吴恩达机器学习python作业之单变量线性回归
第一个方法读取数据用的是pandas,第二个方法读数据用的是numpy。
第一种方法是梯度下降法,第二种方法是正规方程法。
跟着佬们的思路写写改改,如果有错误请私信或评论哦。
数据集理解:
ex1data1.txt的数据集是两列,第一列是population(自变量x),第二列是profit(因变量y),利用单变量线性回归进行拟合。
方法一:梯度下降法
参考链接:黄海广博士的github作业链接
https://github.com/fengdu78/Coursera-ML-AndrewNg-Notes/blob/master/code/ex1-linear%20regression/ML-Exercise1.ipynb
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
#使用pandas包读取数据
dt = pd.read_csv("E:\机器学习\吴恩达\data_sets\ex1data1.txt",names = ["population" , "profit"] )
#读取的数据是pandas.DataFrame格式,将其转化为numpy.array格式
x_pd = dt["population"]
m = x_pd.size #97,是样本数
x = np.array(x_pd)
#(1, 97)
a = np.ones(m)
y_pd = dt["profit"]
y = np.array(y_pd)
# #先进行绘图查看数据分布
plt.scatter(x,y)
# plt.show()
x = np.column_stack((a,x))
x = np.matrix(x) #(97, 2)
#print(x.shape)
y = np.matrix(y)
y = y.T #(97, 1)
#print(y.shape)
theta = np.matrix(np.array([0,0])) #(1,2)
print(theta.shape[1])
#print(calculateCost(x,y,theta))
#print(type(theta)) #1.从txt文件中读取数据
#方法一:使用pandas包中的read_csv读取数据
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
#使用pandas包读取数据
dt = pd.read_csv("E:\机器学习\吴恩达\data_sets\ex1data1.txt",names = ["population" , "profit"] )
#读取的数据是pandas.DataFrame格式,将其转化为numpy.array格式
x_pd = dt["population"]
m = x_pd.size #97,是样本数
x = np.array(x_pd)
#(1, 97)
a = np.ones(m)
y_pd = dt["profit"]
y = np.array(y_pd)
#方法二:使用numpy包里的loadtxt函数
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
#使用pandas包读取数据
dt = np.loadtxt("E:\博士\学习资料\机器学习\吴恩达\data_sets\ex1data1.txt",delimiter=',')
#读取的数据是pandas.DataFrame格式,将其转化为numpy.array格式
x = dt[:,0]
m = len(x) #记录样本数
a = np.ones(m)
y = dt[:,1]
2.先用matplotlib查看数据集分布
#先进行绘图查看数据分布
plt.scatter(x,y)
# plt.show()
3.将array数据格式转换为matrix数据格式,方便后期进行矩阵运算
x = np.column_stack((a,x))
x = np.matrix(x) #(97, 2)
#print(x.shape)
y = np.matrix(y)
y = y.T #(97, 1)
#print(y.shape)
theta = np.matrix(np.array([0,0])) #(1,2)
print(theta.shape[1])
#print(calculateCost(x,y,theta))
#print(type(theta)) #4.利用矩阵运算计算损失函数
#计算损失函数
def calculateCost(X,Y,theta):
inner = np.power((X * theta.T - Y) , 2)
return np.sum(inner / (2 * m))
5.利用矩阵运算进行梯度下降算法的实现
def gradientDescent(X,Y,theta,alpha,iters,m):
"""
实现梯度下降算法
:param X: 1*97的矩阵,记录了各个城市的人口
:param Y: 1*97的矩阵,记录了各个城市的利润
:param theta: h(theta) = theta_1*x+theta_0
:param alpha: 学习率
:param iters: 迭代次数
:param m:样本数
:return: theta
"""
result = np.matrix(np.zeros(theta.shape))
for i in range(iters):
#实现求导公式
temp = X * theta.T - Y
for j in range(2):
inner = np.multiply(temp , X[:,j])
result[0,j] = theta[0,j] - alpha * np.sum(inner) / m
theta = result
return theta
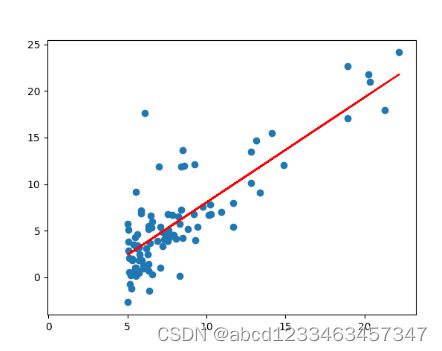
6.绘制曲线观察拟合程度
learningRate = 0.01
iterTimes = 1000
gg = gradientDescent(x,y,theta,learningRate,iterTimes,m)
#[[-3.24140214 1.1272942 ]]
print(calculateCost(x,y,gg))
#4.515955503078913
f = gg[0,0] + gg[0,1] * x
plt.plot(x,f,'r')
plt.show()
方法二:正规方程法
参考链接:
(7条消息) 吴恩达|机器学习作业1.0单变量线性回归_学吧学吧终成学霸的博客-CSDN博客
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
#1.读取数据并进行处理
dt = np.loadtxt("E:\博士\学习资料\机器学习\吴恩达\data_sets\ex1data1.txt",delimiter=",")
#dt类型: