自动机器学习框架介绍与使用(flaml、h2o)
一、介绍
二、数据介绍
三、flaml框架
3.1、flaml简介
3.2、使用flaml
3.2.1、下载flaml库
3.2.2、导入相关库
3.2.3、数据处理
3.2.4、调用flaml
四、h2o框架
4.1、h2o简介
4.2、h2o使用
4.2.1、下载h2o
4.2.2、导入相关库
4.2.3、数据处理
4.2.4、启动h2o的jar包
4.2.5、调用h2o
五、总结
一、介绍
自动机器学习(Automl),是一种将传统机器学习变成自动化,start—end全自动实现。目前市场流行的自动机器学习框架有:Flaml、H20等等。本章记录这两个框架的使用方式。
二、数据介绍
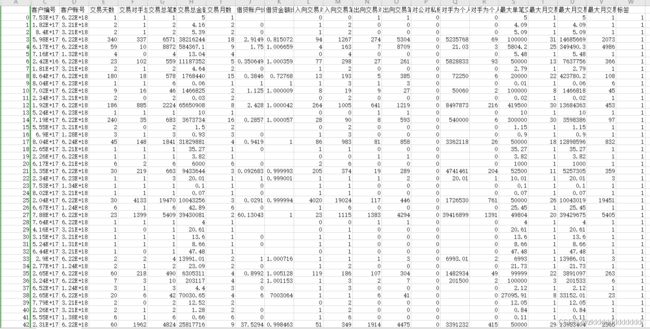
数据为自己造的银行交易流水指。共有23列数据,其中有18列特征数据,1列标签数据,4列用户信息数据。
三、flaml框架
3.1、flaml简介
Flaml是微软推出的一款自动机器学习框架,支持自定义学习器及参数,并提供了一种快速的自动调整工具。flaml可以在自定义的学习器中找到具有低计算资源的准确 ML 模型。它将用户从选择学习者和超参数中解放出来。使用起来非常方便。
3.2、使用flaml
3.2.1、下载flaml库
pip install flaml3.2.2、导入相关库
from flaml import AutoML
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
from sklearn.datasets import load_boston
import pandas as pd
import sys,logging
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix,classification_report,recall_score,accuracy_score,f1_score,precision_score
from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler
from imblearn.over_sampling import RandomOverSampler
import time3.2.3、数据处理
# 数据所在路径
data_path = r"source/data_jianhang.csv"
input_data_all = pd.read_csv(data_path,encoding="gbk",index_col=0)
# 提取预测客户信息 【客户名称、客户编号、客户账号】
customer_info = input_data_all.iloc[:,:3]
print(customer_info)
# 特征
input_data_target = input_data_all["标签"]
input_data_feature = input_data_all.iloc[:, 3:-1]
# 选取input_data_all的所有行,第三列到最后一列(包头不包尾)
input_data = input_data_all.iloc[:, 3:]
# 将空值补为0
input_data.fillna(0, inplace=True)
# 输出前五行查看
print(input_data.head())
# 针对正负样本不平衡情况进行随机过采样
f = RandomOverSampler(random_state=0)
data, target = f.fit_resample(input_data.iloc[:,:-1], input_data.iloc[:,-1])
# 数据最大最小归一化
data = MinMaxScaler().fit_transform(data)
# 输出样本数量情况
print(target.to_frame().value_counts())
# 切分数据 X:特征集 y:标签
X,y = input_data.iloc[:,:-1],input_data.iloc[:,-1]
X = MinMaxScaler().fit_transform(X)3.2.4、调用flaml
查看程序打印的日志我们可以发现,通过参数estimator_list,在调用flaml的过程中,flaml自动为我们比较lgbm、rf、xgboost分类器的效果,最后打印并使用最优的分类器以及参数去训练模型。整个过程都是自动化,完全不需要人为的操作比较。这也是自动化机器学习的一个特点。
t1 = time.time()
# 初始化flaml自动化建模框架
flaml_automl = AutoML()
# 传入训练数据x和y进行fit训练
flaml_automl.fit(data,target,task='classification',log_file_name="xxx.log",metric="f1",estimator_list = ['lgbm', 'rf', 'xgboost'])
# fit常用参数介绍
'''
# X_train=None, 训练数据特征集合
# y_train=None, 训练数据标签集合
# estimator_list = ['lgbm', 'rf', 'xgboost', 'extra_tree', 'xgb_limitdepth', 'lrl1']
# metric: 'accuracy', 'roc_auc', 'roc_auc_ovr', 'roc_auc_ovo','f1', 'micro_f1', 'macro_f1', 'log_loss', 'mae', 'mse', 'r2','mape'.
