【操作系统】Linux 进程间通信(IPC)—共享内存(System V与POSIX API实现,基于生产者消费者问题)
Linux 进程间通信(IPC)—共享内存
实验内容:进程间通信—共享内存
- 编译运行课件Lecture08例程代码:
- producer-consumer 问题的 POSIX API 应用示例:alg.8-4 ~ alg.8-6.
- reader-writer 问题的 Linux 系统调用示例 alg.8-1 ~ alg.8-3 只处理单个存储结点。修改示例程序将共享空间组织成一个FIFO循环队列(参考数据结构课程相关内容),队列结点具有结构类型(比如学号、姓名、 成绩),并采用共享内存变量控制队列数据的同步。思考:并发进程对共享空间的访问出现冲突的情况。
Prepared Knowledge
1.Linux 共享内存
共享内存 (Shared Memory/Memory Sharing) 是进程间通信 (Interprocess Communication, IPC) 的主要手段之一,在进程间进行通信时,需要建立它们之间进行通信的链接(可以是物理上的,也就是这里的共享内存,也可以是逻辑上的)以及相互交换的信息。
共享内存所在的地址空间是由发起共享的进程所分配的,进程可以将写或者读的信息放入这块内存空间中,再进行读或者写,在这期间无需内核 (Kernel) 进行干预或者辅助。
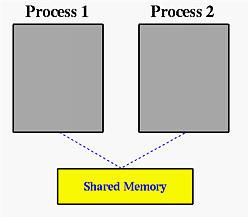
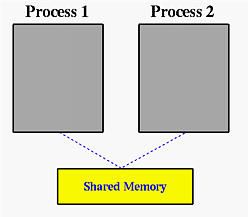
如上图,进程1创建一块共享内存,写下message后退出,进程2根据key得到进程1创建的共享内存,然后进行读取。
在进程分配共享内存地址空间后,其他参与通信的进程需要attatch到这块地址空间上。
进行共享的数据的地址或者形式完全由进程来控制,操作系统不进行干预,此外,进程需要保证不同时进行写操作。
2.相关函数
【函数说明参考 man7 Linux manual pages: section 3 的函数Reference】
-
ftok()(头文件) 函数原型:
key_t ftok(const char *pathname, int proj_id)函数功能: 对给定的文件名(pathname)进行检测, 若文件不存在返回-1, 反之将proj_id的低8位与其生成system V IPC key
-
shmget()(头文件) 函数原型:
int semget(key_t key, int nsems, int semflg)函数功能:创建共享内存,参数中的key用于为共享内存段命名,nsems为共享内存的容量,semflg指定创建或打开的标志和读写的权限,有效的标志包括IPC_CREAT和IPC_EXCL,其中:
IPC_CREAT: 如果共享内存不存在,则创建一个共享内存,否则直接打开已存在的。
IPC_EXCL:只有在共享内存不存在的时候,新的内存才建立,否则就产生错误。
返回值: 函数返回信号量集标识符(非负整数)通常记为shmid,失败返回-1,由
errno生成错误信息 -
shmat()(头文件) 函数原型:
void *shmat(int shmid, const void *shmaddr, int shmflg)函数功能: 当前进程attach到由shmid (shmget()函数返回的标识符)指定的共享内存空间;
指针shmaddr如果为NULL,则由系统attatch到第一个可用的地址上;若指针shmaddr不为NULL且指定SHM_RND,则 此段链接到shmaddr所指的地址上;如果shmaddr非零且指定SHM_RND,则此段链接到shmaddr - (shmaddr mod SHMLBA)所表示的地址上。
返回值: 如果成功,返回共享内存空间地址,失败返回-1
-
shmdt()(头文件) 函数原型:
int shmdt(const void *shmaddr)函数功能: 对于给定的shmaddr,即共享内存地址,与当前进程进行detach操作,并将shmid_ds结构中的shm_nattch字段的计数器值减1
返回值: 成功:0,失败返回-1,由
error生成错误信息 -
shmctl()(头文件) 函数原型:
int shmctl(int shmid, int cmd, struct shmid_ds *buf)函数功能: 完成对共享内存的控制,由所传入的cmd对标识符为shmid的共享内存空间进行对应的操作,包括:
IPC_STAT:得到共享内存的状态,把共享内存的shmid_ds结构复制到buf中
IPC_SET:改变共享内存的状态,把buf所指的shmid_ds结构中的uid、gid、mode复制到共享内存的shmid_ds结构内
IPC_RMID:删除这片共享内存
返回值: 成功:0,失败返回-1,由
error生成错误信息 -
creat()(头文件) 函数原型:
int creat(const char * pathname, mode_tmode)函数功能: 创建文件,由pathname指定文件名,mode_tmode指定创建模式(针对三种用户设置:所处用户,所处用户组,其他用户)读,写,执行
返回值: 文件描述符,值为一个整数,发生错误时返回-1
Linux管道符号:
管道符号 | (将前A命令的输出作为B命令的输入)
Command A | Command B
如:sprintf(cmd_str, "ipcs -m | grep '%d'\n", shmid);
在ipcs -m(shared memory segments) 的输出中用grep指令寻找含有shmid关键字的信息
I. System V Shared Memory
在Linux中提供了与进程的共享空间相关的函数,以下共有4个例程代码,实现reader-writer 问题的系统调用示例,代码中定义的共享空间只处理单个存储结点,在运行完例程代码后,将修改代码中的共享空间设计,将其组织成一个FIFO循环队列,队列结点具有结构类型(比如学号、姓名、 成绩),并采用共享内存变量控制队列数据的同步。
1. 例程代码验证
以下是例程代码:(生产者/消费者问题)
alg.8-0-shmdata.h
#define TEXT_SIZE 4*1024 /* = PAGE_SIZE, size of each message */
#define TEXT_NUM 1 /* maximal number of mesages */
/* total size can not exceed current shmmax,
or an 'invalid argument' error occurs when shmget */
/* a demo structure, modified as needed */
struct shared_struct {
int written; /* flag = 0: buffer writable; others: readable */
char mtext[TEXT_SIZE]; /* buffer for message reading and writing */
};
#define PERM S_IRUSR|S_IWUSR|IPC_CREAT
#define ERR_EXIT(m) \
do { \
perror(m); \
exit(EXIT_FAILURE); \
} while(0)
代码说明: 在该.h文件中主要包含对一些关键变量的定义,如结构体shared_struct,包含了written读写标记符,mtext为读写buffer
此外,还定义了每次读写的message的数量为1,大小为4k;
alg.8-1-shmcon.c
#include 代码说明:
代码中与共享内存相关的函数调用在相关函数一节中已介绍,现针对实现的原理和细节进行说明:
首先调用 key = ftok(pathname, 0x27) 结合pathname与0x27来生成IPC key, 随后调用shmid = shmget((*key_t*)key, shmsize, 0666|PERM) 结合IPC key,分配共享内存段,返回共享内存ID,之后调用 shmptr = shmat(shmid, 0, 0)将shmid指定的共享内存空间attach到当前的进程中,由系统决定共享内存出现在进程内存地址的位置(注意,在vfork后子进程会继承这部分共享内存地址,执行exec后子进程与已链接的共享内存地址自动脱离),这里,shmptr获得的是共享内存地址。
在上述工作完成后,当前进程开始调用 childpid1 = vfork() 创建子进程1和2 ,首先,子进程1调用execv("./alg.8-2-shmread.o", argv1) ,这里将会执行的是alg.8-2-shmread.o,之后父进程 调用childpid2 = vfork()创建子进程2,其调用 execv("./alg.8-3-shmwrite.o", argv1) ,执行的是alg.8-3-shmwrite.o,注意这里的参数argv1为:{" ", key_str, 0},将上述的IPC key作为参数传入调用的程序中 (执行的细节会在后面两份例程代码中详细说明)。
alg.8-2-shmread.c
#include 代码说明:
这部分主要完成的是进程进行读操作的工作,要注意的是,shmid = shmget((key_t)key, TEXT_NUM*sizeof(struct shared_struct), 0666|PERM) 根据子进程调用函数execv()时所传入的PID key得到父进程所创建的共享内存的标识符,此外,如果shared->written 为0,表明共享内存目前处于写状态,那么该进程就会进入sleep(1)休眠,直到共享内存目前处于读状态(shared->written 为1),当读到所写入的内容为’end’时通过执行exit() ,结束程序调用。
alg.8-3-shmwrite.c
#include 代码说明:
这部分主要完成的是进程进行写操作的工作,大部分细节与读操作的部分一致,这里同样用到了,shared->written 为1时,表明共享内存目前处于读状态,那么该进程就会进入sleep(1)休眠,直到共享内存目前处于写状态(shared->written 为0)。当读到所写入的内容为’end’时结束进程。这里用了char数组作为临时buffer来写入共享内存的buffer中。
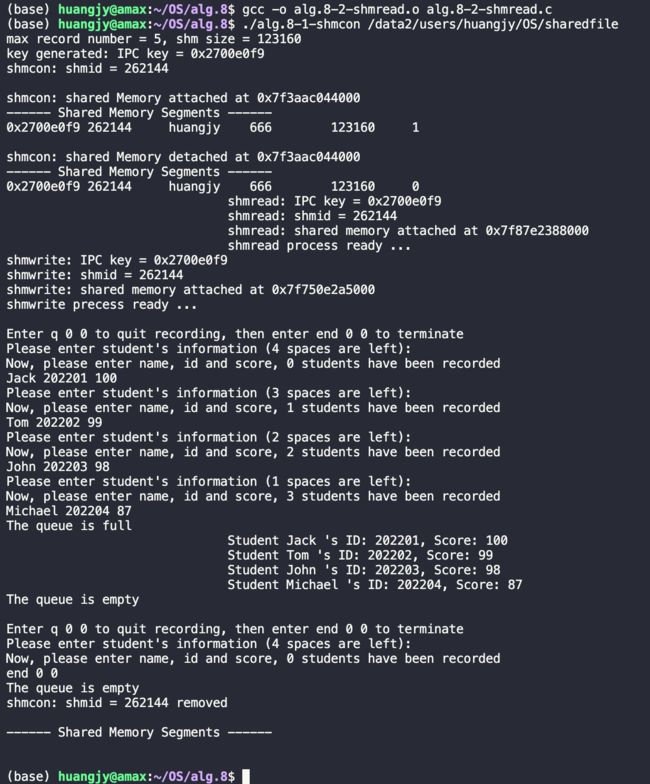
运行结果:
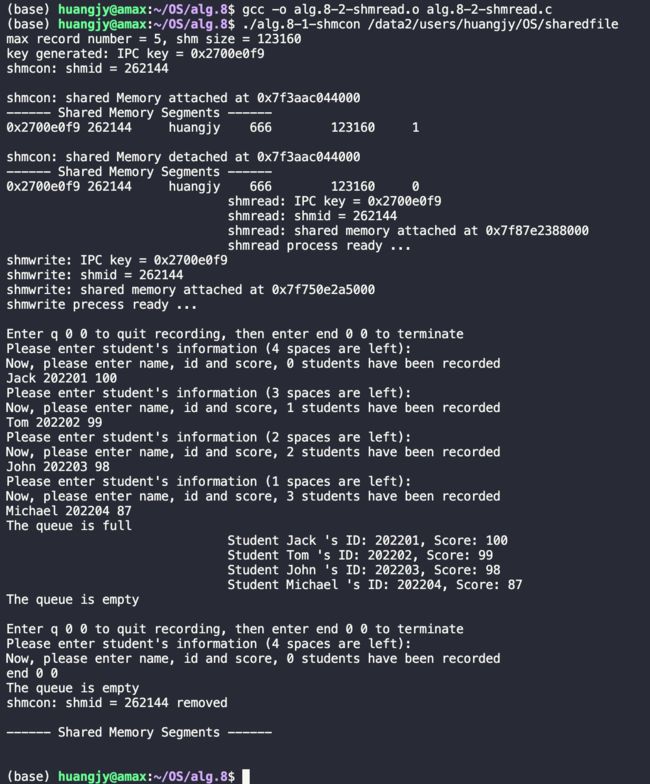
初始状态:
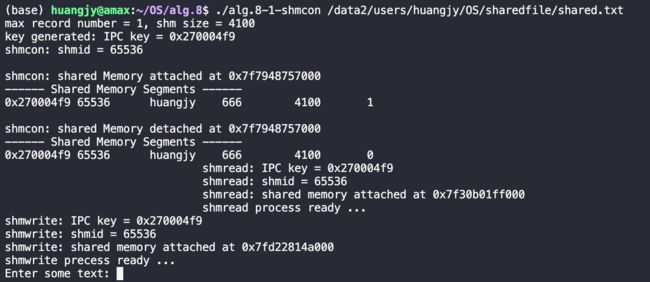
