Seq2Seq+Attention 的 tensorflow-1.14 实现
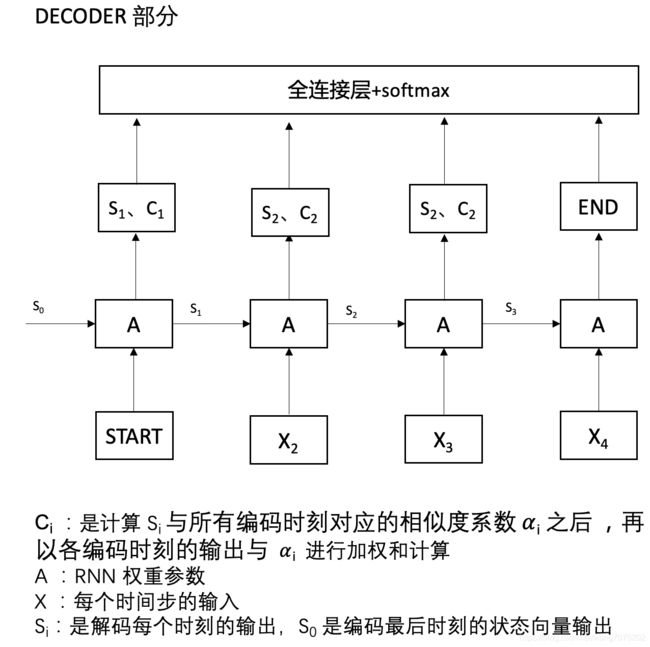
attention 的原理自己找,这里只展示原理,用来进行翻译功能。解码过程的原理如图所示,将当前时刻的隐层输出向量和上下文向量拼接得到该时刻的输出向量,以供后续的全连接层和 softmax 的计算。
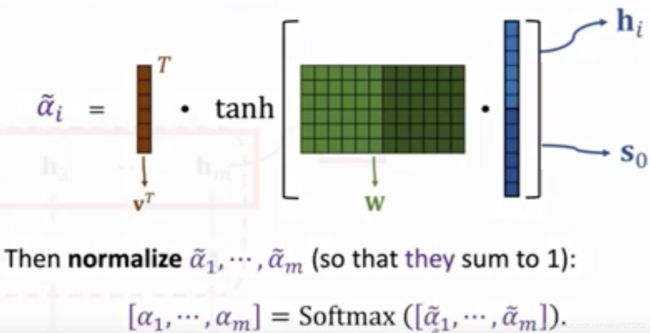
所用到的相似度计算方法,这里用到了如图所示的方法,这张图说明了 decoder 到 s0 时刻,s0 的输出向量和 encoder 的所有时间步输出 hi 的相似度方法。
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
tf.reset_default_graph()
# 创造了 3 个简单的样本,每个样本的输出和输出都直接给出,只为说明原理,实际数据处理类似拼接起始符号、结束符号、占位符
sentences = [['ich mochte ein bier P', 'S i want a beer P', 'i want a beer P E'],
['sa fdgf cvb fgb P', 'S i hate tow boys P', 'i hate tow boys P E'],
['lxvbi gf bf snsn P', 'S i like a qizi P', 'i like a qizi P E']]
# 词典
words = []
for sentence in sentences:
for word in ' '.join(sentence).split(' '):
if word not in words:
words.append(word)
# 词和索引的映射
word2idx = {v:k for k,v in enumerate(words)}
idx2word = {k:v for k,v in enumerate(words)}
# 生成 encoder 输入, decoder 的输出、目标
def make_batch(sentences):
input_batch, output_batch, target_batch = [], [], []
for sentence in sentences:
input = [word2idx[word] for word in sentence[0].split(' ')]
output = [word2idx[word] for word in sentence[1].split(' ')]
target = [word2idx[word] for word in sentence[2].split(' ')]
input_batch.append(input)
output_batch.append(output)
target_batch.append(target)
return input_batch, output_batch, target_batch
# 构造模型
class Model:
def __init__(self):
# 词典大小
self.V = len(words)
# 时间步长
self.step = 5
# 隐层大小
self.hidden = 256
# 词向量维度
self.dim = 32
# 初始化词向量
self.embedding = tf.get_variable(name='embedding', shape=[self.V, self.dim], initializer=tf.random_normal_initializer())
# 计算相似度的向量所用到的 W 和 T 向量,不懂看图
self.W = tf.get_variable(name="W",shape=[self.hidden*2, self.hidden],initializer=tf.random_normal_initializer())
self.T = tf.get_variable(name="T", shape=[self.hidden, 1], initializer=tf.random_normal_initializer())
# 输出分类时用到的向量
self.out = tf.get_variable(name="out", shape=[self.hidden*2, self.V], initializer=tf.random_normal_initializer())
# 初始化 dropout
self.dropout = tf.placeholder(tf.float32)
# 初始化 encoder 输入
self.enc_inputs = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, shape=[None, None])
# 初始化 decoder 输入
self.dec_inputs = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, shape=[None, None])
# 初始化 decoder 输出
self.targets = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, shape=[None, None])
# 构造图
with tf.variable_scope('net') as scope:
self.buile_net()
def buile_net(self):
# encoder 的输入词嵌入
enc_inputs_embedding = tf.nn.embedding_lookup(self.embedding, self.enc_inputs) # [batch_size, step+1, dim]
# decoder 的输入词嵌入
dec_inputs_embedding = tf.nn.embedding_lookup(self.embedding, self.dec_inputs) # [batch_size, step+1, dim]
# 计算所有 batch 样本的该时间步的 encode 输出与对应样本的 dec_output 的相似度,因为有 batch_size 个样本, 所以返回结果有 batch_size 个权重参数
# dec_hidden:[batch_size, hidden] enc_output:[batch_size, hidden]
def get_att_score(dec_hidden, enc_output):
dec_output_enc_output = tf.concat([dec_hidden, enc_output], axis=1) # [batch_size, 2*hidden]将该时间步上的 encode 输出和 decode 输出拼接
tmp = tf.nn.tanh(tf.matmul(dec_output_enc_output, self.W)) # (batch_size, hidden)
