Netty01——NIO 基础
目录
- 1.三大组件
-
- 1.1.Channel & Buffer
- 1.2.Selector
-
- 1.2.1.多线程版设计
- 1.2.2.线程池版设计
- 1.2.3.selector 版设计
- 2.ByteBuffer
-
- 2.1.ByteBuffer 使用方式
- 2.2.ByteBuffer 结构
-
- 2.2.1.ByteBuffer 的属性
- 2.2.2.调试工具类
- 2.2.3.使用调试工具类
- 2.3.ByteBuffer 常见方法
-
- 2.3.1.分配空间
- 2.3.2.向 buffer 写入数据
- 2.3.3.从 buffer 读取数据
- 2.3.4.mark 和 reset
- 2.3.5.字符串与 ByteBuffer 互转
- 2.4 Scattering Reads
- 2.5 Gathering Writes
- 2.6 练习
- 3.文件编程
-
- 3.1.FileChannel
- 3.2.两个 Channel 传输数据
-
- 3.3.Path
- 3.4.Files
- 4.网络编程
-
- 4.1.阻塞 vs 非阻塞
-
- 4.1.1.阻塞
- 4.1.2.非阻塞
- 4.1.3.多路复用
- 4.2.Selector
- 4.3.处理 accept 事件
- 4.4.处理 read 事件
-
- 4.4.1.代码演示
- 4.4.2.处理客户端断开
- 4.4.3.消息边界处理
- 4.4.4.ByteBuffer 大小分配
- 4.5.处理 write 事件
- 4.6.更进一步
-
- 4.6.1.利用多线程优化
- 4.6.2.如何拿到 CPU 个数
- 4.7.UDP
- 5.NIO vs BIO
-
- 5.1.stream vs channel
- 5.2.IO 模型
- 5.3.零拷贝
-
- 5.3.1.传统 IO 问题
- 5.3.2.NIO 优化
- 5.3.AIO
-
- 5.3.1.文件 AIO
- 5.3.2.网络 AIO
本文笔记整理来自尚硅谷视频https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1py4y1E7oA/?p=2,相关资料可在视频评论区进行获取。
non-blocking io 非阻塞 IO
1.三大组件
1.1.Channel & Buffer
(1)channel 有一点类似于 stream,它就是读写数据的双向通道,可以从 channel 将数据读入 buffer,也可以将 buffer 的数据写入 channel,而之前的 stream 要么是输入,要么是输出,channel 比 stream 更为底层。
常见的 Channel 有
- FileChannel
- DatagramChannel
- SocketChannel
- ServerSocketChannel
(2)buffer 则用来缓冲读写数据,常见的 buffer 有:
- ByteBuffer(常用)
- MappedByteBuffer
- DirectByteBuffer
- HeapByteBuffer
- ShortBuffer
- IntBuffer
- LongBuffer
- FloatBuffer
- DoubleBuffer
- CharBuffer
1.2.Selector
selector 单从字面意思不好理解,需要结合服务器的设计演化来理解它的用途。
1.2.1.多线程版设计
⚠️ 多线程版缺点
- 内存占用高
- 线程上下文切换成本高
- 只适合连接数少的场景
1.2.2.线程池版设计
⚠️ 线程池版缺点
- 阻塞模式下,线程仅能处理一个 socket 连接
- 仅适合短连接场景
1.2.3.selector 版设计
(1)selector 的作用就是配合一个线程来管理多个 channel,获取这些 channel 上发生的事件,这些 channel 工作在非阻塞模式下,不会让线程吊死在一个 channel 上。适合连接数特别多,但流量低的场景 (low traffic)。
(2)调用 selector 的 select() 会阻塞直到 channel 发生了读写就绪事件,这些事件发生,select 方法就会返回这些事件交给 thread 来处理。
“没有什么是加一层不能解决的,如果有,那就再加一层!”
2.ByteBuffer
(1)入门案例:channel 和 bytebuffer 的基本使用。有一位于当前项目根目录下的普通文本文件 data.txt,内容如下:
1234567890abcd
使用 FileChannel 来读取文件内容
package cn.itcast.netty.c1;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel;
@Slf4j
public class TestByteBuffer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (FileChannel channel = new FileInputStream("data.txt").getChannel()) {
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(10);
do {
// 从 channel 读取数据,并向 buffer 写入
int len = channel.read(buffer);
log.debug("读到字节数:{}", len);
if (len == -1) {
break;
}
// 切换 buffer 读模式
buffer.flip();
while(buffer.hasRemaining()) {
log.debug("{}", (char)buffer.get());
}
// 切换 buffer 写模式
buffer.clear();
} while (true);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
输出结果如下:
19:10:06 [DEBUG] [main] c.i.n.c.ChannelDemo1 - 读到字节数:10
19:10:06 [DEBUG] [main] c.i.n.c.ChannelDemo1 - 1
19:10:06 [DEBUG] [main] c.i.n.c.ChannelDemo1 - 2
19:10:06 [DEBUG] [main] c.i.n.c.ChannelDemo1 - 3
19:10:06 [DEBUG] [main] c.i.n.c.ChannelDemo1 - 4
19:10:06 [DEBUG] [main] c.i.n.c.ChannelDemo1 - 5
19:10:06 [DEBUG] [main] c.i.n.c.ChannelDemo1 - 6
19:10:06 [DEBUG] [main] c.i.n.c.ChannelDemo1 - 7
19:10:06 [DEBUG] [main] c.i.n.c.ChannelDemo1 - 8
19:10:06 [DEBUG] [main] c.i.n.c.ChannelDemo1 - 9
19:10:06 [DEBUG] [main] c.i.n.c.ChannelDemo1 - 0
19:10:06 [DEBUG] [main] c.i.n.c.ChannelDemo1 - 读到字节数:4
19:10:06 [DEBUG] [main] c.i.n.c.ChannelDemo1 - @
19:10:06 [DEBUG] [main] c.i.n.c.ChannelDemo1 - a
19:10:06 [DEBUG] [main] c.i.n.c.ChannelDemo1 - b
19:10:06 [DEBUG] [main] c.i.n.c.ChannelDemo1 - c
19:10:06 [DEBUG] [main] c.i.n.c.ChannelDemo1 - 读到字节数:-1
(2)上述代码中使用到的 logback 的配置如下:
<configuration
xmlns="http://ch.qos.logback/xml/ns/logback"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://ch.qos.logback/xml/ns/logback logback.xsd">
<appender name="STDOUT" class="ch.qos.logback.core.ConsoleAppender">
<encoder>
<pattern>%date{HH:mm:ss} [%-5level] [%thread] %logger{17} - %m%n pattern>
encoder>
appender>
<logger name="cn.itcast" level="DEBUG" additivity="false">
<appender-ref ref="STDOUT"/>
logger>
<logger name="io.netty.handler.logging.LoggingHandler" level="DEBUG" additivity="false">
<appender-ref ref="STDOUT"/>
logger>
<root level="ERROR">
<appender-ref ref="STDOUT"/>
root>
configuration>
(3)上述代码所处的 maven 项目的 pom.xml 配置如下:
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0modelVersion>
<groupId>org.examplegroupId>
<artifactId>netty-demoartifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOTversion>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>1.8maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>1.8maven.compiler.target>
properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.nettygroupId>
<artifactId>netty-allartifactId>
<version>4.1.42.Finalversion>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombokgroupId>
<artifactId>lombokartifactId>
<version>1.16.18version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.google.code.gsongroupId>
<artifactId>gsonartifactId>
<version>2.8.5version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.google.guavagroupId>
<artifactId>guavaartifactId>
<version>19.0version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>ch.qos.logbackgroupId>
<artifactId>logback-classicartifactId>
<version>1.2.3version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.google.protobufgroupId>
<artifactId>protobuf-javaartifactId>
<version>3.11.3version>
dependency>
dependencies>
project>
2.1.ByteBuffer 使用方式
- 向 buffer 写入数据,例如调用 channel.read(buffer)
- 调用 flip() 切换至读模式
- 从 buffer 读取数据,例如调用 buffer.get()
- 调用 clear() 或 compact() 切换至写模式
- 重复 1~4 步骤
2.2.ByteBuffer 结构
2.2.1.ByteBuffer 的属性
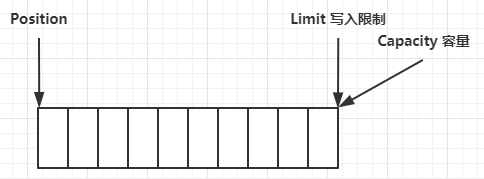
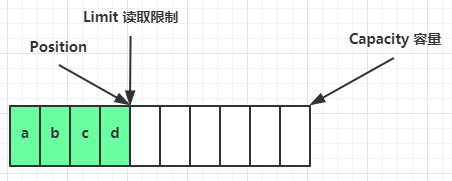
(1)ByteBuffer 有以下重要属性:
- capacity:容量
- position:读写下标
- limit:读写限制
(2)具体操作过程如下:
一开始
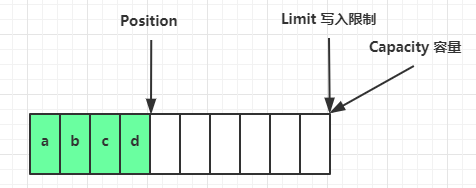
写模式下,position 是写入位置,limit 等于容量,下图表示写入了 4 个字节后的状态
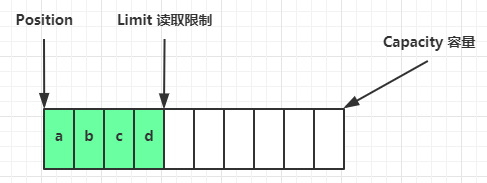
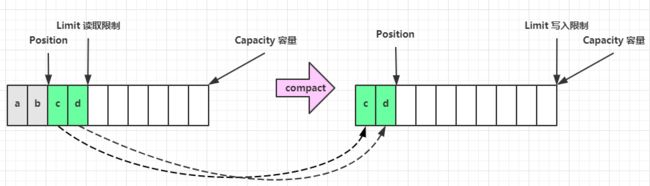
flip 动作发生后,position 切换为读取位置,limit 切换为读取限制
读取 4 个字节后,状态
clear 动作发生后,状态
compact 方法,是把未读完的部分向前压缩,然后切换至写模式
2.2.2.调试工具类
package cn.itcast.netty.c1;
import io.netty.util.internal.StringUtil;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import static io.netty.util.internal.MathUtil.isOutOfBounds;
import static io.netty.util.internal.StringUtil.NEWLINE;
public class ByteBufferUtil {
private static final char[] BYTE2CHAR = new char[256];
private static final char[] HEXDUMP_TABLE = new char[256 * 4];
private static final String[] HEXPADDING = new String[16];
private static final String[] HEXDUMP_ROWPREFIXES = new String[65536 >>> 4];
private static final String[] BYTE2HEX = new String[256];
private static final String[] BYTEPADDING = new String[16];
static {
final char[] DIGITS = "0123456789abcdef".toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < 256; i++) {
HEXDUMP_TABLE[i << 1] = DIGITS[i >>> 4 & 0x0F];
HEXDUMP_TABLE[(i << 1) + 1] = DIGITS[i & 0x0F];
}
int i;
// Generate the lookup table for hex dump paddings
for (i = 0; i < HEXPADDING.length; i++) {
int padding = HEXPADDING.length - i;
StringBuilder buf = new StringBuilder(padding * 3);
for (int j = 0; j < padding; j++) {
buf.append(" ");
}
HEXPADDING[i] = buf.toString();
}
// Generate the lookup table for the start-offset header in each row (up to 64KiB).
for (i = 0; i < HEXDUMP_ROWPREFIXES.length; i++) {
StringBuilder buf = new StringBuilder(12);
buf.append(NEWLINE);
buf.append(Long.toHexString(i << 4 & 0xFFFFFFFFL | 0x100000000L));
buf.setCharAt(buf.length() - 9, '|');
buf.append('|');
HEXDUMP_ROWPREFIXES[i] = buf.toString();
}
// Generate the lookup table for byte-to-hex-dump conversion
for (i = 0; i < BYTE2HEX.length; i++) {
BYTE2HEX[i] = ' ' + StringUtil.byteToHexStringPadded(i);
}
// Generate the lookup table for byte dump paddings
for (i = 0; i < BYTEPADDING.length; i++) {
int padding = BYTEPADDING.length - i;
StringBuilder buf = new StringBuilder(padding);
for (int j = 0; j < padding; j++) {
buf.append(' ');
}
BYTEPADDING[i] = buf.toString();
}
// Generate the lookup table for byte-to-char conversion
for (i = 0; i < BYTE2CHAR.length; i++) {
if (i <= 0x1f || i >= 0x7f) {
BYTE2CHAR[i] = '.';
} else {
BYTE2CHAR[i] = (char) i;
}
}
}
/**
* 打印所有内容
*
* @param buffer
*/
public static void debugAll(ByteBuffer buffer) {
int oldlimit = buffer.limit();
buffer.limit(buffer.capacity());
StringBuilder origin = new StringBuilder(256);
appendPrettyHexDump(origin, buffer, 0, buffer.capacity());
System.out.println("+--------+-------------------- all ------------------------+----------------+");
System.out.printf("position: [%d], limit: [%d]\n", buffer.position(), oldlimit);
System.out.println(origin);
buffer.limit(oldlimit);
}
/**
* 打印可读取内容
*
* @param buffer
*/
public static void debugRead(ByteBuffer buffer) {
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder(256);
appendPrettyHexDump(builder, buffer, buffer.position(), buffer.limit() - buffer.position());
System.out.println("+--------+-------------------- read -----------------------+----------------+");
System.out.printf("position: [%d], limit: [%d]\n", buffer.position(), buffer.limit());
System.out.println(builder);
}
private static void appendPrettyHexDump(StringBuilder dump, ByteBuffer buf, int offset, int length) {
if (isOutOfBounds(offset, length, buf.capacity())) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(
"expected: " + "0 <= offset(" + offset + ") <= offset + length(" + length
+ ") <= " + "buf.capacity(" + buf.capacity() + ')');
}
if (length == 0) {
return;
}
dump.append(
" +-------------------------------------------------+" +
NEWLINE + " | 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |" +
NEWLINE + "+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+");
final int startIndex = offset;
final int fullRows = length >>> 4;
final int remainder = length & 0xF;
// Dump the rows which have 16 bytes.
for (int row = 0; row < fullRows; row++) {
int rowStartIndex = (row << 4) + startIndex;
// Per-row prefix.
appendHexDumpRowPrefix(dump, row, rowStartIndex);
// Hex dump
int rowEndIndex = rowStartIndex + 16;
for (int j = rowStartIndex; j < rowEndIndex; j++) {
dump.append(BYTE2HEX[getUnsignedByte(buf, j)]);
}
dump.append(" |");
// ASCII dump
for (int j = rowStartIndex; j < rowEndIndex; j++) {
dump.append(BYTE2CHAR[getUnsignedByte(buf, j)]);
}
dump.append('|');
}
// Dump the last row which has less than 16 bytes.
if (remainder != 0) {
int rowStartIndex = (fullRows << 4) + startIndex;
appendHexDumpRowPrefix(dump, fullRows, rowStartIndex);
// Hex dump
int rowEndIndex = rowStartIndex + remainder;
for (int j = rowStartIndex; j < rowEndIndex; j++) {
dump.append(BYTE2HEX[getUnsignedByte(buf, j)]);
}
dump.append(HEXPADDING[remainder]);
dump.append(" |");
// Ascii dump
for (int j = rowStartIndex; j < rowEndIndex; j++) {
dump.append(BYTE2CHAR[getUnsignedByte(buf, j)]);
}
dump.append(BYTEPADDING[remainder]);
dump.append('|');
}
dump.append(NEWLINE +
"+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+");
}
private static void appendHexDumpRowPrefix(StringBuilder dump, int row, int rowStartIndex) {
if (row < HEXDUMP_ROWPREFIXES.length) {
dump.append(HEXDUMP_ROWPREFIXES[row]);
} else {
dump.append(NEWLINE);
dump.append(Long.toHexString(rowStartIndex & 0xFFFFFFFFL | 0x100000000L));
dump.setCharAt(dump.length() - 9, '|');
dump.append('|');
}
}
public static short getUnsignedByte(ByteBuffer buffer, int index) {
return (short) (buffer.get(index) & 0xFF);
}
}
2.2.3.使用调试工具类
package cn.itcast.netty.c1;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import static cn.itcast.netty.c1.ByteBufferUtil.debugAll;
public class TestByteBufferReadWrite {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(10);
buffer.put((byte) 0x61); // 'a'
debugAll(buffer);
buffer.put(new byte[]{0x62, 0x63, 0x64}); // 'b', 'c', 'd'
debugAll(buffer);
// 如果不切换为读模式,那么直接读取的数据是错误的
// System.out.println(buffer.get());
buffer.flip();
System.out.println(buffer.get());
debugAll(buffer);
buffer.compact();
debugAll(buffer);
buffer.put(new byte[]{0x65, 0x66}); // 'e', 'f'
debugAll(buffer);
}
}
结果输出如下:
+--------+-------------------- all ------------------------+----------------+
position: [1], limit: [10]
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 61 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |a......... |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
+--------+-------------------- all ------------------------+----------------+
position: [4], limit: [10]
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 61 62 63 64 00 00 00 00 00 00 |abcd...... |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
97
+--------+-------------------- all ------------------------+----------------+
position: [1], limit: [4]
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 61 62 63 64 00 00 00 00 00 00 |abcd...... |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
Process finished with exit code 0
2.3.ByteBuffer 常见方法
2.3.1.分配空间
(1)可以使用 allocate 方法或者 allocateDirect 方法为 ByteBuffer 分配空间,其它 buffer 类也有该方法。
Bytebuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(16);
Bytebuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(16);
(2)上述两种分配方法的区别:
package cn.itcast.netty.c1;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
public class TestByteBufferAllocate {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(ByteBuffer.allocate(16).getClass());
System.out.println(ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(16).getClass());
}
}
结果如下:
class java.nio.HeapByteBuffer
class java.nio.DirectByteBuffer
① allocate 方法分配的是 Java 堆内存,并且由于收到 GC 的影响,其读写效率较低;
② allocateDirect 方法分配的是直接内存,其不会收到 GC 的影响,读写效率高(少一次拷贝),但是分配的效率较低;
具体细节后面会详细介绍。
2.3.2.向 buffer 写入数据
向 buffer 写入数据有以下两种办法:
- 调用 channel 的 read 方法
- 调用 buffer 自己的 put 方法
int readBytes = channel.read(buf);
buf.put((byte)127);
2.3.3.从 buffer 读取数据
从 buffer 读取数据同样有两种办法
- 调用 channel 的 write 方法
- 调用 buffer 自己的 get 方法
int writeBytes = channel.write(buf);
byte b = buf.get();
get 方法会让 position 读指针向后走,如果想重复读取数据
- 可以调用 rewind 方法将 position 重新置为 0
- 或者调用 get(int i) 方法获取索引 i 的内容,它不会移动读指针
2.3.4.mark 和 reset
mark 是在读取时,做一个标记,即使 position 改变,只要调用 reset 就能回到 mark 的位置
注意
rewind 和 flip 都会清除 mark 位置
package cn.itcast.netty.c1;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import static cn.itcast.netty.c1.ByteBufferUtil.debugAll;
public class TestBufferRead {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(10);
buffer.put(new byte[]{'a', 'b', 'c', 'd'});
buffer.flip();
// rewind:从头开始读
buffer.get(new byte[4]);
debugAll(buffer);
buffer.rewind();
System.out.println((char) buffer.get());
/*
mark & reset
mark:做一个标记,记录 position 的位置
reset:将 position 重置到 mark 的位置(类似于存档-读档操作)
*/
System.out.println((char) buffer.get());
System.out.println((char) buffer.get());
buffer.mark(); //在索引为 2 的位置加标记
System.out.println((char) buffer.get());
System.out.println((char) buffer.get());
buffer.reset(); //将 position 重置到索引 2
System.out.println((char) buffer.get());
System.out.println((char) buffer.get());
// get(i):不改变 position,就是按照索引读取
System.out.println((char) buffer.get(2));
debugAll(buffer);
}
}
2.3.5.字符串与 ByteBuffer 互转
package cn.itcast.netty.c1;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import static cn.itcast.netty.c1.ByteBufferUtil.debugAll;
public class TestByteBufferString {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//字符串转为 ByteBuffer
//1.
ByteBuffer buffer1 = ByteBuffer.allocate(16);
buffer1.put("hello".getBytes());
debugAll(buffer1);
//2. Charset
ByteBuffer buffer2 = StandardCharsets.UTF_8.encode("hello");
debugAll(buffer2);
//3. wrap
ByteBuffer buffer3 = ByteBuffer.wrap("hello".getBytes());
debugAll(buffer3);
//ByteBuffer 转为字符串
String str1 = StandardCharsets.UTF_8.decode(buffer2).toString();
System.out.println(str1); // hello
buffer1.flip();
String str2 = StandardCharsets.UTF_8.decode(buffer1).toString();
System.out.println(str2); // hello
}
}
结果如下:
+--------+-------------------- all ------------------------+----------------+
position: [5], limit: [16]
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 68 65 6c 6c 6f 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |hello...........|
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
+--------+-------------------- all ------------------------+----------------+
position: [0], limit: [5]
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 68 65 6c 6c 6f |hello |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
+--------+-------------------- all ------------------------+----------------+
position: [0], limit: [5]
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 68 65 6c 6c 6f |hello |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
hello
hello
Buffer 是非线程安全的
2.4 Scattering Reads
分散读取,有一个文本文件 3parts.txt
onetwothree
使用如下方式读取,可以将数据填充至多个 buffer。
package cn.itcast.netty.c1;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.RandomAccessFile;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel;
import static cn.itcast.netty.c1.ByteBufferUtil.debugAll;
public class TestScatteringReads {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (FileChannel channel = new RandomAccessFile("words.txt", "r").getChannel()) {
ByteBuffer b1 = ByteBuffer.allocate(3);
ByteBuffer b2 = ByteBuffer.allocate(3);
ByteBuffer b3 = ByteBuffer.allocate(5);
channel.read(new ByteBuffer[]{b1, b2, b3});
b1.flip();
b2.flip();
b3.flip();
debugAll(b1);
debugAll(b2);
debugAll(b3);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
结果如下:
+--------+-------------------- all ------------------------+----------------+
position: [0], limit: [3]
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 6f 6e 65 |one |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
+--------+-------------------- all ------------------------+----------------+
position: [0], limit: [3]
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 74 77 6f |two |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
+--------+-------------------- all ------------------------+----------------+
position: [0], limit: [5]
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 74 68 72 65 65 |three |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
2.5 Gathering Writes
使用如下方式写入,可以将多个 buffer 的数据填充至 channel
package cn.itcast.netty.c1;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.RandomAccessFile;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
public class TestGatheringWrites {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ByteBuffer b1 = StandardCharsets.UTF_8.encode("hello");
ByteBuffer b2 = StandardCharsets.UTF_8.encode("world");
ByteBuffer b3 = StandardCharsets.UTF_8.encode("你好");
try (FileChannel channel = new RandomAccessFile("words2.txt", "rw").getChannel()) {
channel.write(new ByteBuffer[]{b1, b2, b3});
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
words2.txt 中的内容如下:
helloworld你好
2.6 练习
网络上有多条数据发送给服务端,数据之间使用 \n 来进行分隔,但是由于某种原因这些数据在接收时,被进行了重新组合,例如原始数据有 3 条为:
- Hello,world\n
- I’m zhangsan\n
- How are you?\n
变成了下面的两个 byteBuffer (黏包,半包)
- Hello,world\nI’m zhangsan\nHo
- w are you?\n
现在要求你编写程序,将错乱的数据恢复成原始的按 \n 分隔的数据
package cn.itcast.netty.c1;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import static cn.itcast.netty.c1.ByteBufferUtil.debugAll;
public class TestByteBufferExam {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ByteBuffer source = ByteBuffer.allocate(32);
// 11 24
source.put("Hello,world\nI'm zhangsan\nHo".getBytes());
split(source);
source.put("w are you?\nhaha!\n".getBytes());
split(source);
}
private static void split(ByteBuffer source) {
source.flip();
int oldLimit = source.limit();
for (int i = 0; i < oldLimit; i++) {
if (source.get(i) == '\n') {
System.out.println(i);
ByteBuffer target = ByteBuffer.allocate(i + 1 - source.position());
// 0 ~ limit
source.limit(i + 1);
target.put(source); // 从source 读,向 target 写
debugAll(target);
source.limit(oldLimit);
}
}
source.compact();
}
}
结果如下:
11
+--------+-------------------- all ------------------------+----------------+
position: [12], limit: [12]
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 48 65 6c 6c 6f 2c 77 6f 72 6c 64 0a |Hello,world. |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
24
+--------+-------------------- all ------------------------+----------------+
position: [13], limit: [13]
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 49 27 6d 20 7a 68 61 6e 67 73 61 6e 0a |I'm zhangsan. |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
12
+--------+-------------------- all ------------------------+----------------+
position: [13], limit: [13]
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 48 6f 77 20 61 72 65 20 79 6f 75 3f 0a |How are you?. |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
18
+--------+-------------------- all ------------------------+----------------+
position: [6], limit: [6]
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 68 61 68 61 21 0a |haha!. |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
3.文件编程
3.1.FileChannel
⚠️ FileChannel 工作模式
FileChannel 只能工作在阻塞模式下。
获取
不能直接打开 FileChannel,必须通过 FileInputStream、FileOutputStream 或者 RandomAccessFile 来获取 FileChannel,它们都有 getChannel 方法
- 通过 FileInputStream 获取的 channel 只能读
- 通过 FileOutputStream 获取的 channel 只能写
- 通过 RandomAccessFile 是否能读写根据构造 RandomAccessFile 时的读写模式决定
读取
会从 channel 读取数据填充 ByteBuffer,返回值表示读到了多少字节,-1 表示到达了文件的末尾
int readBytes = channel.read(buffer);
写入
写入的正确方式如下, SocketChannel
ByteBuffer buffer = ...;
buffer.put(...); // 存入数据
buffer.flip(); // 切换读模式