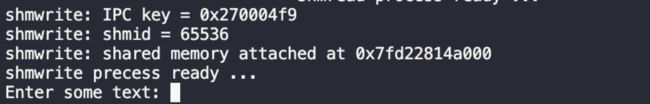
这里,我们在路径/data2/users/huangjy/OS/sharedfile 建立了一个‘共享内存空间,能过存储的信息数为1,大小为4100b,生成的IPC key:0x270004f9 正是在代码中写的proj_id的低8位(0x27),这块共享内存空间的ID = 65536;
在调用shmptr = shmat(shmid, 0, 0) 后返回的地址为0x7f7948757000 指向的是共享内存空间的虚基地址(映射到我们上述指定的物理共享内存空间);
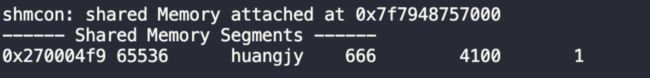
调用命令行指令ipcs -m | grep shmid 后打印出shmid对应的ipcs -m相关字段的信息,这里的字段如下图所示:
分别是 IPC Key、 共享内存的ID、拥有者、权限、共享内存大小、attach的进程数、状态。
回到第一张图对照上述字段信息,与我们指定的一致。
随后程序调用shmdt(shmptr) 进行detach,输出;
可以发现nattch字段的值减一,说明当前执行shmdt()已经成功地从共享内存中detach;
随后,当前进程开始调用vfork()生成子进程,分别执行读和写的操作,第一个vfork()生成的子进程1开始执行alg.8-2-shmread.c中的程序;在这之中,子进程1作为消费者,通过父进程传过来的IPC key链接到父进程分配的共享内存空间中(IPC key、shmid、共享内存地址均与上述在父进程调用的信息一致),而此时处于 “写状态”, 因此子进程1进入休眠状态,这时父进程执行第二个vfork()生成子进程2,同样地,也需要通过父进程传过来的IPC key链接到父进程分配的共享内存空间,如下图所示:
注意到生产者和消费者都有相同的IPC Key,而attach共享空间所保存的虚拟地址不相同;
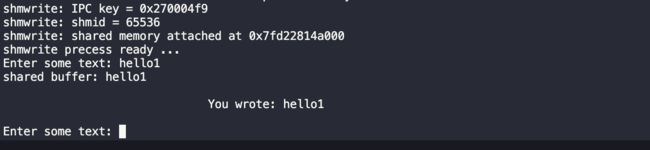
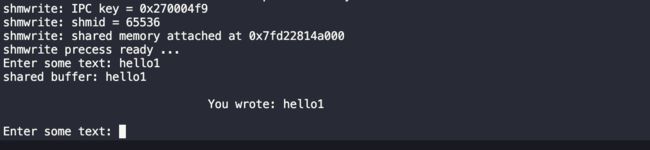
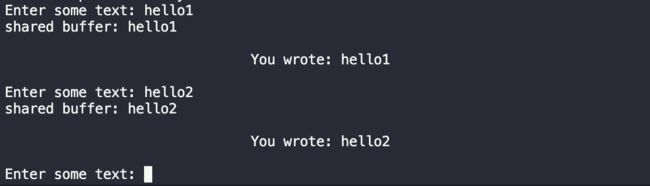
键入hello1:
当写入hello1后,生产者(也就是子进程2)将它写入buffer中的信息拷贝到共享内存中并且打印出写入的内容,同时将共享空间中的written字段置为1,之后进入休眠状态。此时消费者(也就是子进程1)获得执行权,并且此时written字段为1,开始从共享空间中读取信息,可以看到,输出为you wrote: hello1 与预期的一致。
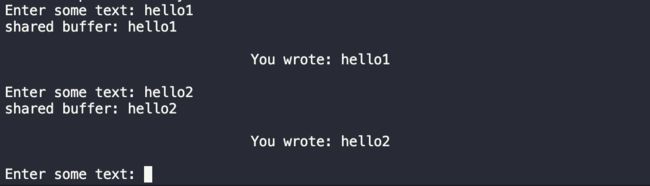
键入hello2:
与上述同理。
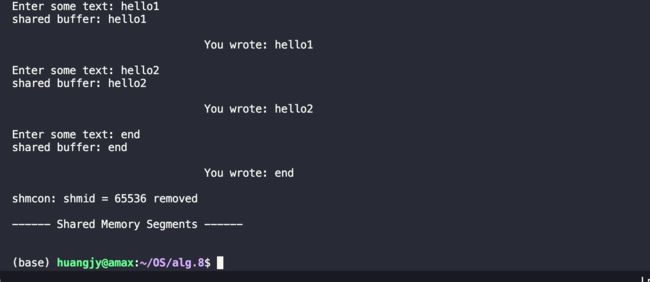
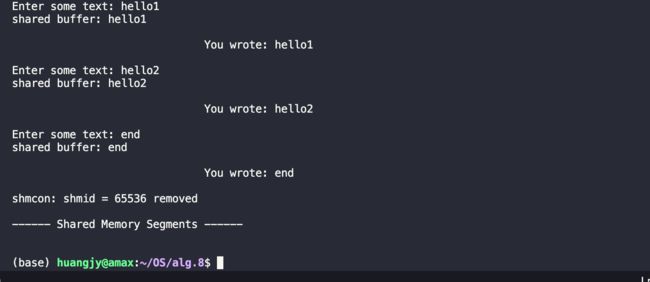
键入end:
最终,在输入end结束标志后,子进程2退出while循环,利用函数shmdt()与共享内存进行detach操作,最后执行exit() 结束当前调用的程序,随后子进程1通过在共享内存中读取到子进程2写入的end结束标志,同样地执行上述操作,退出程序。最后由父进程进行收尾工作,父进程通过调用wait(&childpid) 将其fork出来的子进程的地址作为参数,对子进程进行回收操作;
随后父进程调用 shmctl(shmid, IPC_RMID, 0) 对shmid指定的共享内存空间进行清除,最后调用命令行指令ipcs -m | grep shmid ,可以看到在共享内存段里没有该shmid的信息,即该共享内存空间已经成功清除。
2. 例程代码修改
修改目标:将共享空间组织成一个FIFO循环队列,队列结点具有结构类型(比如学号、姓名、 成绩),并采用共享内存变量控制队列数据的同步。
alg.8-0-shmdata.h
#define TEXT_SIZE 4*1024 /* = PAGE_SIZE, size of each message */
#define TEXT_NUM 5 /* maximal number of mesages */
/* total size can not exceed current shmmax,
or an 'invalid argument' error occurs when shmget */
/* a demo structure, modified as needed */
typedef struct student{
char name[TEXT_SIZE];
int score;
int id;
}queue; //队列结点
struct shared_struct {
int written; /* flag = 0: buffer writable; others: readable */
char mtext[TEXT_SIZE]; /* buffer for message reading and writing */
queue stu[TEXT_NUM]; //循环队列
int in; //入队指针
int out; //出队指针
int size; //队列大小
};
#define PERM S_IRUSR|S_IWUSR|IPC_CREAT
