QT从入门到入土之常用控件(一)——菜单栏和对话框
引言
QMainWindow 是一个为用户提供主窗口程序的类,包含一个菜单栏(menu bar)、多个工具栏(tool bars)、多个锚接部件(dock widgets)、一个状态栏(status bar)及一个中心部件(central widget),是许多应用程序的基础,如文本编辑器,图片编辑器等。(本篇主要介绍菜单栏和工具栏)

**
一,菜单栏
**
一个主窗口最多只有一个菜单栏。位于主窗口顶部、主窗口标题栏下面。
创建菜单栏。
QMenuBar* menuBar = new QMenuBar(this);
创建菜单,调用 QMenu 的成员函数 addMenu 来添加菜单
QAction* addMenu(QMenu * menu)
QMenu* addMenu(const QString & title)
QMenu* addMenu(const QIcon & icon, const QString & title)
创建菜单项,调用 QMenu 的成员函数 addAction 来添加菜单项
QAction* activeAction()
QAction* addAction(const QString & text)
QAction* addAction(const QIcon & icon, const QString & text)
QAction* addAction(const QString & text, const QObject * receiver, const char * member, const QKeySequence & shortcut = 0)
QAction* addAction(const QIcon & icon, const QString & text, const QObject * receiver, const char * member,const QKeySequence & shortcut = 0)
实例演示:(vs2019+qt5)
//创建菜单栏
QMenuBar* menuBar = new QMenuBar(this);
//创建菜单(用addMenu方法添加入菜单栏)
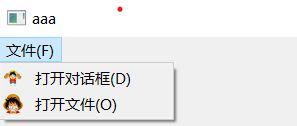
QMenu* filename = menuBar->addMenu(QStringLiteral("文件(&F)"));
//创建菜单项
QAction* openfile = new QAction(QStringLiteral("打开文件(&O)"));
QAction* opendlg = new QAction(QStringLiteral("打开对话框(&D)"));
//给菜单项添入图标
openfile->setIcon(QIcon(":/D:/image/Luffy.png"));
opendlg->setIcon(QIcon(":/D:/image/LuffyQ.png"));
//用addAction加入菜单项
filename->addAction(opendlg);
filename->addAction(openfile);
注意:使用 QStringLiteral 宏可以在编译期把代码里的常量字符串 str 直接构造为 QString 对象,于是运行时就不再需要额外的构造开销了。
资源文件的添加
openfile->setIcon(QIcon(":/D:/image/Luffy.png"));
对于该句代码":/D:/image/Luffy.png"是以相对路径添加的(即以:/开头的是资源文件),那么如何添加资源文件呢?
添加->新建项->Qt->Qt Resource File。
**在Resource1.qrc中添加说需要的资源(比如图片)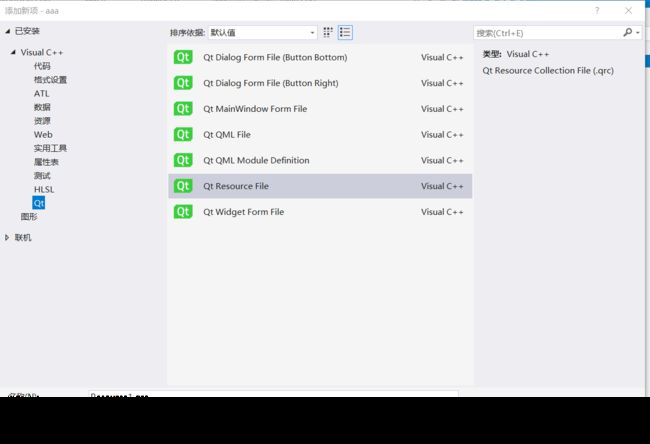
最后以**冒号+前缀+名称(相对路径)**写入资源。
**
二,工具栏
**
主窗口的工具栏上可以有多个工具条,通常采用一个菜单对应一个工具条的的方式,也可根据需要进行工具条的划分。
添加头文件
- 直接调用 QMainWindow 类的 addToolBar()函数获取主窗口的工具条对象,每增加一个工具条都需要调用一次该函数
插入属于工具条的动作,即在工具条上添加操作。通过 QToolBar 类的 addAction 函数添加
工具条是一个可移动的窗口,它的停靠区域由 QToolBar 的 allowAreas 决定,包括:
1.Qt::LeftToolBarArea 停靠在左侧
2.Qt::RightToolBarArea停靠在右侧
3.Qt::TopToolBarArea 停靠在顶部
4.Qt::BottomToolBarArea停靠在底部
5.Qt::AllToolBarAreas以上四个位置都可停靠
使用 setAllowedAreas()函数指定停靠区域:
setAllowedAreas(Qt::LeftToolBarArea | Qt::RightToolBarArea)
使用 setMoveable()函数设定工具栏的可移动性:
setMoveable(false)//工具条不可移动, 只能停靠在初始化的位置上
**
三,对话框 QDialog
**
对话框是 GUI 程序中不可或缺的组成部分。很多不能或者不适合放入主窗口的功能组件都必须放在对话框中设置。对话框通常会是一个顶层窗口,出现在程序最上层,用于实现短期任务或者简洁的用户交互。
