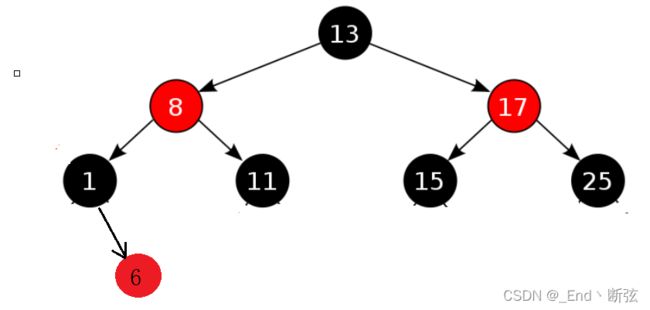
用一棵红黑树同时封装出set和map
一棵红黑树同时封装set和map
- 红黑树代码
- 红黑树的模板参数
- 红黑树结点的数据存储
- 仿函数的增加
- 正向迭代器的实现
-
- operator++
- operator--
- 封装后的set和map
-
- set的代码
- map的代码
- 测试set和map的迭代器
快速导航和本篇相关的文章
| set和map的基本使用 | 点击直达文章 |
|---|---|
| 红黑树 | 点击直达文章 |
红黑树代码
我们要对KV模型的红黑树进行封装,模拟实现set和map,用到的代码如下
#include红黑树的模板参数
通过前面set和map的使用后我们知道set是K模型的,map是KV模型的,那要怎么用一棵红黑树实现set和map呢?
set容器,它传入底层红黑树的模板参数就是Key和Key:
template<class K>
class set
{
public:
//...
private:
RBTree<K, K> _t;
};
map容器传入就是Key和键值对:
template<class K, class V>
class set
{
public:
//...
private:
RBTree<K, pair<K,V> _t;
};
所以我们的红黑树原来的模板参数由V变成T。
template<class K, class T>
class RBTree
{}
红黑树能不能不要第一个模板参数,答案是不能的。
对于set容器是没有问题的,它的2个参数都是Key。但是map就行了,map的find和erase接口只提供Key的,没有第一个模板参数就出问题了。
红黑树结点的数据存储
我们可以先看看源码是怎么实现的:

我们可以看到源码中结点是存了Value。set的key,key传给了Key和value_type,而map的Key和pair<>传给了value_type。Value中是Key那结点中存的就是Key,是pair那结点中存的就是pair。
那我们自己实现就用T即可。
更新后的代码:
enum Color
{
RED,
BLACK
};
template<class T>
struct RBTreeNode
{
RBTreeNode<T>* _left;//结点的左孩子
RBTreeNode<T>* _right;//结点的右孩子
RBTreeNode<T>* _parent;//结点的双亲
T _data;//存储的数据
Color _color;//该结点的颜色
RBTreeNode(const T& x)
:_left(nullptr)
,_right(nullptr)
,_parent(nullptr)
,_data(x)
,_color(RED)
{}
};
这样就不用管你是K还是KV,你是啥我就是啥了。
仿函数的增加
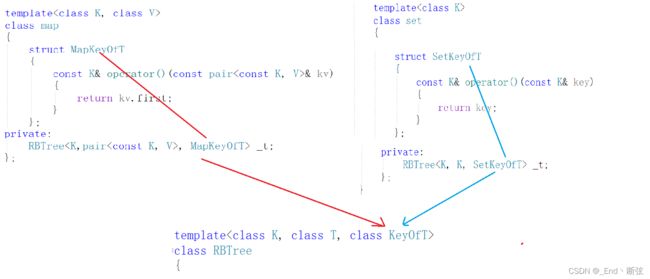
还有问题没有解决,红黑树中T存的可能是K,也可能是pair<>。那我们插入的时候该怎么比较结点的大小呢?对于set是没有问题的,直接可以用T比较,但是map就不行了,我们要取出pair<>的first来进行比较。这是就要实现一个仿函数。
仿函数就是重载了operator(),这个类就可像函数一样的使用了。
template<class K, class V>
class map
{
struct MapKeyOfT
{
const K& operator()(const pair<const K, V>& kv)
{
return kv.first;
}
};
private:
RBTree<K,pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT> _t;
};
}
但是底层的红黑树不知道是Key还是pair<>,所以红黑树都会通过仿函数来获取Key值来进行比较。所以set也需要增加仿函数。对于set好像多此一举但是底层的红黑树不知道啊,所以仿函数必不可少。
template<class K>
class set
{
struct SetKeyOfT
{
const K& operator()(const K& key)
{
return key;
}
};
private:
RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT> _t;
};
}
set传入底层就是set的仿函数,map传入底层就是map的仿函数。
正向迭代器的实现
迭代器就是对一个结点的指针进行了封装,里面只有一个成员变量,就是结点的指针。
template<class T,class Ref,class Ptr>
struct _TreeIterator
{
typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;//结点的类型
typedef _TreeIterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self;//正向迭代器的类型
Node* _node;//封装的指针
};
所以我们通过一个结点的指针就可以构造出一个迭代器
//构造函数
_TreeIterator(Node* node)
:_node(node)
{}
当迭代器解引用操作,我们就返回结点数据的引用
Ref operator*()
{
return _node->_data;
}
当迭代器进行->操作,我们就返回结点数据的指针
Ptr operator->()
{
return &_node->_data;
}
还需要实现==和!=来判断结点是不是同一个。
bool operator !=(const Self& s) const
{
return _node != s._node;
}
bool operator ==(const Self& s) const
{
return _node == s._node;
}
operator++
红黑树中的迭代器的begin和end:
- begin返回中序的第1个结点的迭代器,就是最左结点
- end返回中序最后一个结点的下一个位置的迭代器,这里就用空指针即可。
template<class K, class T, class KeyOfT>
class RBTree
{
typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;
public:
RBTree()