a = tf. matmul(tmp, self.T) # [batch_size, 1]
a = tf.squeeze(a, [1]) # [batch_size]
return a
# 计算 batch 中每一个样本输出 enc_output 的对应的权重参数,因为有 batch_size 个样本,有 step 个时间步,所有返回结果是 [batch_size, step] 大小
# dec_hidden:[batch_size, hidden], enc_outputs:[batch_size, step, hidden]
def get_att_weight(dec_hidden, enc_outputs):
attn_scores = [] # [step , ]
enc_outputs = tf.transpose(enc_outputs, [1, 0, 2]) # 将 enc_outputs 的时间维度放到前面 [step, batch_size, n_hidden]
for i in range(self.step):
a = get_att_score(dec_hidden, enc_outputs[i]) # [batch_size] 因为有 batch_size 个样本,所有有 batch_size 个权重参数
attn_scores.append(a)
attn_scores = tf.transpose(tf.convert_to_tensor(attn_scores),[1,0]) # 从 [step, batch_size] 转换为 [batch_size, step], 每一行都是该样本对于 dec_output 的每个时间步上的权重参数
sfmx = tf.nn.softmax(attn_scores) # [batch_size, step] 每一行都是经过 softmax 的权重参数
return sfmx
# encoder
with tf.variable_scope('encode'):
enc_cell = tf.nn.rnn_cell.BasicRNNCell(self.hidden)
enc_cell = tf.nn.rnn_cell.DropoutWrapper(enc_cell, output_keep_prob=self.dropout)
# enc_outputs : [batch_size, step, hidden],enc_hidden : [batch_size, hidden]
enc_outputs, enc_hidden = tf.nn.dynamic_rnn(enc_cell, enc_inputs_embedding, dtype=tf.float32)
# 存放 decoder 每个时间步的输出概率矩阵
model = [] # [step+1, batch_size, V]
# decoder
with tf.variable_scope('decode'):
dec_cell = tf.nn.rnn_cell.BasicRNNCell(self.hidden)
dec_cell = tf.nn.rnn_cell.DropoutWrapper(dec_cell, output_keep_prob=self.dropout)
# deocoder 输入转换为以时间步为主的矩阵
inputs = tf.transpose(dec_inputs_embedding, [1, 0, 2]) # [max_time, batch_size, dim]
dec_hidden = enc_hidden
# 遍历所有时间步,每个时间步进行相似度计算,解码
for i in range(self.step+1):
# dec_output: [1, batch_size, hidden] , dec_hidden: [batch_size, hidden]
dec_output, dec_hidden = tf.nn.dynamic_rnn(dec_cell, tf.expand_dims(inputs[i], 0), initial_state=dec_hidden, dtype=tf.float32, time_major=True)
# dec_hidden:[batch_size, , hidden], enc_outputs:[batch_size, step, hidden]
attn_weights = get_att_weight(dec_hidden, enc_outputs) # attn_weights : [batch_size, step]
# matrix-matrix product of matrices [batch_size, 1, step] x [batch_size, step, hidden] = [batch_size, 1, hidden]
context = tf.matmul(tf.expand_dims(attn_weights, 1), enc_outputs) # 扩展 attn_weights 维度,方便其与编码各时刻输出 enc_outputs 的权重特征和 [batch_size, 1, hidden]
context = tf.squeeze(context, 1) # 得到的上下文特征向量,去掉第二维度 [batch_size, hidden]
r = tf.matmul(tf.concat((dec_hidden, context), 1), self.out) # 将该时间步的隐层输出和 context 拼接得到的特征向量去进行计算得到概率矩阵 [batch_size, V]
model.append(r)
model = tf.transpose(model, [1, 0, 2]) # 从 [step+1, batch_size, V] 转为 [batch_size, step+1, V]
# 预测
self.prediction = tf.argmax(model, 2)
# 计算损失
self.cost = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=model, labels=self.targets)) # logits : [batch_size, step+1, V], labels: [batch_size, step+1]
# 优化
self.optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(0.001).minimize(self.cost)
# 初始化 Model
m = Model()
# 初始化 tf
sess = tf.Session()
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
sess.run(init)
# 训练模型
for epoch in range(5000):
input_batch, output_batch, target_batch = make_batch(sentences)
_, loss = sess.run([m.optimizer, m.cost], feed_dict={m.enc_inputs: input_batch, m.dec_inputs: output_batch, m.targets: target_batch, m.dropout:0.5})
if (epoch + 1) % 200 == 0:
print('Epoch:', '%06d' % (epoch + 1), 'cost =', '{:.8f}'.format(loss))
# 简单预测
def translate(sentence):
words = [[word2idx[word] for word in sentence.split()]]
predict_batch = [[word2idx['S']]+[word2idx[n] for n in ['P']*m.step]]
result = sess.run(m.prediction, feed_dict={m.enc_inputs: words, m.dec_inputs: predict_batch, m.dropout:1.}) # m.dropout:1 预测的时候不需要 dropout
decoded = [idx2word[idx]for idx in result[0]]
return ' '.join(decoded).replace('P','').replace('E','')
print('ich mochte ein bier --->', translate('ich mochte ein bier P'))
print('sa fdgf cvb fgb --->', translate('sa fdgf cvb fgb P'))
print('lxvbi gf bf snsn --->', translate('lxvbi gf bf snsn P'))
打印结果:
Epoch: 000200 cost = 0.00000014
Epoch: 000400 cost = 0.00000291
Epoch: 000600 cost = 0.02432251
Epoch: 000800 cost = 0.00000000
Epoch: 001000 cost = 0.00000000
Epoch: 001200 cost = 0.00000000
Epoch: 001400 cost = 0.00000000
Epoch: 001600 cost = 0.00000000
Epoch: 001800 cost = 0.00000000
Epoch: 002000 cost = 0.00000000
Epoch: 002200 cost = 0.00000000
Epoch: 002400 cost = 0.00000000
Epoch: 002600 cost = 0.00000000
Epoch: 002800 cost = 0.00000000
Epoch: 003000 cost = 0.00000000
Epoch: 003200 cost = 0.00000000
Epoch: 003400 cost = 0.00000000
Epoch: 003600 cost = 0.00000000
Epoch: 003800 cost = 0.00000000
Epoch: 004000 cost = 0.00000000
Epoch: 004200 cost = 0.00000000
Epoch: 004400 cost = 0.00000000
Epoch: 004600 cost = 0.00000000
Epoch: 004800 cost = 0.00000000
Epoch: 005000 cost = 0.00000000
ich mochte ein bier ---> i want a beer
sa fdgf cvb fgb ---> i hate tow boys
lxvbi gf bf snsn ---> i like a qizi
其他方法
对于计算 attention 相似度还有一种类似 transformer 的方法如下图
只需要将上面的代码中的 get_att_score 方法替换成下面的即可
def get_att_score(dec_hidden, enc_output):
k = tf.expand_dims(tf.matmul(enc_output, self.WK), 1) # 抽取编码输出特征 [batch_size, 1, hdidden]
q = tf.expand_dims(tf.matmul(dec_hidden, self.WQ), 2) # 抽取解码输出特征 [batch_size, hidden, 1]
a = tf.matmul(k, q) # (batch_size, 1, 1)
a = tf.squeeze(a, [1, 2]) # [batch_size]
return a
结果打印:
Epoch: 000200 cost = 0.00049959
Epoch: 000400 cost = 0.00007502
Epoch: 000600 cost = 0.00000001
Epoch: 000800 cost = 0.00000665
Epoch: 001000 cost = 0.00011789
Epoch: 001200 cost = 0.00000470
Epoch: 001400 cost = 0.00000001
Epoch: 001600 cost = 0.00000000
Epoch: 001800 cost = 0.00000000
Epoch: 002000 cost = 0.00000001
Epoch: 002200 cost = 0.00000011
Epoch: 002400 cost = 0.00000001
Epoch: 002600 cost = 0.00000000
Epoch: 002800 cost = 0.00000000
Epoch: 003000 cost = 0.00000000
Epoch: 003200 cost = 0.00000000
Epoch: 003400 cost = 0.00000000
Epoch: 003600 cost = 0.00000000
Epoch: 003800 cost = 0.00000057
Epoch: 004000 cost = 0.00000002
Epoch: 004200 cost = 0.00000001
Epoch: 004400 cost = 0.00000000
Epoch: 004600 cost = 0.00000000
Epoch: 004800 cost = 0.00196500
Epoch: 005000 cost = 0.00000001
ich mochte ein bier ---> i want a beer
sa fdgf cvb fgb ---> i hate tow boys
lxvbi gf bf snsn ---> i like a qizi