Qt 中使用 QDialog 类实现对话框。就像主窗口一样,我们通常会设计一个类继承 QDialog。QDialog(及其子类,以及所有 Qt::Dialog 类型的类)的对于其parent 指针都有额外的解释:如果 parent 为 NULL,则该对话框会作为一个顶
层窗口,否则则作为其父组件的子对话框(此时,其默认出现的位置是 parent的中心)。
顶层窗口与非顶层窗口的区别在于,顶层窗口在任务栏会有自己的位置,而非顶层窗口则会共享其父组件的位置。
Qt的内置对话框大致分为以下几类:
QColorDialog: 选择颜色
QFileDialog: 选择文件或者目录
QFontDialog: 选择字体
QInputDialog: 允许用户输入一个值,并将其值返回
QMessageBox:模态对话框,用于显示信息、询问问题,消息,警告,错误。
QPageSetupDialog:为打印机提供纸张相关的选项
QPrintDialog:打印机配置
QPrintPreviewDialog:打印预览
QProgressDialog:显示操作过程
1️⃣对话框分为模态对话框和非模态对话框。
模态对话框,就是会阻塞同一应用程序中其它窗口的输入。模态对话框很常见,比如“打开文件”功能。你可以尝试一下记事本的打开文件,当打开文件对话框出现时,我们是不能对除此对话框之外的窗口部分进行操作的。
与此相反的是非模态对话框,例如查找对话框,我们可以在显示着查找对话框的同时,继续对记事本的内容进行编辑。
模态与非模态的实现:
使用 QDialog::exec()实现应用程序级别的模态对话框
当该种模态的对话框出现时,用户必须首先对对话框进行交互,直到关闭对话框,然后才能访问程序中其他的窗口。
使用 QDialog::open()实现窗口级别的模态对话框
该模态仅仅阻塞与对话框关联的窗口,但是依然允许用户与程序中其它窗口交互。窗口级别的模态尤其适用于多窗口模式。
使用 QDialog::show()实现非模态对话框
模态对话框实例:
我们调用了 exec()将对话框显示出来,因此这就是一个模态对话框。当对话框出现时,我们不能与主窗口进行任何交互,直到我们关闭了该对话框。
QDialog dlg1(this);
dlg1.resize(300,200);
dlg1.setWindowTitle(QStringLiteral("模态对话框"));
dlg1.exec();
非模态对话框实例:
下面我们试着将 exec()修改为 show(),看看非模态对话框:
QDialog dlg1(this);
dlg1.resize(300,200);
dlg1.setWindowTitle(QStringLiteral("模态对话框"));
dlg1.show();
是不是事与愿违?对话框竟然一闪而过!这是因为,show()函数不会阻塞当前线程,对话框会显示出来,然后函数立即返回,代码继续执行。注意,dialog 是建立在栈上的,show()函数返回,函数结束,dialog超出作用域被析构,因此对话框消失了。知道了原因就好改了,我们将 dialog改成堆上建立(即new一个对象),当然就没有这个问题了。
*QDialog dlg2 = new QDialog();
dlg2->resize(200, 200);
dlg2->setAttribute(Qt::WA_DeleteOnClose);//关闭时清理内存
dlg2->show();
注意:在堆上就不能用点(.)了,要用->。而且由于使用 new 在堆上分配空间,却一直没有 delete。因此我们用setAttribute()函数设置对话框关闭时,自动销毁对话框。
2️⃣消息对话框 (QMessageBox)
QMessageBox :模态对话框,用于显示信息、询问问题等;我们一般会使用该类提供的几个 static成员函数:(静态成员函数有两种访问方式:1 创建对象 ;2 直接通过类名去调用)
显示关于对话框
void about(QWidget * parent, const QString & title, const QString & text)
这是一个最简单的对话框,其标题是 title,内容是 text,父窗口是parent。对话框只有一个 OK 按钮。
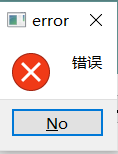
显示错误对话框
StandardButton critical(QWidget * parent, const QString & title, const QString & text, StandardButtons buttons = Ok, StandardButton defaultButton = NoButton)
这个对话框将显示一个红色的错误符号。我们可以通过 buttons 参数指明其显示的按钮 。 默认情况下只有一个Ok按钮 ,我们可以使用StandardButtons 类型指定多种按钮,指令如下:

示例:
QMessageBox::critical(this, QStringLiteral("error"), QStringLiteral("错误"),QMessageBox::No);
第一个参数是 父类,第二个是标题,第三个是内容,第四个是按钮名称(类型为StandardButtons,可以有两个做选择),第五个参数是默认(按钮类型为StandardButtons)。
显示信息对话框
StandardButton information(QWidget * parent, const QString & title, const QString & text, StandardButtons buttons = Ok, StandardButton defaultButton = NoButton)
示例:
QMessageBox::information(this, QStringLiteral("信息"), "infor", QMessageBox::Ok);
显示问题对话框
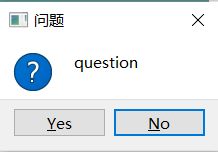
StandardButton question(QWidget * parent, const QString & title,const QString & text, StandardButtons buttons = StandardButtons( Yes | No ), StandardButton defaultButton = NoButton)
示例:
//获取点击信息
if (QMessageBox::Yes== QMessageBox::question(this, QStringLiteral("问题"), "question", QMessageBox::Yes | QMessageBox::No, QMessageBox::No))
{
qDebug() << "click yes";
}
else
{
qDebug() << "click no";
}
3️⃣标准文件对话框
QFileDialog,也就是文件对话框。
我们使用 QFileDialog::getOpenFileName()来获取需要打开的文件的路径。这个函数原型如下:
QString getOpenFileName(QWidget * parent = 0, //父窗口
const QString & caption = QString(), //对话框标题
const QString & dir = QString(), //对话框打开的默认路径
const QString & filter = QString(), //过滤器(例如我们使用“imagefile(*.jpg*.png)”则只显示jpg和png文件。多个过滤器用“;;”分割。
QString * selectedFilter = 0, //默认选择的过滤器
Options options = 0 //对话框的参数设定
)
QFileDialog::getOpenFileName()返回值是选择的文件路径。我们将其赋值给path。通过判断 path 是否为空,可以确定用户是否选择了某一文件。只有当用户选择了一个文件时,我们才执行下面的操作。
下面是最主要的 openFile()和 saveFile()这两个函数的代码:
//打开文件
void MainWindow::openFile()
{
QString path = QFileDialog::getOpenFileName(this, tr("Open File"), ".", tr("Text Files(*.txt)"));
if(!path.isEmpty())
{
QFile file(path);
if (!file.open(QIODevice::ReadOnly | QIODevice::Text))
{
QMessageBox::warning(this, tr("Read File"), tr("Cannot open file:\n%1").arg(path));
return;
}
QTextStream in(&file);
textEdit->setText(in.readAll());
file.close();
}
else
{
QMessageBox::warning(this, tr("Path"), tr("You did not select any file."));
}
}
//保存文件
void MainWindow::saveFile()
{
QString path = QFileDialog::getSaveFileName(this, tr("Open File"), ".", tr("Text Files(*.txt)"));
if(!path.isEmpty())
{
QFile file(path);
if (!file.open(QIODevice::WriteOnly | QIODevice::Text))
{
QMessageBox::warning(this, tr("Write File"), tr("Cannot open file:\n%1").arg(path));
return;
}
QTextStream out(&file);
out << textEdit->toPlainText();
file.close();
}
else
{
QMessageBox::warning(this, tr("Path"), tr("You did not select any file."));
}
}
4️⃣其他对话框
颜色对话框
QColor color= QColorDialog::getColor(QColor(255, 0, 0));//设置默认颜色:红色,用color接收选取的颜色
字体对话框
bool flag;
QFont font = QFontDialog::getFont(&flag, QFont("华文彩云", 36));
演示示例
在菜单栏中打开上述对话框,并制定界面。
#include "aaa.h"
#include"qmenubar.h"
#include"qdialog.h"
#include"qfiledialog.h"
#include"qtoolbar.h"
#include"qmessagebox.h"
#include"qdebug.h"
#include"qcolordialog.h"
#include"qfontdialog.h"
aaa::aaa(QWidget *parent)
: QWidget(parent)
{
//菜单文件
// 使用 QStringLiteral 宏可以在编译期把代码里的常量字符串 str 直接构造为 QString 对象,于是运行时就不再需要额外的构造开销了。
QMenuBar* menuBar = new QMenuBar(this);
QMenu* filename = menuBar->addMenu(QStringLiteral("文件(&F)"));
QAction* openfile = new QAction(QStringLiteral("打开文件(&O)"));
QAction* opendlg = new QAction(QStringLiteral("打开对话框(&D)"));
QAction* openmessage = new QAction(QStringLiteral("打开消息对话框(&D)"));
QAction* opencolor = new QAction(QStringLiteral("打开颜色对话框(&D)"));
QAction* openfont = new QAction(QStringLiteral("打开字体对话框(&D)"));
//设置图标
opencolor->setIcon(QIcon(":/D:/image/sunny.png"));
openfile->setIcon(QIcon(":/D:/image/Luffy.png"));
opendlg->setIcon(QIcon(":/D:/image/LuffyQ.png"));
openmessage->setIcon(QIcon(":/D:/image/up.png"));
openfont->setIcon(QIcon(":/D:/image/sunny.png"));
//加入主菜单
filename->addAction(openmessage);
filename->addAction(opendlg);
filename->addAction(openfile);
filename->addAction(opencolor);
filename->addAction(openfont);
//打开对话框
connect(opendlg, &QAction::triggered, [=]() {
//模态对话框(不可对其他对话框操作)
QDialog dlg1(this);
dlg1.resize(300,200);
dlg1.setWindowTitle(QStringLiteral("模态对话框"));
dlg1.exec();
//非模态对话框(可以对其他对话框操作)
// QDialog *dlg2 = new QDialog();
//dlg2->resize(200, 200);
//dlg2->setAttribute(Qt::WA_DeleteOnClose);//关闭时清理内存
//dlg2->show();
});
//打开文件
connect(openfile, &QAction::triggered, [=]() {
QFileDialog fdlg(this);
fdlg.getOpenFileName(this, QStringLiteral("选择文件"), "D:\\", tr("Image(*.jpg*.png)"));
});
//打开消息对话框
connect(openmessage, &QAction::triggered, [=]() {
if (QMessageBox::Yes== QMessageBox::question(this, QStringLiteral("问题"), "question", QMessageBox::Yes | QMessageBox::No, QMessageBox::No))
{
qDebug() << "click yes";
}
else
{
qDebug() << "click no";
}
});
//打开颜色对话框
connect(opencolor, &QAction::triggered, [=]() {
QColor color= QColorDialog::getColor(QColor(255, 0, 0));//设置默认颜色:红色,用color接收选取的颜色
});
//打开字体对话框
connect(openfont, &QAction::triggered, [=]() {
bool flag;
QFont font = QFontDialog::getFont(&flag, QFont("华文彩云", 36));
qDebug() << QStringLiteral("字体") << font.family() << QStringLiteral("字号") << font.pointSize();
});
ui.setupUi(this);
}