:_root(nullptr)
{}
typedef _TreeIterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;
iterator begin()
{
Node* left = _root;
while (left && left->_left)
{
left = left->_left;
}
return iterator(left);
}
iterator end()
{
return iterator(nullptr);
}
private:
Node* _root;
};
我们进行++就是找到中序的下一个结点,具体逻辑如下:
1.当前结点的右子树不为空,那么++就要找到右子树的最左结点
2.当前结点的右子树为空,++则要找孩子不在父亲右的那个祖先
Self& operator++()
{
if (_node->_right)
{
// 下一个访问就是右树中,中序的第一个节点
Node* left = _node->_right;
while (left->_left)
{
left = left->_left;
}
_node = left;//++后变成该结点
}
else //右子树为空
{
//找孩子不在父亲右的祖先
Node* cur = _node;
Node* parent = cur->_parent;
while (parent && cur == parent->_right)
{
cur = cur->_parent;
parent = parent->_parent;
}
_node = parent;//++后变成该结点
}
return *this;
}
operator–
一个结点的正向迭代器进行--操作后,就是红黑树中序遍历找到的结点的前一个结点。也就是跟++反过来。
具体逻辑如下:
1.当前结点的左子树不为空,--后找到左子树中的最右结点
2.当前结点的左子树为空,--找到孩子不在父亲左的祖先
Self& operator--()
{
if (_node->_left)
{
// 下一个访问就是右树中,中序的第一个节点
Node* left = _node->_left;
while (right->_right)
{
right = right->_right;
}
_node = right;
}
else
{
Node* cur = _node;
Node* parent = cur->_parent;
while (parent && cur == parent->_left)
{
cur = cur->_parent;
parent = parent->_parent;
}
_node = parent;
}
return *this;
}
封装后的set和map
set的代码
下面就可以直接调用红黑树的插入,查找了。博主没有实现红黑树的删除。
namespace p
{
template<class K>
class set
{
struct SetKeyOfT
{
const K& operator()(const K& key)
{
return key;
}
};
public:
typedef typename RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT> ::iterator iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _t.begin();
}
iterator end()
{
return _t.end();
}
//插入
bool insert(const K& k)
{
_t.insert(k);
return true;
}
//查找
iterator find(const K& k)
{
return _t.Find(key);
}
private:
RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT> _t;
};
}
map的代码
namespace g
{
template<class K, class V>
class map
{
struct MapKeyOfT
{
const K& operator()(const pair<const K, V>& kv)
{
return kv.first;
}
};
public:
typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::iterator iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _t.begin();
}
iterator end()
{
return _t.end();
}
//插入
pair<iterator,bool> insert(const pair<const K, V>& kv)
{
return _t.insert(kv);
}
//operator[]
V& operator[](const K& key)
{
pair<iterator, bool> ret = Insert(make_pair(key, V()));
iterator it = ret.first;
return it->second;
}
//查找
iterator find(const K& k)
{
return _t.Find(key);
}
private:
RBTree<K,pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT> _t;
};
}
封装的红黑树代码点击即可
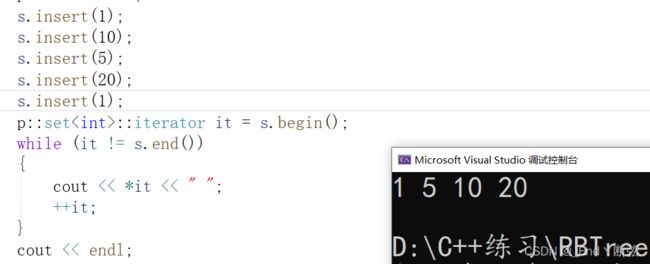
测试set和map的迭代器
这里博主只测试迭代器
void Test_set()
{
p::set<int> s;
s.insert(1);
s.insert(10);
s.insert(5);
s.insert(20);
s.insert(1);
p::set<int>::iterator it = s.begin();
while (it != s.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
cout << endl;
}
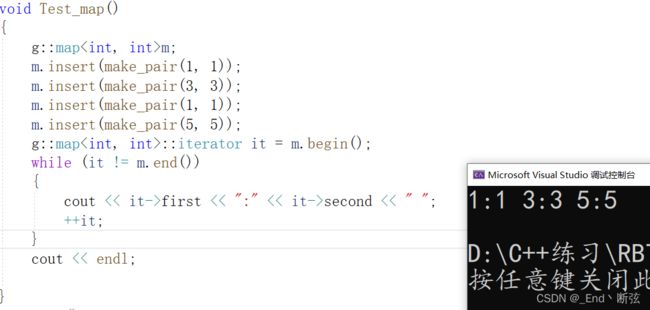
map的迭代器测试:
模拟实现并不是要自己造轮子,可以更深的知道底层结构,以后在用的时候会得心应手。本篇博客到就结束了。