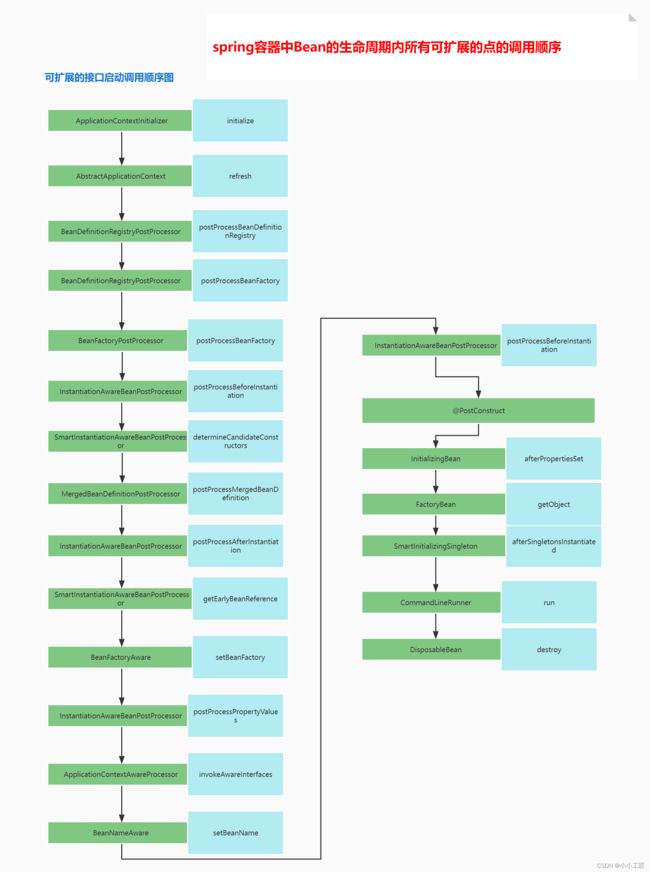
Spring - BeanFactoryPostProcessor 扩展接口
文章目录
- Pre
- org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanFactoryPostProcessor
- 源码探究
-
- 1 是否实现BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 接口,分别写入集合
- 2 处理实现了的PriorityOrdered和 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors 的 bean
- 3. 处理实现了的Ordered和BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors 的 bean
- 4 处理其他实现了BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor的bean
- 5 invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors
- 6 除了试下BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor之外的其他 实现了BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口的bean 分类
- 7 处理 PriorityOrdered ,invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors
- 8 处理 Ordered ,invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors
- 9 处理剩下的 ,invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors
- 10 invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors & invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors 分析
- BeanFactoryPostProcessor的处理流程
- 扩展方式
![]()
Pre
Spring Boot - 扩展接口一览
org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanFactoryPostProcessor
这个接口是beanFactory的扩展接口,调用时机在spring在读取beanDefinition信息之后,实例化bean之前。
在这个时机,用户可以通过实现这个扩展接口来自行处理一些东西,比如修改已经注册的beanDefinition的元信息
package org.springframework.beans.factory.config;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
/**
* Factory hook that allows for custom modification of an application context's
* bean definitions, adapting the bean property values of the context's underlying
* bean factory.
*
* Useful for custom config files targeted at system administrators that
* override bean properties configured in the application context. See
* {@link PropertyResourceConfigurer} and its concrete implementations for
* out-of-the-box solutions that address such configuration needs.
*
*
A {@code BeanFactoryPostProcessor} may interact with and modify bean
* definitions, but never bean instances. Doing so may cause premature bean
* instantiation, violating the container and causing unintended side-effects.
* If bean instance interaction is required, consider implementing
* {@link BeanPostProcessor} instead.
*
*
Registration
* An {@code ApplicationContext} auto-detects {@code BeanFactoryPostProcessor}
* beans in its bean definitions and applies them before any other beans get created.
* A {@code BeanFactoryPostProcessor} may also be registered programmatically
* with a {@code ConfigurableApplicationContext}.
*
*
Ordering
* {@code BeanFactoryPostProcessor} beans that are autodetected in an
* {@code ApplicationContext} will be ordered according to
* {@link org.springframework.core.PriorityOrdered} and
* {@link org.springframework.core.Ordered} semantics. In contrast,
* {@code BeanFactoryPostProcessor} beans that are registered programmatically
* with a {@code ConfigurableApplicationContext} will be applied in the order of
* registration; any ordering semantics expressed through implementing the
* {@code PriorityOrdered} or {@code Ordered} interface will be ignored for
* programmatically registered post-processors. Furthermore, the
* {@link org.springframework.core.annotation.Order @Order} annotation is not
* taken into account for {@code BeanFactoryPostProcessor} beans.
*
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @author Sam Brannen
* @since 06.07.2003
* @see BeanPostProcessor
* @see PropertyResourceConfigurer
*/
@FunctionalInterface
public interface BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
/**
* Modify the application context's internal bean factory after its standard
* initialization. All bean definitions will have been loaded, but no beans
* will have been instantiated yet. This allows for overriding or adding
* properties even to eager-initializing beans.
* @param beanFactory the bean factory used by the application context
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors
*/
void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException;
}
spring容器初始化时,从资源中读取到bean的相关定义后,保存在beanFactory的成员变量中(DefaultListableBeanFactory#beanDefinitionMap)
private final Map<String, BeanDefinition> beanDefinitionMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(256);
实例化bean的操作就是依据这些BeanDefinition来做的。
在实例化之前,spring允许我们通过自定义扩展来改变bean的定义,定义一旦变了,后面的实例也就变了,而beanFactory后置处理器BeanFactoryPostProcessor就是用来改变bean定义的。
源码探究
AbstractApplicationContext#refresh 继续走起
继续
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
主要功能是: 找出所有beanFactory后置处理器,并且调用这些处理器来改变bean的定义
继续 org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext#invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors
/**
* Instantiate and invoke all registered BeanFactoryPostProcessor beans,
* respecting explicit order if given.
* Must be called before singleton instantiation.
*/
protected void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory, getBeanFactoryPostProcessors());
.......
我们重点关注PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate#invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors
PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory, getBeanFactoryPostProcessors());
代码比较长,我们逐段看一下
1 是否实现BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 接口,分别写入集合
for (BeanFactoryPostProcessor postProcessor : beanFactoryPostProcessors) {
if (postProcessor instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) {
BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor registryProcessor =
(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) postProcessor;
registryProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(registry);
registryProcessors.add(registryProcessor);
}
else {
regularPostProcessors.add(postProcessor);
}
}
遍历入参 beanFactoryPostProcessors , 是否实现了BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor,分别放入两个集合:registryProcessors和regularPostProcessors;
2 处理实现了的PriorityOrdered和 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors 的 bean
// First, invoke the BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered.
String[] postProcessorNames =
beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
processedBeans.add(ppName);
}
}
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry, beanFactory.getApplicationStartup());
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();
找出所有实现了BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口和PriorityOrdered接口的bean,放入registryProcessors集合,根据PriorityOrdered接口来排序,然后这些bean会被invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors方法执行;
3. 处理实现了的Ordered和BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors 的 bean
// Next, invoke the BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement Ordered.
postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName) && beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
processedBeans.add(ppName);
}
}
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry, beanFactory.getApplicationStartup());
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();
找出所有实现了BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口和Ordered接口的bean,放入registryProcessors集合,根据Ordered接口来排序,然后这些bean会被invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors方法执行;
4 处理其他实现了BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor的bean
// Finally, invoke all other BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors until no further ones appear.
boolean reiterate = true;
while (reiterate) {
reiterate = false;
postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName)) {
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
processedBeans.add(ppName);
reiterate = true;
}
}
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry, beanFactory.getApplicationStartup());
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();
}
对于那些实现了BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口,但是没有实现PriorityOrdered和Ordered的bean也被找出来,然后这些bean会被invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors方法执行
5 invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors
// Now, invoke the postProcessBeanFactory callback of all processors handled so far.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(registryProcessors, beanFactory);
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(regularPostProcessors, beanFactory);
6 除了试下BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor之外的其他 实现了BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口的bean 分类
// Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans
// uninitialized to let the bean factory post-processors apply to them!
String[] postProcessorNames =
beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
// Separate between BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered,
// Ordered, and the rest.