#define ERR_EXIT(m) \
do { \
perror(m); \
exit(EXIT_FAILURE); \
} while(0)
代码说明:
这部分在原代码的基础上增添了循环队列必要的变量:采用结构体组织了队列结点,使其具有学号、姓名、 成绩的数据,并加入了队列指针in和out作为循环队列的控制变量;
alg.8-1-shmcon.c
#include 代码说明:
这部分在循环队列的实现上并不需要改动太多,具体只在父进程vfork()创建子进程后,在子进程执行execv()时多增加了传递给程序的参数,即循环队列的大小(详见注释)。
alg.8-2-shmread.c
#include 代码说明:
这部分代码主要负责读取循环队列中结点的信息,具体的实现为:当队列不空时,持续地读取队列中的元素。
alg.8-3-shmwrite.c
#include 代码说明:
这部分代码主要负责写队列的操作,具体操作为:依次输入学生的姓名、学号、成绩,以空格隔开;
若输入q 0 0,则表示取消入队操作,输入end 0 0表示退出当前程序;
运行结果:
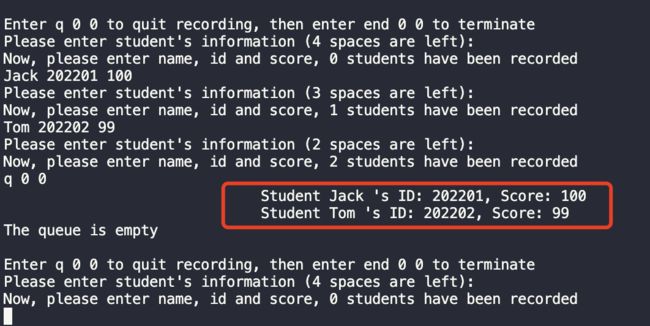
大部分的输出内容与例程代码类似,现主要说明加入循环队列之后的输出结果:
首先,生产者(子进程1)开始执行写队列操作,此时输出循环队列的大小为5,而实际上能用到的空间为4(需要浪费一个空间判断队满),0个学生被记录,之后开始输入学生的姓名、学号和成绩,如 Jack 202201 100,以此类推,最后队列已满,退出当前循环,生产者进入休眠状态;消费者(子进程2)开始读取队列中结点的信息,如运行结果所示,读取的信息符合FIFO的逻辑,首先输出的是最先输入的Student Jack's ID: 202201, Score: 100 ; 最后,队列空,输入end 0 0,终止程序。
以上演示输入两位学生的信息后输入q 0 0的运行结果,可见输入后之间取消入队操作,直接进行出队
II.POSIX Shared Memory
POSIX, Portable Operating System Interface, 可移植操作系统接口
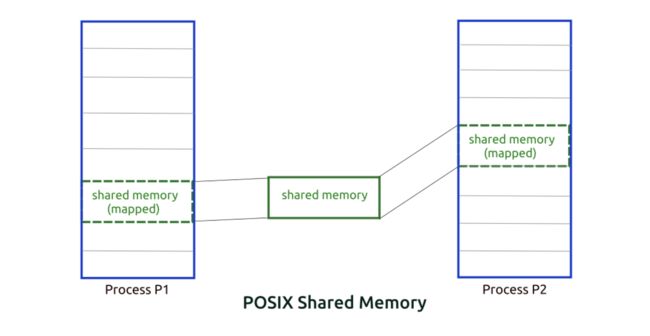
POSIX共享内存是第二种共享内存形式,它可以供无亲缘进程间访问共享内存区,POSIX共享内存使用内存映射文件来组织,也就是将共享内存与文件联系起来。
POSIX API说明
-
shm_open()(头文件) 函数原型:
int shm_open(const char *path, int flags, mode_t mode)**函数功能:**创建共享内存或者打开一个已经存在的共享内存对象,path为共享内存对象名称(这里的名称可以让任何想访问该共享内 存对象的进程使用),flags为操作方式,包含:
O_CREAT:创建新的共享内存
O_RDWR: 打开可以读写的共享内存对象
mode为共享内存访问权限;
操作成功后,会在/dev/shm/创建共享内存文件.
**返回值:**成功后返回共享内存区对象的文件描述符(整型),失败返回-1
-
ftruncate()(头文件) 函数原型:
int ftruncate(int fd, off_t length)**函数功能:**根据所创建的共享内存的fd(即shm_open的返回值:文件描述符)以Bytes为单位,分配length大小的空间
其中该文件必须是以写入模式打开的文件
**返回值:**成功返回0, 失败返回-1
-
mmap()(头文件) 函数原型:
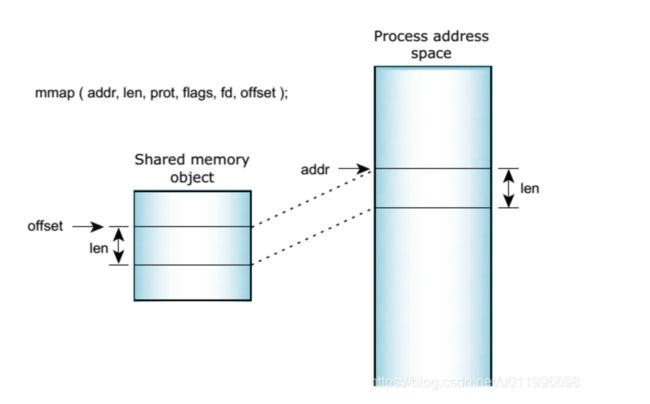
void *mmap(void *__addr, size_t __len, int __prot, int __flags, int __fd, off_t __offset)**函数功能:**根据共享内存的文件描述符将共享内存对象映射到当前调用进程的地址空间
这里一共有5个参数,对应下图来理解会更方便。
__addr为映射到进程中地址空间的位置, __len为映射的共享内存对象的长度,__prot为memory_protection内存受到的 保护,映射将根据flags进行,fd为共享内存对象的文件描述符,__offset为映射的共享内存对象距离其基址的 偏移量;
**返回值:**返回用于访问共享内存对象的指针
映射方式如下图所示:
(图片来自:程序员资料)
-
shm_unlink()(头文件)
函数原型:int shm_unlink(const char *__name)
**函数功能:**移除共享内存
**返回值:**成功返回0, 失败返回-1
POSIX共享内存的API在编译时需要引入指定的库:Realtime Extensions library
gcc -lrt ,其中-l是链接指定库
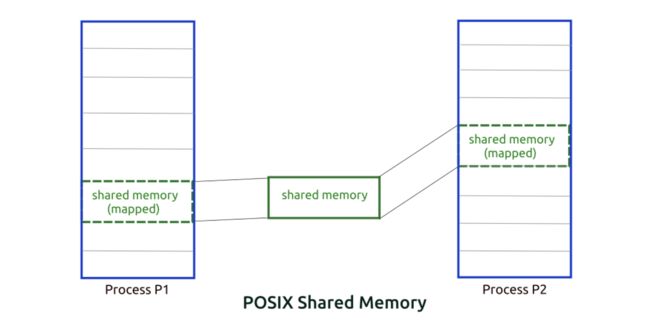
POSIX共享内存的组织形式如下图所示:
(图片来自:Gitbook)
例程代码:(Producer and Consumer)
alg.8-4-shmpthreadcon.c
/* gcc -lrt */
#include 代码说明:(注释中有详细说明)
执行这部分代码的进程作为父进程首先使用shm_open()函数结合命令行中输入的文件名,分配了一块共享内存空间,并获得了文件描述符,创建的文件保存在/dev/shm/目录下,再利用ftruncate()函数为创建好的共享内存对象设定为指定的大小,
