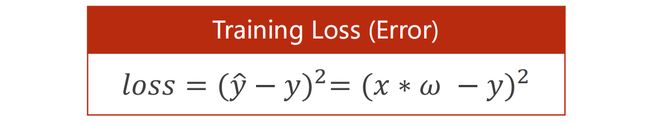Linear Model 线性模型
文章目录
-
- 1、Linear Model 线性模型
-
- 1.1 问题引入
- 1.2 选择模型
- 1.3 损失 Loss
- 1.4 均方误差 MSE
- 1.5 代码
- 1.6 更换模型
1、Linear Model 线性模型
B站视频教程传送门:PyTorch深度学习实践 - 线性模型
1.1 问题引入
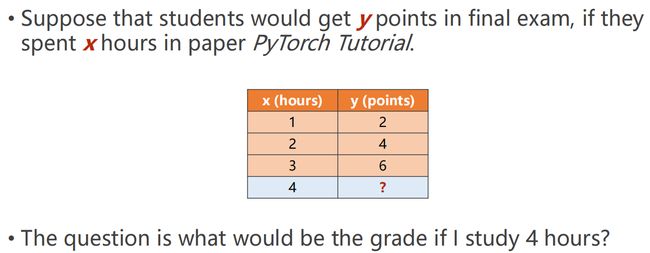
假设学生在期末考试中得到y分,如果他们花了x小时学习PyTorch教程,如果我学习4个小时,成绩会是多少?
监督学习:可参考 机器学习两种方法——监督学习和无监督学习(通俗理解)
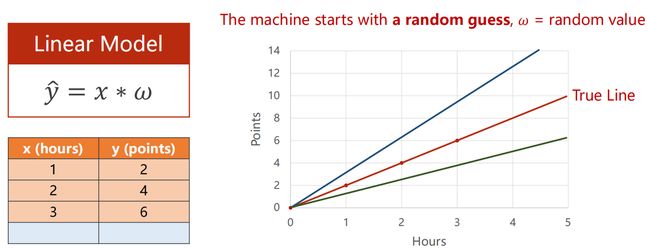
1.2 选择模型
To simplify the model 简化该模型
参数 w 为权重,是一个随机值,不同的 w 会导致结果的不同!
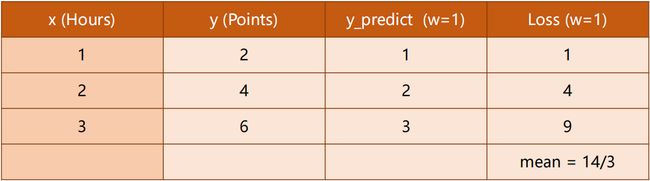
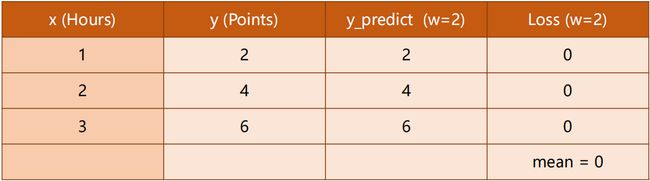
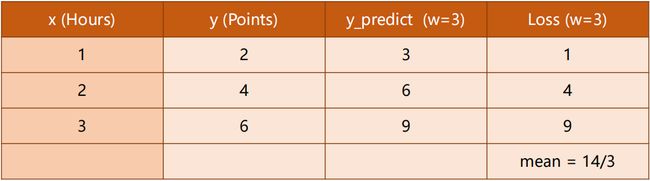
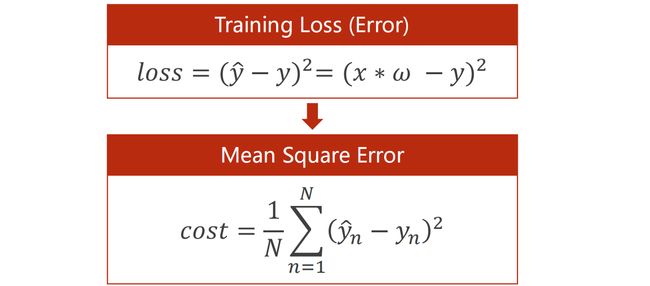
1.3 损失 Loss
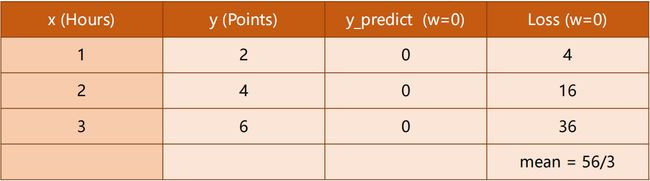
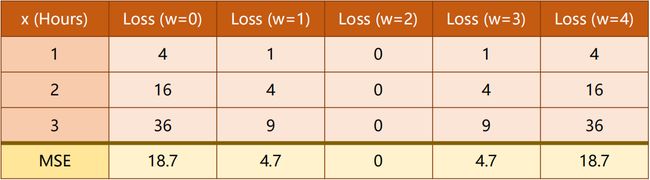
当我们 W 从 0、1、2、… 一直取下去,观察 Loss 的变化情况:
我们发现:
Loss (w=2)均为 0 即没有损失,说明这是最理想状态。
1.4 均方误差 MSE
在实际情况中,我们往往习惯用 MSE(平均平方误差)来代替Loss(损失值),可以更为直观的表现出来。
MSE:机器学习中的预测评价指标MSE、RMSE、MAE、MAPE、SMAPE
1.5 代码
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x_data = [1.0, 2.0, 3.0]
y_data = [2.0, 4.0, 6.0]
def forward(x):
return x * w
def loss(x, y):
y_pred = forward(x)
return (y_pred - y) ** 2
w_list = []
mse_list = []
for w in np.arange(0.0, 4.1, 0.1):
print("w=", round(w, 2))
l_sum = 0
for x_val, y_val in zip(x_data, y_data):
y_pred_val = forward(x_val)
loss_val = loss(x_val, y_val)
l_sum += loss_val
print('\t', round(x_val, 2), round(y_val, 2), round(y_pred_val, 2), round(loss_val, 2))
print('MSE=', l_sum / 3)
w_list.append(w)
mse_list.append(l_sum / 3)
plt.plot(w_list, mse_list)
plt.ylabel('MSE')
plt.xlabel('W')
plt.show()
w= 0.0
1.0 2.0 0.0 4.0
2.0 4.0 0.0 16.0
3.0 6.0 0.0 36.0
MSE= 18.666666666666668
w= 0.1
1.0 2.0 0.1 3.61
2.0 4.0 0.2 14.44
3.0 6.0 0.3 32.49
MSE= 16.846666666666668
w= 0.2
1.0 2.0 0.2 3.24
2.0 4.0 0.4 12.96
3.0 6.0 0.6 29.16
MSE= 15.120000000000003
...
