.1 Matx
Matx是个轻量级的矩阵,必须在使用前确定其尺寸与类型.
源码定义:
/** @brief Template class for small matrices whose type and size are known at compilation time**/
template<typename _Tp, int m, int n> class Matx
使用范例:
Matx33f m(1, 2, 3,
4, 5, 6,
7, 8, 9);
cout << sum(Mat(m*m.t())) << endl;
1.2.2 Vec
vec是一个模板类,主要用于数值向量。我们可以定义任何类型的向量和大量的组件:
源码定义:
template<typename _Tp, int cn> class Vec : public Matx<_Tp, cn, 1>
使用范例:
Vec<double,19> myVector;
上面的代码表示我们这一类Vec中数据以double类型存储,每个Vec对象可以存储19个值。同理,double可以换为int,float等类型,19也可以变化。显然不能为非正数和极大数。
当然也可以用宏定义:
typedef Vec<uchar,2> Vec2b;
typedef Vec<uchar,3> Vec3b;
typedef Vec<short,2> Vec2s;
typedef Vec<short,3> Vec3s;
typedef Vec<ushort, 2> Vec2w;
typedef Vec<ushort, 3> Vec3w;
typedef Vec<int, 2> Vec2i;
typedef Vec<int, 3> Vec3i;
typedef Vec<float, 2> Vec2f;
typedef Vec<float, 3> Vec3f;
typedef Vec<double, 4> Vec4d;
typedef Vec<double, 6> Vec6d;
1.2.3 Scalar
Scalar是常量,在opencv中通常用于传递与设置像素值,如RGB的颜色值。而RGB的颜色值为三个参数(三通道),对与Scalar函数来说,第四个参数可以忽略不写出。
源码定义:
/** @brief Template class for a 4-element vector derived from Vec.
*/
template<typename _Tp> class Scalar_ : public Vec<_Tp, 4>
1.2.4 Point
Point2i Point2f Point3f Point3i
使用范例:
Point2f p1(6,2);
Point3f p2(1,2,3);
即可定义二维点和三维点。
1.2.5 Size
The primary difference between the two is that the point
classes’ data members are named x and y , while the corresponding data members in
the size classes are named width and height .
源码定义:
//! the area (width*height)
_Tp area() const;
//! aspect ratio (width/height)
double aspectRatio() const;
1.2.6 Rect
1.2.7 Range
Range类通常用于确定图片的一块范围.
源码定义:
class Range
{
public:
Range(int _start, int _end);
/*...*/
int start, end;
};
使用实例:
roi_img = src_img(Range(0,100),Range(50,200));
这里截取的就是原图第0行至第99行,第50列至199列的区域图像.
这里要注意的就是Range的两个参数范围分别为左闭右开
1.3 Mat
1.3.1特点:
最强大的类.不再需要手动分配其大小并且不再需要手动释放它,OpenCV 函数将手动自动其输出数据。
Mat本质上是由两个数据部分组成的类:
矩阵头(包含信息有矩阵的大小,用于存储的方法,矩阵存储的地址等)
一个指针,指向包含了像素值的矩阵(可根据选择用于存储的方法采用任何维度存储数据)。
注意:使用拷贝构造函数和赋值运算符只是进行了矩阵头和指针的拷贝,矩阵像素值并没有得到相应的拷贝!
Mat A, C; //仅创建了头部
A = imread(argv[1], CV_LOAD_IMAGE_COLOR); //在此我们知道使用的方法(分配矩阵)
Mat B(A); //使用拷贝构造函数
C = A; //赋值运算符
对于深拷贝,你需要做的是clone 或者 copyTo
Mat F = A.clone();
Mat G;
A.copyTo(G);
1.3.2成员属性:
int flags;
//! the matrix dimensionality, >= 2
int dims;
//! the number of rows and columns or (-1, -1) when the matrix has more than 2 dimensions
int rows, cols;
//! pointer to the data
uchar* data;
1.3.2.1 关于flags:
/*! includes several bit-fields:
- the magic signature
- continuity flag
- depth
- number of channels
*/
参考网站:https://blog.csdn.net/yiyuehuan/article/details/43701797
int Mat::type() const
{
return CV_MAT_TYPE(flags);
/*
#define CV_MAT_TYPE(flags) ((flags) & CV_MAT_TYPE_MASK)
#define CV_MAT_TYPE_MASK (CV_DEPTH_MAX*CV_CN_MAX - 1) = 12'1111 1111 1111
#define CV_CN_MAX 512
#define CV_CN_SHIFT 3
#define CV_DEPTH_MAX (1 << CV_CN_SHIFT) == 8
*/
== > CV_MAT_TYPE(flags)=((flags) & (12'1111 1111 1111))
}
1.3.2.2 关于类型:
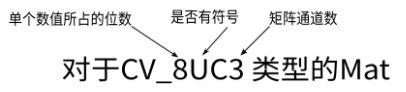
CV_ [每一项的位数] [有符号或无符号] [类型前缀] C [通道数]
参考网站:https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000015653101
1.3.3 元素访问
at方法:
返回的是一个元素类型!
ptr 方法:
比at更快
格式: img.ptr< type >(row)[col];
if the array type is CV_32FC3 , the return value will be of type float*
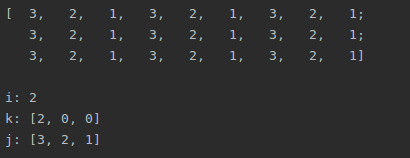
Mat m(3,3,CV_8UC3,Scalar(3,2,1));
cout<<m<<endl;
auto i =m.ptr(0)[1];
Vec3b k =m.ptr(0)[1];//默认char*
Vec3b j =m.at<Vec3b>(0,1);
cout<<"\ni: "<<(int)i<<"\nk: "<<k<<" \nj: "<<j<<endl;
// 三通道
Mat_<Vec3b>::iterator it = image.begin<Vec3b>() ;
Mat_<Vec3b>::iterator itend = image.end<Vec3b>() ;
for(;it != itend ; ++ it){
std::cout << (*it)[0] << std::endl;
std::cout << (*it)[1] << std::endl;
std::cout << (*it)[2] << std::endl;
}
// 单通道
std::cout << (*it1) << std::endl;
continuous+channels (最好):
int nRows = image.rows ;
int nCols = image.cols * image.channels() ;
if(image.isContinuous()){
nCols = nRows * nCols ;
nRows = 1 ;
}
for(int h = 0 ; h < nRows ; ++ h){
uchar *ptr = image.ptr<double>(h) ;
for(int w = 0 ; w < nCols ; ++ w)
std::cout << *ptr++ << std::endl;
}
1.3.4 初始化方法
平地起高楼:
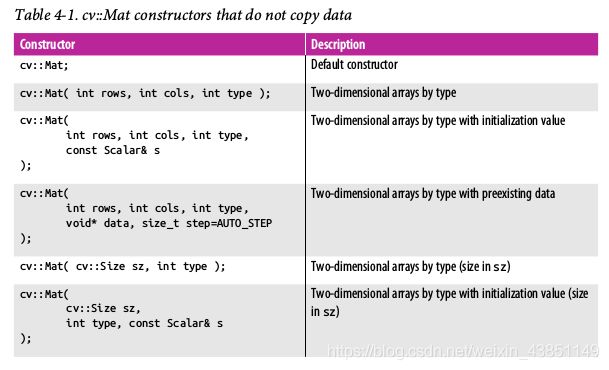

从其他Mat进行浅拷贝:(注意,仍然是矩阵头的拷贝)

Mat m(3,3,CV_8UC3,Scalar(3,2,1));
Mat n(m,Range(0,2),Range(0,2));
n.ptr(0)[1]=55;
cout<<"m: \n"<<m<<"\nn: \n"<<n<<endl;