【动手学习pytorch笔记】18.微调
微调
在大样本数据集上进行预训练,再在子任务上进行微调,这样可以使我的可学习参数不用从头开始学习,微调也是CV领域中很重要的一个技术,NLP也在向这个方向发展,也是因为微调,深度学习才在工业上取得了比较好的效果。
%matplotlib inline
import os
import torch
import torchvision
from torch import nn
from d2l import torch as d2l
train_imgs = torchvision.datasets.ImageFolder(os.path.join('./hotdog', 'train'))
test_imgs = torchvision.datasets.ImageFolder(os.path.join('./hotdog','test'))
hotdogs = [train_imgs[i][0] for i in range(8)]
not_hotdogs = [train_imgs[-i - 1][0] for i in range(8)]
d2l.show_images(hotdogs + not_hotdogs, 2, 8, scale=1.4);
下载了一个热狗数据集
二分类问题,热狗作为正类,其他作为父类
# 使用RGB通道的均值和标准差,以标准化每个通道
normalize = torchvision.transforms.Normalize(
[0.485, 0.456, 0.406], [0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
train_augs = torchvision.transforms.Compose([
torchvision.transforms.RandomResizedCrop(224),
torchvision.transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(),
torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(),
normalize])
test_augs = torchvision.transforms.Compose([
torchvision.transforms.Resize(256),
torchvision.transforms.CenterCrop(224),
torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(),
normalize])
因为在ImageNet上进行了上述处理,所以在我们自己的数据集上也要做相同的处理
torchvision.transforms.Normalize()中的mean和std参数做什么用呢?疑问1:
按照我的理解,归一化就是要把图片3个通道中的数据整理到[-1, 1]区间。 x = (x - mean(x))/stddev(x)
只要输入数据集x确定了,mean(x)和stddev(x)也就是确定的数值了,为什么Normalize()函数还需要输入mean和std的数值呢?答:mean 和 std肯定要在normalize之前自己先算好再传进去的,不然每次normalize程序就得把所有的图片都读取一遍算这两个数
疑问2: RGB单个通道的值不是[0, 255]吗?所以一个通道的均值应该在127附近才对。如果Normalize()函数按照下面的版式去计算 x = (x - mean)/std 因为RGB是[0,255],算出来的x就不可能落在[-1, 1]区间了。
答:有两种情况:
- 如果是imagenet数据集,那么ImageNet的数据在加载的时候就已经转换成了[0, 1].
- 应用了torchvision.transforms.ToTensor,其作用是 ( Converts a PIL Image ornumpy.ndarray (H x W x C) in the range [0, 255] to a torch.FloatTensorof shape (C x H x W) in the range [0.0, 1.0] )
疑问3: 可我看很多代码里面是这样的: torchvision.transforms.Normalize(mean=[0.485,
0.456, 0.406], std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225]) 这一组值是怎么来的? 为什么这三个通道的均值都是小于1的值呢?答:[0.485, 0.456, 0.406]这一组平均值是从imagenet训练集中抽样算出来的。
这就是ImageNet上用ResNet18训练的预训练模型
pretrained_net = torchvision.models.resnet18(pretrained=True)
注意参数
pretrained=True
Downloading: "https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnet18-f37072fd.pth" to C:\Users\我YMK/.cache\torch\hub\checkpoints\resnet18-f37072fd.pth
查看预训练模型的输出层
pretrained_net.fc
输出
Linear(in_features=512, out_features=1000, bias=True)
可以看到预训练模型的输出层是ImageNet上的分类任务,有1000个种类
然后我们自己构建的模型
finetune_net = torchvision.models.resnet18(pretrained=True)
finetune_net.fc = nn.Linear(finetune_net.fc.in_features, 2)
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(finetune_net.fc.weight)
finetune_net.fc = nn.Linear(finetune_net.fc.in_features, 2)改变输出层,因为我们要做的是热狗的二分类问题
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(finetune_net.fc.weight);对输出层的权重进行初始化,
xavier输入和输出相同
训练
# 如果param_group=True,输出层中的模型参数将使用十倍的学习率
def train_fine_tuning(net, learning_rate, batch_size=128, num_epochs=5,
param_group=True):
train_iter = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(torchvision.datasets.ImageFolder(
os.path.join('./hotdog', 'train'), transform=train_augs),
batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True)
test_iter = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(torchvision.datasets.ImageFolder(
os.path.join('./hotdog', 'test'), transform=test_augs),
batch_size=batch_size)
devices = d2l.try_all_gpus()
loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss(reduction="none")
if param_group:
params_1x = [
param for name, param in net.named_parameters()
if name not in ["fc.weight", "fc.bias"]]
trainer = torch.optim.SGD([{'params': params_1x},
{'params': net.fc.parameters(),
'lr': learning_rate * 10}],
lr=learning_rate, weight_decay=0.001)
else:
trainer = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=learning_rate,
weight_decay=0.001)
d2l.train_ch13(net, train_iter, test_iter, loss, trainer, num_epochs,
devices)
除最后一层外的学习率使用默认的学习率
最后一层的学习率*10
因为我们不想让前面预训练的层变化的太多
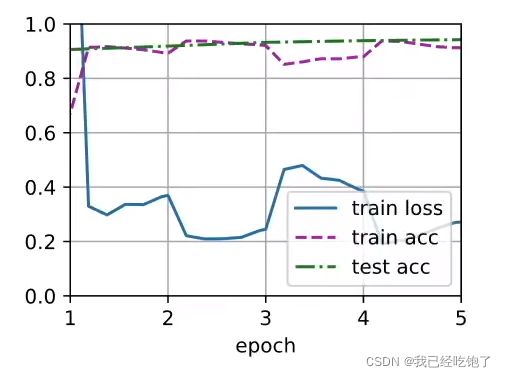
train_fine_tuning(finetune_net, 5e-5)