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> orderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> nonOrderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (processedBeans.contains(ppName)) {
// skip - already processed in first phase above
}
else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {
priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {
orderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
else {
nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
}
找出实现了BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口的bean,注意这里已将前面实现了BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口的bean给剔除了
if (processedBeans.contains(ppName)) {
// skip - already processed in first phase above
}
将这些bean分为三类:
- 实现了PriorityOrdered接口的放入priorityOrderedPostProcessors,
- 实现了Ordered接口的放入orderedPostProcessorNames,
- 其他的放入nonOrderedPostProcessorNames,这段代码是关键,自定义的实现BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口的bean就会在此处被查找出来。
7 处理 PriorityOrdered ,invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors
// First, invoke the BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered.
sortPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
8 处理 Ordered ,invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors
// Next, invoke the BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement Ordered.
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(orderedPostProcessorNames.size());
for (String postProcessorName : orderedPostProcessorNames) {
orderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
sortPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
9 处理剩下的 ,invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors
// Finally, invoke all other BeanFactoryPostProcessors.
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> nonOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.size());
for (String postProcessorName : nonOrderedPostProcessorNames) {
nonOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(nonOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
10 invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors & invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors 分析
从上面的分析可以发现,所有实现了BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口的bean,都被作为入参,然后调用了invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors或者invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors方法去处理
/**
* Invoke the given BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor beans.
*/
private static void invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(
Collection<? extends BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> postProcessors, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, ApplicationStartup applicationStartup) {
for (BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor postProcessor : postProcessors) {
StartupStep postProcessBeanDefRegistry = applicationStartup.start("spring.context.beandef-registry.post-process")
.tag("postProcessor", postProcessor::toString);
postProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(registry);
postProcessBeanDefRegistry.end();
}
}
/**
* Invoke the given BeanFactoryPostProcessor beans.
*/
private static void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(
Collection<? extends BeanFactoryPostProcessor> postProcessors, ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
for (BeanFactoryPostProcessor postProcessor : postProcessors) {
StartupStep postProcessBeanFactory = beanFactory.getApplicationStartup().start("spring.context.bean-factory.post-process")
.tag("postProcessor", postProcessor::toString);
postProcessor.postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
postProcessBeanFactory.end();
}
}
对每个BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口的实现类,都调用了其接口方法。
不同的是 对于实现了BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口的bean,调用其postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry方法的时候,入参是BeanDefinitionRegistry,而非BeanFactory,因此,实现了BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口的bean,其postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry在被调用时,可以通过入参BeanDefinitionRegistry来做更多和bean的定义有关的操作,例如注册bean等等、
BeanFactoryPostProcessor的处理流程
小结一下:
ApplicationContext扩展类可以调用AbstractApplicationContext.addBeanFactoryPostProcessor方法,将自定义的BeanFactoryPostProcessor实现类保存到ApplicationContext中;- spring容器初始化时,上一步中被加入到
ApplicationContext的bean会被优先调用其postProcessBeanFactory方法; - 自定义的
BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口实现类,也会被找出来,然后调用其postProcessBeanFactory方法; postProcessBeanFactory方法被调用时,beanFactory会被作为参数传入,自定义类中可以使用该参数来处理bean的定义,达到业务需求;- 此时的spring容器还没有开始实例化bean,因此自定义的
BeanFactoryPostProcessor实现类不要做与bean实例有关的操作,而是做一些与bean定义有关的操作,例如修改某些字段的值,这样后面实例化的bean的就会有相应的改变;
扩展方式
package com.artisan.bootspringextend.testextends;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanFactoryPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableListableBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
/**
* @author 小工匠
* @version 1.0
* @date 2022/11/27 16:58
* @mark: show me the code , change the world
*/
@Slf4j
@Configuration
public class ExtendBeanFactoryPostProcessor implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
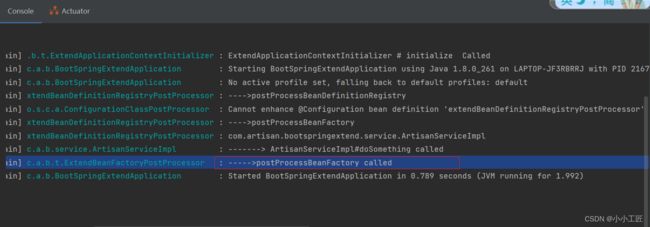
log.info("----->postProcessBeanFactory called ");
}
}