第八周PCL学习-点云分割(八)
目录
一、点云分割
1.1 概述
1.2 PCL库中点云分割方法
1.3 算法原理
1.3.1 Plane model segmentation (平面模型分割)
1.3.2 Cylinder model segmentation(圆柱模型分割)
1.3.3 Euclidean Cluster Extraction (欧几里德聚类提取)
1.3.4 Region growing segmentation(区域蔓延分割)
1.3.5 Color-based region growing segmentation (基于彩色信息区域蔓延分割)
1.3.6 Min-cut Based Segmentation (基于最少切割的分割)
1.4 实验
1.4.1 Plane model segmentation (平面模型分割实验)
1.4.2 Cylinder model segmentation(圆柱模型分割实验)
1.4.3 Euclidean Cluster Extraction (欧几里德聚类提取实验)
1.4.4 Region growing segmentation(区域蔓延分割实验)
1.4.5 Color-based region growing segmentation (基于彩色信息区域蔓延分割实验)
1.4.6 Min-cut Based Segmentation (基于最少切割的分割实验)
二、总结
三、参考文献
前言
点云分割往往是许多应用的前提,例如,在逆向工程CAD/CAM 领域对零件的不同扫描表面进行分割,然后才能更好地进行孔洞修复 、曲面重建、特征描述和提取,进而进行基于3D内容的检索、组合重用等。 在激光遥感领域,同样需要对地物首先进行分类处理,然后才能进行后期地物的识别、重建。
一、点云分割
1.1 概述
点云分割是根据空间、几何和纹理等特征对点云进行划分,使得同一划分内的点云拥有相似的特征。
1.2 PCL库中的点云分割方法
- Plane model segmentation (平面模型分割)
- Cylinder model segmentation(圆柱模型分割)
- Euclidean Cluster Extraction (欧几里德聚类提取)
- Region growing segmentation (区域蔓延分割)
- Color-based region growing segmentation (基于彩色信息区域蔓延分割)
- Min-cut Based Segmentation (基于最少切割的分割)
- Conditional Euclidean Clustering(有条件的欧几里德群聚类生成)
- Difference of Normals Based Segmentation (基于局部法线间不同值的分割)
- Clustering of Pointclouds into Supervoxels (把点云聚类为超体元)
- Identifying ground returns using ProgressiveMorphologicalFilter segementation (渐进型形态学过滤器分割)
- Filtering a PointCloud using ModelOutlierRemoval (基于移除模型离群值的方法过滤点云)
下面我们对这些方法进行介绍。
1.3 算法原理
1.3.1 Plane model segmentation (平面模型分割)
其是基于RANSAC(随机采样一致性)的来做平面拟合的。在这个Plane Model Segmentation算法里,RANSAC为了找到点云的平面,不停的改变平面模型(ax+by+cz+d=0)的参数:a, b, c和d。经过多次调参后,找出哪一组的参数能使得这个模型一定程度上拟合最多的点。这个程度就是由distance threshold这个参数来设置。那找到这组参数后,这些能够被拟合的点就是平面的点。
其只有一个参数distance threshold,如果把这调大,离平面更远的点也被算进平面来。distance threshold 可以等同于平面厚度阈值。
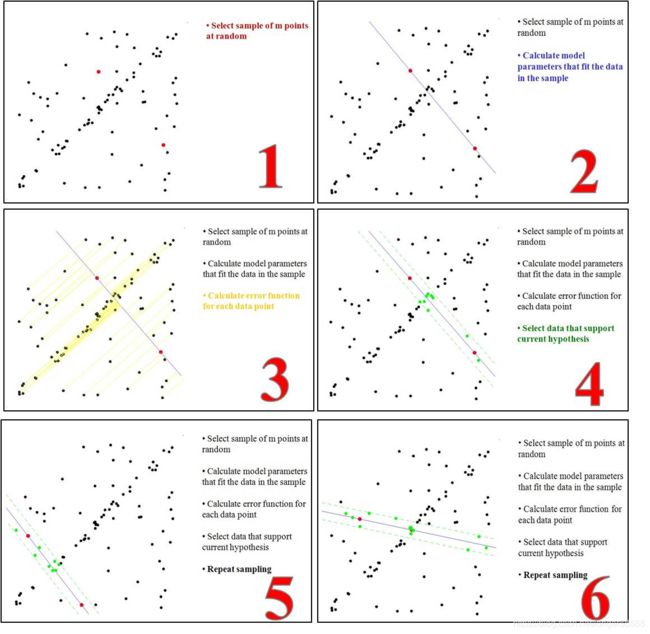
RANSAC:
RANSAC的使用条件是:
1.输入是一组带污染的观测数据,其中的可信数据占了大多数;
2.有一个可以解释可信观测数据的参数化模型
RANSAC的思想:
1、从观测数据中随机选择一个子集,称之为hypothetical inliers。
2、估计出适合于这些个hypothetical inliers的模型
3、用这个模型测试其他的数据,根据损失函数,得到符合这个模型的点,称为一致性集合:consensus set。
4、 如果足够多的数据都被归类于一致性集合,那么说明这个估计的模型是正确的;如果这个集合中的数据太少,那么说明模型不合适,弃之,返回第一步。
最后,根据一致性集合中的数据(可以认为是可靠的数据了),用最小二乘的方法重新估计模型。
1.3.2 Cylinder model segmentation(圆柱模型分割)
其和Planer是相似的,都是基于RANSAC的。只是有限制的半径setRadiusLimits和距离setDistanceThreshold两个参数。
有疑问的地方就是圆柱的高不用进行限制吗?当然不用,这个模型分割只是为分割出圆柱,所以它的高可以忽略。
1.3.3 Euclidean Cluster Extraction (欧几里德聚类提取)
基于欧式距离的分割和基于区域生长的分割本质上都是用区分邻里关系远近来完成的。由于点云数据提供了更高维度的数据,故有很多信息可以提取获得。
欧几里得算法使用邻居之间距离作为判定标准,而区域生长算法则利用了法线,曲率,颜色等信息来判断点云是否应该聚成一类。
欧几里德算法
具体的实现方法大致是:
(1)找到空间中某点p10,有kdTree找到离他最近的n个点,判断这n个点到p的距离。将距离小于阈值r的点p12,p13,p14…放在类Q里
(2)在 Q去除p10的区间里找到一点p12,重复1
(3)在 Q去除p10,p12 找到一点,重复1,找到p22,p23,p24…全部放进Q里
(4)当 Q 再也不能有新点加入了,则完成搜索了
因为点云总是连成片的,很少有什么东西会浮在空中来区分。所以要结合其他算法进行聚类,比如平面切割后。其还可以查找离群点(因为其和其他点云不是相连接的)
当然,一旦桌面被剔除,桌上的物体就自然成了一个个的浮空点云团。就能够直接用欧几里德算法进行分割了,这样就可以提取出我们想要识别的东西;
在这里我们就可以使用提取平面,平面去掉,利用聚类的方法再显示剩下的所有聚类的结果。
1.3.4 Region growing segmentation (区域蔓延分割)
其算法是从曲率小的面播种,从种子的位置出发,开始往四周搜索点,然后比对点于点之间的曲率和法线方向,如果差距小于阈值就视为同一个cluster。如果一个cluster无法再蔓延,在剩下的点云里再找曲率小的面播种,然后继续重复直到遍历完毕。
适合情况:这个算法适合分割规则的物体或者说四四方方的东西,像房屋轮廓,纸箱折叠的情景。
对于物体之间的转折处法线和曲率变化小的,算法比较难分割物体。如果点云有噪音,那就是灾难级的表现。而且算法对调参要求高,鲁棒性和普适性低。
PCL官网上关于此分割的介绍算法
1.3.5 Color-based region growing segmentation (基于彩色信息区域蔓延分割)
此算法和区域生成算法是一样的
不同之处在于:一、该算法使用颜色测试代替了法线测试。二、利用合并算法来控制过分割或欠分割。
在分割过程中,若两个相邻聚类的平均颜色相差较少,则将两个聚类合并。然后进行第二步合并,再次步骤中,检查每一个聚类所包含的点的数量,如果这个数量小于用户定义的值,则当前聚类与最近邻聚类合并在一起。
1.3.6 Min-cut Based Segmentation (基于最少切割的分割)
算法如下:
(1)构造图
1、找到每个点最近的n个点
2 、将这n个点和父点连接
3 、找到距离最小的两个块(A块中某点与B块中某点距离最小),并连接
4、 重复3,直至只剩一个块
现在已经有了“图”,只要给图附上合适的权值,就完成了所有任务。物体分割给人一个直观印象就是属于该物体的点,应该相互之间不会太远。也就是说,可以用点与点之间的欧式距离来构造权值。所有线的权值可映射为线长的函数。
(1)连接输入点云各点之间的边,为上述的边赋予的权值称为平滑代价。
 式子中dist是各点之间的距离,两个点之间的距离越大,该两点之间被切断的可能性就越大。
式子中dist是各点之间的距离,两个点之间的距离越大,该两点之间被切断的可能性就越大。
(2)连接输入点云中的点与源点的边,该边赋予的权值被称为前景惩罚
![]()
式子中的distanceToCenter是点到前景点云(目标物体)预期中心的水平距离
 Radius为该算法的输入参数,可以粗略看成前景点云(目标物体)的水平半径,小于该半径的点作为前景点云(目标物体),大于该半径的点作为背景点云(其他物体)。
Radius为该算法的输入参数,可以粗略看成前景点云(目标物体)的水平半径,小于该半径的点作为前景点云(目标物体),大于该半径的点作为背景点云(其他物体)。
(3)对上述的图通过最小割计算,即可将点云二分为前景点云(目标物体)和背景点云(其他物体)。
1.4 实验
1.4.1 Plane model segmentation
这个实验通过自定义的无序点云为输入,分割模型为PLANE,采样为RANSAC的平面切割实验,可以很好的把z轴不为1的点切割出来。另外求出了切割平面的参数。
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int
main(int argc, char** argv)
{
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud;
//填充点云数据
cloud->width = 15;
cloud->height = 1;
cloud->points.resize(cloud->width * cloud->height);
//生成数据
for (size_t i = 0; i < cloud->points.size(); ++i)
{
cloud->points[i].x = 1024 * rand() / (RAND_MAX + 1.0f);
cloud->points[i].y = 1024 * rand() / (RAND_MAX + 1.0f);
cloud->points[i].z = 1.0;
}
//设置几个局外点
cloud->points[0].z = 2.0;
cloud->points[3].z = -2.0;
cloud->points[6].z = 4.0;
cout << "Point cloud data: " << cloud->points.size() << " points" << endl;
for (size_t i = 0; i < cloud->points.size(); ++i)
cout << " " << cloud->points[i].x << " "
<< cloud->points[i].y << " "
<< cloud->points[i].z << endl;
// 定义模型对象,用来存放平面参数
pcl::ModelCoefficients::Ptr coefficients(new pcl::ModelCoefficients);
// 定义点云索引
pcl::PointIndices::Ptr inliers(new pcl::PointIndices);
//创建分割对象
pcl::SACSegmentation seg;
//可选设置
seg.setOptimizeCoefficients(true);
//必须设置
seg.setModelType(pcl::SACMODEL_PLANE); // 设置分割类型为平面
seg.setMethodType(pcl::SAC_RANSAC); // 设置随机采样
seg.setDistanceThreshold(0.01); // 设置距离平面为0.01m的点为局外点
seg.setInputCloud(cloud->makeShared()); // 点云进行排序
seg.segment(*inliers, *coefficients); // 进行分割,存储平面上的索引和平面模型参数
if (inliers->indices.size() == 0)
{
PCL_ERROR("Could not estimate a planar model for the given dataset.");
return (-1);
}
// 因为平面模型参数ax+by+cz+d=0,有四个参数
cout << "Model coefficients: " << coefficients->values[0] << " "
<< coefficients->values[1] << " "
<< coefficients->values[2] << " "
<< coefficients->values[3] << endl;
cout << "Model inliers: " << inliers->indices.size() << endl;
// 打印索引
for (size_t i = 0; i < inliers->indices.size(); ++i)
cout << inliers->indices[i] << " " << cloud->points[inliers->indices[i]].x << " "
<< cloud->points[inliers->indices[i]].y << " "
<< cloud->points[inliers->indices[i]].z << endl;
return (0);
}
1.4.2 Cylinder model segmentation(圆柱模型分割)
这个实验通过读取一个pcd文件,切割出平面模型和圆柱模型,比较简单,这是PCL官网上的一个代码。
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
typedef pcl::PointXYZ PointT;
int
main(int argc, char** argv)
{
// 需要的对象
pcl::PCDReader reader;
pcl::PassThrough pass;
pcl::NormalEstimation ne;
pcl::SACSegmentationFromNormals seg;
pcl::PCDWriter writer;
pcl::ExtractIndices extract;
pcl::ExtractIndices extract_normals;
pcl::search::KdTree::Ptr tree(new pcl::search::KdTree());
// 各种数据的定义
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud(new pcl::PointCloud);
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud_filtered(new pcl::PointCloud);
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud_normals(new pcl::PointCloud);
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud_filtered2(new pcl::PointCloud);
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud_normals2(new pcl::PointCloud);
pcl::ModelCoefficients::Ptr coefficients_plane(new pcl::ModelCoefficients), coefficients_cylinder(new pcl::ModelCoefficients);
pcl::PointIndices::Ptr inliers_plane(new pcl::PointIndices), inliers_cylinder(new pcl::PointIndices);
// 读取数据
reader.read("pcd/table_scene_mug_stereo_textured.pcd", *cloud);
cout << "PointCloud has: " << cloud->points.size() << " data points." << endl;
// Passthrough方法过滤点云数据(还可以去除NAN数据)
pass.setInputCloud(cloud);
pass.setFilterFieldName("z");
pass.setFilterLimits(0, 1.5);
pass.filter(*cloud_filtered);
cout << "PointCloud after filtering has: " << cloud_filtered->points.size() << " data points." << endl;
// 估计法线
ne.setSearchMethod(tree);
ne.setInputCloud(cloud_filtered);
ne.setKSearch(50);
ne.compute(*cloud_normals);
// 创建切割对象,得到平面模型参数
seg.setOptimizeCoefficients(true);
seg.setModelType(pcl::SACMODEL_NORMAL_PLANE); // 法线平面
seg.setNormalDistanceWeight(0.1); // 设置法线距离权值
seg.setMethodType(pcl::SAC_RANSAC); // 基于随机采样
seg.setMaxIterations(100); // 最大迭代次数
seg.setDistanceThreshold(0.03); // 设置距离阈值
seg.setInputCloud(cloud_filtered);
seg.setInputNormals(cloud_normals);
// 获取平面参数
seg.segment(*inliers_plane, *coefficients_plane);
cout << "Plane coefficients: " << *coefficients_plane << endl;
// 提取平面上数据的索引
extract.setInputCloud(cloud_filtered);
extract.setIndices(inliers_plane);
extract.setNegative(false);
// 把平面索引对应的数据存放到文件中去
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud_plane(new pcl::PointCloud());
extract.filter(*cloud_plane);
cout << "PointCloud representing the planar component: " << cloud_plane->points.size() << " data points." << endl;
writer.write("table_scene_mug_stereo_textured_plane.pcd", *cloud_plane, false);
// 把平面去掉,提取剩下的点云索引
extract.setNegative(true);
extract.filter(*cloud_filtered2);
extract_normals.setNegative(true);
extract_normals.setInputCloud(cloud_normals);
extract_normals.setIndices(inliers_plane);
extract_normals.filter(*cloud_normals2);
// 创建圆柱切割对象
seg.setOptimizeCoefficients(true);
seg.setModelType(pcl::SACMODEL_CYLINDER);
seg.setMethodType(pcl::SAC_RANSAC);
seg.setNormalDistanceWeight(0.1); // 设置表面法线权重
seg.setMaxIterations(10000);
seg.setDistanceThreshold(0.05); // 设置内点到模型的距离允许最大值
seg.setRadiusLimits(0, 0.1); // 设置估计出的圆柱模型的半径范围
seg.setInputCloud(cloud_filtered2);
seg.setInputNormals(cloud_normals2);
// 获取圆柱上点云索引和圆柱参数
seg.segment(*inliers_cylinder, *coefficients_cylinder);
cout << "Cylinder coefficients: " << *coefficients_cylinder << endl;
// Write the cylinder inliers to disk
extract.setInputCloud(cloud_filtered2);
extract.setIndices(inliers_cylinder);
extract.setNegative(false);
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud_cylinder(new pcl::PointCloud());
extract.filter(*cloud_cylinder);
if (cloud_cylinder->points.empty())
cout << "Can't find the cylindrical component." << endl;
else
{
cout << "PointCloud representing the cylindrical component: " << cloud_cylinder->points.size() << " data points." << endl;
writer.write("table_scene_mug_stereo_textured_cylinder.pcd", *cloud_cylinder, false);
}
pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer viewer("切割可视化");
int v1(0), v2(1), v3(2);
viewer.createViewPort(0, 0, 0.5, 1.0, v1);
viewer.setBackgroundColor(0, 0, 0, v1);
pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom filter_color(0, 1, 0);
viewer.addPointCloud(cloud_filtered, filter_color, "cloud_filtered", v1);
/*viewer.addPointCloudNormals(cloud_normals,100,0.02,"normal",0);*/
viewer.createViewPort(0.5, 0, 1.0, 0.5, v2);
viewer.setBackgroundColor(1, 0.5, 0, v2);
pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom color(1, 0, 0);
//viewer.addPointCloud(cloud_filtered, filter_color, "cloud_filtered2", v2);
viewer.addPointCloud(cloud_plane, color, "cloud_plane", v2);
viewer.createViewPort(0.5, 0.5, 1.0, 1.0, v3);
viewer.setBackgroundColor(0, 0, 1, v3);
//viewer.addPointCloud(cloud_filtered, filter_color, "cloud_filtered1", v3);
viewer.addPointCloud(cloud_cylinder, color, "cloud_cylinder", v3);
viewer.setPointCloudRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_POINT_SIZE, 4, "CLOUD", v3);
while (!viewer.wasStopped()) {
viewer.spinOnce();
}
return (0);
}
1.4.3 Euclidean Cluster Extraction (欧几里德聚类提取)
我们通过切割平面后,得到了多个散的点云集合,然后通过聚类算法进行切割,最后进行可视化。1. 加载点云,滤波;2. 分割平面模型;3. 去除所有平面点云,
对余下的点进行聚类分割;4. 显示聚类分割结果。
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int color_bar[][3] =
{
{ 255,0,0},
{ 0,255,0 },
{ 0,0,255 },
{ 0,255,255 },
{ 255,255,0 },
{ 255,255,255 },
{ 255,0,255 }
};
int
main(int argc, char** argv)
{
// 读取点云数据
pcl::PCDReader reader;
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud(new pcl::PointCloud), cloud_f(new pcl::PointCloud);
reader.read("pcd/table_scene_lms400.pcd", *cloud);
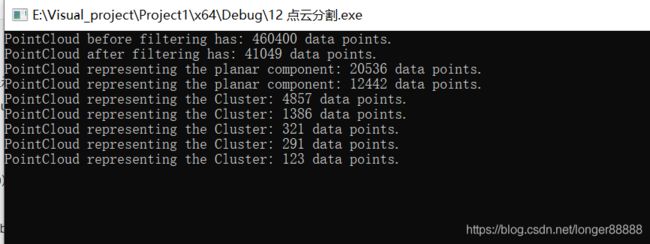
std::cout << "PointCloud before filtering has: " << cloud->points.size() << " data points." << std::endl; //*
// 下采样过滤(设置叶子为1cm),VoxelGrid过滤
pcl::VoxelGrid vg;
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud_filtered(new pcl::PointCloud);
vg.setInputCloud(cloud);
vg.setLeafSize(0.01f, 0.01f, 0.01f);
vg.filter(*cloud_filtered);
cout << "PointCloud after filtering has: " << cloud_filtered->points.size() << " data points." << endl; //*
// 可视化
pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer viewer("聚类分割");
// 显示过滤后的原点云数据
int v1(0), v2(1), v3(2);
viewer.createViewPort(0, 0, 0.5, 1.0, v1);
viewer.setBackgroundColor(0, 0, 0, v1);
pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom filter_color(0, 1, 0);
viewer.addPointCloud(cloud_filtered, filter_color, "cloud_filtered", v1);
// 为了可视化切割的平面和去除平面之后的模型
viewer.createViewPort(0.5, 0, 1.0, 0.5, v2);
viewer.setBackgroundColor(1, 0.5, 0, v2);
// 为了可视化聚类
viewer.createViewPort(0.5, 0.5, 1.0, 1.0, v3);
viewer.setBackgroundColor(0, 0, 0, v3);
// 切割对象
pcl::SACSegmentation seg;
pcl::PointIndices::Ptr inliers(new pcl::PointIndices);
pcl::ModelCoefficients::Ptr coefficients(new pcl::ModelCoefficients);
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud_plane(new pcl::PointCloud());
pcl::PCDWriter writer;
seg.setOptimizeCoefficients(true); // 优化
seg.setModelType(pcl::SACMODEL_PLANE); // 平面切割
seg.setMethodType(pcl::SAC_RANSAC);
seg.setMaxIterations(100);
seg.setDistanceThreshold(0.02);
int i = 0, nr_points = (int)cloud_filtered->points.size();
// 多次切割平面
while (cloud_filtered->points.size() > 0.3 * nr_points)
{
i++;
// 从点云切割出最大的平面
seg.setInputCloud(cloud_filtered);
seg.segment(*inliers, *coefficients);
if (inliers->indices.size() == 0)
{
cout << "Could not estimate a planar model for the given dataset." << endl;
break;
}
// 提取平面索引
pcl::ExtractIndices extract;
extract.setInputCloud(cloud_filtered);
extract.setIndices(inliers);
extract.setNegative(false);
// 把切割出来的平面保存到磁盘中
extract.filter(*cloud_plane);
cout << "PointCloud representing the planar component: " << cloud_plane->points.size() << " data points." << endl;
// 切割平面可视化
pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom cloud_in_color(1, 0, 0);//赋予显示点云的颜色
viewer.addPointCloud(cloud_plane, cloud_in_color, "planer" + to_string(i), v2);
// 删除平面索引
extract.setNegative(true);
extract.filter(*cloud_f);
cloud_filtered = cloud_f;
}
// 可视化去除平面后的模型
pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom cloud_in(cloud,
color_bar[i][0],
color_bar[i][1],
color_bar[i][2]);//赋予显示点云的颜色
viewer.addPointCloud(cloud_filtered, cloud_in,"cloud", v2);
// KdTree的搜索方式
pcl::search::KdTree::Ptr tree(new pcl::search::KdTree);
tree->setInputCloud(cloud_filtered);
std::vector cluster_indices;
// 欧几里德聚类提取
pcl::EuclideanClusterExtraction ec;
ec.setClusterTolerance(0.02); // 设置空间聚类误差2cm
ec.setMinClusterSize(100); // 设置有效聚类包含的最小的个数
ec.setMaxClusterSize(25000); // 设置有效聚类包含的最大的个数
ec.setSearchMethod(tree); // 设置搜索方法
ec.setInputCloud(cloud_filtered);
ec.extract(cluster_indices); // 获取切割之后的聚类索引保存到cluster_indices
int j = 0;
// 获取每个聚类的索引个数
for (std::vector::const_iterator it = cluster_indices.begin(); it != cluster_indices.end(); ++it)
{
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud_cluster(new pcl::PointCloud);
for (std::vector::const_iterator pit = it->indices.begin(); pit != it->indices.end(); pit++)
cloud_cluster->points.push_back(cloud_filtered->points[*pit]); //*
cloud_cluster->width = cloud_cluster->points.size();
cloud_cluster->height = 1;
cloud_cluster->is_dense = true;
cout << "PointCloud representing the Cluster: " << cloud_cluster->points.size() << " data points." << endl;
std::stringstream ss;
ss << "cloud_cluster_" << j << ".pcd";
writer.write(ss.str(), *cloud_cluster, false); //*
j++;
// 聚类可视化
pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom cloud_in_color_h(cloud,
color_bar[j][0],
color_bar[j][1],
color_bar[j][2]);//赋予显示点云的颜色
viewer.addPointCloud(cloud_cluster, cloud_in_color_h, "cluster" + to_string(j), v3);
}
while (!viewer.wasStopped()) {
viewer.spinOnce(100);
boost::this_thread::sleep(boost::posix_time::microseconds(100000));
}
return (0);
}
运行结果:在可视乎中,坐标是原模型,右下角为切割平面后的点云数据,白色的是切割平面,蓝色部分是剩余的数据。而右上角是把切割后的点云数据进行聚类的结果。

1.4.4 Region growing segmentation 区域蔓延分割实验
这个算法主要有4个参数来设置,主要要设置聚类点数上下界,蔓延时候搜索出来多少个附近点,面平滑阈值还有面的曲率阈值。
参数调试
面平滑阈值(用于对比法线)还有面的曲率阈值(用于对比曲率)是最重要的参数。如果调大了,不仅仅是同一个平面,两个平面
(它们的连着处弧度变化小的)都被视为同一个cluster.
这个代码来自于PCL官网
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int
main(int argc, char** argv)
{
// 点云指针
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud(new pcl::PointCloud);
// 读取文件
if (pcl::io::loadPCDFile ("pcd/cow.pcd", *cloud) == -1)
{
cout << "Cloud reading failed." << endl;
return (-1);
}
// 定义查询方式
pcl::search::Search::Ptr tree(new pcl::search::KdTree);
pcl::PointCloud ::Ptr normals(new pcl::PointCloud );
// 法线评估
pcl::NormalEstimation normal_estimator;
normal_estimator.setSearchMethod(tree);
normal_estimator.setInputCloud(cloud);
normal_estimator.setKSearch(50);
normal_estimator.compute(*normals); // 计算法线
// 定义索引指针
pcl::IndicesPtr indices(new std::vector );
// Passthrough滤波
pcl::PassThrough pass;
pass.setInputCloud(cloud);
pass.setFilterFieldName("z");
pass.setFilterLimits(0.0, 1.0);
pass.filter(*indices);
// 区域蔓延分割对象
pcl::RegionGrowing reg;
reg.setMinClusterSize(50); // 设置有效聚类的最小个数
reg.setMaxClusterSize(1000000); // 设置有效聚类的最大个数
reg.setSearchMethod(tree); // 定义查询方式
reg.setNumberOfNeighbours(30); // 邻居个数
reg.setInputCloud(cloud);
//reg.setIndices (indices);
reg.setInputNormals(normals);
reg.setSmoothnessThreshold(3.0 / 180.0 * M_PI); // 平滑阈值
reg.setCurvatureThreshold(1.0); // 曲线阈值
vector clusters;
reg.extract(clusters); // 分割之后的索引
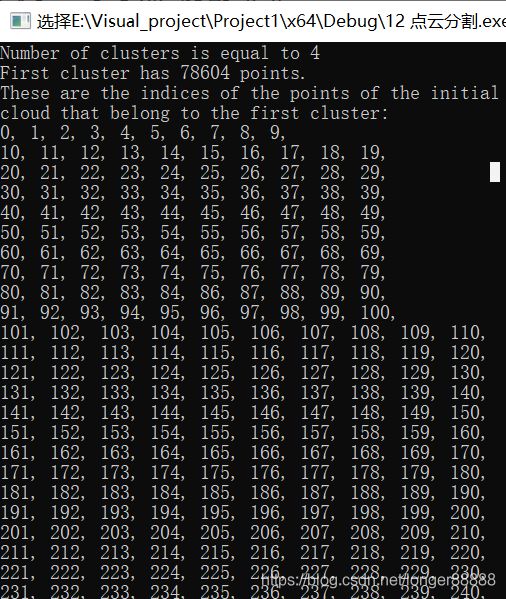
cout << "Number of clusters is equal to " << clusters.size() << endl;
cout << "First cluster has " << clusters[0].indices.size() << " points." << endl;
cout << "These are the indices of the points of the initial" <<
endl << "cloud that belong to the first cluster:" << endl;
int counter = 0;
while (counter < clusters[0].indices.size())
{
cout << clusters[0].indices[counter] << ", ";
counter++;
if (counter % 10 == 0)
cout << endl;
}
cout << endl;
// 获得颜色
pcl::PointCloud ::Ptr colored_cloud = reg.getColoredCloud();
pcl::visualization::CloudViewer viewer("Cluster viewer");
viewer.showCloud(colored_cloud);
while (!viewer.wasStopped())
{
}
return (0);
}
运行结果
reg.setSmoothnessThreshold(3.0 / 180.0 * M_PI); // 平滑阈值

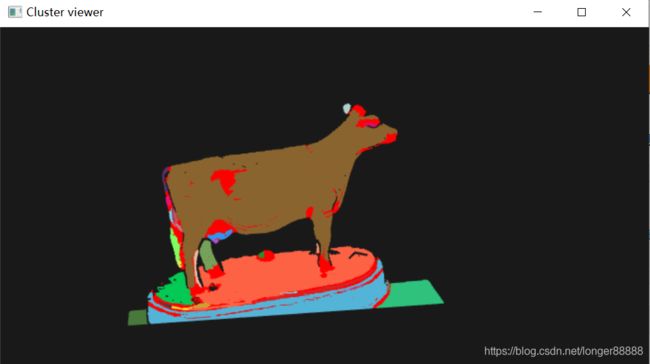 增大平缓阈值,reg.setSmoothnessThreshold(10.0 / 180.0 * M_PI); // 平滑阈值,可以发现几乎整个模型都成了一类了
增大平缓阈值,reg.setSmoothnessThreshold(10.0 / 180.0 * M_PI); // 平滑阈值,可以发现几乎整个模型都成了一类了

1.4.5 Color-based region growing segmentation (基于彩色信息区域蔓延分割)
这个算法参数比较多,只是把区域蔓延算法由法线方式改成了颜色相似性判断。
其参数有DistanceThreshold 为距离阈值(为了判断点云中两点是否为相邻点),
ColorThreshold 为两点颜色阈值(判断两点之间的颜色RGB的距离),
RegionColorThreshold为两个聚类之间的颜色阈值(用于聚类合并阶段),
MinClusterSize 为一个聚类的最少点数目
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int
main(int argc, char** argv)
{
// 定义时间
time_t start, end, diff[5], option;
start = time(0);
bool Bool_Cuting = true, b_n = true;
int MinClusterSize = 600, KN_normal = 50; // 最小聚类的个数
//
float far_cuting = 10, near_cuting = 0, DistanceThreshold = 10.0, ColorThreshold = 6, RegionColorThreshold = 5,
SmoothnessThreshold = 30.0, CurvatureThreshold = 0.05;
// 读取点云数据
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud(new pcl::PointCloud);
if (pcl::io::loadPCDFile ("pcd/07/two_human1.pcd", *cloud) == -1)
{
cout << "Cloud reading failed." << endl;
return (-1);
}
end = time(0); // 结束时间
diff[0] = difftime(end, start); // 计算时间差(读取点云读取的时间)
PCL_INFO("\Loading pcd file takes(seconds): %d\n", diff[0]);
//创建一个指向kd数搜索的指针
pcl::search::Search ::Ptr tree = boost::shared_ptr >(new pcl::search::KdTree);
// 法线评估步骤 Noraml estimation step(1 parameter)
pcl::search::Search::Ptr tree1 = boost::shared_ptr >(new pcl::search::KdTree);
pcl::PointCloud ::Ptr normals(new pcl::PointCloud );
pcl::NormalEstimation normal_estimator;
normal_estimator.setSearchMethod(tree);
normal_estimator.setInputCloud(cloud);
normal_estimator.setKSearch(KN_normal);
normal_estimator.compute(*normals); // 计算法线
end = time(0);
diff[1] = difftime(end, start) - diff[0]; // 计算法线所需的时间
PCL_INFO("\Estimating normal takes(seconds): %d\n", diff[1]);
// Optional step: cutting away the clutter scene too far away from camera
pcl::IndicesPtr indices(new std::vector );
if (Bool_Cuting)//是否通过z轴范围对待处理数据进行裁剪
{
// Passthrough过滤
pcl::PassThrough pass;
pass.setInputCloud(cloud);
pass.setFilterFieldName("z");
pass.setFilterLimits(near_cuting, far_cuting);
pass.filter(*indices);
}
// 基于颜色的区域蔓延的实例
pcl::RegionGrowingRGB reg;
reg.setInputCloud(cloud);
if (Bool_Cuting) reg.setIndices(indices);
reg.setSearchMethod(tree);
reg.setDistanceThreshold(DistanceThreshold);
reg.setPointColorThreshold(ColorThreshold);
reg.setRegionColorThreshold(RegionColorThreshold);
reg.setMinClusterSize(MinClusterSize);
if (b_n)
{
reg.setSmoothModeFlag(true);
reg.setCurvatureTestFlag(true);
reg.setInputNormals(normals);
reg.setSmoothnessThreshold(SmoothnessThreshold / 180.0 * M_PI);
reg.setCurvatureThreshold(CurvatureThreshold);
}
std::vector clusters;
reg.extract(clusters);
end = time(0);
diff[2] = difftime(end, start) - diff[0] - diff[1];
PCL_INFO("\RGB region growing takes(seconds): %d\n", diff[2]);
// reg.getColoredCloud()对于不同的聚类分割结果,随机赋予颜色,但是不能保证所有聚类的颜色都不同
pcl::PointCloud ::Ptr colored_cloud = reg.getColoredCloud();
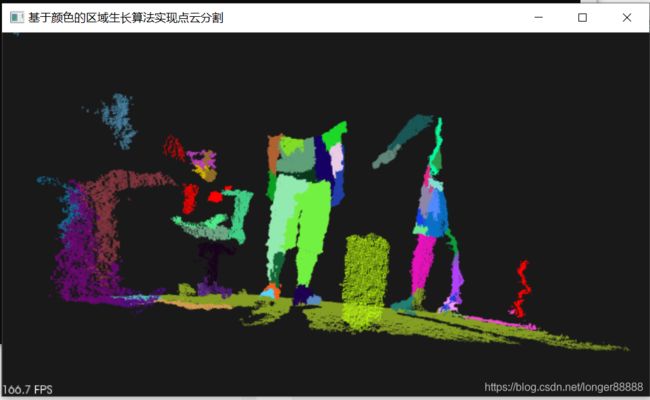
pcl::visualization::CloudViewer viewer("基于颜色的区域生长算法实现点云分割");
viewer.showCloud(colored_cloud);
while (!viewer.wasStopped())
{
boost::this_thread::sleep(boost::posix_time::microseconds(100));
}
return (0);
}
运行结果:
1.4.6 Min-cut Based Segmentation (基于最少切割的分割)
代码来源于PCL官网。
这种方法参数很多,调试出好的效果需要太多次,所以很麻烦。另外鲁棒性很不好,我认为这种方法作为了解比较好。
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
pcl::PointCloud ::Ptr cloud(new pcl::PointCloud );
// 读取点云数据
if (pcl::io::loadPCDFile ("pcd/min_cut_segmentation_tutorial.pcd", *cloud) == -1)
{
std::cout << "Cloud reading failed." << std::endl;
return (-1);
}
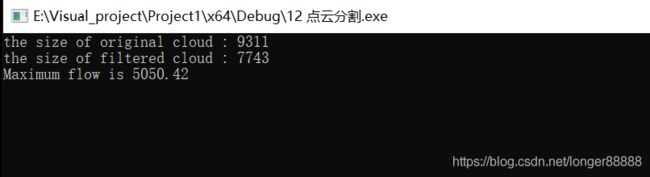
cout << "the size of original cloud : " << cloud->points.size() << endl;
pcl::IndicesPtr indices(new std::vector );
// 直通滤波过滤
pcl::PassThrough pass;
pass.setInputCloud(cloud);
pass.setFilterFieldName("z");
pass.setFilterLimits(0, 1.0);
pass.filter(*indices);
cout << "the size of filtered cloud : " << indices->size() << endl;
// 创建PointXYZ最小割对象
pcl::MinCutSegmentation seg;
seg.setInputCloud(cloud); // 输入点云数据
seg.setIndices(indices); // 输入点云索引
// 定义前景点云(目标点云)指针
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr foreground_points(new pcl::PointCloud());
pcl::PointXYZ point;
point.x = 68.97;
point.y = -18.55;
point.z = 0.57;
foreground_points->points.push_back(point);
seg.setForegroundPoints(foreground_points); // 设置前景点云的中心点
// 最小割的参数设置
seg.setSigma(0.25); // 设置平滑成本的Sigma值
seg.setRadius(3.0433856); // 设置背景惩罚权重的半径
seg.setNumberOfNeighbours(14); // 设置临近点数目
seg.setSourceWeight(0.8); // 设置前景惩罚权重
std::vector clusters;
seg.extract(clusters); // 获取分割的结果,把分割结果保存在点云索引的向量中
std::cout << "Maximum flow is " << seg.getMaxFlow() << std::endl; // 设置分割期间所计算出的流
pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer viewer("最小割的分割算法");
//int v1(0), v2(1);
//viewer.createViewPort(0, 0, 0.5, 1.0, v1);
//viewer.setBackgroundColor(0, 0, 0, v1);
//viewer.addPointCloud(cloud, "cloud", v1);
//viewer.createViewPort(0.5, 0, 1.0, 1.0, v2);
//viewer.setBackgroundColor(0, 0, 0, v2);
pcl::PointCloud ::Ptr colored_cloud = seg.getColoredCloud();
viewer.addPointCloud(colored_cloud, "colored");
可视化原图
//pcl::visualization::CloudViewer origin("原图");
//origin.showCloud(cloud);
获得点云自身的颜色
//pcl::PointCloud ::Ptr colored_cloud = seg.getColoredCloud();
//pcl::visualization::CloudViewer viewer("最小割的分割算法");
//viewer.showCloud(colored_cloud);
while (!viewer.wasStopped())
{
viewer.spinOnce();
}
return (0);
}
二、总结
本周学习了前六个点云分割方法,明白了点云分割的作用所在,剩下的几个分割算法会在后续补充。
三、参考文献
RANSAC的介绍(这个博客很清楚了讲解什么是RANSAC和一致性)
点云分割(这篇博客用作者自己的看法讲解了几个分割算法)