while(buffer.hasRemaining()) {
channel.write(buffer);
}
在 while 中调用 channel.write 是因为 write 方法并不能保证一次将 buffer 中的内容全部写入 channel
关闭
channel 必须关闭,不过调用了 FileInputStream、FileOutputStream 或者 RandomAccessFile 的 close() 会间接地调用 channel 的 close()
位置
获取当前位置
long pos = channel.position();
设置当前位置
long newPos = ...;
channel.position(newPos);
设置当前位置时,如果设置为文件的末尾
- 这时读取会返回 -1
- 这时写入,会追加内容,但要注意如果 position 超过了文件末尾,再写入时在新内容和原末尾之间会有空洞(00)
大小
使用 size 方法获取文件的大小
强制写入
操作系统出于性能的考虑,会将数据缓存,不是立刻写入磁盘。可以调用 force(true) 方法将文件内容和元数据(文件的权限等信息)立刻写入磁盘
3.2.两个 Channel 传输数据
String FROM = "helloword/data.txt";
String TO = "helloword/to.txt";
long start = System.nanoTime();
try (FileChannel from = new FileInputStream(FROM).getChannel();
FileChannel to = new FileOutputStream(TO).getChannel();
) {
from.transferTo(0, from.size(), to);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
long end = System.nanoTime();
System.out.println("transferTo 用时:" + (end - start) / 1000_000.0);
输出
transferTo 用时:8.2011
超过 2G 大小的文件传输
public class TestFileChannelTransferTo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (
FileChannel from = new FileInputStream("data.txt").getChannel();
FileChannel to = new FileOutputStream("to.txt").getChannel();
) {
// 效率高,底层会利用操作系统的零拷贝进行优化
long size = from.size();
// left 变量代表还剩余多少字节
for (long left = size; left > 0; ) {
System.out.println("position:" + (size - left) + " left:" + left);
left -= from.transferTo((size - left), left, to);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
实际传输一个超大文件
position:0 left:7769948160
position:2147483647 left:5622464513
position:4294967294 left:3474980866
position:6442450941 left:1327497219
3.3.Path
jdk7 引入了 Path 和 Paths 类:
- Path 用来表示文件路径
- Paths 是工具类,用来获取 Path 实例
Path source = Paths.get("1.txt"); // 相对路径 使用 user.dir 环境变量来定位 1.txt
Path source = Paths.get("d:\\1.txt"); // 绝对路径 代表了 d:\1.txt
Path source = Paths.get("d:/1.txt"); // 绝对路径 同样代表了 d:\1.txt
Path projects = Paths.get("d:\\data", "projects"); // 代表了 d:\data\projects
.代表了当前路径..代表了上一级路径
例如目录结构如下所示:
d:
|- data
|- projects
|- a
|- b
代码
Path path = Paths.get("d:\\data\\projects\\a\\..\\b");
System.out.println(path);
System.out.println(path.normalize()); // 正常化路径
输出结果如下:
d:\data\projects\a\..\b
d:\data\projects\b
3.4.Files
检查文件是否存在
Path path = Paths.get("helloword/data.txt");
System.out.println(Files.exists(path));
创建一级目录
Path path = Paths.get("helloword/d1");
Files.createDirectory(path);
- 如果目录已存在,会抛异常 FileAlreadyExistsException
- 不能一次创建多级目录,否则会抛异常 NoSuchFileException
创建多级目录用
Path path = Paths.get("helloword/d1/d2");
Files.createDirectories(path);
拷贝文件
Path source = Paths.get("helloword/data.txt");
Path target = Paths.get("helloword/target.txt");
Files.copy(source, target);
- 如果文件已存在,会抛异常 FileAlreadyExistsException
如果希望用 source 覆盖掉 target,需要用 StandardCopyOption 来控制
Files.copy(source, target, StandardCopyOption.REPLACE_EXISTING);
移动文件
Path source = Paths.get("helloword/data.txt");
Path target = Paths.get("helloword/data.txt");
Files.move(source, target, StandardCopyOption.ATOMIC_MOVE);
- StandardCopyOption.ATOMIC_MOVE 保证文件移动的原子性
删除文件
Path target = Paths.get("helloword/target.txt");
Files.delete(target);
- 如果文件不存在,会抛异常 NoSuchFileException
删除目录
Path target = Paths.get("helloword/d1");
Files.delete(target);
- 如果目录还有内容,会抛异常 DirectoryNotEmptyException
遍历目录文件
package cn.itcast.netty.c1;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.file.*;
import java.nio.file.attribute.BasicFileAttributes;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
public class TestFilesWalkFileTree {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Path path = Paths.get("D:\\software\\JDK\\JDK8");
AtomicInteger dirCount = new AtomicInteger();
AtomicInteger fileCount = new AtomicInteger();
Files.walkFileTree(path, new SimpleFileVisitor<Path>(){
@Override
public FileVisitResult preVisitDirectory(Path dir, BasicFileAttributes attrs)
throws IOException, IOException {
System.out.println(dir);
dirCount.incrementAndGet();
return super.preVisitDirectory(dir, attrs);
}
@Override
public FileVisitResult visitFile(Path file, BasicFileAttributes attrs)
throws IOException {
System.out.println(file);
fileCount.incrementAndGet();
return super.visitFile(file, attrs);
}
});
System.out.println(dirCount); // 133
System.out.println(fileCount); // 1479
}
}
统计 jar 的数目
Path path = Paths.get("C:\\Program Files\\Java\\jdk1.8.0_91");
AtomicInteger fileCount = new AtomicInteger();
Files.walkFileTree(path, new SimpleFileVisitor<Path>(){
@Override
public FileVisitResult visitFile(Path file, BasicFileAttributes attrs)
throws IOException {
if (file.toFile().getName().endsWith(".jar")) {
fileCount.incrementAndGet();
}
return super.visitFile(file, attrs);
}
});
System.out.println(fileCount); // 724
删除多级目录
Path path = Paths.get("d:\\a");
Files.walkFileTree(path, new SimpleFileVisitor<Path>(){
@Override
public FileVisitResult visitFile(Path file, BasicFileAttributes attrs)
throws IOException {
Files.delete(file);
return super.visitFile(file, attrs);
}
@Override
public FileVisitResult postVisitDirectory(Path dir, IOException exc)
throws IOException {
Files.delete(dir);
return super.postVisitDirectory(dir, exc);
}
});
删除是危险操作,确保要递归删除的文件夹没有重要内容!
拷贝多级目录
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
String source = "D:\\Snipaste-1.16.2-x64";
String target = "D:\\Snipaste-1.16.2-x64aaa";
Files.walk(Paths.get(source)).forEach(path -> {
try {
String targetName = path.toString().replace(source, target);
// 是目录
if (Files.isDirectory(path)) {
Files.createDirectory(Paths.get(targetName));
}
// 是普通文件
else if (Files.isRegularFile(path)) {
Files.copy(path, Paths.get(targetName));
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(end - start);
4.网络编程
4.1.阻塞 vs 非阻塞
4.1.1.阻塞
(1)阻塞模式
- 阻塞模式下,相关方法都会导致线程暂停
- ServerSocketChannel.accept():会在没有连接建立时让线程暂停;
- SocketChannel.read():会在没有数据可读时让线程暂停;
- 阻塞的表现其实就是线程暂停了,暂停期间不会占用 cpu,但线程相当于闲置;
- 单线程下,阻塞方法之间相互影响,几乎不能正常工作,需要多线程支持
- 但多线程下,有新的问题,体现在以下方面:
- 32 位 jvm 一个线程 320k,64 位 jvm 一个线程 1024k,如果连接数过多,必然导致 OOM,并且线程太多,反而会因为频繁上下文切换导致性能降低;
- 可以采用线程池技术来减少线程数和线程上下文切换,但治标不治本,如果有很多连接建立,但长时间 inactive,会阻塞线程池中所有线程,因此不适合长连接,只适合短连接;
(2)案例
服务器端
package cn.itcast.netty.c4;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import static cn.itcast.netty.c1.ByteBufferUtil.debugRead;
@Slf4j
public class Server {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 使用 nio 来理解阻塞模式, 单线程
// 0. ByteBuffer
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(16);
// 1. 创建服务器
ServerSocketChannel ssc = ServerSocketChannel.open();
// 2. 绑定监听端口(客户端向服务器端发送信息需要直到服务器端的端口号)
ssc.bind(new InetSocketAddress(8080));
// 3. 连接集合
List<SocketChannel> channels = new ArrayList<>();
while (true) {
// 4. accept 建立与客户端连接, SocketChannel 用来与客户端之间通信
log.debug("connecting...");
// accept(): 阻塞方法,会在没有连接建立时让线程暂停
SocketChannel sc = ssc.accept();
log.debug("connected... {}", sc);
channels.add(sc);
for (SocketChannel channel : channels) {
// 5. 接收客户端发送的数据
log.debug("before read... {}", channel);
// read(): 阻塞方法,会在没有数据可读时让线程暂停
channel.read(buffer);
buffer.flip();
debugRead(buffer);
buffer.clear();
log.debug("after read...{}", channel);
}
}
}
}
客户端
package cn.itcast.netty.c4;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
SocketChannel sc = SocketChannel.open();
//与服务器建立连接
sc.connect(new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 8080));
System.out.println("waiting...");
}
}
演示1:一个客户端
① 运行服务器段代码
② 调试客户端代码
③ 客户端发送数据
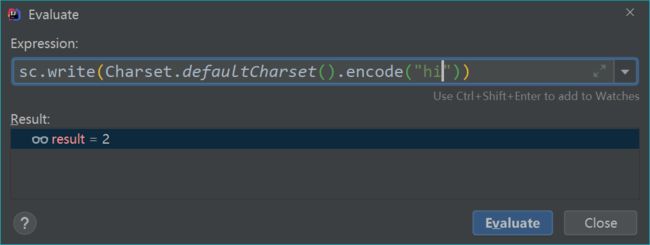
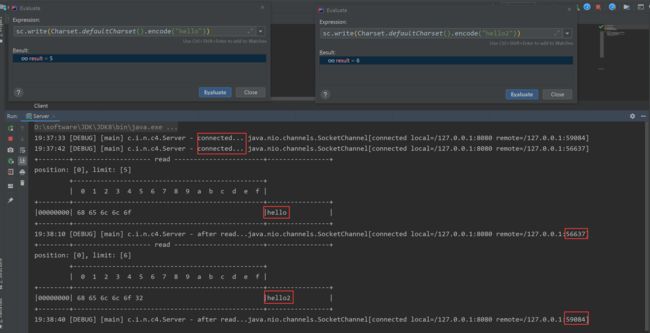
sc.write(Charset.defaultCharset().encode("hello"))
① 在 IDEA 中设置一个程序可以多次运行。
② 接着演示 1 的操作,继续发送一条数据:
sc.write(Charset.defaultCharset().encode("hello"))
此时会发现服务器端仍在等待连接中:

③ 再次调试客户端(相当于 Client.java 运行了 2 次),此时发现 “hi” 被打印出来了,但是由于第 2 次运行的客户端(端口号为 56230)并未传输数据,所以服务器端又阻塞在 read() 处。
4.1.2.非阻塞
- 非阻塞模式下,相关方法都会不会让线程暂停
- 在 ServerSocketChannel.accept() 在没有连接建立时,会返回 null,继续运行;
- SocketChannel.read() 在没有数据可读时,会返回 0,但线程不必阻塞,可以去执行其它 SocketChannel 的 read 或是去执行 ServerSocketChannel.accept();
- 写数据时,线程只是等待数据写入 Channel 即可,无需等 Channel 通过网络把数据发送出去;
- 但非阻塞模式下,即使没有连接建立,和可读数据,线程仍然在不断运行,白白浪费了 CPU 资源
- 数据复制过程中,线程实际还是阻塞的(AIO 改进的地方)
服务器端代码
package cn.itcast.netty.c4;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import static cn.itcast.netty.c1.ByteBufferUtil.debugRead;
@Slf4j
public class Server {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 使用 nio 来理解阻塞模式, 单线程
// 0. ByteBuffer
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(16);
// 1. 创建了服务器
ServerSocketChannel ssc = ServerSocketChannel.open();
// 设置 ServerSocketChannel 为非阻塞模式(默认是阻塞模式),会影响 accept() 方法
ssc.configureBlocking(false);
// 2. 绑定监听端口
ssc.bind(new InetSocketAddress(8080));
// 3. 连接集合
List<SocketChannel> channels = new ArrayList<>();
while (true) {
// 4. accept 建立与客户端连接, SocketChannel 用来与客户端之间通信
//log.debug("connecting...");
// 非阻塞,线程还会继续运行,如果没有连接建立,但 sc 是 null
SocketChannel sc = ssc.accept();
if (sc != null) {
log.debug("connected... {}", sc);
// 设置 SocketChannel 为非阻塞模式(默认是阻塞模式),会影响 read() 方法
sc.configureBlocking(false);
channels.add(sc);
}
for (SocketChannel channel : channels) {
// 5. 接收客户端发送的数据
// 非阻塞,线程仍然会继续运行,如果没有读到数据,read 返回 0
int read = channel.read(buffer);
if (read > 0) {
buffer.flip();
debugRead(buffer);
buffer.clear();
log.debug("after read...{}", channel);
}
}
}
}
}
客户端代码
package cn.itcast.netty.c4;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
SocketChannel sc = SocketChannel.open();
sc.connect(new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 8080));
System.out.println("waiting...");
}
}
4.1.3.多路复用
单线程可以配合 Selector 完成对多个 Channel 可读写事件的监控,这称之为多路复用。
- 多路复用仅针对网络 IO、普通文件 IO 没法利用多路复用
- 如果不用 Selector 的非阻塞模式,线程大部分时间都在做无用功,而 Selector 能够保证
- 有可连接事件时才去连接
- 有可读事件才去读取
- 有可写事件才去写入
- 限于网络传输能力,Channel 未必时时可写,一旦 Channel 可写,会触发 Selector 的可写事件
4.2.Selector
优点
- 一个线程配合 selector 就可以监控多个 channel 的事件,事件发生线程才去处理,避免非阻塞模式下所做无用功
- 让这个线程能够被充分利用
- 节约了线程的数量
- 减少了线程上下文切换
创建
Selector selector = Selector.open();
绑定 Channel 事件
也称之为注册事件,绑定的事件 selector 才会关心
channel.configureBlocking(false);
SelectionKey key = channel.register(selector, 绑定事件);
- channel 必须工作在非阻塞模式
- FileChannel 没有非阻塞模式,因此不能配合 selector 一起使用
- 绑定的事件类型可以有
- connect - 客户端连接成功时触发
- accept - 服务器端成功接受连接时触发
- read - 数据可读入时触发,有因为接收能力弱,数据暂不能读入的情况
- write - 数据可写出时触发,有因为发送能力弱,数据暂不能写出的情况
监听 Channel 事件
可以通过下面三种方法来监听是否有事件发生,方法的返回值代表有多少 channel 发生了事件
方法1:阻塞直到绑定事件发生
int count = selector.select();
方法2:阻塞直到绑定事件发生,或是超时(时间单位为 ms)
int count = selector.select(long timeout);
方法3:不会阻塞,也就是不管有没有事件,立刻返回,自己根据返回值检查是否有事件
int count = selector.selectNow();
select 何时不阻塞
- 事件发生时
- 客户端发起连接请求,会触发 accept 事件
- 客户端发送数据过来,客户端正常、异常关闭时,都会触发 read 事件,另外如果发送的数据大于 buffer 缓冲区,会触发多次读取事件
- channel 可写,会触发 write 事件
- 在 linux 下 nio bug 发生时
- 调用 selector.wakeup()
- 调用 selector.close()
- selector 所在线程 interrupt
4.3.处理 accept 事件
服务器端代码
package cn.itcast.netty.c4;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
import static cn.itcast.netty.c1.ByteBufferUtil.debugRead;
@Slf4j
public class Server {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1.创建 selector,可以管理多个 channel
Selector selector = Selector.open();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(16);
ServerSocketChannel ssc = ServerSocketChannel.open();
ssc.configureBlocking(false);
//2.建立 selector 与 channel 之间的联系(注册)
// SelectionKey 就是将来事件发生后,通过它可以知道事件和哪个 channel 的事件
SelectionKey sscKey = ssc.register(selector, 0, null);
sscKey.interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
log.debug("register key: {}", sscKey);
//绑定监听端口
ssc.bind(new InetSocketAddress(8080));
while (true) {
//3.select 方法,没有事件发生,线程阻塞;有事件发生时,线程才会恢复运行
// select 在有事件未处理时,它不会阻塞
selector.select();
//4.处理事件,selectedKeys 内部包含了所有发生的事件
Iterator<SelectionKey> iter = selector.selectedKeys().iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = iter.next();
log.debug("key: {}", key);
//通过 key 获取 channel
ServerSocketChannel channel = (ServerSocketChannel) key.channel();
SocketChannel sc = channel.accept();
log.debug("{}", sc);
//处理事件:取消该事件
key.cancel();
}
}
}
}
客户端代码
package cn.itcast.netty.c4;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
SocketChannel sc = SocketChannel.open();
sc.connect(new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 8080));
System.out.println("waiting...");
}
}
事件发生后能否不处理?
事件发生后,要么处理,要么取消(cancel),不能什么都不做,否则下次该事件仍会触发,这是因为 nio 底层使用的是水平触发。例如,上面的服务器端代码中的 key.cancel()。
4.4.处理 read 事件
4.4.1.代码演示
服务器端代码
package cn.itcast.netty.c4;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
import static cn.itcast.netty.c1.ByteBufferUtil.debugRead;
@Slf4j
public class Server {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1.创建 selector,可以管理多个 channel
Selector selector = Selector.open();
ServerSocketChannel ssc = ServerSocketChannel.open();
ssc.configureBlocking(false);
//2.建立 selector 与 channel 之间的联系(注册)
// SelectionKey 就是将来事件发生后,通过它可以知道事件和哪个 channel 的事件
SelectionKey sscKey = ssc.register(selector, 0, null);
sscKey.interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
log.debug("register key: {}", sscKey);
//绑定监听端口
ssc.bind(new InetSocketAddress(8080));
while (true) {
//3.select 方法,没有事件发生,线程阻塞;有事件发生时,线程才会恢复运行
selector.select();
//4.处理事件,selectedKeys 内部包含了所有发生的事件
Iterator<SelectionKey> iter = selector.selectedKeys().iterator(); // accept, read
while (iter.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = iter.next();
//处理 key 时,要从 selectedKeys 集合中删除,否则下次处理就会有问题(空指针异常)
iter.remove();
log.debug("key: {}", key);
//5.区分事件类型
if (key.isAcceptable()) {
//通过 key 获取 channel
ServerSocketChannel channel = (ServerSocketChannel) key.channel();
SocketChannel sc = channel.accept();
//设置为非阻塞模式,会影响 read() 方法
sc.configureBlocking(false);
//注册
SelectionKey scKey = sc.register(selector, 0, null);
scKey.interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_READ);
log.debug("{}", sc);
} else if (key.isReadable()) {
SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(16);
channel.read(buffer);
buffer.flip();
debugRead(buffer);
}
}
}
}
}
客户端代码
package cn.itcast.netty.c4;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
SocketChannel sc = SocketChannel.open();
sc.connect(new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 8080));
System.out.println("waiting...");
}
}
为何要 iter.remove()
因为 select 在事件发生后,就会将相关的 key 放入 selectedKeys 集合,但不会在处理完后从 selectedKeys 集合中移除,需要我们自己编码删除。例如
cancel 的作用
cancel 会取消注册在 selector 上的 channel,并从 keys 集合中删除 key 后续不会再监听事件。
4.4.2.处理客户端断开
while (iter.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = iter.next();
log.debug("key: {}", key);
if (key.isAcceptable()) {
ServerSocketChannel channel = (ServerSocketChannel) key.channel();
SocketChannel sc = channel.accept();
sc.configureBlocking(false);
SelectionKey scKey = sc.register(selector, 0, null);
scKey.interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_READ);
log.debug("{}", sc);
} else if (key.isReadable()) {
try {
SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(16);
//如果客户端正常断开,read 方法的返回值是 -1
int read = channel.read(buffer);
if (read == -1) {
key.cancel();
} else {
buffer.flip();
debugRead(buffer);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
//客户端断开,因此需要将 key 取消(从 selector 的 keys 集合中真正删除 key)
key.cancel();
}
}
//如果不进行 remove,就会出现空指针异常
iter.remove();
}
4.4.3.消息边界处理
⚠️ 不处理边界的问题
以前有同学写过这样的代码,思考注释中两个问题,以 bio 为例,其实 nio 道理是一样的。
public class Server {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ServerSocket ss=new ServerSocket(9000);
while (true) {
Socket s = ss.accept();
InputStream in = s.getInputStream();
// 这里这么写,有没有问题
byte[] arr = new byte[4];
while(true) {
int read = in.read(arr);
// 这里这么写,有没有问题
if(read == -1) {
break;
}
System.out.println(new String(arr, 0, read));
}
}
}
}
客户端代码
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Socket max = new Socket("localhost", 9000);
OutputStream out = max.getOutputStream();
out.write("hello".getBytes());
out.write("world".getBytes());
out.write("你好".getBytes());
max.close();
}
}
输出如下
hell
owor
ld�
�好
为什么?
- 一种思路是固定消息长度,数据包大小一样,服务器按预定长度读取,缺点是浪费带宽;
- 另一种思路是按分隔符拆分,缺点是效率低;
- TLV 格式,即 Type 类型、Length 长度、Value 数据,类型和长度已知的情况下,就可以方便获取消息大小,分配合适的 buffer,缺点是 buffer 需要提前分配,如果内容过大,则影响 server 吞吐量;
- Http 1.1 是 TLV 格式
- Http 2.0 是 LTV 格式
服务器端代码
package cn.itcast.netty.c4;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
import static cn.itcast.netty.c1.ByteBufferUtil.debugRead;
import static cn.itcast.netty.c1.ByteBufferUtil.debugAll;
@Slf4j
public class Server {
private static void split(ByteBuffer source) {
source.flip();
int oldLimit = source.limit();
for (int i = 0; i < oldLimit; i++) {
if (source.get(i) == '\n') {
System.out.println(i);
ByteBuffer target = ByteBuffer.allocate(i + 1 - source.position());
// 0 ~ limit
source.limit(i + 1);
target.put(source); // 从source 读,向 target 写
debugAll(target);
source.limit(oldLimit);
}
}
source.compact();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1.创建 selector,可以管理多个 channel
Selector selector = Selector.open();
ServerSocketChannel ssc = ServerSocketChannel.open();
ssc.configureBlocking(false);
//2.建立 selector 与 channel 之间的联系(注册)
// SelectionKey 就是将来事件发生后,通过它可以知道事件和哪个 channel 的事件
SelectionKey sscKey = ssc.register(selector, 0, null);
sscKey.interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
log.debug("register key: {}", sscKey);
//绑定监听端口
ssc.bind(new InetSocketAddress(8080));
while (true) {
//3.select 方法,没有事件发生,线程阻塞;有事件发生时,线程才会恢复运行
selector.select();
//4.处理事件,selectedKeys 内部包含了所有发生的事件
Iterator<SelectionKey> iter = selector.selectedKeys().iterator(); // accept, read
while (iter.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = iter.next();
//如果不进行 remove,就会出现空指针异常
iter.remove();
log.debug("key: {}", key);
//5.区分事件类型
if (key.isAcceptable()) {
//通过 key 获取 channel
ServerSocketChannel channel = (ServerSocketChannel) key.channel();
SocketChannel sc = channel.accept();
//设置为非阻塞模式,会影响 read() 方法
sc.configureBlocking(false);
//将 ByteBuffer 作为附件关联到 SelectionKey 上
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(16); //attachment
//注册
SelectionKey scKey = sc.register(selector, 0, buffer);
scKey.interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_READ);
log.debug("{}", sc);
log.debug("{}", scKey);
} else if (key.isReadable()) {
try {
SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
//获取 SelectionKey 上 关联的 attach
ByteBuffer buffer = (ByteBuffer) key.attachment();
//如果客户端正常断开,read 方法的返回值是 -1
int read = channel.read(buffer);
if (read == -1) {
key.cancel();
} else {
split(buffer);
if (buffer.position() == buffer.limit()) {
ByteBuffer newBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(buffer.capacity() * 2);
buffer.flip();
newBuffer.put(buffer);
//替换原来的 buffer
key.attach(newBuffer);
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
//客户端断开,因此需要将 key 取消(从 selector 的 keys 集合中真正删除 key)
key.cancel();
}
}
}
}
}
}
客户端代码
package cn.itcast.netty.c4;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.net.SocketAddress;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
SocketChannel sc = SocketChannel.open();
sc.connect(new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 8080));
SocketAddress address = sc.getLocalAddress();
sc.write(Charset.defaultCharset().encode("hellohellohellohellohello\nworld\n"));
System.in.read();
//System.out.println("waiting...");
}
}
4.4.4.ByteBuffer 大小分配
- 每个 channel 都需要记录可能被切分的消息,因为 ByteBuffer 不能被多个 channel 共同使用,因此需要为每个 channel 维护一个独立的 ByteBuffer;
- ByteBuffer 不能太大,比如一个 ByteBuffer 1Mb 的话,要支持百万连接就要 1Tb 内存,因此需要设计大小可变的 ByteBuffer