随后父进程调用vfork() 创建两个子进程,分别作为生产者和消费者执行各自的程序,其中传入的参数为命令行中输入的文件名,最后父进程调用shm_unlink()将这块共享内存移除。
alg.8-5-shmproducer.c
/* gcc -lrt */
#include 代码说明:
这部分代码负责完成生产者的工作,往共享内存中写入信息,首先调用该程序的进程将传入的参数——文件名,调用shm_open() 获得父进程创建的这块共享内存的文件描述符,之后调用mmap() 将该共享内存对象映射到当前调用的进程的地址空间,获取指向共享内存对象的指针,利用sprintf()向当中写入"Hello World!"。
alg.8-6-shmconsumer.c
/* gcc -lrt */
#include 代码说明:
这部分代码负责完成消费者的工作,从共享内存中读取信息,首先调用shm_open() 以文件名作为参数,获取生产者创建的共享内存对象的文件描述符,再调用mmap() 将该共享内存对象映射到当前调用的进程的地址空间,获取指向共享内存对象的指针,并输出其中的值。
运行结果:
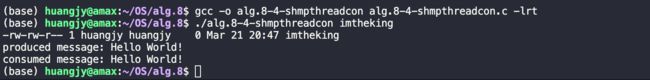
在编译时务必链接rt库。
从结果上可以看到,系统调用ls -l /dev/shm/|grep huangjy 之后显示了目录/dev/shm/下的文件信息,这里正是父进程创建的imtheking文件,其中生产者向这块共享内存空间中写入了"Hello World!", 消费者从中成功读取到"Hello World!"。
代码改进:
改进后,基于生产者和消费者问题,对实现方式做改动:实现由生产者输入学生学号,消费者从共享空间中读取学生学号
alg.8.0-shmdata_M.h
#define TEXT_SIZE 4*1024 /* = PAGE_SIZE, size of each message */
#define ID_SIZE 8
#define STU_NUM 1
/* total size can not exceed current shmmax,
or an 'invalid argument' error occurs when shmget */
/* a demo structure, modified as needed */
struct shared_struct {
int written; /* flag = 0: buffer writable; others: readable */
char stuid[ID_SIZE];
};
#define PERM S_IRUSR|S_IWUSR|IPC_CREAT
#define ERR_EXIT(m) \
do { \
perror(m); \
exit(EXIT_FAILURE); \
} while(0)
代码说明:
在原来的基础上增加了char stuid[ID_SIZE]用于存放学生学号
alg.8-4-shmpthreadcon_M.c
/* gcc -lrt */
#include 代码说明:
这部分代码实现上不需要改动;
alg.8-5-shmproducer_M.c
/* gcc -lrt */
#include 代码说明:
这部分代码负责生产者的工作,首先利用struct shared_struct* shared结构体指针,获取mmap()的返回值(指向共享内存文件的指针),如此shared指针就指向了共享内存文件,并且将共享内存内部数据组织成结构体的组织方式,由键盘输入学生学号,并存入共享内存空间中。
alg.8-6-shmconsumer_M.c
/* gcc -lrt */
#include 代码说明:
这部分代码负责消费者的工作,同样利用struct shared_struct* shared结构体指针,获取mmap()的返回值,为了避免并发进程的冲突,代码中加了sleep(1) ,避免与生产者进程产生竞争,那么,生产者写入信息后,消费值可以读取当中的信息,即学号。
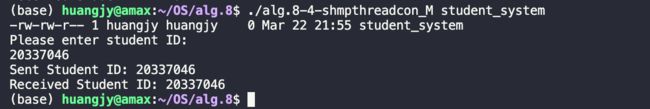
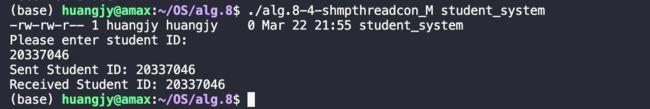
运行结果:
从运行结果中可以看出,在/dev/shm/路径下生成了studen_system的文件,在输入学生学号后,消费者读取到了写入的学号,并打印输出。
III.总结
在本实验中,以生产者和消费者问题为基础,展现了在Linux中实现进程间通信的方法,其主要针对的是共享内存模型,进程之间共享同一块内存,以这块内存作为中介,进而实现通信;在实现中,分别采用了System V和POSIX API,这两者之间存在着共同与不同点,System V共享内存的实现需要利用pathname生成IPC Key,进而利用它为共享内存空间命名,其他子进程访问这块空间都需要提供对应的IPC Key;POSIX共享内存的实现主要是将共享内存映射成文件,而后映射到调用进程的地址空间中,通过文件名来实现对共享内存的访问。
实验内容:进程间通信—共享内存
- 编译运行课件Lecture08例程代码:
- producer-consumer 问题的 POSIX API 应用示例:alg.8-4 ~ alg.8-6.