# n_jobs:传入整数,开启多线程
# n_splits:传入整数,交叉验证的折叠数
# log_file_name:日志输出,如果不想输出日志,传入空字符串 ’’ 即可
# estimator_list:模型列表,可选【‘lgbm’,’xgboot’,’xgb_limitdepth’,’catboost’,’rf’,’extra_tree’】,最终会输出best模型。
# time_budget:时间限制,以秒为单位。若限制10s,则在十秒的时候输出最优模型。不限制时间传入-1
# sample:布尔值,默认False。是否对传入的数据进行采样。
# early_stop:布尔值,默认False。若模型搜索收敛,则提前停止。
'''
# flaml打印的最优模型及参数
'''
[flaml.automl: 03-09 14:52:24] {2694} INFO - retrain lgbm for 1.3s
[flaml.automl: 03-09 14:52:24] {2699} INFO - retrained model: LGBMClassifier(colsample_bytree=0.5716563773446997,
global_max_steps=9223372036854775807,
learning_rate=0.7886932330930241, max_bin=511,
min_child_samples=7, n_estimators=181, num_leaves=1006,
reg_alpha=0.007095760722363662, reg_lambda=0.3005614400342159,
verbose=-1)
[flaml.automl: 03-09 14:52:24] {2077} INFO - fit succeeded
[flaml.automl: 03-09 14:52:24] {2079} INFO - Time taken to find the best model: 23.60042953491211
'''
# 打印一些结果
print("消耗时间: ",time.time()-t1)
print(flaml_automl.estimator_list)
print("最优模型",flaml_automl.model)
print("最优参数",flaml_automl.best_config)
print("训练时间",flaml_automl.best_config_train_time)
print("分类器",flaml_automl.best_estimator)
print("损失",flaml_automl.best_loss)
# 调用predict预测X
y_pred = flaml_automl.predict(X)
# 输出预测结果
print(y_pred)
# 打印指标、分类效果
print("混淆矩阵:\n",confusion_matrix(y,y_pred))
print("分类报告:\n",classification_report(y,y_pred))
print("召回率:",recall_score(y,y_pred))
print("准确率:",accuracy_score(y,y_pred))
print("f1分值:",f1_score(y,y_pred))
print("精确率:",precision_score(y,y_pred))
print("总消耗时间: ",time.time()-t1)四、h2o框架
4.1、h2o简介
h2o框架是一个开源,分布式的基于java的机器学习框架。h2o是由(h2o.AI)公司开发并发布。他们公司的网址 :H2O.ai | AI Cloud Platform。h20还支持用户任务进行可视化分析。
4.2、h2o使用
4.2.1、下载h2o
pip install h204.2.2、导入相关库
import h2o
from h2o.automl import H2OAutoML
from h2o.estimators.random_forest import H2ORandomForestEstimator
from h2o.estimators.gbm import H2OGradientBoostingEstimator
from h2o.estimators.stackedensemble import H2OStackedEnsembleEstimator
from h2o.grid.grid_search import H2OGridSearch
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import time
from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix,classification_report,recall_score,accuracy_score,f1_score,precision_score
from imblearn.over_sampling import RandomOverSampler4.2.3、数据处理
同3.2.3章节完全一样,这里不在赘述,直接复制3.2.3章节数据处理代码即可。
4.2.4、启动h2o的jar包
1)下载免费:自动化机器学习h2o启动jar包-机器学习文档类
2)打开cmd,输入java -jar h2o.jar 启动
3)访问web页面: http://localhost:54321
4.2.5、调用h2o
##``"DRF"``,``"GLM"``,``"XGBoost"``,``"GBM"``,``"DeepLearning"``,``"StackedEnsemble"``.
# 初始化
automl_estimator = H2OAutoML(max_runtime_secs=50,balance_classes=True,exclude_algos=["DeepLearning"],stopping_metric="auc",sort_metric="auc")
# 训练
automl_estimator.train(x=train_data_h2o.names[0:-1],y="target",training_frame=train_data_h2o)
print("时间2:",time.time()-t1)
# predict进行预测,并输出预测结果
h2o_result = automl_estimator.predict(test_data_h2o[:-1])[:,0]
print(h2o_result)
#打印指标
print("混淆矩阵:\n",confusion_matrix(test_data_h2o[:,-1].as_data_frame(),h2o_result.as_data_frame()))
print("分类报告:\n",classification_report(test_data_h2o[:,-1].as_data_frame(),h2o_result.as_data_frame()))
print("召回率:",recall_score(test_data_h2o[:,-1].as_data_frame(),h2o_result.as_data_frame()))
print("准确率:",accuracy_score(test_data_h2o[:,-1].as_data_frame(),h2o_result.as_data_frame()))
print("f1分值:",f1_score(test_data_h2o[:,-1].as_data_frame(),h2o_result.as_data_frame()))
print("精确率:",precision_score(test_data_h2o[:,-1].as_data_frame(),h2o_result.as_data_frame()))
print("时间3:",time.time()-t1)五、总结
因为对h2o理解比较少,所以关于h2o框架方面的代码没有过多的解释。我个人还是比较倾向于使用flaml做自动化机器学习。至于效果还是挺好的,这里就不贴效果截图了。有兴趣的可以自己线下实践实践。