- 一种思路是首先分配一个较小的 buffer,例如 4k,如果发现数据不够,再分配 8k 的 buffer,将 4k buffer 内容拷贝至 8k buffer,优点是消息连续容易处理,缺点是数据拷贝耗费性能,参考实现 http://tutorials.jenkov.com/java-performance/resizable-array.html;
- 另一种思路是用多个数组组成 buffer,一个数组不够,把多出来的内容写入新的数组,与前面的区别是消息存储不连续解析复杂,优点是避免了拷贝引起的性能损耗;
4.5.处理 write 事件
(1)一次无法写完例子
- 非阻塞模式下,无法保证把 buffer 中所有数据都写入 channel,因此需要追踪 write 方法的返回值(代表实际写入字节数);
- 用 selector 监听所有 channel 的可写事件,每个 channel 都需要一个 key 来跟踪 buffer,但这样又会导致占用内存过多,就有两阶段策略
- 当消息处理器第一次写入消息时,才将 channel 注册到 selector 上;
- selector 检查 channel 上的可写事件,如果所有的数据写完了,就取消 channel 的注册;
- 如果不取消,会每次可写均会触发 write 事件;
服务器端代码
package cn.itcast.netty.c4;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class WriteServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ServerSocketChannel ssc = ServerSocketChannel.open();
ssc.configureBlocking(false);
ssc.bind(new InetSocketAddress(8080));
Selector selector = Selector.open();
ssc.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
while (true) {
selector.select();
Iterator<SelectionKey> iter = selector.selectedKeys().iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = iter.next();
iter.remove();
if (key.isAcceptable()) {
SocketChannel sc = ssc.accept();
sc.configureBlocking(false);
SelectionKey scKey = sc.register(selector, 0, null);
scKey.interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_READ);
// 1. 向客户端发送内容
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < 5000000; i++) {
sb.append("a");
}
ByteBuffer buffer = Charset.defaultCharset().encode(sb.toString());
// 2. write 表示实际写了多少字节
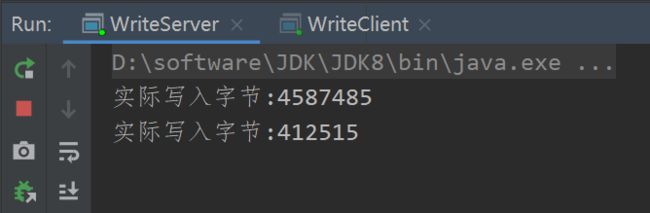
int write = sc.write(buffer);
System.out.println("实际写入字节:" + write);
// 3. 如果有剩余未读字节,才需要关注写事件
if (buffer.hasRemaining()) {
// 4.在原有关注事件的基础上,多关注写事件
scKey.interestOps(scKey.interestOps() + SelectionKey.OP_WRITE);
//scKey.interestOps(scKey.interestOps() | SelectionKey.OP_WRITE);
// 5.把 buffer 作为附件加入 scKey
scKey.attach(buffer);
}
} else if (key.isWritable()) {
ByteBuffer buffer = (ByteBuffer) key.attachment();
SocketChannel sc = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
int write = sc.write(buffer);
System.out.println("实际写入字节:" + write);
// 写完了
if (!buffer.hasRemaining()) {
//清除 buffer
key.attach(null);
//无需关注可写事件
key.interestOps(key.interestOps() - SelectionKey.OP_WRITE);
}
}
}
}
}
}
客户端
package cn.itcast.netty.c4;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
public class WriteClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
SocketChannel sc = SocketChannel.open();
sc.connect(new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 8080));
//接受服务器端发过来的数据
int count = 0;
while (true) {
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024 * 1024);
count += sc.read(buffer);
System.out.println(count);
buffer.clear();
}
}
}
只要向 channel 发送数据时,socket 缓冲可写,这个事件会频繁触发,因此应当只在 socket 缓冲区写不下时再关注可写事件,数据写完之后再取消关注。
4.6.更进一步
4.6.1.利用多线程优化
(1)现在都是多核 CPU,设计时要充分考虑别让 CPU 资源被白白浪费。
(2)前面的代码只有一个选择器,没有充分利用多核 CPU,如何改进呢?分两组选择器:
- 单线程配一个选择器,专门处理 accept 事件;
- 创建 CPU 核心数的线程,每个线程配一个选择器,轮流处理 read 事件;
服务器端代码
package cn.itcast.netty.c4;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.*;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentLinkedQueue;
import static cn.itcast.netty.c1.ByteBufferUtil.debugAll;
@Slf4j
public class MultiThreadServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Thread.currentThread().setName("boss");
ServerSocketChannel ssc = ServerSocketChannel.open();
ssc.configureBlocking(false);
Selector boss = Selector.open();
SelectionKey bossKey = ssc.register(boss, 0, null);
bossKey.interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
ssc.bind(new InetSocketAddress(8080));
//创建固定数量的 worker
Worker worker = new Worker("worker-0");
while (true) {
boss.select();
Iterator<SelectionKey> iter = boss.selectedKeys().iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = iter.next();
iter.remove();
if (key.isAcceptable()) {
SocketChannel sc = ssc.accept();
sc.configureBlocking(false);
log.debug("connected...{}", sc.getRemoteAddress());
//关联 selector
log.debug("before register...{}", sc.getRemoteAddress());
// boss 线程调用,初始化 selector,启动 worker-0
worker.register(sc);
log.debug("after register{}", sc.getRemoteAddress());
}
}
}
}
//检测读写事件
static class Worker implements Runnable{
private Thread thread;
private Selector selector;
private String name;
//标记线程是否已初始化
private volatile boolean start = false;
private ConcurrentLinkedQueue<Runnable> queue = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue<>();
public Worker(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
//初始化线程和 selector
public void register(SocketChannel sc) throws IOException {
if (!start) {
selector = Selector.open();
thread = new Thread(this, name);
thread.start();
start = true;
}
//向队列添加了任务,但这个任务并没有立刻执行
queue.add(() -> {
try {
sc.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ, null);
} catch (ClosedChannelException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
//唤醒 select 方法
selector.wakeup();
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
try {
//检测是否有新的事件
selector.select();
Runnable task = queue.poll();
if (task != null) {
//执行 sc.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ, null);
task.run();
}
Iterator<SelectionKey> iter = selector.selectedKeys().iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = iter.next();
iter.remove();
if (key.isReadable()) {
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(16);
SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
log.debug("read...{}", channel.getRemoteAddress());
channel.read(buffer);
buffer.flip();
debugAll(buffer);
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
客户端代码
package cn.itcast.netty.c4;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
public class TestClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
SocketChannel sc = SocketChannel.open();
sc.connect(new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 8080));
sc.write(Charset.defaultCharset().encode("hello"));
System.in.read();
}
}
开启两个客户端进行测试:

register() 方法的另外一种写法(不需要 ConcurrentLinkedQueue):
public void register(SocketChannel sc) throws IOException {
if (!start) {
selector = Selector.open();
thread = new Thread(this, name);
thread.start();
start = true;
}
//唤醒 select 方法
selector.wakeup();
sc.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ, null);
}
4.6.2.如何拿到 CPU 个数
(1)Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors() 如果工作在 docker 容器下,因为容器不是物理隔离的,会拿到物理 CPU 个数,而不是容器申请时的个数。这个问题直到 jdk 10 才修复,使用 jvm 参数 UseContainerSupport 配置, 默认开启。
(2)代码如下:
Worker[] workers = new Worker[Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors()];
for (int i = 0; i < workers.length; i++) {
workers[i] = new Worker("worker-" + i);
}
...
//关联 selector
log.debug("before register...{}", sc.getRemoteAddress());
// round robin 轮询
workers[index.getAndIncrement() % workers.length].register(sc); // boss 线程调用,初始化 selector,启动 worker-0
log.debug("after register{}", sc.getRemoteAddress());
4.7.UDP
- UDP 是无连接的,client 发送数据不会管 server 是否开启
- server 这边的 receive 方法会将接收到的数据存入 byte buffer,但如果数据报文超过 buffer 大小,多出来的数据会被默默抛弃
首先启动服务器端
public class UdpServer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (DatagramChannel channel = DatagramChannel.open()) {
channel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(9999));
System.out.println("waiting...");
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(32);
channel.receive(buffer);
buffer.flip();
debug(buffer);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
输出
waiting...
运行客户端
public class UdpClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (DatagramChannel channel = DatagramChannel.open()) {
ByteBuffer buffer = StandardCharsets.UTF_8.encode("hello");
InetSocketAddress address = new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 9999);
channel.send(buffer, address);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
接下来服务器端输出
+-------------------------------------------------+
| 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
|00000000| 68 65 6c 6c 6f |hello |
+--------+-------------------------------------------------+----------------+
5.NIO vs BIO
5.1.stream vs channel
- stream 不会自动缓冲数据,channel 会利用系统提供的发送缓冲区、接收缓冲区(更为底层);
- stream 仅支持阻塞 API,channel 同时支持阻塞、非阻塞 API,网络 channel 可配合 selector 实现多路复用;
- 二者均为全双工(读写可以同时进行),即读写可以同时进行;
5.2.IO 模型
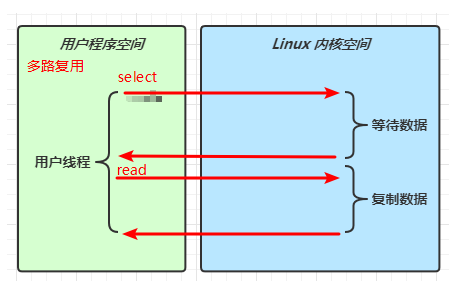
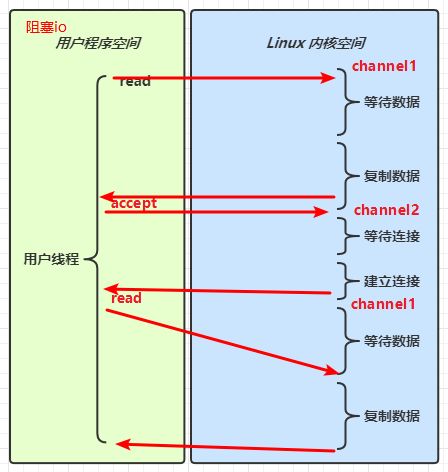
(1)同步阻塞、同步非阻塞、同步多路复用、异步阻塞(没有此情况)、异步非阻塞。
- 同步:线程自己去获取结果(一个线程);
- 异步:线程自己不去获取结果,而是由其它线程送结果(至少两个线程);
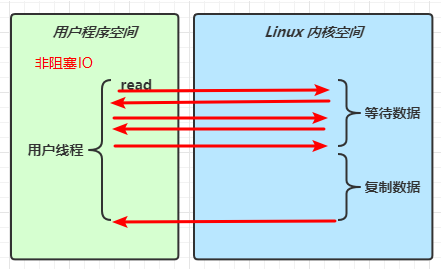
(2)当调用一次 channel.read 或 stream.read 后,会切换至操作系统内核态来完成真正数据读取,而读取又分为两个阶段,分别为:
- 阻塞 IO vs 多路复用
参考:UNIX 网络编程 - 卷 I
5.3.零拷贝
5.3.1.传统 IO 问题
(1)传统的 IO 将一个文件通过 socket 写出。
File f = new File("helloword/data.txt");
RandomAccessFile file = new RandomAccessFile(file, "r");
byte[] buf = new byte[(int)f.length()];
file.read(buf);
Socket socket = ...;
socket.getOutputStream().write(buf);
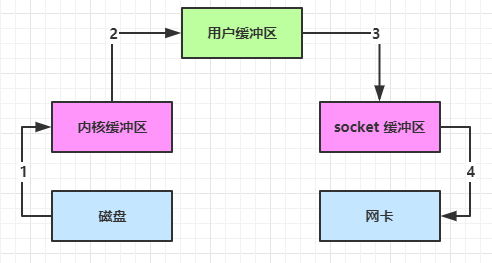
(2)内部工作流程是这样的:
-
java 本身并不具备 IO 读写能力,因此 read 方法调用后,要从 java 程序的用户态切换至内核态,去调用操作系统(Kernel)的读能力,将数据读入内核缓冲区。这期间用户线程阻塞,操作系统使用 DMA(Direct Memory Access)来实现文件读,其间也不会使用 CPU;
DMA 也可以理解为硬件单元,用来解放 cpu 完成文件 IO
-
从内核态切换回用户态,将数据从内核缓冲区读入用户缓冲区(即 byte[] buf),这期间 cpu 会参与拷贝,无法利用 DMA;
-
调用 write 方法,这时将数据从用户缓冲区(byte[] buf)写入 socket 缓冲区,cpu 会参与拷贝;
-
接下来要向网卡写数据,这项能力 java 又不具备,因此又得从用户态切换至内核态,调用操作系统的写能力,使用 DMA 将 socket 缓冲区的数据写入网卡,不会使用 CPU;
(3)可以看到中间环节较多,java 的 IO 实际不是物理设备级别的读写,而是缓存的复制,底层的真正读写是操作系统来完成的。
- 用户态与内核态的切换发生了 3 次,这个操作比较重量级。
- 数据拷贝了共 4 次。
5.3.2.NIO 优化
(1)通过 DirectByteBuf:
- ByteBuffer.allocate(10) HeapByteBuffer 使用的还是 java 内存;
- ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(10) DirectByteBuffer 使用的是操作系统内存;
(2)大部分步骤与优化前相同,不再赘述,唯有一点:java 可以使用 DirectByteBuf 将堆外内存映射到 jvm 内存中来直接访问使用。
- 这块内存不受 jvm 垃圾回收的影响,因此内存地址固定,有助于 IO 读写;
- java 中的 DirectByteBuf 对象仅维护了此内存的虚引用,内存回收分成两步:
- DirectByteBuf 对象被垃圾回收,将虚引用加入引用队列;
- 通过专门线程访问引用队列,根据虚引用释放堆外内存;
- 减少了一次数据拷贝,用户态与内核态的切换次数没有减少;
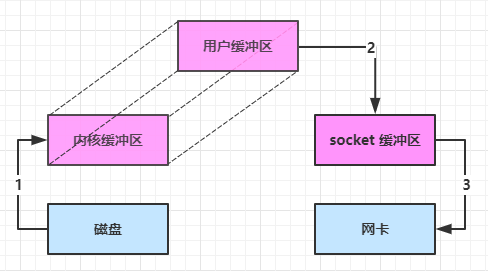
(3)进一步优化(底层采用了 linux 2.1 后提供的 sendFile 方法),java 中对应着两个 channel 调用 transferTo/transferFrom 方法拷贝数据。
- java 调用 transferTo 方法后,要从 java 程序的用户态切换至内核态,使用 DMA 将数据读入内核缓冲区,不会使用 CPU;
- 数据从内核缓冲区传输到 socket 缓冲区,CPU 会参与拷贝;
- 最后使用 DMA 将 socket 缓冲区的数据写入网卡,不会使用 CPU;
可以看到:
- 只发生了一次用户态与内核态的切换;
- 数据拷贝了 3 次;
(4)进一步优化(linux 2.4)
- java 调用 transferTo 方法后,要从 java 程序的用户态切换至内核态,使用 DMA 将数据读入内核缓冲区,不会使用 CPU;
- 只会将一些 offset 和 length 信息拷入 socket 缓冲区,几乎无消耗;
- 使用 DMA 将 内核缓冲区的数据写入网卡,不会使用 CPU;
整个过程仅只发生了一次用户态与内核态的切换,数据拷贝了 2 次。所谓的【零拷贝】,并不是真正无拷贝,而是在不会拷贝重复数据到 JVM 内存中,零拷贝的优点有:
- 更少的用户态与内核态的切换;
- 不利用 CPU 计算,减少 CPU 缓存伪共享;
- 零拷贝适合小文件传输;
5.3.AIO
AIO(异步 IO)用来解决数据复制阶段的阻塞问题:
- 同步意味着,在进行读写操作时,线程需要等待结果,还是相当于闲置
- 异步意味着,在进行读写操作时,线程不必等待结果,而是将来由操作系统来通过回调方式由另外的线程来获得结果
异步模型需要底层操作系统(Kernel)提供支持。
- Windows 系统通过 IOCP 实现了真正的异步 IO;
- Linux 系统异步 IO 在 2.6 版本引入,但其底层实现还是用多路复用模拟了异步 IO,性能没有优势;
5.3.1.文件 AIO
先来看看 AsynchronousFileChannel。
package cn.itcast.netty.c5;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.AsynchronousFileChannel;
import java.nio.channels.CompletionHandler;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.nio.file.StandardOpenOption;
import static cn.itcast.netty.c1.ByteBufferUtil.debugAll;
@Slf4j
public class AioFileChannel {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
try (AsynchronousFileChannel channel = AsynchronousFileChannel.open(Paths.get("data.txt"), StandardOpenOption.READ)) {
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(16);
log.debug("read begin...");
/*
参数1:ByteBuffer
参数2:读取的起始位置
参数3:附件
参数4:回调对象 CompletionHandler
*/
channel.read(buffer, 0, buffer, new CompletionHandler<Integer, ByteBuffer>() {
// read 成功
@Override
public void completed(Integer result, ByteBuffer attachment) {
log.debug("read completed...{}", result);
attachment.flip();
debugAll(attachment);
}
// read 失败
@Override
public void failed(Throwable exc, ByteBuffer attachment) {
exc.printStackTrace();
}
});
log.debug("read end...");
System.in.read();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
输出如下:
守护线程:默认文件 AIO 使用的线程都是守护线程,所以最后要执行
System.in.read()以避免守护线程意外结束。
5.3.2.网络 AIO
public class AioServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
AsynchronousServerSocketChannel ssc = AsynchronousServerSocketChannel.open();
ssc.bind(new InetSocketAddress(8080));
ssc.accept(null, new AcceptHandler(ssc));
System.in.read();
}
private static void closeChannel(AsynchronousSocketChannel sc) {
try {
System.out.printf("[%s] %s close\n", Thread.currentThread().getName(), sc.getRemoteAddress());
sc.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private static class ReadHandler implements CompletionHandler<Integer, ByteBuffer> {
private final AsynchronousSocketChannel sc;
public ReadHandler(AsynchronousSocketChannel sc) {
this.sc = sc;
}
@Override
public void completed(Integer result, ByteBuffer attachment) {
try {
if (result == -1) {
closeChannel(sc);
return;
}
System.out.printf("[%s] %s read\n", Thread.currentThread().getName(), sc.getRemoteAddress());
attachment.flip();
System.out.println(Charset.defaultCharset().decode(attachment));
attachment.clear();
// 处理完第一个 read 时,需要再次调用 read 方法来处理下一个 read 事件
sc.read(attachment, attachment, this);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void failed(Throwable exc, ByteBuffer attachment) {
closeChannel(sc);
exc.printStackTrace();
}
}
private static class WriteHandler implements CompletionHandler<Integer, ByteBuffer> {
private final AsynchronousSocketChannel sc;
private WriteHandler(AsynchronousSocketChannel sc) {
this.sc = sc;
}
@Override
public void completed(Integer result, ByteBuffer attachment) {
// 如果作为附件的 buffer 还有内容,需要再次 write 写出剩余内容
if (attachment.hasRemaining()) {
sc.write(attachment);
}
}
@Override
public void failed(Throwable exc, ByteBuffer attachment) {
exc.printStackTrace();
closeChannel(sc);
}
}
private static class AcceptHandler implements CompletionHandler<AsynchronousSocketChannel, Object> {
private final AsynchronousServerSocketChannel ssc;
public AcceptHandler(AsynchronousServerSocketChannel ssc) {
this.ssc = ssc;
}
@Override
public void completed(AsynchronousSocketChannel sc, Object attachment) {
try {
System.out.printf("[%s] %s connected\n", Thread.currentThread().getName(), sc.getRemoteAddress());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(16);
// 读事件由 ReadHandler 处理
sc.read(buffer, buffer, new ReadHandler(sc));
// 写事件由 WriteHandler 处理
sc.write(Charset.defaultCharset().encode("server hello!"), ByteBuffer.allocate(16), new WriteHandler(sc));
// 处理完第一个 accpet 时,需要再次调用 accept 方法来处理下一个 accept 事件
ssc.accept(null, this);
}
@Override
public void failed(Throwable exc, Object attachment) {
exc.printStackTrace();
}
}
}