- reader-writer 问题的 Linux 系统调用示例 alg.8-1 ~ alg.8-3 只处理单个存储结点。修改示例程序将共享空间组织成一个FIFO循环队列(参考数据结构课程相关内容),队列结点具有结构类型(比如学号、姓名、 成绩),并采用共享内存变量控制队列数据的同步。思考:并发进程对共享空间的访问出现冲突的情况。
- 对实验内容的原理性和实现细节解释,对示例代码的改进,每个 Linux系统调用和 POSIX API 调用的作用过程和结果,以及必要的运行截图
Prepared Knowledge
1.Linux 共享内存
共享内存 (Shared Memory/Memory Sharing) 是进程间通信 (Interprocess Communication, IPC) 的主要手段之一,在进程间进行通信时,需要建立它们之间进行通信的链接(可以是物理上的,也就是这里的共享内存,也可以是逻辑上的)以及相互交换的信息。
共享内存所在的地址空间是由发起共享的进程所分配的,进程可以将写或者读的信息放入这块内存空间中,再进行读或者写,在这期间无需内核 (Kernel) 进行干预或者辅助。
如上图,进程1创建一块共享内存,写下message后退出,进程2根据key得到进程1创建的共享内存,然后进行读取。
在进程分配共享内存地址空间后,其他参与通信的进程需要attatch到这块地址空间上。
进行共享的数据的地址或者形式完全由进程来控制,操作系统不进行干预,此外,进程需要保证不同时进行写操作。
2.相关函数
【函数说明参考 man7 Linux manual pages: section 3 的函数Reference】
-
ftok()(头文件) 函数原型:
key_t ftok(const char *pathname, int proj_id)函数功能: 对给定的文件名(pathname)进行检测, 若文件不存在返回-1, 反之将proj_id的低8位与其生成system V IPC key
-
shmget()(头文件) 函数原型:
int semget(key_t key, int nsems, int semflg)函数功能:创建共享内存,参数中的key用于为共享内存段命名,nsems为共享内存的容量,semflg指定创建或打开的标志和读写的权限,有效的标志包括IPC_CREAT和IPC_EXCL,其中:
IPC_CREAT: 如果共享内存不存在,则创建一个共享内存,否则直接打开已存在的。
IPC_EXCL:只有在共享内存不存在的时候,新的内存才建立,否则就产生错误。
返回值: 函数返回信号量集标识符(非负整数)通常记为shmid,失败返回-1,由
errno生成错误信息 -
shmat()(头文件) 函数原型:
void *shmat(int shmid, const void *shmaddr, int shmflg)函数功能: 将当前进程attach到由shmid (shmget()函数返回的标识符)指定的共享内存空间;
指针shmaddr如果为NULL,则由系统attatch到第一个可用的地址上;若指针shmaddr不为NULL且指定SHM_RND,则 此段链接到shmaddr所指的地址上;如果shmaddr非零且指定SHM_RND,则此段链接到shmaddr - (shmaddr mod SHMLBA)所表示的地址上。
返回值: 如果成功,返回共享内存空间地址,失败返回-1
-
shmdt()(头文件) 函数原型:
int shmdt(const void *shmaddr)函数功能: 对于给定的shmaddr,即共享内存地址,与当前进程进行detach操作,并将shmid_ds结构中的shm_nattch字段的计数器值减1
返回值: 成功:0,失败返回-1,由
error生成错误信息 -
shmctl()(头文件) 函数原型:
int shmctl(int shmid, int cmd, struct shmid_ds *buf)函数功能: 完成对共享内存的控制,由所传入的cmd对标识符为shmid的共享内存空间进行对应的操作,包括:
IPC_STAT:得到共享内存的状态,把共享内存的shmid_ds结构复制到buf中
IPC_SET:改变共享内存的状态,把buf所指的shmid_ds结构中的uid、gid、mode复制到共享内存的shmid_ds结构内
IPC_RMID:删除这片共享内存
返回值: 成功:0,失败返回-1,由
error生成错误信息 -
creat()(头文件) 函数原型:
int creat(const char * pathname, mode_tmode)函数功能: 创建文件,由pathname指定文件名,mode_tmode指定创建模式(针对三种用户设置:所处用户,所处用户组,其他用户)读,写,执行
返回值: 文件描述符,值为一个整数,发生错误时返回-1
Linux管道符号:
管道符号 | (将前A命令的输出作为B命令的输入)
Command A | Command B
如:sprintf(cmd_str, "ipcs -m | grep '%d'\n", shmid);
在ipcs -m(shared memory segments) 的输出中用grep指令寻找含有shmid关键字的信息
I. System V Shared Memory
在Linux中提供了与进程的共享空间相关的函数,以下共有4个例程代码,实现reader-writer 问题的系统调用示例,代码中定义的共享空间只处理单个存储结点,在运行完例程代码后,将修改代码中的共享空间设计,将其组织成一个FIFO循环队列,队列结点具有结构类型(比如学号、姓名、 成绩),并采用共享内存变量控制队列数据的同步。
1. 例程代码验证
以下是例程代码:(生产者/消费者问题)
alg.8-0-shmdata.h
#define TEXT_SIZE 4*1024 /* = PAGE_SIZE, size of each message */
#define TEXT_NUM 1 /* maximal number of mesages */
/* total size can not exceed current shmmax,
or an 'invalid argument' error occurs when shmget */
/* a demo structure, modified as needed */
struct shared_struct {
int written; /* flag = 0: buffer writable; others: readable */
char mtext[TEXT_SIZE]; /* buffer for message reading and writing */
};
#define PERM S_IRUSR|S_IWUSR|IPC_CREAT
#define ERR_EXIT(m) \
do { \
perror(m); \
exit(EXIT_FAILURE); \
} while(0)
代码说明: 在该.h文件中主要包含对一些关键变量的定义,如结构体shared_struct,包含了written读写标记符,mtext为读写buffer
此外,还定义了每次读写的message的数量为1,大小为4k;
alg.8-1-shmcon.c
#include 代码说明:
代码中与共享内存相关的函数调用在相关函数一节中已介绍,现针对实现的原理和细节进行说明:
首先调用 key = ftok(pathname, 0x27) 结合pathname与0x27来生成IPC key, 随后调用shmid = shmget((*key_t*)key, shmsize, 0666|PERM) 结合IPC key,分配共享内存段,返回共享内存ID,之后调用 shmptr = shmat(shmid, 0, 0)将shmid指定的共享内存空间attach到当前的进程中,由系统决定共享内存出现在进程内存地址的位置(注意,在vfork后子进程会继承这部分共享内存地址,执行exec后子进程与已链接的共享内存地址自动脱离),这里,shmptr获得的是共享内存地址。
在上述工作完成后,当前进程开始调用 childpid1 = vfork() 创建子进程1和2 ,首先,子进程1调用execv("./alg.8-2-shmread.o", argv1) ,这里将会执行的是alg.8-2-shmread.o,之后父进程 调用childpid2 = vfork()创建子进程2,其调用 execv("./alg.8-3-shmwrite.o", argv1) ,执行的是alg.8-3-shmwrite.o,注意这里的参数argv1为:{" ", key_str, 0},将上述的IPC key作为参数传入调用的程序中 (执行的细节会在后面两份例程代码中详细说明)。
