深度学习之wandb的基本使用
wandb 的基本使用
在深度学习训练网络的过程中,由于网络训练过程时间长,不可能一直关注训练中的每一轮结果,因此我们需要将训练过程中的结果可视化,留作后续的查看,从而确定训练过程是否出错。因此,我们需要使用到可视化工具,常用的几种可视化工具有:
wandb(在线可视化)、tensorboard、这里主要介绍wandb的基本使用,tensorboard的使用可参考我的另一篇博客 Tensorboard 的详细使用。
1、安装 wandb 库
pip install wandb
2、注册 wandb 账号
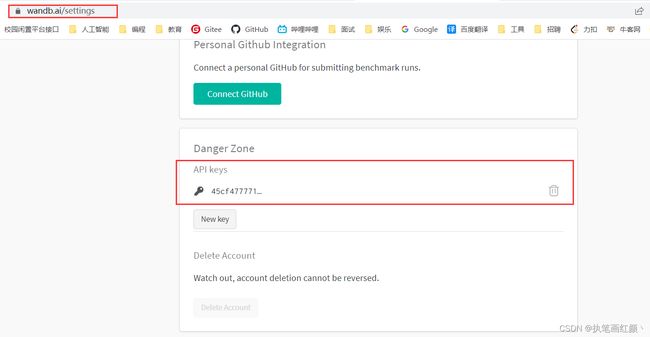
进入官网:https://wandb.ai/ 注册自己的账号,并依据提示,创建属于自己的 Team (相当于一个名称标识,后续需要用到),找到自己账户的 API密钥 ,记录下来。
3、登录 wandb 账号
# 在终端中输入 wandb login 进行登录,输入后,提示输入自身账号的API密钥,将上一步得到的密钥复制进去即可。
wandb login
PS D:\PythonProjects\Object-Detection> wandb login
wandb: Logging into wandb.ai. (Learn how to deploy a W&B server locally: https://wandb.me/wandb-server)
wandb: You can find your API key in your browser here: https://wandb.ai/authorize
wandb: Paste an API key from your profile and hit enter, or press ctrl+c to quit: 输入自己账号的密钥
# 此时登录成功,后续可以在代码中直接使用wandb库了。
wandb: Appending key for api.wandb.ai to your netrc file: C:\Users\LIULUSHENG/.netrc
4、基本使用
import wandb
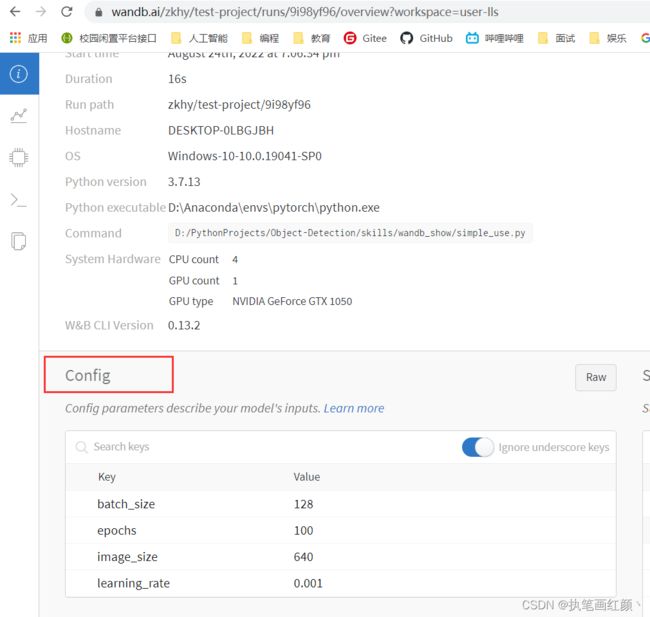
# 自定义一些本次训练的起始参数信息(数据集名称等等)(可选)
config = {
"learning_rate": 0.001,
"epochs": 100,
"batch_size": 128,
"image_size": 640
}
# 初始化(必填)
wandb.init(
entity="zkhy", # wandb上对应的team名称(必填)
project="test-project", # 本次的项目名称(必填)
name="hello", # 本次实验的名称(可选,如果不设置,wandb会自动生成本次实验名称)
tags=["yolo", "lanes-detection"], # 本次实验的标签(可选)
notes="this is a training exp", # 本次实验的备注(可选)
config=config, # 本次实验的配置说明(可选)
)
5、常见用法
5.1 使用 wandb.log() 记录数值信息
import wandb
# 设置一些本次训练的起始参数信息(数据集名称等等)
config = {
"learning_rate": 0.001,
"epochs": 100,
"batch_size": 128,
"image_size": 640
}
# 初始化
wandb.init(
project="test-project", # 本次的项目名称
entity="zkhy", # wandb上对应的team名称
name="hello", # 本次实验的名称(可选,如果不设置,wandb会自动生成本次实验名称)
tags=["yolo", "lanes-detection"], # 本次实验的标签
notes="this is a training exp", # 本次实验的备注
config=config, # 本次实验的配置说明
)
epochs = 10
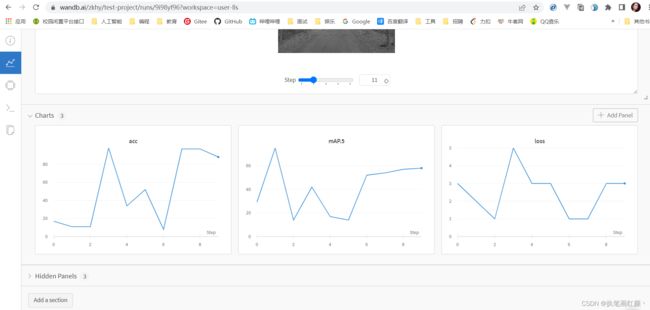
# 通过wandb.log() 添加普通的数值图表信息
for i in range(epochs):
# log中字典里的每一项都会生成一个图表信息
wandb.log({
"loss": random.randint(1, 6),
"acc": random.randint(1, 100),
"mAP.5": random.randint(10, 100)
})
5.2 使用 wandb.Image() 记录图像信息
wandb.Image()接收的是一个numpy格式的图像数据。
- 法一:直接使用
numpy格式的图像数据
import wandb
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 自定义一些本次训练的起始参数信息(数据集名称等等)(可选)
config = {
"learning_rate": 0.001,
"epochs": 100,
"batch_size": 128,
"image_size": 640
}
# 初始化(必填)
wandb.init(
entity="zkhy", # wandb上对应的team名称(必填)
project="test-project", # 本次的项目名称(必填)
name="hello", # 本次实验的名称(可选,如果不设置,wandb会自动生成本次实验名称)
tags=["yolo", "lanes-detection"], # 本次实验的标签(可选)
notes="this is a training exp", # 本次实验的备注(可选)
config=config, # 本次实验的配置说明(可选)
)
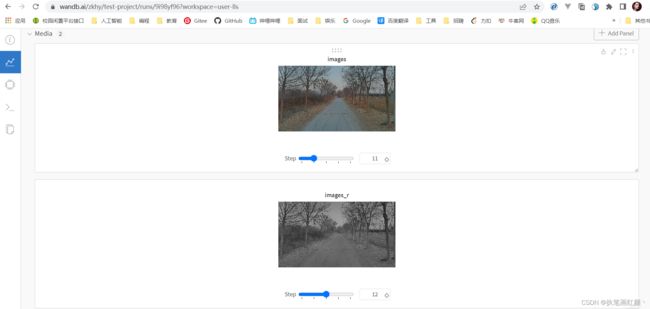
# 通过wandb.log() 和 wandb.Image() 添加图像信息
# 这里注意:由于上面代码已经使用了wandb.log(),并且迭代了10次,所以下面的wandb.log()会从10开始迭代5轮。
for i in range(5):
# 读取图片,读取的图片是numpy格式数组(HWC)
img = plt.imread("../../left_color.png")
# print(type(img), img.shape)
wandb.log({
"images": wandb.Image(img), # 接收的是一个numpy格式的数组
"images_r": wandb.Image(img[:, :, 0]) # 切其中一个通道上传
})
- 法二:通过
matplotlib绘制图像,再将绘制的图像转换成numpy格式的图像数据进行上传
import wandb
import numpy as np
from matplotlib.backends.backend_agg import FigureCanvasAgg
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 自定义一些本次训练的起始参数信息(数据集名称等等)(可选)
config = {
"learning_rate": 0.001,
"epochs": 100,
"batch_size": 128,
"image_size": 640
}
# 初始化(必填)
wandb.init(
entity="zkhy", # wandb上对应的team名称(必填)
project="test-project", # 本次的项目名称(必填)
name="hello", # 本次实验的名称(可选,如果不设置,wandb会自动生成本次实验名称)
tags=["yolo", "lanes-detection"], # 本次实验的标签(可选)
notes="this is a training exp", # 本次实验的备注(可选)
config=config, # 本次实验的配置说明(可选)
)
# 定义一个方法,将plt的图像转换为numpy格式数组
def plt_to_numpy(plt):
canvas = FigureCanvasAgg(plt.gcf())
# 绘制图像
canvas.draw()
# 获取图像尺寸
w, h = canvas.get_width_height()
# 解码string 得到argb图像
buf = np.frombuffer(canvas.tostring_argb(), dtype=np.uint8)
# 重构成w h 4(argb)图像
buf.shape = (w, h, 4)
# 转换为 RGBA
buf = np.roll(buf, 3, axis=2)
# 得到 Image RGBA图像对象 (需要Image对象的同学到此为止就可以了)
image = Image.frombytes("RGBA", (w, h), buf.tobytes())
# 转换为numpy array rgba四通道数组
image = np.asarray(image)
# print(type(image))
return image
# 添加plt绘制的图像信息,上传到wandb
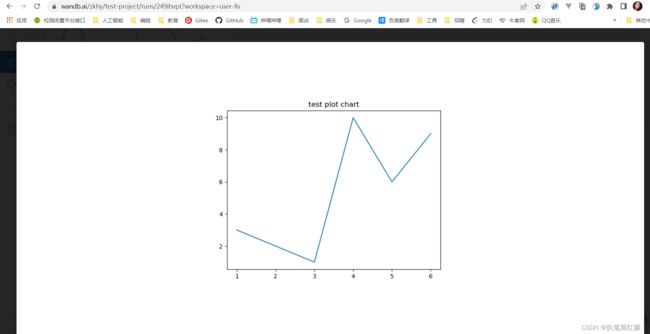
x = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
y = [3, 2, 1, 10, 6, 9]
# 绘制折线图
plt.plot(x, y)
# 设置标题
plt.title("test plot chart")
# 将plt图像转换为numpy数组
to_numpy = plt_to_numpy(plt)
# 上传图像到wandb
wandb.log({
"plt": wandb.Image(to_numpy)
})