可以发现 当 =2 时,MSE 将是最小的。
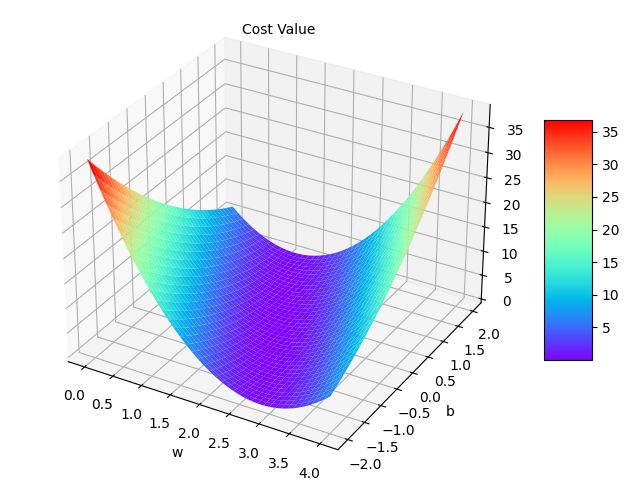
1.6 更换模型
在一开始,我们使用的是 y ^ = x ∗ w \hat {y} = x * w y^=x∗w ,如果我们想要加个截距b:即 y ^ = x ∗ w + b \hat {y} = x * w + b y^=x∗w+b ,结果又会怎样?
-
绘制三维图形:https://matplotlib.org/stable/tutorials/toolkits/mplot3d.html
-
np.meshgrid()矢量化计算:https://numpy.org/doc/stable/reference/generated/numpy.meshgrid.html#numpy.meshgrid
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
x_data = [1.0, 2.0, 3.0]
y_data = [2.0, 4.0, 6.0]
def forward(x):
return x * w + b
def loss(x, y):
y_pred = forward(x)
return (y_pred - y) ** 2
mse_list = []
W = np.arange(0.0, 4.1, 0.1)
B = np.arange(-2.0, 2.1, 0.1)
[w, b] = np.meshgrid(W, B)
l_sum = 0
for x_val, y_val in zip(x_data, y_data):
y_pred_val = forward(x_val)
print(y_pred_val)
loss_val = loss(x_val, y_val)
l_sum += loss_val
fig = plt.figure()
ax = Axes3D(fig)
ax.set_xlabel("w")
ax.set_ylabel("b")
ax.text(0.2, 2, 43, "Cost Value")
surf = ax.plot_surface(w, b, l_sum / 3, cmap=plt.get_cmap('rainbow'))
fig.colorbar(surf, shrink=0.5, aspect=5)
plt.show()
[[-2. -1.9 -1.8 ... 1.8 1.9 2. ]
[-1.9 -1.8 -1.7 ... 1.9 2. 2.1]
[-1.8 -1.7 -1.6 ... 2. 2.1 2.2]
...
[ 1.8 1.9 2. ... 5.6 5.7 5.8]
[ 1.9 2. 2.1 ... 5.7 5.8 5.9]
[ 2. 2.1 2.2 ... 5.8 5.9 6. ]]
[[-2. -1.8 -1.6 ... 5.6 5.8 6. ]
[-1.9 -1.7 -1.5 ... 5.7 5.9 6.1]
[-1.8 -1.6 -1.4 ... 5.8 6. 6.2]
...
[ 1.8 2. 2.2 ... 9.4 9.6 9.8]
[ 1.9 2.1 2.3 ... 9.5 9.7 9.9]
[ 2. 2.2 2.4 ... 9.6 9.8 10. ]]
[[-2. -1.7 -1.4 ... 9.4 9.7 10. ]
[-1.9 -1.6 -1.3 ... 9.5 9.8 10.1]
[-1.8 -1.5 -1.2 ... 9.6 9.9 10.2]
...
[ 1.8 2.1 2.4 ... 13.2 13.5 13.8]
[ 1.9 2.2 2.5 ... 13.3 13.6 13.9]
[ 2. 2.3 2.6 ... 13.4 13.7 14. ]]