alg.8-2-shmread.c
#include 代码说明:
这部分主要完成的是进程进行读操作的工作,要注意的是,shmid = shmget((key_t)key, TEXT_NUM*sizeof(struct shared_struct), 0666|PERM) 根据子进程调用函数execv()时所传入的PID key得到父进程所创建的共享内存的标识符,此外,如果shared->written 为0,表明共享内存目前处于写状态,那么该进程就会进入sleep(1)休眠,直到共享内存目前处于读状态(shared->written 为1),当读到所写入的内容为’end’时通过执行exit() ,结束程序调用。
alg.8-3-shmwrite.c
#include 代码说明:
这部分主要完成的是进程进行写操作的工作,大部分细节与读操作的部分一致,这里同样用到了,shared->written 为1时,表明共享内存目前处于读状态,那么该进程就会进入sleep(1)休眠,直到共享内存目前处于写状态(shared->written 为0)。当读到所写入的内容为’end’时结束进程。这里用了char数组作为临时buffer来写入共享内存的buffer中。
运行结果:
初始状态:
这里,我们在路径/data2/users/huangjy/OS/sharedfile 建立了一个‘共享内存空间,能过存储的信息数为1,大小为4100b,生成的IPC key:0x270004f9 正是在代码中写的proj_id的低8位(0x27),这块共享内存空间的ID = 65536;
在调用shmptr = shmat(shmid, 0, 0) 后返回的地址为0x7f7948757000 指向的是共享内存空间的虚基地址(映射到我们上述指定的物理共享内存空间);
调用命令行指令ipcs -m | grep shmid 后打印出shmid对应的ipcs -m相关字段的信息,这里的字段如下图所示:
分别是 IPC Key、 共享内存的ID、拥有者、权限、共享内存大小、attach的进程数、状态。
回到第一张图对照上述字段信息,与我们指定的一致。
随后程序调用shmdt(shmptr) 进行detach,输出;
可以发现nattch字段的值减一,说明当前执行shmdt()已经成功地从共享内存中detach;
随后,当前进程开始调用vfork()生成子进程,分别执行读和写的操作,第一个vfork()生成的子进程1开始执行alg.8-2-shmread.c中的程序;在这之中,子进程1作为消费者,通过父进程传过来的IPC key链接到父进程分配的共享内存空间中(IPC key、shmid、共享内存地址均与上述在父进程调用的信息一致),而此时处于 “写状态”, 因此子进程1进入休眠状态,这时父进程执行第二个vfork()生成子进程2,同样地,也需要通过父进程传过来的IPC key链接到父进程分配的共享内存空间,如下图所示:
注意到生产者和消费者都有相同的IPC Key,而attach共享空间所保存的虚拟地址不相同;
键入hello1:
当写入hello1后,生产者(也就是子进程2)将它写入buffer中的信息拷贝到共享内存中并且打印出写入的内容,同时将共享空间中的written字段置为1,之后进入休眠状态。此时消费者(也就是子进程1)获得执行权,并且此时written字段为1,开始从共享空间中读取信息,可以看到,输出为you wrote: hello1 与预期的一致。
键入hello2:
与上述同理。
键入end:
最终,在输入end结束标志后,子进程2退出while循环,利用函数shmdt()与共享内存进行detach操作,最后执行exit() 结束当前调用的程序,随后子进程1通过在共享内存中读取到子进程2写入的end结束标志,同样地执行上述操作,退出程序。最后由父进程进行收尾工作,父进程通过调用wait(&childpid) 将其fork出来的子进程的地址作为参数,对子进程进行回收操作;
随后父进程调用 shmctl(shmid, IPC_RMID, 0) 对shmid指定的共享内存空间进行清除,最后调用命令行指令ipcs -m | grep shmid ,可以看到在共享内存段里没有该shmid的信息,即该共享内存空间已经成功清除。
2. 例程代码修改
修改目标:将共享空间组织成一个FIFO循环队列,队列结点具有结构类型(比如学号、姓名、 成绩),并采用共享内存变量控制队列数据的同步。
alg.8-0-shmdata.h
#define TEXT_SIZE 4*1024 /* = PAGE_SIZE, size of each message */
#define TEXT_NUM 5 /* maximal number of mesages */
/* total size can not exceed current shmmax,
or an 'invalid argument' error occurs when shmget */
/* a demo structure, modified as needed */
typedef struct student{
char name[TEXT_SIZE];
int score;
int id;
}queue; //队列结点
struct shared_struct {
int written; /* flag = 0: buffer writable; others: readable */
char mtext[TEXT_SIZE]; /* buffer for message reading and writing */
queue stu[TEXT_NUM]; //循环队列
int in; //入队指针
int out; //出队指针
int size; //队列大小
};
#define PERM S_IRUSR|S_IWUSR|IPC_CREAT
#define ERR_EXIT(m) \
do { \
perror(m); \
exit(EXIT_FAILURE); \
} while(0)
代码说明:
这部分在原代码的基础上增添了循环队列必要的变量:采用结构体组织了队列结点,使其具有学号、姓名、 成绩的数据,并加入了队列指针in和out作为循环队列的控制变量;
alg.8-1-shmcon.c
#include 代码说明:
这部分在循环队列的实现上并不需要改动太多,具体只在父进程vfork()创建子进程后,在子进程执行execv()时多增加了传递给程序的参数,即循环队列的大小(详见注释)。
alg.8-2-shmread.c
#include 代码说明:
这部分代码主要负责读取循环队列中结点的信息,具体的实现为:当队列不空时,持续地读取队列中的元素。
alg.8-3-shmwrite.c
#include 代码说明:
这部分代码主要负责写队列的操作,具体操作为:依次输入学生的姓名、学号、成绩,以空格隔开;
若输入q 0 0,则表示取消入队操作,输入end 0 0表示退出当前程序;
运行结果:
大部分的输出内容与例程代码类似,现主要说明加入循环队列之后的输出结果:
首先,生产者(子进程1)开始执行写队列操作,此时输出循环队列的大小为5,而实际上能用到的空间为4(需要浪费一个空间判断队满),0个学生被记录,之后开始输入学生的姓名、学号和成绩,如 Jack 202201 100,以此类推,最后队列已满,退出当前循环,生产者进入休眠状态;消费者(子进程2)开始读取队列中结点的信息,如运行结果所示,读取的信息符合FIFO的逻辑,首先输出的是最先输入的Student Jack's ID: 202201, Score: 100 ; 最后,队列空,输入end 0 0,终止程序。
以上演示输入两位学生的信息后输入q 0 0的运行结果,可见输入后之间取消入队操作,直接进行出队
II.POSIX Shared Memory
POSIX, Portable Operating System Interface, 可移植操作系统接口
POSIX共享内存是第二种共享内存形式,它可以供无亲缘进程间访问共享内存区,POSIX共享内存使用内存映射文件来组织,也就是将共享内存与文件联系起来。
POSIX API说明
-
shm_open()(头文件) 函数原型:
int shm_open(const char *path, int flags, mode_t mode)函数功能: 创建共享内存或者打开一个已经存在的共享内存对象,path为共享内存对象名称(这里的名称可以让任何想访问该共享内 存对象的进程使用),flags为操作方式,包含:
O_CREAT:创建新的共享内存
O_RDWR: 打开可以读写的共享内存对象
mode为共享内存访问权限;
操作成功后,会在/dev/shm/创建共享内存文件.
**返回值:**成功后返回共享内存区对象的文件描述符(整型),失败返回-1
-
ftruncate()(头文件) 函数原型:
int ftruncate(int fd, off_t length)函数功能: 根据所创建的共享内存的fd(即shm_open的返回值:文件描述符)以Bytes为单位,分配length大小的空间
其中该文件必须是以写入模式打开的文件
返回值: 成功返回0, 失败返回-1
-
mmap()(头文件) 函数原型:
void *mmap(void *__addr, size_t __len, int __prot, int __flags, int __fd, off_t __offset)函数功能: 根据共享内存的文件描述符将共享内存对象映射到当前调用进程的地址空间
这里一共有5个参数,对应下图来理解会更方便。
__addr为映射到进程中地址空间的位置, __len为映射的共享内存对象的长度,__prot为memory_protection内存受到的 保护,映射将根据flags进行,fd为共享内存对象的文件描述符,__offset为映射的共享内存对象距离其基址的 偏移量;
返回值: 返回用于访问共享内存对象的指针
映射方式如下图所示:
(图片来自:程序员资料)
-
shm_unlink()(头文件)
函数原型:int shm_unlink(const char *__name)
函数功能: 移除共享内存
返回值: 成功返回0, 失败返回-1
POSIX共享内存的API在编译时需要引入指定的库:Realtime Extensions library
gcc -lrt ,其中-l是链接指定库
POSIX共享内存的组织形式如下图所示:
(图片来自:Gitbook)
例程代码:(Producer and Consumer)
alg.8-4-shmpthreadcon.c
/* gcc -lrt */
#include 代码说明:(注释中有详细说明)
执行这部分代码的进程作为父进程首先使用shm_open()函数结合命令行中输入的文件名,分配了一块共享内存空间,并获得了文件描述符,创建的文件保存在/dev/shm/目录下,再利用ftruncate()函数为创建好的共享内存对象设定为指定的大小,
随后父进程调用vfork() 创建两个子进程,分别作为生产者和消费者执行各自的程序,其中传入的参数为命令行中输入的文件名,最后父进程调用shm_unlink()将这块共享内存移除。
alg.8-5-shmproducer.c
/* gcc -lrt */
#include 代码说明:
这部分代码负责完成生产者的工作,往共享内存中写入信息,首先调用该程序的进程将传入的参数——文件名,调用shm_open() 获得父进程创建的这块共享内存的文件描述符,之后调用mmap() 将该共享内存对象映射到当前调用的进程的地址空间,获取指向共享内存对象的指针,利用sprintf()向当中写入"Hello World!"。
alg.8-6-shmconsumer.c
/* gcc -lrt */
#include 代码说明:
这部分代码负责完成消费者的工作,从共享内存中读取信息,首先调用shm_open() 以文件名作为参数,获取生产者创建的共享内存对象的文件描述符,再调用mmap() 将该共享内存对象映射到当前调用的进程的地址空间,获取指向共享内存对象的指针,并输出其中的值。
运行结果:
在编译时务必链接rt库。
从结果上可以看到,系统调用ls -l /dev/shm/|grep huangjy 之后显示了目录/dev/shm/下的文件信息,这里正是父进程创建的imtheking文件,其中生产者向这块共享内存空间中写入了"Hello World!", 消费者从中成功读取到"Hello World!"。
代码改进:
改进后,基于生产者和消费者问题,对实现方式做改动:实现由生产者输入学生学号,消费者从共享空间中读取学生学号
alg.8.0-shmdata_M.h
#define TEXT_SIZE 4*1024 /* = PAGE_SIZE, size of each message */
#define ID_SIZE 8
#define STU_NUM 1
/* total size can not exceed current shmmax,
or an 'invalid argument' error occurs when shmget */
/* a demo structure, modified as needed */
struct shared_struct {
int written; /* flag = 0: buffer writable; others: readable */
char stuid[ID_SIZE];
};
#define PERM S_IRUSR|S_IWUSR|IPC_CREAT
#define ERR_EXIT(m) \
do { \
perror(m); \
exit(EXIT_FAILURE); \
} while(0)
代码说明:
在原来的基础上增加了char stuid[ID_SIZE]用于存放学生学号
alg.8-4-shmpthreadcon_M.c
/* gcc -lrt */
#include 代码说明:
这部分代码实现上不需要改动;
alg.8-5-shmproducer_M.c
/* gcc -lrt */
#include 代码说明:
这部分代码负责生产者的工作,首先利用struct shared_struct* shared结构体指针,获取mmap()的返回值(指向共享内存文件的指针),如此shared指针就指向了共享内存文件,并且将共享内存内部数据组织成结构体的组织方式,由键盘输入学生学号,并存入共享内存空间中。
alg.8-6-shmconsumer_M.c
/* gcc -lrt */
#include 代码说明:
这部分代码负责消费者的工作,同样利用struct shared_struct* shared结构体指针,获取mmap()的返回值,为了避免并发进程的冲突,代码中加了sleep(1) ,避免与生产者进程产生竞争,那么,生产者写入信息后,消费值可以读取当中的信息,即学号。
运行结果:
从运行结果中可以看出,在/dev/shm/路径下生成了studen_system的文件,在输入学生学号后,消费者读取到了写入的学号,并打印输出。
III.总结
在本实验中,以生产者和消费者问题为基础,展现了在Linux中实现进程间通信的方法,其主要针对的是共享内存模型,进程之间共享同一块内存,以这块内存作为中介,进而实现通信;在实现中,分别采用了System V和POSIX API,这两者之间存在着共同与不同点,System V共享内存的实现需要利用pathname生成IPC Key,进而利用它为共享内存空间命名,其他子进程访问这块空间都需要提供对应的IPC Key;POSIX共享内存的实现主要是将共享内存映射成文件,而后映射到调用进程的地址空间中,通过文件名来实现对共享内存的访问。