机器学习实战-使用matplotlib绘制决策树
matplotlib注解
本文中使用matplotlib中的注解功能绘制树形图,它可以对文字着色并提供多种形状用以选择,而且我们还可以翻转箭头,将他指向数据或者节点。废话不多,刚代码,先完成使用文本注解绘制树节点。先来解决一个matplotlib中文显示乱码的问题,加入如下代码即可:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei']
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False.py文件的开头加入就好。后面就是用文本注释绘制树节点的代码:
decisionNode = dict(boxstyle="sawtooth", fc='0.8')
leafNode = dict(boxstyle="round4", fc='0.8')
arrow_args = dict(arrowstyle="<-")
def plotNode(nodeTxt, centrePt, parentPt, nodeType):
creatPlot.ax1.annotate(nodeTxt, xy = parentPt, xycoords = "axes fraction", \
xytext = centrePt, textcoords = 'axes fraction', \
va = 'center', ha = 'center', bbox = nodeType, \
arrowprops = arrow_args)
def creatPlot():
fig = plt.figure(1, facecolor='white')
creatPlot.ax1 = plt.subplot(111, frameon=False)
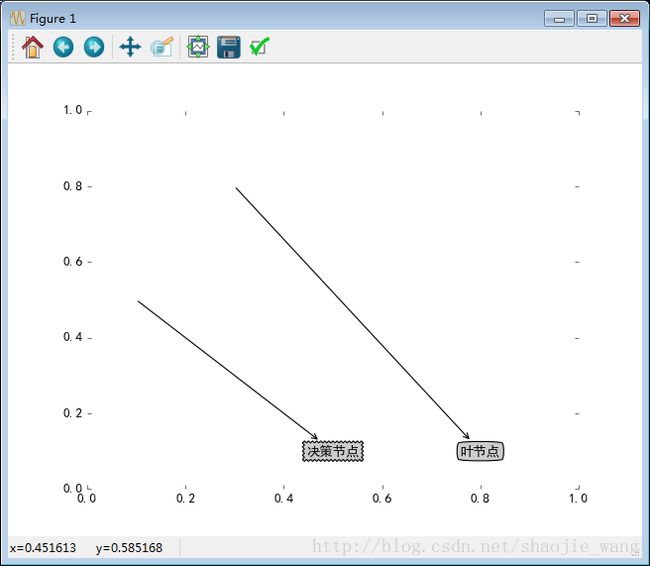
plotNode(u'决策节点', (0.5,0.1), (0.1, 0.5), decisionNode)
plotNode(u'叶节点', (0.8, 0.1), (0.3, 0.8), leafNode)
plt.show()运行结果如下图:
是不是觉得666,我也是这种感觉。。。太村了。。。以后会越来越高端的。
构造注解树
先要计算出树的子叶节点个数和深度,以便计算每个子树的偏移。为了方便测试代码,还增加了一个生成树的函数,代码刚起来:
def getNumLeaves(myTree):
numLeaves = 0
firstStr = list(myTree.keys())[0]
nextDict = myTree[firstStr]
for key in nextDict.keys():
if type(nextDict[key]).__name__ == 'dict':
numLeaves += getNumLeaves(nextDict[key])
else:
numLeaves += 1
return numLeaves
def getDepthTree(myTree):
depthTree = 0
firststr = list(myTree.keys())[0]
nextDict = myTree[firststr]
for key in nextDict.keys():
if type(nextDict[key]).__name__ == 'dict':
thisDepth = 1 + getDepthTree(nextDict[key])
else:
thisDepth = 1
if thisDepth > depthTree:
depthTree = thisDepth
return depthTree
def retrieveTrees():
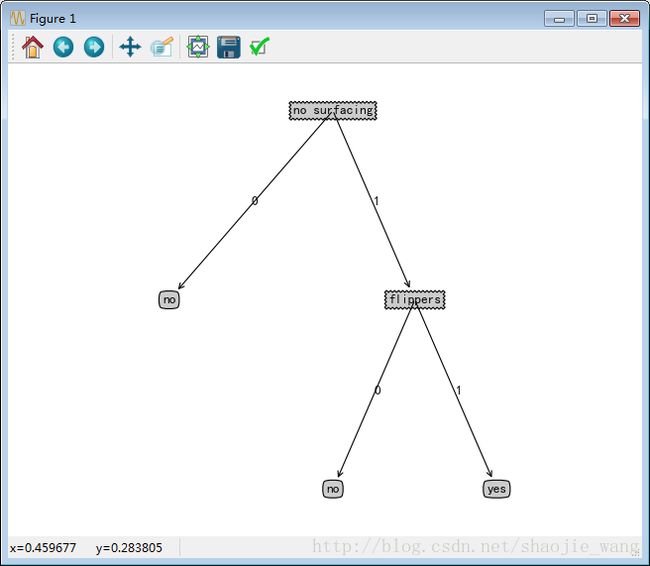
listOfTrees = [{'no surfacing': {0: 'no', 1: {'flippers': {0: 'no', 1: 'yes'}}}}]
return listOfTrees[0]在获取叶节点个数和树的层数时,都是用了递归调用的方法,先判断子树是否为字典,如果是字典则递归调用。函数retrieveTree的目的是创造一棵树,测试代码的正确性。测试代码如下所示:
if __name__ == '__main__':
myTree = retrieveTrees()
print(type(myTree.keys()))
depthTree = getDepthTree(myTree)
leafNum = getNumLeaves(myTree)
print("tree depth = %d, leaf num = %d" % (depthTree, leafNum))运行结果如下:
然后添加如下代码:
def plotMidText(cntrPt, parentPt, txtString):
xMid = (parentPt[0] - cntrPt[0]) / 2.0 + cntrPt[0]
yMid = (parentPt[1] - cntrPt[1]) / 2.0 + cntrPt[1]
creatPlot.ax1.text(xMid, yMid, txtString)
def plotTree(myTree, parentPt, nodeTxt):
numLeafs = getNumLeaves(myTree)
depth = getDepthTree(myTree)
firstStr = list(myTree.keys())[0]
cntrPt = (plotTree.xOff + (1.0 + float(numLeafs)) / 2.0 / plotTree.totalW, \
plotTree.yOff)
plotMidText(cntrPt, parentPt, nodeTxt)
plotNode(firstStr, cntrPt, parentPt, decisionNode)
secondDict = myTree[firstStr]
plotTree.yOff = plotTree.yOff - 1.0 / plotTree.totalD
for key in secondDict.keys():
if type(secondDict[key]).__name__ == 'dict':
plotTree(secondDict[key], cntrPt, str(key))
else:
plotTree.xOff = plotTree.xOff + 1.0 / plotTree.totalW
plotNode(secondDict[key], (plotTree.xOff, plotTree.yOff), \
cntrPt, leafNode)
plotMidText((plotTree.xOff, plotTree.yOff), cntrPt, str(key))
plotTree.yOff = plotTree.yOff + 1.0 / plotTree.totalD
def creatPlot(inTree):
fig = plt.figure(1, facecolor='white')
fig.clf()
axprops = dict(xticks = [], yticks = [])
creatPlot.ax1 = plt.subplot(111, frameon=False, **axprops)
plotTree.totalW = float(getNumLeaves(inTree))
plotTree.totalD = float(getDepthTree(inTree))
plotTree.xOff = -0.5 / plotTree.totalW
plotTree.yOff = 1.0
plotTree(inTree, (0.5, 1.0), '')
plt.show()plt的clf方法是指clear figure的意思。Python中的**表示传参按照字典的方式理解(http://blog.csdn.net/whhit111/article/details/47759267)。中间的过程如下:1、计算标注的起始点;2、计算text的中点;3、给指示箭头添加文字。与上文中计算层数和叶节点个数类似,plottree也会使用递归方法。
测试代码很简单:
if __name__ == '__main__':
myTree = retrieveTrees()
#print(type(myTree.keys()))
#depthTree = getDepthTree(myTree)
#leafNum = getNumLeaves(myTree)
#print("tree depth = %d, leaf num = %d" % (depthTree, leafNum))
creatPlot(myTree)能够画出下图就是成功了: