图像笔记(一)——目标检测
注:ubuntu系统对vlc播放器支持较好,因此推荐安装vlc。
sudo apt install vlc
1.1 简介
目标检测发展
基于传统手工特征的检测算法时期:基于手工特征所构建的。通过设计多元化的检测算法来拟补手工特征表达能力的缺陷。
- VJ(Viola-Jones检测器)
- HOG(HOG行人检测器)
- DPM(可变性部件模型)
基于深度学习的检测算法时期 - CNN
基于一体化卷积网络的检测 - OverFeat
- YOLO
- SSD
- Retina_Net
基于Object Proposal的检测 - RCNN
- SPPNet
- Fast RCNN
- Faster RCNN
- Pyramid Networks
目标检测的发展则分别经历了“包围框回归”、“深度神经网络兴起”、“多参考窗口(Multi-References,又称Anchors)”、“难样本挖掘与聚焦”以及“多尺度多端口检测”几个里程碑式的技术进步
1.2 VJ-Haar分类器
1.2.1 haar分类原理解析
目前的人脸检测方法主要有两大类:基于知识和基于统计。
“基于知识的方法主要利用先验知识将人脸看作器官特征的组合,根据眼睛、眉毛、嘴巴、鼻子等器官的特征以及相互之间的几何位置关系来检测人脸。基于统计的方法则将人脸看作一个整体的模式——二维像素矩阵,从统计的观点通过大量人脸图像样本构造人脸模式空间,根据相似度量来判断人脸是否存在。在这两种框架之下,发展了许多方法。目前随着各种方法的不断提出和应用条件的变化,将知识模型与统计模型相结合的综合系统将成为未来的研究趋势。”(来自论文《基于Adaboost的人脸检测方法及眼睛定位算法研究》)
基于知识的人脸检测方法
-
模板匹配
-
人脸特征
-
形状与边缘
-
纹理特性
-
颜色特征
基于统计的人脸检测方法 -
主成分分析与特征脸
-
神经网络方法
-
支持向量机
-
隐马尔可夫模型
-
Adaboost算法
Haar分类器 = Haar-like特征 + 积分图方法 + AdaBoost + 级联
1. 人脸 Haar-like特征检测
人脸有一些特征,一张正脸图像中,人眼睛区域会比脸颊区域暗,嘴唇区域也会比四周的区域暗,但鼻子区域会比两边脸颊要亮。基于这些特征,VJ使用可四种矩形特征:
 A,B为边界特性,C为细节特征,D为对角线特征
A,B为边界特性,C为细节特征,D为对角线特征
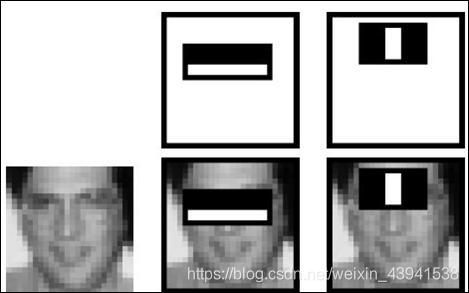 Haar特征分别对白色区域和黑色区域的像素求和,然后求这两种和的差;可以通过图像卷积实现
Haar特征分别对白色区域和黑色区域的像素求和,然后求这两种和的差;可以通过图像卷积实现
后续提出更多特征检测算子

2. 建立积分图像,利用积分图像快速获取集中不同的矩形特征
对于积分图像中的任何一点,该点的积分图像值等于位于该点左上角所有像素之和。
S ( x , y ) = ∑ x ′ ≤ x ∑ y ′ ≤ y f ( x ′ , y ′ ) S(x,y)=\sum_{x^{'}≤x}\sum_{y^{'}≤y}f(x^{'},y^{'}) S(x,y)=x′≤x∑y′≤y∑f(x′,y′)
积分图像满足以下公式:
s ( x , y ) = f ( x , y ) + s ( x − 1 , y ) + s ( x , y − 1 ) − s ( x − 1 , y − 1 ) s(x,y)=f(x,y)+s(x-1,y)+s(x,y-1)-s(x-1,y-1) \\ s(x,y)=f(x,y)+s(x−1,y)+s(x,y−1)−s(x−1,y−1)
还满足以下特点:
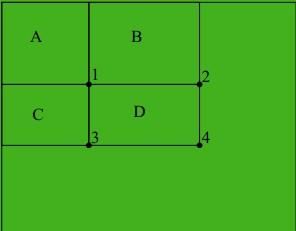 上图像中标识出了四个区域:A, B , C ,D
上图像中标识出了四个区域:A, B , C ,D
1 处像素点对应的在积分图像中的值为:sum(A);
2 处像素点对应的在积分图像中的值为:sum(A+B);
3 处像素点对应的在积分图像中的值为:sum(A+C);
4 处像素点对应的在积分图像中的值为:sum(A+B+C+D);
则:
区域D所有的像素点灰度值之和为:
sum(A+B+C+D) - sum(A+C) - sum(A+B) + sum(A)
3. 获取图像特征
由于采用了四种矩形来提取人脸特征
| 特征 | 描述像素个数 | 特征情形 |
|---|---|---|
| 二邻接矩形 | 最少2个像素点表示 | 横竖两种情况(A,B) |
| 三邻接矩形C | 最少需要3个像素点表示 | 横竖两种情况 |
| 四邻接矩形D | 最少需要4个像素点表示 | 只有一种情况 |
根据图像卷积,一个W*H的图像与m*n的filter卷积,得到的图像大小为:(W-m+1)*(H-n+1)(默认stride为1)。新图像的每一个像素点的值就是原图一个m*n的local patch 与m*n的filter的乘积和。新图像有多少个像素点,原图就有多少个m*n的矩形。
4. 利用Adaboost算法进行训练-(提取有用特征)
由于采用haar特征提取后,生成的特征非常多,对于24*24的图像,采用二,三,四邻矩形提取特征,可以生成162336个特征向量,需要在巨大的特征中提取出有用的特征信息,VJ采用Adaboost算法进行训练,提取有用的特征。
AdaBoost 是一种具有一般性的分类器提升算法,它使用的分类器并不局限某一特定算法。利用AdaBoost算法可以帮助我们选择更好的矩阵特征组合,这里矩阵特征组合就是分类器,分类器将矩阵组合以二叉决策树的形式存储起来。
Adaboosting原理
VJ中AdaBoost算法流程
5. 建立层级分类器
- 最初的弱分类器可能只是一个最基本的Haar-like特征,计算输入图像的Haar-like特征值,和最初的弱分类器的特征值比较,以此来判断输入图像是不是人脸,然而这个弱分类器太简陋了,可能并不比随机判断的效果好.
- 对弱分类器的孵化就是训练弱分类器成为最优弱分类器,注意这里的最优不是指强分类器,只是一个误差相对稍低的弱分类器,训练弱分类器实际上是为分类器进行设置的过程。
- 至于如何设置分类器,设置什么,我们首先分别看下弱分类器的数学结构和代码结构。

一个弱分类器由子窗口图像x,一个特征f,指示不等号方向的p和阈值组成。P的作用是控制不等式的方向,使得不等式都是<号,形式方便。
/*
* CART classifier
*/
typedef struct CvCARTHaarClassifier
{
CV_INT_HAAR_CLASSIFIER_FIELDS()
int count;
int* compidx;
CvTHaarFeature* feature;
CvFastHaarFeature* fastfeature;
float* threshold;
int* left;
int* right;
float* val;
} CvCARTHaarClassifier;
强分类器的诞生需要T轮的迭代,具体操作如下:
- 给定训练样本集S,共N个样本,其中X和Y分别对应于正样本和负样本; T为训练的最大循环次数;
- 初始化样本权重为1/N ,即为训练样本的初始概率分布;
- 第一次迭代训练N个样本,得到第一个最优弱分类器
- 提高上一轮中被误判的样本的权重;
- 将新的样本和上次本分错的样本放在一起进行新一轮的训练。
- 循环执行4-5步骤,T轮后得到T个最优弱分类器。
- 组合T个最优弱分类器得到强分类器
- 训练级联分类器的目的就是为了检测的时候,更加准确,这涉及到Haar分类器的另一个体系,检测体系,检测体系是以现实中的一幅大图片作为输入,然后对图片中进行多区域,多尺度的检测,所谓多区域,是要对图片划分多块,对每个块进行检测,由于训练的时候用的照片一般都是20*20左右的小图片,所以对于大的人脸,还需要进行多尺度的检测,多尺度检测机制一般有两种策略,一种是不改变搜索窗口的大小,而不断缩放图片,这种方法显然需要对每个缩放后的图片进行区域特征值的运算,效率不高,而另一种方法,是不断初始化搜索窗口size为训练时的图片大小,不断扩大搜索窗口,进行搜索,解决了第一种方法的弱势。
6. 非极大值抑制
VJ
vj
1.2.2 OpenCV 之 HaarTraining算法剖析
harrTraing
- 准备正负样本
制作相同大小的人脸样本
制作正样本描述文件,用于描述正样本文件名,正样本数目以及各正样本在图片中的位置和大小。 - 用CreateSamples程序建正样本集
运行createSamples程序,输出结果到samples.vec
3.制作负样本 - HaarTraining 程序训练,得到分类器模型(xml文件)
代码测试使用的是opencv库中训练好的人脸检测分类器模型,安装好opencv后,可以在/usr/share/opencv/haarcascades文件夹下找到。
#include 人脸检测必读文章
1.3 HOG(HOG行人检测器)
1.3.1 Hog算子( 方向梯度直方图-Histogram of Oriented Gradient, HOG)
1.HOG简介
- 在一副图像中,局部目标的表象和形状(appearance and shape)能够被梯度或边缘的方向密度分布很好地描述。(本质:梯度的统计信息,而梯度主要存在于边缘的地方)。
- HOG算法首先将图像分成小的连通区域,我们把它叫细胞单元(cell)。然后采集细胞单元中各像素点的梯度的或边缘的方向直方图。最后把这些直方图组合起来就可以构成特征描述器。
- 把这些局部直方图在图像的更大的范围内(我们把它叫区间或block)进行对比度归一化(contrast-normalized),所采用的方法是:先计算各直方图在这个区间(block)中的密度,然后根据这个密度对区间中的各个细胞单元做归一化。通过这个归一化后,能对光照变化和阴影获得更好的效果。
- 与其他的特征描述方法相比,HOG有很多优点。
首先,由于HOG是在图像的局部方格单元上操作,所以它对图像几何的和光学的形变都能保持很好的不变性,这两种形变只会出现在更大的空间领域上。
其次,在粗的空域抽样、精细的方向抽样以及较强的局部光学归一化等条件下,只要行人大体上能够保持直立的姿势,可以容许行人有一些细微的肢体动作,这些细微的动作可以被忽略而不影响检测效果。
因此HOG特征是特别适合于做图像中的人体检测的。
2.HOG算子提取特征过程
- 灰度化(将图像看做一个x,y,z(灰度)的三维图像);
- 采用Gamma校正法对输入图像进行颜色空间的标准化(归一化);目的是调节图像的对比度,降低图像局部的阴影和光照变化所造成的影响,同时可以抑制噪音的干扰;
- 计算图像每个像素的梯度(包括大小和方向);主要是为了捕获轮廓信息,同时进一步弱化光照的干扰。
- 将图像划分成小cells(例如6*6像素/cell);
- 统计每个cell的梯度直方图(不同梯度的个数),即可形成每个cell的descriptor;
- 将每几个cell组成一个block(例如3*3个cell/block),一个block内所有cell的特征descriptor串联起来便得到该block的HOG特征descriptor。
- 将图像image内的所有block的HOG特征descriptor串联起来就可以得到该image(你要检测的目标)的HOG特征descriptor了。这个就是最终的可供分类使用的特征向量了。
HOG特征简介
1.3.2 HOG检测器训练
- 训练过程中正样本大小统一为128*64,即检测窗口的大小;
- 该样本图片可以包含1个或多个行人。
- 对该图片提取的hog特征长度刚好为3780维,每一个特征对应一个正样本标签进行训练。
- 在实际的训练过程中,我们收集包含行人的任意图片(尺寸最好比128*64大),然后手工对这些正样本进行标注,即对有行人的地方画个矩形,其实也就是存了2个顶点的坐标而已,并把这个矩形的信息存储起来;
- 负样本不需要统一尺寸,只需比12864大,且图片中不能包含任何行人,不需要人工进行标注。程序中可以对该图片随机进行截取12864大小的图片,并提取出其hog特征作为负样本。
- 训练过程
 检测过程中用到的函数为detectMultiScale()。
检测过程中用到的函数为detectMultiScale()。
HOG特征提取
1.3.3 HOG行人检测器
#include training+detect
#include 原文链接
python版本
HOG特征提取
1.4 DPM(可变性部件模型)
1.4.1 DPM简介
由于HOG有一个缺点:很难处理遮挡问题,人体姿势动作幅度过大或物体方向改变也不易检测
DPM=HOG+SVM+滑动窗
- 要有根模型(root filter)和若干部件模型(part filter)和部件模型的偏离损失。这些东西就是通过已有的人体,四肢等样本提取HOG特征然后经过svm训练而来的。
- 用root filter提取原始图像的DMP特征图,再对DMP特征图用root filter和part filter计算响应图。(实际上就是一个模版匹配)
- 加权平均root的和part的,得到最终的融合特征图
- 对融合特征进行传统分类,回归得到目标位置。
DPM算法思想:输入一幅图像,对图像提取图像特征,针对某个物件制作出相应的激励模板,在原始的图像中计算,得到该激励效果图,根据激励的分布,确定目标位置。
制作激励模板就相当于人为地设计一个卷积核,一个比较复杂的卷积核,拿这个卷积核与原图像进行卷积运算得到一幅特征图。比如拿一个静止站立的人的HOG特征形成的卷积核,与原图像的梯度图像进行一个卷积运算,那么目标区域就会被加密。
那么说到这里就会出现一个问题,人在图像中可能有各种的姿态,比如躺着,趴着,坐着等等,我们只用一个静止站立状态的人的激励模板去做探测就会失败。也就是说图像中的物件可能会发生形变,那么我们用固定的激励模板去探测目标物件的时候就不再适用,那么该如何解决这一问题呢,这就引出了局部模板,也就是说,我们不做一个整体的人的激励模板,转而去做人的部分组件的模板,比如头、胳膊、腿等,其实这就是DPM算法。
再概括一下,HOG的特征提取比较死板,一定要是一个人,这个人还只能是特定的姿态比如站立,动作幅度改变不能太大。而DMP就是先检测整个人,再检测四肢,然后综合两者的信息去判断。
1.4.2 DPM实现
opencv contrib 中包含DPM模块,其中包含DPM训练,使用demo和DPM模型文件。
#include 1.5 AlexNet
ALEXnet
Environments
- Python 3.7.3
- cuda 10.0
- PyTorch 1.3.0
- torchvision 0.4.1
prepare pytorch-summary
pytorch-summary is a very useful tool for understanding the model structure, for example it can output the dimensions of each layer.
Clone, and cd into the repo directory.
git clone https://github.com/sksq96/pytorch-summary
python setup.py build
python setup.py install
train
model.py
import torch.nn as nn
import torch
'''
使用nn.Sequential, 将一系列的层结构打包,形成一个整体
'''
class AlexNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_classes=1000, init_weights=False):
super(AlexNet, self).__init__()
# 专门用来提取图像特征
self.features = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(3, 48, kernel_size=11, stride=4, padding=2), # input[3, 224, 224] output[48, 55, 55]
nn.ReLU(inplace=True), # inPlace=True, 增加计算量减少内存使用的一个方法
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2), # output[48, 27, 27]
nn.Conv2d(48, 128, kernel_size=5, padding=2), # output[128, 27, 27]
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2), # output[128, 13, 13]
nn.Conv2d(128, 192, kernel_size=3, padding=1), # output[192, 13, 13]
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(192, 192, kernel_size=3, padding=1), # output[192, 13, 13]
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(192, 128, kernel_size=3, padding=1), # output[128, 13, 13]
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2), # output[128, 6, 6]
)
# 将全连接层作为一个整体,通过Dropout使其防止过拟合,一般放在全连接层和全连接层之间
self.classifier = nn.Sequential(
nn.Dropout(p=0.5),
nn.Linear(128 * 6 * 6, 2048),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Dropout(p=0.5),
nn.Linear(2048, 2048),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Linear(2048, num_classes),
)
if init_weights:
self._initialize_weights()
def forward(self, x):
x = self.features(x)
x = torch.flatten(x, start_dim=1) # 展平处理,从channel维度开始展平,(第一个维度为channel)
x = self.classifier(x)
return x
def _initialize_weights(self):
for m in self.modules(): # 返回一个迭代器,遍历我们网络中的所有模块
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d): # 判断层结构是否为所给定的层,比如此处判断是否为卷积层
nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out', nonlinearity='relu')
if m.bias is not None: # 此处判断该层偏置是否为空
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
elif isinstance(m, nn.Linear): # 如果是全连接层
nn.init.normal_(m.weight, 0, 0.01) # 通过正态分布来给权重赋值
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
train.py
# coding=UTF-8
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from torchvision import transforms, datasets, utils
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import torch.optim as optim
from model import AlexNet
import os
import json
import time
device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
print(device)
# 数据预处理,定义data_transform这个字典
data_transform = {
"train": transforms.Compose([transforms.RandomResizedCrop(224), # 随机裁剪,裁剪到224*224
transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(), # 水平方向随机翻转
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize((0.5, 0.5, 0.5), (0.5, 0.5, 0.5))]),
"val": transforms.Compose([transforms.Resize((224, 224)), # cannot 224, must (224, 224)
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize((0.5, 0.5, 0.5), (0.5, 0.5, 0.5))])}
# os.getcwd()获取当前文件所在目录, "../.."返回上上层目录,".."返回上层目录
data_root = os.path.abspath(os.path.join(os.getcwd(), "..")) # get data root path
image_path = data_root + "/alexnet/flower_data" # flower data set path
train_dataset = datasets.ImageFolder(root=image_path + "/train",
transform=data_transform["train"])
train_num = len(train_dataset)
flower_list = train_dataset.class_to_idx # 获取分类的名称所对应的索引,即{'daisy':0, 'dandelion':1, 'roses':2, 'sunflower':3, 'tulips':4}
cla_dict = dict((val, key) for key, val in flower_list.items()) # 遍历获得的字典,将key和value反过来,即key变为0,val变为daisy
# 将key和value反过来的目的是,预测之后返回的索引可以直接通过字典得到所属类别
# write dict into json file
json_str = json.dumps(cla_dict, indent=4)
with open('class_indices.json', 'w') as json_file: # 保存入json文件
json_file.write(json_str)
batch_size = 32
train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(train_dataset,
batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True,
num_workers=0)
validate_dataset = datasets.ImageFolder(root=image_path + "/val",
transform=data_transform["val"])
val_num = len(validate_dataset)
validate_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(validate_dataset,
batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=False,
num_workers=0)
# test_data_iter = iter(validate_loader)
# test_image, test_label = test_data_iter.next()
#
# def imshow(img):
# img = img / 2 + 0.5 # unnormalize
# npimg = img.numpy()
# plt.imshow(np.transpose(npimg, (1, 2, 0)))
# plt.show()
#
# print(' '.join('%5s' % flower_list[test_label[j]] for j in range(4)))
# imshow(utils.make_grid(test_image))
net = AlexNet(num_classes=5, init_weights=True)
net.to(device)
loss_function = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
pata = list(net.parameters()) # 查看net内的参数
optimizer = optim.Adam(net.parameters(), lr=0.0002)
save_path = './AlexNet.pth'
best_acc = 0.0
for epoch in range(10):
# train
net.train() # 在训练过程中调用dropout方法
running_loss = 0.0
t1 = time.perf_counter() # 统计训练一个epoch所需时间
for step, data in enumerate(train_loader, start=0):
images, labels = data
optimizer.zero_grad()
outputs = net(images.to(device))
loss = loss_function(outputs, labels.to(device))
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
# print statistics
running_loss += loss.item()
# print train process
rate = (step + 1) / len(train_loader)
a = "*" * int(rate * 50)
b = "." * int((1 - rate) * 50)
print("\rtrain loss: {:^3.0f}%[{}->{}]{:.3f}".format(int(rate * 100), a, b, loss))
print()
print(time.perf_counter()-t1)
# validate
net.eval() # 在测试过程中关掉dropout方法,不希望在测试过程中使用dropout
acc = 0.0 # accumulate accurate number / epoch
with torch.no_grad():
for data_test in validate_loader:
test_images, test_labels = data_test
outputs = net(test_images.to(device))
predict_y = torch.max(outputs, dim=1)[1]
acc += (predict_y == test_labels.to(device)).sum().item()
accurate_test = acc / val_num
if accurate_test > best_acc:
best_acc = accurate_test
torch.save(net.state_dict(), save_path)
print('[epoch %d] train_loss: %.3f test_accuracy: %.3f' %
(epoch + 1, running_loss / step, acc / val_num))
print('Finished Training')
predict.py
import torch
from model import AlexNet
from PIL import Image
from torchvision import transforms
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import json
data_transform = transforms.Compose(
[transforms.Resize((224, 224)),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize((0.5, 0.5, 0.5), (0.5, 0.5, 0.5))])
# load image
img = Image.open("../tulips.jpg")
plt.imshow(img)
# [N, C, H, W]
img = data_transform(img) # 预处理的时候已经将channel这个维度提到最前面
# expand batch dimension
img = torch.unsqueeze(img, dim=0) # 在最前面增加一个batch维度
# read class_indict
try:
json_file = open('./class_indices.json', 'r')
class_indict = json.load(json_file)
except Exception as e:
print(e)
exit(-1)
# create model
model = AlexNet(num_classes=5)
# load model weights
model_weight_path = "./AlexNet.pth"
model.load_state_dict(torch.load(model_weight_path))
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
# predict class
output = torch.squeeze(model(img)) # 将batch维度压缩掉
predict = torch.softmax(output, dim=0) # 变成概率分布
predict_cla = torch.argmax(predict).numpy() # 获得最大概率处的索引值
print(class_indict[str(predict_cla)], predict[predict_cla].item())
plt.show()
split_data.py
import os
from shutil import copy
import random
def mkfile(file):
if not os.path.exists(file):
os.makedirs(file)
file = 'flower_data'
flower_class = [cla for cla in os.listdir(file) if ".txt" not in cla]
mkfile('flower_data/train')
for cla in flower_class:
mkfile('flower_data/train/'+cla)
mkfile('flower_data/val')
for cla in flower_class:
mkfile('flower_data/val/'+cla)
split_rate = 0.1
for cla in flower_class:
cla_path = file + '/' + cla + '/'
images = os.listdir(cla_path)
num = len(images)
eval_index = random.sample(images, k=int(num*split_rate))
for index, image in enumerate(images):
if image in eval_index:
image_path = cla_path + image
new_path = 'flower_data/val/' + cla
copy(image_path, new_path)
else:
image_path = cla_path + image
new_path = 'flower_data/train/' + cla
copy(image_path, new_path)
print("\r[{}] processing [{}/{}]".format(cla, index+1, num), end="")
print()
print("processing done!")
Run
alexnet.py
import torch
from torch import nn
from torch.nn import functional as F
import torchvision
def main():
print('cuda device count: ', torch.cuda.device_count())
net = torchvision.models.alexnet(pretrained=True)
#net.fc = nn.Linear(512, 2)
net.eval()
net = net.to('cuda:0')
print(net)
tmp = torch.ones(2, 3, 224, 224).to('cuda:0')
out = net(tmp)
print('alexnet out:', out.shape)
torch.save(net, "alexnet.pth")
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
inference.py
import torch
from torch import nn
import torchvision
import os
import struct
from torchsummary import summary
def main():
print('cuda device count: ', torch.cuda.device_count())
net = torch.load('alexnet.pth')
net = net.to('cuda:0')
net.eval()
print('model: ', net)
#print('state dict: ', net.state_dict().keys())
tmp = torch.ones(1, 3, 224, 224).to('cuda:0')
print('input: ', tmp)
out = net(tmp)
#for l in list(net.classifier.modules())[1:]:
# print('-', l)
print('output:', out)
summary(net, (3, 224, 224))
f = open("alexnet.wts", 'w')
f.write("{}\n".format(len(net.state_dict().keys())))
for k,v in net.state_dict().items():
print('key: ', k)
print('value: ', v.shape)
vr = v.reshape(-1).cpu().numpy()
f.write("{} {}".format(k, len(vr)))
for vv in vr:
f.write(" ")
f.write(struct.pack(">f", float(vv)).hex())
f.write("\n")
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
run
cd alexnet
python alexnet.py // do inference and save model into .pth firstly.
python inference.py // then do inference and save weights file
1.6 OverFeat
1.6.1 overFeat简介
overFeat简介
Overfeat
(1) FCN-全卷积神经网络
(2) offset max-pooling
1.6.2 overFeat 实践
1.7 YOLO
1.8 SSD
1.8.1 SSD简介
SSD简介
SSD主要设计思想是特征分层提取,并依此进行边框回归和分类。具有以下特点:
- 从YOLO中继承了将detection转化为regression的思路,同时依此即可完成网络训练
- 基于faster rcnn中的anchor,提出了相似的prior box;
- 加入基于特征金字塔(pyramidal feature hierarchy)的检测方式,相当于半个FPN思路
- SSD 采用了特征金字塔结构进行检测,检测时利用了conv4-3,conv-7(FC7),conv6-2,conv7-2,conv8_2,conv9_2这些大小不同的feature maps,在多个featuremaps上同时进行softmax分类和位置回归
- SSD按照如下规则生成prior box:(1)以feature map上每个点的中点为中心(offset=0.5),生成一些列同心的prior box(然后中心点的坐标会乘以step,相当于从feature map位置映射回原图位置)
