详细介绍用MATLAB实现基于A*算法的路径规划(附完整的代码,代码逐行进行解释)(三)--------总结及A*算法的优化处理
本系列文章主要介绍基于A*算法的路径规划的实现,并使用MATLAB进行仿真演示。本文作为本系列的第三篇文章主要对前两篇文章总结以及对前文中的 A * 算法进行进一步的优化处理
本系列文章链接:
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
详细介绍用MATLAB实现基于 A * 算法的路径规划(附完整的代码,代码逐行进行解释)(一)--------A * 算法简介和环境的创建
详细介绍用MATLAB实现基于 A * 算法的路径规划(附完整的代码,代码逐行进行解释)(二)--------利用 A * 算法进行路径规划
详细介绍用MATLAB实现基于 A * 算法的路径规划(附完整的代码,代码逐行进行解释)(三)--------总结及 A * 算法的优化处理
详细介绍用MATLAB实现基于 A * 算法的路径规划(附完整的代码,代码逐行进行解释) (四)--------固定障碍物,进一步对比
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
八 、总结
1、代码的整体思路
①对环境进行设定:首先我们需要设定我们生成的环境的大小,生成的方格数为nxn,也就是对参数n的设定,然后设定障碍物的多少,也就是对参数wallpercent进行设定
②设定完这两个参数后,我们调用我们编写的initializeField函数来随机生成包含障碍物,起始点,终止点等信息的矩阵
③接着我们调用我们编写的 createFigure函数利用initializeField函数生成的数据来进行环境的创建,也就是绘制出随机生成的要进行路径规划的场景,包括障碍物,起始点,终止点等
④开始路径规划前,要对路径规划中要到的一些矩阵进行初始化
⑤开始路径规划,从起始点开始利用循环进行迭代来寻找终止点,在进行点的拓展的时我们调用编写的findFValue函数来拓展寻找子节点以及子节点的代价
⑥如果在上一步的路径规划中我们找到了从起始点到终止点的路,就调用我们编写的findWayBack函数进行路径回溯,并绘制出从起始点到终止点的路径曲线
2、环境中“点”的身份
环境中的一个点他起初的身份是有障碍物点,没有障碍物点,以及特殊的点-----起始点和终止点,然后在路径规划进行点的拓展时,没有障碍物点又多了几重身份,首先是当他被他的父节点拓展出来后放到矩阵posinds中,如果符合要求,他就升级为待选点,放到setOpen矩阵中,每次循环都从setOpen矩阵中找一个最优的点,升级为下一次进行拓展的父节点,放到矩阵setClosed中,最后在找到终止点后,通过回溯出来的点放到矩阵p中,这些点就是我们真正要找的点,利用这些点我们就能找到规划的路径,并将其绘制出来。
3、路径规划的实现思路
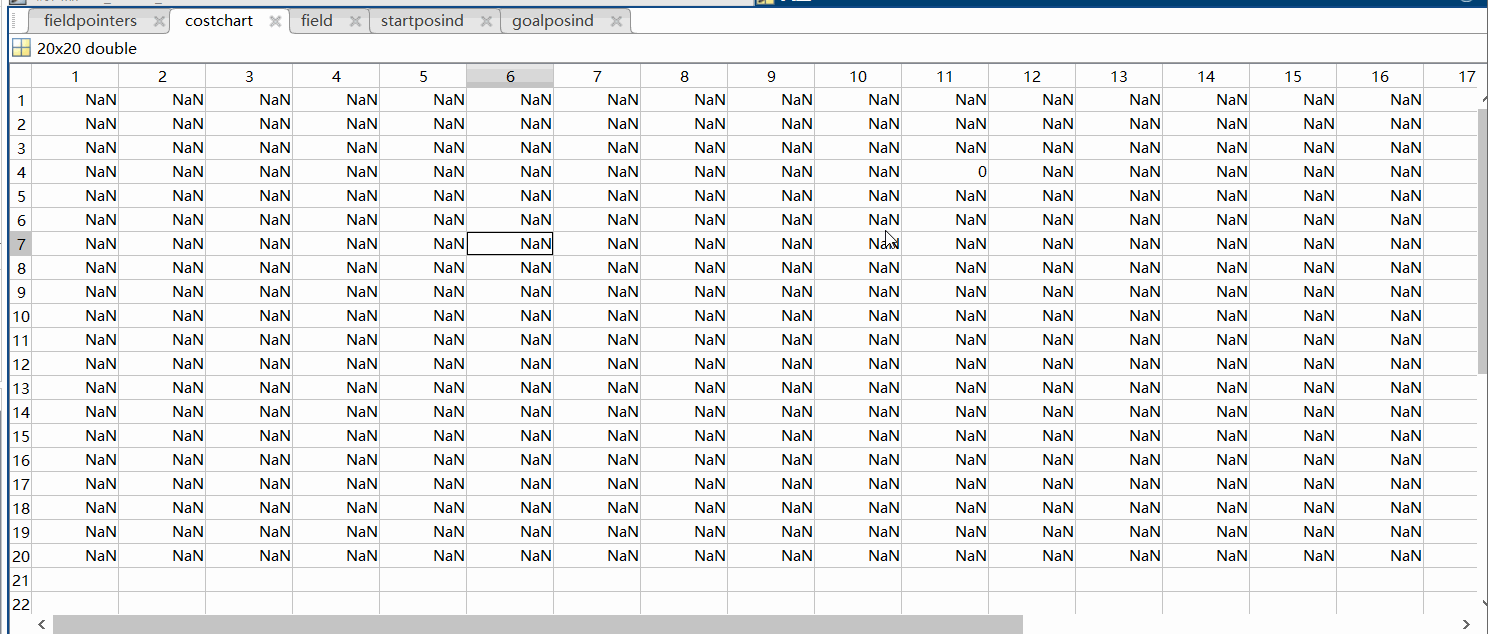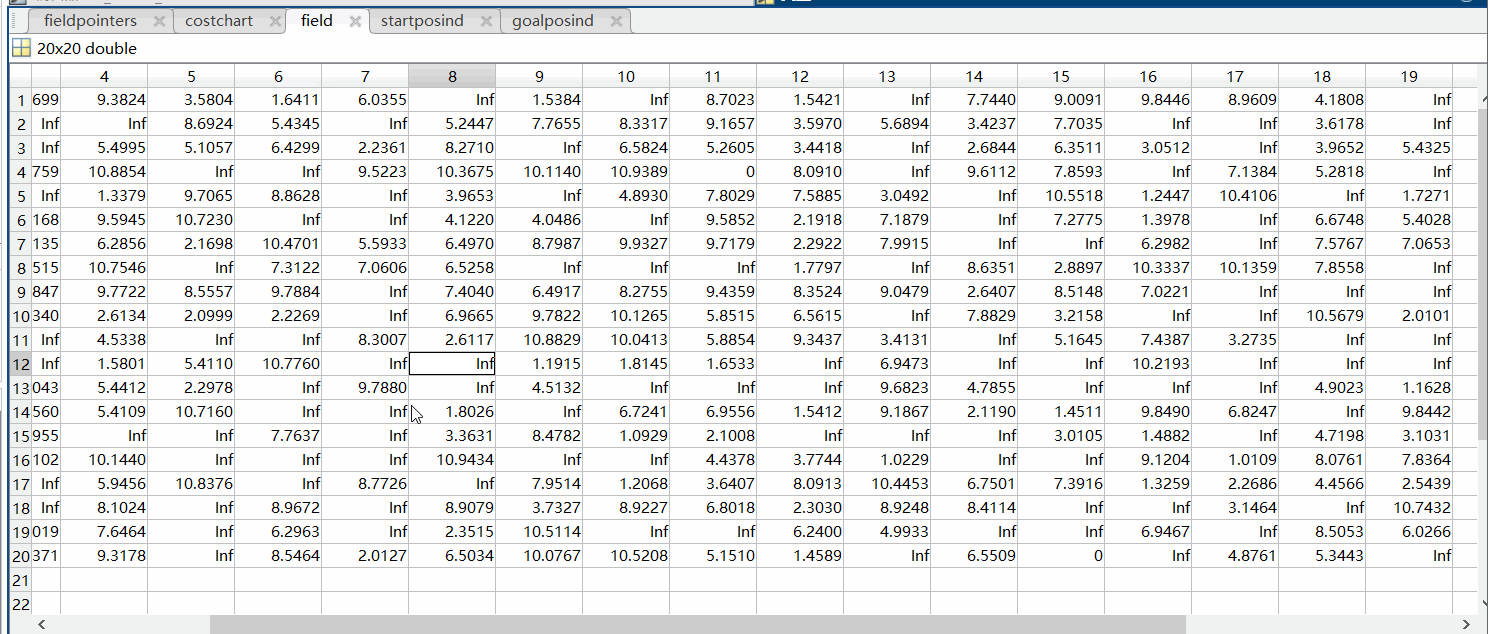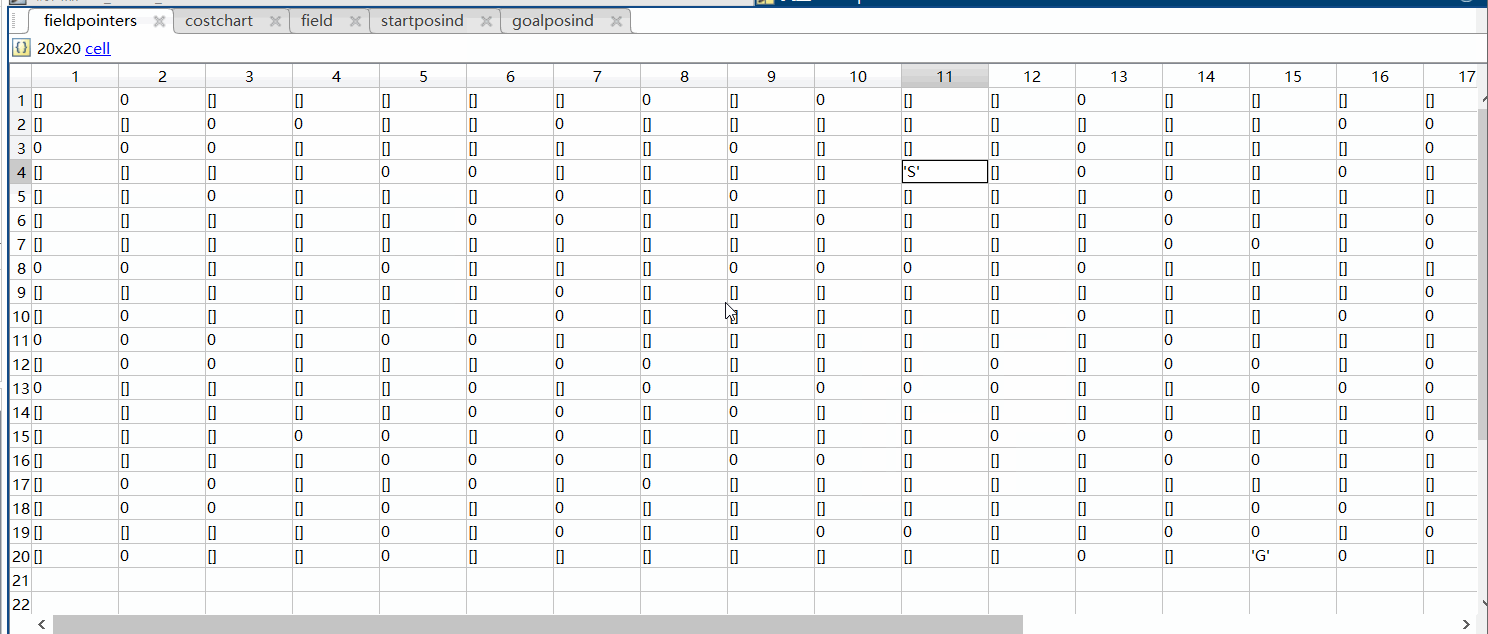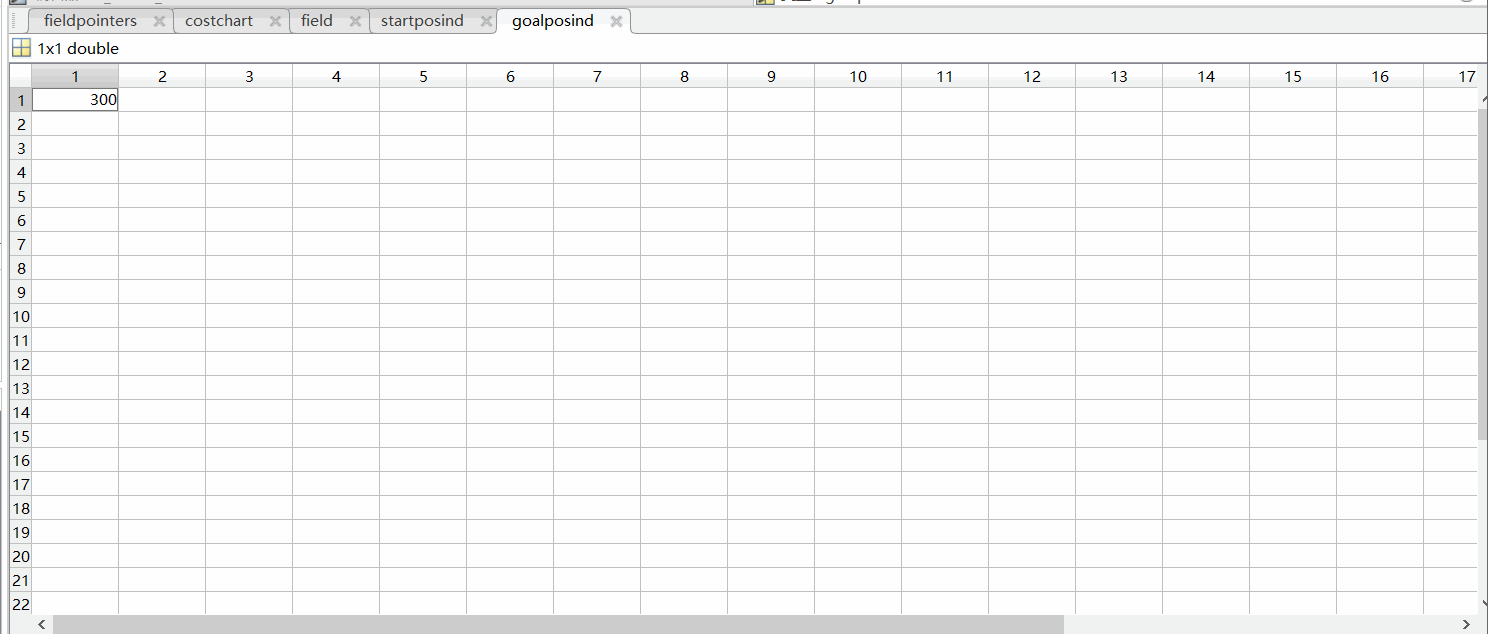
①首先在之前我们已经通过initializeField函数生成了矩阵costchart,在矩阵costchart中起始点位置存放的内容为0,其他位置存放的内容为NaN,生成的field矩阵起始点和终止点存放的内容为0,没有障碍物的点存放的内容为1到11的随机数,有障碍物的点存放的内容为最大值Inf,生成了一个元胞数组fieldpointers里面在有障碍物的地方存放的内容为0,在起始点处存放的内容为S,终止点处存放G,其他位置为空[],除此之外我们还得到了起始点的索引值startposind,终止点的索引值goalposind
②在进行路径规划时,我们还需要用到一些矩阵,我们对其进行初始化,setOpen矩阵用来存放待选点的索引值,初始化为起始点的索引值,这个很好理解,一开始的时候只能从起始点出发,因此刚开始的时候只有起始点一个待选点;setOpenCosts矩阵存放该待选点与起始点的代价,由于目前该待选点就是起始点,所以初始化为0,setOpenHeuristics矩阵存放该待选点与终止点的距离,因为目前还不知道能不能找到到终止点的路,所以先初始化为最大值Inf,这里需要说明一下,初始化的时候,这三个矩阵内都只存放了一个待选点,但是随着路径规划的进行会不断的将符合要求的待选点串到(新增)到矩阵中,这三个矩阵是配套使用的,也就是说这三个矩阵的同一行中存放的是同一个待选点的信息,分别存放该待选点的索引值,到起始点的代价,到终止点的代价,因此要往setOpen中增加或者删除待选点时,必须同时对另外两个矩阵进行增加或删除,来保证其对应关系
③在文章中还初始化了两个矩阵setClosed = []; 和setClosedCosts = [];分别用来存放下一次进行拓展的父节点的索引值,以及改点到起始点的代价,其实这两个矩阵在进行路径规划的时候并没有用到,也没有发挥任何作用,只是可以用来帮助我们进行分析罢了
④初始化完矩阵,接下来就要开始进行拓展了,那么对那个点进行拓展呢,我们从setOpen矩阵中的待选点中选取一个最优点进行拓展,选取标准就是这个待选点距离起始点和终止点的代价的和最小,那么这个待选点我们就认为他是最优的待选点,那么就将这个点作为下一次拓展的父节点(当然既然这个点已经作为下一次拓展的父节点了,就应该把这个点从setOpen矩阵中删除),每次拓展把拓展出来的符合要求的点放到矩阵setOpen中作为待选点,这样不断的迭代循环,直到无路可走(没有可拓展的点了)或者直到终止点,结束拓展,路径规划结束
⑤在这里顺便说一下,我认为代码中对于相邻两个点之间距离采用随机数的方式生成是有问题的,也就是fieid矩阵中的1到11的随机数,因为我们更加倾向于相邻两个方格的距离是相同的(方格的大小一样的),这样才更符合我们的视觉习惯,在下文中我会对其进行优化处理
九 、对前文介绍A*算法进行优化
1、将两个方格间的距离设为相同的值
在前文中两个没有障碍物的方格间的距离是不相等的随机数,也就是fieid中1到11的随机数,现在我们把两个没有障碍物的方格间的距离设为相同的数值10,进行的修改如下:
(1)将initializeField函数中第一行代码如下:
field = ones(n,n) + 10*rand(n,n);%生成一个n*n的单位矩阵+0到10范围内的一个随机数
修改为:
field = 10*ones(n,n);%设置任意两方格间的距离为10
(2)将findFValue函数中所有的以下语句:
heuristic(1) = abs(goalpos(2)-newx) + abs(goalpos(1)-newy);
修改为:
heuristic(1) = 10*abs(goalpos(2)-newx) + 10*abs(goalpos(1)-newy);
我们先来看一下这两步优化前,也就是前两篇博文介绍的传统的A*算法的视频效果演示,如下所示:
传统A星算法100x100方格效果视频演示.mp4
我们再来看一下经过这两步优化后的效果,如下所示:
初步改进后的A星算法100x100方格效果视频演示.mp4
我们很容易发现经过上面这两步简单的优化后,在大多数情况下搜索的速度明显加快,搜索的效率明显提高了,搜索更加具有启发性,目的性
2、将前文介绍的传统的A星算法,优化为动态衡量启发式A星算法
启发式函数可以控制A*的行为:
(1)一种极端情况,如果h(n)是0,则只有g(n)起作用。
(2) 如果h(n)经常都比从n移动到目标的实际代价小(或者相等),则A * 保证能找到一条最短路径。h(n)越小,A*扩展的结点越多,运行就得越慢。
(3)如果h(n)精确地等于从n移动到目标的代价,则A * 将会仅仅寻找最佳路径而不扩展别的任何结点,这会运行得非常快。尽管这不可能在所有情况下发生,你仍可以在一些特殊情况下让它们精确地相等。只要提供完美的信息,A * 会运行得很完美。
(4)如果h(n)有时比从n移动到目标的实际代价高,则A*不能保证找到一条最短路径,但它运行得更快。
(5)另一种极端情况,如果h(n)比g(n)大很多,则只有h(n)起作用。
传统的 A * 算法的总代价计算公式为f(n) = g(n) + h(n) ,与传统的A星不同的是,原本的h(n) ,变成了 w(n) * h(n) , 其中 w(n) >= 1 。w(n) 可以影响评估值。在搜索过程中,我们可以通过改变w(n) 来影响搜索过程如上面提到的 h(n) 对A星算法的影响。
了解了动态衡量启发式A星算法的基本内容和原理,下面我们继续对初步优化后的传统的A星算法进行进一步的优化,将其升级为动态衡量启发式A星算法
① 在我们初始设定的参数中,增加了h(n) 的权重系数Weights,通过设定这个系数的大小就可以控制A*的行为,效果和原理见上文的介绍
n = 100; % 产生一个n x n的方格,修改此值可以修改生成图片的方格数
wallpercent = 0.4; % 这个变量代表生成的障碍物占总方格数的比例 ,如0.5 表示障碍物占总格数的50%
Weights=1; %动态衡量启发式A星算法中的h(n)权重系数
② 要想这个系数发挥作用,我们需要修改寻找最优点的方案,也就是将利用循环进行迭代来寻找终止点的while循环里的第一行代码(也就是下面这行代码)
[temp, ii] = min(setOpenCosts + setOpenHeuristics); %寻找拓展出来的最小值
修改为:
[temp, ii] = min(setOpenCosts +Weights*setOpenHeuristics); %寻找拓展出来的最小值
经过之前两部简单优化后的A*算法,其实就相当于Weights=1的情况,现在我们将Weights的值设为2,我们再来看一下效果:
动态衡量启发式A星算法100x100方格视频效果演示.mp4
我们很容易发现,相比于Weights=1的情况,在Weights=2时,搜索的效率,速度明显加快了不少,但是与此同时,随着拓展点的减少,他所找出来的路径有可能不是最短路径,所以在实际应用时,可以灵活的根据需要调节参数Weights,这也是动态衡量启发式A星算法相对于传统的A星算法的优势,顺便再提一下,当将Weights设为0时A星算法就变成了Dijkstra算法。当将Weights设为较大的数时A星算法就变成了BFS算法。在这里就不做演示了,有兴趣的可以把代码放到matlab中,或者直接下载文章的附件,自己修改参数查看效果。
3、对上文的动态衡量式A星算法进行拐角优化
在搜索效率和速度方面的优化就先到上文为止,但我们可以发现无论是传统的A星算法还是动态衡量启发式的他找出来的路只是数学上的最优路径(或者说近似最优路径,随着搜索速度的提高,找到的路可能不是最短的),他规划出来的路线有一些转弯是完全可以省去的(用一个转弯去取代多个转弯)
因为我们最终的目标还是要控制实物去移动,所以要尽量减少转弯的次数,下文就介绍如何写一个函数对其进行进一步的优化,使其在保证不增加路程的基础上尽量减少转弯次数
(1)一般来说大多数不必要转弯分为两种情况,如下图所示:
第一种情况:如上图的标号②处所示,我们可以通过接下来要介绍的函数将其优化成图中白线所示的轨迹,像这种情况每优化一次可能会减少2个不必要的转弯
第二种情况:如上图的标号①处所示,这种转弯,我们不能通过将要介绍的函数将其优化成白线所示轨迹,因为A星算法在进行拓展的时候是对总代价最小的点来拓展,在①号标注处向下拓展比向左拓展要花费的总代价小(虽然由于后续存在障碍物的原因,让其实际花费的代价相同,但是在当时拓展时是不知道的),所以类似这种远离终止点的拐角无法得到优化。
(2)先来大体说一下优化的思路,在我们从setOPen矩阵中,找到最小总代价的点在setOPen中的索引值ii时,也就是得到将要拓展的点在fieldpointers元胞数组中的索引值setOPen(ii),然后通过该点在元胞数组fieldpointers中储存的方向信息,就可以知道这个点是由那个点拓展出来的,进而得到其父节点的索引值,也就可以知道其父节点在元胞数组fieldpointers中储存的方向信息,也就知道了我们期望的下一步要走的点的位置了,(举个例子,如果其父节点在元胞数组fieldpointers中储存的信息是R,就说明这个父节点是由其右边的点拓展出来的,现在如果我想走直线,那么我们期望的点就是父节点左边的那个点),得到这个期望要走的的点位置后,就查看这个点是否位于待选点矩阵setOPen中,如果在,那么计算一下这个点要花费的总代价,如果跟原来我们要走的点代价相同,则用这个期望的点代替原来的点进行优化,否则不进行优化
(3)要做的一些准备工作
①增加功能参数Corner_amend,选择是否进行拐角的修正,该变量设为0则不进行拐角优化,设为1则进行拐角优化,增加这个参数后大家可以自由的选择是否进行该优化
%功能参数的设定部分
n = 30; % 产生一个n x n的方格,修改此值可以修改生成图片的方格数
wallpercent = 0.4; % 这个变量代表生成的障碍物占总方格数的比例 ,如0.5 表示障碍物占总格数的50%
Weights=1; %动态衡量启发式A星算法中的h(n)权重系数
Corner_amend=1; %选择是否进行拐角的修正,该变量设为0则不进行拐角修正,设为1则进行拐角修正
②修改initializeField函数生成元胞数组fieldpointers的代码如下(这样做是为了防止在拐角优化时搜索到非字符向量而报错)(将原来代表障碍物的0改成了‘ 0’,将原来的空白处改成了‘1’)
% 生成元胞数组
fieldpointers = cell(n,n);%生成元胞数组n*n
fieldpointers(:)= {'1'};
fieldpointers{startposind} = 'S'; fieldpointers{goalposind} = 'G'; %将元胞数组的起始点的位置处 设为 'S',终止点处设为'G'
fieldpointers(field==inf)={'0'};
③初始化一些进行路径的修正需要用到的变量(这些变量在下文再介绍其作用)
%初始化一些进行路径的修正需要用到的变量
Parent_node=0; %Parent_node初始化,否则会报错
Expected_note=0;%Expected_note初始化,否则会报错
untext_ii=0; %未经过检验的新的ii
amend_count=0;% 记录修正的次数
(4)我们先来看一下这个函数插在原来的代码中的位置,插在while循环的[temp, ii] = min(setOpenCosts +Weights*setOpenHeuristics);语句之后, [costs,heuristics ,posinds] = findFValue(setOpen(ii),setOpenCosts(ii), field,goalposind,‘euclidean’);语句之前,如下所示
while ~max(ismember(setOpen,goalposind)) && ~isempty(setOpen)
[temp, ii] = min(setOpenCosts +Weights*setOpenHeuristics); %寻找拓展出来的最小值
if ((setOpen(ii)~=startposind) && (Corner_amend==1))
[new_ii,amend_count_1]=Path_optimization(temp, ii,fieldpointers,setOpen,setOpenCosts,startposind,Weights,setOpenHeuristics,Parent_node,Expected_note,untext_ii,amend_count); %进行路径的修正,在保证不增加距离的基础上,使其减少转弯的次数
ii=new_ii;
amend_count=amend_count_1;
end
%这个函数的作用就是把输入的点作为父节点,然后进行拓展找到子节点,并且找到子节点的代价,并且把子节点距离终点的代价找到
[costs,heuristics,posinds] = findFValue(setOpen(ii),setOpenCosts(ii), field,goalposind,'euclidean');
其中if语句中的(setOpen(ii)~=startposind)是判断该点是否是起始点,如果是起始点则跳过优化(起始点无父节点), if中的(Corner_amend==1)就是我们设置的选择是否进行拐角优化的功能参数;之后就是调用Path_optimization函数来进行拐角优化,调用完将其输出变量在while循环中进行更新,也就是得到新的ii和amend_count
(5)介绍实现上述拐角优化的Path_optimization函数,我们先来看一下完整的代码,然后再详细介绍(我感觉我注释写的挺多的,还是再介绍一下吧):
function [new_ii,amend_count_1] = Path_optimization(temp, ii,fieldpointers,setOpen,setOpenCosts,startposind,Weights,setOpenHeuristics,Parent_node,Expected_note,untext_ii,amend_count)
n = length(fieldpointers); %获取矩阵的长度,并赋值给变量n
%获取其父节点的索引值
switch fieldpointers {setOpen(ii)}
case 'L' % ’L’ 表示当前的点是由左边的点拓展出来的
Parent_node = setOpen(ii) - n;
case 'R' % ’R’ 表示当前的点是由右边的点拓展出来的
Parent_node = setOpen(ii) + n;
case 'U' % ’U’ 表示当前的点是由上面的点拓展出来的
Parent_node = setOpen(ii) -1;
case 'D' % ’D’ 表示当前的点是由下边的点拓展出来的
Parent_node = setOpen(ii) + 1;
end
if Parent_node==startposind %如果这个点的父节点是起始点的话,跳过修正
new_ii=ii;
amend_count_1=amend_count;
else
%获取期望下一步要走的点的索引值
switch fieldpointers{Parent_node}
case 'L' % ’L’ 表示当前的点是由左边的点拓展出来的,走直线的话,我们期望要走的下一个点为此点右边的点
Expected_note = Parent_node + n;
case 'R' % ’R’ 表示当前的点是由右边的点拓展出来的,走直线的话,我们期望要走的下一个点为此点左边的点
Expected_note = Parent_node - n;
case 'U' % ’U’ 表示当前的点是由上面的点拓展出来的,走直线的话,我们期望要走的下一个点为此点下面的点
Expected_note = Parent_node +1;
case 'D' % ’D’ 表示当前的点是由下边的点拓展出来的,走直线的话,我们期望要走的下一个点为此点上面的点
Expected_note = Parent_node - 1;
end
if ((Expected_note<=0)||(Expected_note>n*n)) %如果我们期望的点不在待选点矩阵setOpen中,或者超出边界,跳过修正
new_ii=ii;
amend_count_1=amend_count;
else
%计算新的要进行拓展的点在setOPen中的索引值
if fieldpointers{setOpen(ii)}==fieldpointers{Parent_node} %如果修正之前要走的点就是我们期望的构成直线的点,跳出修正
new_ii=ii;
amend_count_1=amend_count;
elseif find(setOpen == Expected_note) %如果我们期望要走的点在待选点矩阵setOpen中
untext_ii=find(setOpen == Expected_note);
now_cost=setOpenCosts(untext_ii) +Weights*setOpenHeuristics(untext_ii); %计算期望点要花费的代价
if temp==now_cost %如果我们期望的点要花费的代价等于修正之前要走的点花费的代价,就进行修正(因为之前要走的点,是待选点矩阵setOPen中代价最小的一个点之一,所以期望的点的代价不可能小于该点)
new_ii=untext_ii; %将新的setOPen矩阵的索引值赋值给new_ii输出
amend_count=amend_count+1;
amend_count_1=amend_count; %amend_count_1中记录了我们进行修正的次数,为了查看这个函数是否有发挥作用
else
new_ii=ii; %如果我们期望的点要花费的代价大于修正之前要走的点花费的代价,就跳过修正(A星算法要保证进行拓展的点是待选点中代价最小的,这也是导致远离终止点的哪一类拐角无法得到修正的原因)
amend_count_1=amend_count;
end
else
new_ii=ii; %如果我们期望的点不在待选点矩阵setOpen中(也就是这个点是障碍物或者超出边界了),则跳过修正
amend_count_1=amend_count;
end
end
end
end
①第一步:我们要得到在进行拐角优化前,原来准备拓展的点的父节点的索引值,通过fieldpointers {setOpen(ii)}我们可以得到原来准备拓展的点在fieldpointers中储存的位置信息,也就是得到这个点是由那个点拓展来的,若该点在fieldpointers中储存的信息是L,则表示当前的点是由左边的点拓展出来的,也就是其父节点的索引值就是在该点的索引值的基础上减去n(n是每一行或者每一列的长度),同理可得其他三个位置信息的处理方法
%获取其父节点的索引值
switch fieldpointers {setOpen(ii)}
case 'L' % ’L’ 表示当前的点是由左边的点拓展出来的
Parent_node = setOpen(ii) - n;
case 'R' % ’R’ 表示当前的点是由右边的点拓展出来的
Parent_node = setOpen(ii) + n;
case 'U' % ’U’ 表示当前的点是由上面的点拓展出来的
Parent_node = setOpen(ii) -1;
case 'D' % ’D’ 表示当前的点是由下边的点拓展出来的
Parent_node = setOpen(ii) + 1;
end
② 第二步:在计算获取期望下一步要走的点的索引值之前,我们先要判断一下,我们上一步中算出来的父节点的索引值是不是等于起始点,如果等于起始点则说明这个点是由起始点拓展出来的点,朝哪走都是直线,就不用优化了,跳过优化,否则进入下一步,这部分代码如下:
if Parent_node==startposind %如果这个点的父节点是起始点的话,跳过修正
new_ii=ii;
amend_count_1=amend_count;
else
amend_count_1中记录了我们进行修正的次数,为了查看这个优化函数是否有发挥作用,每发挥一次作用其值累加1
③ 第三步:利用第一步中得到的父节点的索引值,查看父节点在元胞数组fieldpointers中的位置信息,并通过该位置信息来计算获取期望下一步要走的点的索引值,举个例子,如果其父节点在元胞数组fieldpointers中储存的信息是R,就说明这个父节点是由其右边的点拓展出来的,现在如果我想走直线,那么我们期望的点就是父节点左边的那个点,那么我们期望的要走的点索引值就是在这个父节点的基础上减去n也就是 Expected _note = Parent_node - n;同理可得其他三个方向的处理方法,代码如下:
switch fieldpointers{Parent_node}
case 'L' % ’L’ 表示当前的点是由左边的点拓展出来的,走直线的话,我们期望要走的下一个点为此点右边的点
Expected_note = Parent_node + n;
case 'R' % ’R’ 表示当前的点是由右边的点拓展出来的,走直线的话,我们期望要走的下一个点为此点左边的点
Expected_note = Parent_node - n;
case 'U' % ’U’ 表示当前的点是由上面的点拓展出来的,走直线的话,我们期望要走的下一个点为此点下面的点
Expected_note = Parent_node +1;
case 'D' % ’D’ 表示当前的点是由下边的点拓展出来的,走直线的话,我们期望要走的下一个点为此点上面的点
Expected_note = Parent_node - 1;
end
④ 第四步:接下来我们需要判断一下,我们期望走的点是否超过了我们的环境的边界,如果超出了边界,就跳过优化,因为我们不可能去走边界外的点,这部分对应的代码如下:
if ((Expected_note<=0)||(Expected_note>n*n)) %如果我们期望的点不在待选点矩阵setOpen中,或者超出边界,跳过修正
new_ii=ii;
amend_count_1=amend_count;
else
⑤第五步 计算新的要进行拓展的点在setOPen中的索引值 ,并进行输出,第一种情况:本来我们要拓展的点就是我们期望的走直线的点,那么就也就不用优化了跳过优化,如下所示:
if fieldpointers{setOpen(ii)}==fieldpointers{Parent_node} %如果修正之前要走的点就是我们期望的构成直线的点,跳出修正
new_ii=ii;
amend_count_1=amend_count;
第二种情况:如果我们期望要走的点在待选点矩阵setOpen中,也就是通过find函数能在setOpen中找到其在setOpen中的索引值,赋值给变量untext_ii,并利用这个变量计算这个期望要走的点花费的总代价是否等于本来要进行拓展的点花费的总代价,如果我们期望的点要花费的代价等于修正之前要走的点花费的代价,就进行修正(因为之前要走的点,是待选点矩阵setOPen中代价最小的一个点之一,所以期望的点的代价不可能小于该点,只可能大于或者等于该点)将新的索引值赋值给new_ii进行输出,也就是语句new_ii=untext_ii;,并且让amend_count累加1(表示通过这段代码成功优化掉了几个可能的拐角),并赋值给amend_count_1进行输出,这部分代码如下:
elseif find(setOpen == Expected_note) %如果我们期望要走的点在待选点矩阵setOpen中
untext_ii=find(setOpen == Expected_note);
now_cost=setOpenCosts(untext_ii) +Weights*setOpenHeuristics(untext_ii); %计算期望点要花费的代价
if temp==now_cost %如果我们期望的点要花费的代价等于修正之前要走的点花费的代价,就进行修正(因为之前要走的点,是待选点矩阵setOPen中代价最小的一个点之一,所以期望的点的代价不可能小于该点)
new_ii=untext_ii; %将新的setOPen矩阵的索引值赋值给new_ii输出
amend_count=amend_count+1;
amend_count_1=amend_count; %amend_count_1中记录了我们进行修正的次数,为了查看这个函数是否有发挥作用
第三种情况: 虽然我们期望的这个点在矩阵中setOpen能够找到,但是,通过计算发现期望的点花费的总代价大于原来要走的点,则跳过优化,因为A星算法要保证进行拓展的点是待选点中代价最小的,这也是导致远离终止点的哪一类拐角无法得到修正的原因
else
new_ii=ii; %如果我们期望的点要花费的代价大于修正之前要走的点花费的代价,就跳过修正(A星算法要保证进行拓展的点是待选点中代价最小的,这也是导致远离终止点的哪一类拐角无法得到修正的原因)
amend_count_1=amend_count;
end
其他情况:比如如果我们期望的点不在待选点矩阵setOpen中(也就是这个点是障碍物或者超出边界了),则跳过修正
else
new_ii=ii; %如果我们期望的点不在待选点矩阵setOpen中(也就是这个点是障碍物或者超出边界了),则跳过修正
amend_count_1=amend_count;
end
end
end
end
(6)到这里这个拐角的优化函数就介绍完了,看一下经过拐角优化后的效果的视频演示:
动态衡量式A星算法进行拐角优化后的视频演示.mp4
(7)顺便说一下,我把音乐播放的语句加到了代码的开始,这样在进行拓展的时候也就有音乐了,然后在找到路后是播放其高潮部分
十 、动态衡量启发式A星算法的完整的代码
%matlab初始化
clc; %清除命令窗口的内容
clear all; %清除工作空间的所有变量,函数,和MEX文件
close all; %关闭所有的figure窗口
%方格数、障碍物比例以及h(n)权重系数的设定
n = 20; % 产生一个n x n的方格,修改此值可以修改生成图片的方格数
wallpercent = 0.4; % 这个变量代表生成的障碍物占总方格数的比例 ,如0.5 表示障碍物占总格数的50%
Weights=2; %动态衡量启发式A星算法中的h(n)权重系数
%方格以及障碍物的创建
[field, startposind, goalposind, costchart, fieldpointers] =initializeField(n,wallpercent); %随机生成包含障碍物,起始点,终止点等信息的矩阵
% 路径规划中用到的一些矩阵的初始化
setOpen = [startposind]; setOpenCosts = [0]; setOpenHeuristics = [Inf];
setClosed = []; setClosedCosts = [];
movementdirections = {'R','L','D','U'}; %移动方向
% 这个函数用来随机生成环境,障碍物,起点,终点
axishandle = createFigure(field,costchart,startposind,goalposind); %将随机生成的方格及障碍物的数据生成图像
%%
% 这个while循环是本程序的核心,利用循环进行迭代来寻找终止点
while ~max(ismember(setOpen,goalposind)) && ~isempty(setOpen)
[temp, ii] = min(setOpenCosts +Weights*setOpenHeuristics); %寻找拓展出来的最小值
%这个函数的作用就是把输入的点作为父节点,然后进行拓展找到子节点,并且找到子节点的代价,并且把子节点距离终点的代价找到
[costs,heuristics,posinds] = findFValue(setOpen(ii),setOpenCosts(ii), field,goalposind,'euclidean');
setClosed = [setClosed; setOpen(ii)]; % 将找出来的拓展出来的点中代价最小的那个点串到矩阵setClosed 中
setClosedCosts = [setClosedCosts; setOpenCosts(ii)]; % 将拓展出来的点中代价最小的那个点的代价串到矩阵setClosedCosts 中
% 从setOpen中删除刚才放到矩阵setClosed中的那个点
%如果这个点位于矩阵的内部
if (ii > 1 && ii < length(setOpen))
setOpen = [setOpen(1:ii-1); setOpen(ii+1:end)];
setOpenCosts = [setOpenCosts(1:ii-1); setOpenCosts(ii+1:end)];
setOpenHeuristics = [setOpenHeuristics(1:ii-1); setOpenHeuristics(ii+1:end)];
%如果这个点位于矩阵第一行
elseif (ii == 1)
setOpen = setOpen(2:end);
setOpenCosts = setOpenCosts(2:end);
setOpenHeuristics = setOpenHeuristics(2:end);
%如果这个点位于矩阵的最后一行
else
setOpen = setOpen(1:end-1);
setOpenCosts = setOpenCosts(1:end-1);
setOpenHeuristics = setOpenHeuristics(1:end-1);
end
%%
% 把拓展出来的点中符合要求的点放到setOpen 矩阵中,作为待选点
for jj=1:length(posinds)
if ~isinf(costs(jj)) % 判断该点(方格)处没有障碍物
% 判断一下该点是否 已经存在于setOpen 矩阵或者setClosed 矩阵中
% 如果我们要处理的拓展点既不在setOpen 矩阵,也不在setClosed 矩阵中
if ~max([setClosed; setOpen] == posinds(jj))
fieldpointers(posinds(jj)) = movementdirections(jj);
costchart(posinds(jj)) = costs(jj);
setOpen = [setOpen; posinds(jj)];
setOpenCosts = [setOpenCosts; costs(jj)];
setOpenHeuristics = [setOpenHeuristics; heuristics(jj)];
% 如果我们要处理的拓展点已经在setOpen 矩阵中
elseif max(setOpen == posinds(jj))
I = find(setOpen == posinds(jj));
% 如果通过目前的方法找到的这个点,比之前的方法好(代价小)就更新这个点
if setOpenCosts(I) > costs(jj)
costchart(setOpen(I)) = costs(jj);
setOpenCosts(I) = costs(jj);
setOpenHeuristics(I) = heuristics(jj);
fieldpointers(setOpen(I)) = movementdirections(jj);
end
% 如果我们要处理的拓展点已经在setClosed 矩阵中
else
I = find(setClosed == posinds(jj));
% 如果通过目前的方法找到的这个点,比之前的方法好(代价小)就更新这个点
if setClosedCosts(I) > costs(jj)
costchart(setClosed(I)) = costs(jj);
setClosedCosts(I) = costs(jj);
fieldpointers(setClosed(I)) = movementdirections(jj);
end
end
end
end
%%
if isempty(setOpen) break; end
set(axishandle,'CData',[costchart costchart(:,end); costchart(end,:) costchart(end,end)]);
set(gca,'CLim',[0 1.1*max(costchart(find(costchart < Inf)))]);
drawnow;
end
%%
%调用findWayBack函数进行路径回溯,并绘制出路径曲线
if max(ismember(setOpen,goalposind))
disp('Solution found!');
p = findWayBack(goalposind,fieldpointers); % 调用findWayBack函数进行路径回溯,将回溯结果放于矩阵P中
plot(p(:,2)+0.5,p(:,1)+0.5,'Color',0.2*ones(3,1),'LineWidth',4); %用 plot函数绘制路径曲线
drawnow;
drawnow;
[y,Fs] = audioread('000.wav'); sound(y,Fs); % 播放名为000的音乐,注意该文件需要跟matlab文件位于同一文件夹下,
elseif isempty(setOpen)
disp('No Solution!');
[y,Fs] = audioread('000.wav');
sound(y,Fs);
end
%%
%findWayBack函数用来进行路径回溯,这个函数的输入参数是终止点goalposind和矩阵fieldpointers,输出参数是P
function p = findWayBack(goalposind,fieldpointers)
n = length(fieldpointers); % 获取环境的长度也就是n
posind = goalposind;
[py,px] = ind2sub([n,n],posind); % 将索引值posind转换为坐标值 [py,px]
p = [py px];
%利用while循环进行回溯,当我们回溯到起始点的时候停止,也就是在矩阵fieldpointers中找到S时停止
while ~strcmp(fieldpointers{posind},'S')
switch fieldpointers{posind}
case 'L' % ’L’ 表示当前的点是由左边的点拓展出来的
px = px - 1;
case 'R' % ’R’ 表示当前的点是由右边的点拓展出来的
px = px + 1;
case 'U' % ’U’ 表示当前的点是由上面的点拓展出来的
py = py - 1;
case 'D' % ’D’ 表示当前的点是由下边的点拓展出来的
py = py + 1;
end
p = [p; py px];
posind = sub2ind([n n],py,px);% 将坐标值转换为索引值
end
end
%%
%这个函数的作用就是把输入的点作为父节点,然后进行拓展找到子节点,并且找到子节点的代价,并且把子节点距离终点的代价找到。
%函数的输出量中costs表示拓展的子节点到起始点的代价,heuristics表示拓展出来的点到终止点的距离大约是多少,posinds表示拓展出来的子节点
function [cost,heuristic,posinds] = findFValue(posind,costsofar,field,goalind,heuristicmethod)
n = length(field); % 获取矩阵的长度
[currentpos(1) currentpos(2)] = ind2sub([n n],posind); %将要进行拓展的点(也就是父节点)的索引值拓展成坐标值
[goalpos(1) goalpos(2)] = ind2sub([n n],goalind); %将终止点的索引值拓展成坐标值
cost = Inf*ones(4,1); heuristic = Inf*ones(4,1); pos = ones(4,2); %将矩阵cost和heuristic初始化为4x1的无穷大值的矩阵,pos初始化为4x2的值为1的矩阵
% 拓展方向一
newx = currentpos(2) - 1; newy = currentpos(1);
if newx > 0
pos(1,:) = [newy newx];
switch lower(heuristicmethod)
case 'euclidean'
heuristic(1) = 10*abs(goalpos(2)-newx) + 10*abs(goalpos(1)-newy);
case 'taxicab'
heuristic(1) = 10*abs(goalpos(2)-newx) +10*abs(goalpos(1)-newy);
end
cost(1) = costsofar + field(newy,newx);
end
% 拓展方向二
newx = currentpos(2) + 1; newy = currentpos(1);
if newx <= n
pos(2,:) = [newy newx];
switch lower(heuristicmethod)
case 'euclidean'
heuristic(2) = 10*abs(goalpos(2)-newx) +10*abs(goalpos(1)-newy);
case 'taxicab'
heuristic(2) = 10*abs(goalpos(2)-newx) + 10*abs(goalpos(1)-newy);
end
cost(2) = costsofar + field(newy,newx);
end
% 拓展方向三
newx = currentpos(2); newy = currentpos(1)-1;
if newy > 0
pos(3,:) = [newy newx];
switch lower(heuristicmethod)
case 'euclidean'
heuristic(3) = 10*abs(goalpos(2)-newx) + 10*abs(goalpos(1)-newy);
case 'taxicab'
heuristic(3) = 10*abs(goalpos(2)-newx) + 10*abs(goalpos(1)-newy);
end
cost(3) = costsofar + field(newy,newx);
end
% 拓展方向四
newx = currentpos(2); newy = currentpos(1)+1;
if newy <= n
pos(4,:) = [newy newx];
switch lower(heuristicmethod)
case 'euclidean'
heuristic(4) = 10*abs(goalpos(2)-newx) + 10*abs(goalpos(1)-newy);
case 'taxicab'
heuristic(4) = 10*abs(goalpos(2)-newx) + 10*abs(goalpos(1)-newy);
end
cost(4) = costsofar + field(newy,newx);
end
posinds = sub2ind([n n],pos(:,1),pos(:,2)); % 将拓展出来的子节点的坐标值转换为索引值
end
%%
%这个矩阵的作用就是随机生成环境,障碍物,起始点,终止点等
function [field, startposind, goalposind, costchart, fieldpointers] = initializeField(n,wallpercent)
field = 10*ones(n,n);%设置任意两方格间的距离为10
field(ind2sub([n n],ceil(n^2.*rand(n*n*wallpercent,1)))) = Inf;%向上取整
% 随机生成起始点和终止点
startposind = sub2ind([n,n],ceil(n.*rand),ceil(n.*rand)); %随机生成起始点的索引值
goalposind = sub2ind([n,n],ceil(n.*rand),ceil(n.*rand)); %随机生成终止点的索引值
field(startposind) = 0; field(goalposind) = 0; %把矩阵中起始点和终止点处的值设为0
costchart = NaN*ones(n,n);%生成一个nxn的矩阵costchart,每个元素都设为NaN。就是矩阵初始NaN无效数据
costchart(startposind) = 0;%在矩阵costchart中将起始点位置处的值设为0
% 生成元胞数组
fieldpointers = cell(n,n);%生成元胞数组n*n
fieldpointers{startposind} = 'S'; fieldpointers{goalposind} = 'G'; %将元胞数组的起始点的位置处设为 'S',终止点处设为'G'
fieldpointers(field==inf)={0};
end
% end of this function
%%
%利用随机生成的环境数据来进行环境的绘制
function axishandle = createFigure(field,costchart,startposind,goalposind)
% 这个if..else结构的作用是判断如果没有打开的figure图,则按照相关设置创建一个figure图
if isempty(gcbf) %gcbf是当前返回图像的句柄,isempty(gcbf)假如gcbf为空的话,返回的值是1,假如gcbf为非空的话,返回的值是0
figure('Position',[560 70 700 700], 'MenuBar','none'); %对创建的figure图像进行设置,设置其距离屏幕左侧的距离为450,距离屏幕下方的距离为50,长度和宽度都为700,并且关闭图像的菜单栏
axes('position', [0.01 0.01 0.99 0.99]); %设置坐标轴的位置,左下角的坐标设为0.01,0.01 右上角的坐标设为0.99 0.99 (可以认为figure图的左下角坐标为0 0 ,右上角坐标为1 1 )
else
gcf; cla; %gcf 返回当前 Figure 对象的句柄值,然后利用cla语句来清除它
end
n = length(field); %获取矩阵的长度,并赋值给变量n
field(field < Inf) = 0; %将fieid矩阵中的随机数(也就是没有障碍物的位置处)设为0
pcolor(1:n+1,1:n+1,[field field(:,end); field(end,:) field(end,end)]);%多加了一个重复的(由n X n变为 n+1 X n+1 )
cmap = flipud(colormap('jet')); %生成的cmap是一个256X3的矩阵,每一行的3个值都为0-1之间数,分别代表颜色组成的rgb值
cmap(1,:) = zeros(3,1); cmap(end,:) = ones(3,1); %将矩阵cmap的第一行设为0 ,最后一行设为1
colormap(flipud(cmap)); %进行颜色的倒转
hold on;
axishandle = pcolor([1:n+1],[1:n+1],[costchart costchart(:,end); costchart(end,:) costchart(end,end)]); %将矩阵costchart进行拓展,插值着色后赋给axishandle
[goalposy,goalposx] = ind2sub([n,n],goalposind);
[startposy,startposx] = ind2sub([n,n],startposind);
plot(goalposx+0.5,goalposy+0.5,'ys','MarkerSize',10,'LineWidth',6);
plot(startposx+0.5,startposy+0.5,'go','MarkerSize',10,'LineWidth',6);
%uicontrol('Style','pushbutton','String','RE-DO', 'FontSize',12, 'Position', [1 1 60 40], 'Callback','astardemo');
end
十一 、经过拐角优化后的动态衡量启发式A星算法的完整的代码
%matlab初始化
clc; %清除命令窗口的内容
clear all; %清除工作空间的所有变量,函数,和MEX文件
close all; %关闭所有的figure窗口
[y,Fs] = audioread('001.wav'); sound(y,Fs); % 播放名为001的音乐,注意该文件需要跟matlab文件位于同一文件夹下
%功能参数的设定部分
n = 30; % 产生一个n x n的方格,修改此值可以修改生成图片的方格数
wallpercent = 0.4; % 这个变量代表生成的障碍物占总方格数的比例 ,如0.5 表示障碍物占总格数的50%
Weights=1; %动态衡量启发式A星算法中的h(n)权重系数
Corner_amend=1; %选择是否进行拐角的修正,该变量设为0则不进行拐角修正,设为1则进行拐角修正
%方格以及障碍物的创建
[field, startposind, goalposind, costchart, fieldpointers] =initializeField(n,wallpercent); %随机生成包含障碍物,起始点,终止点等信息的矩阵
% 路径规划中用到的一些矩阵的初始化
setOpen = [startposind]; setOpenCosts = [0]; setOpenHeuristics = [Inf];
setClosed = []; setClosedCosts = [];
movementdirections = {'R','L','D','U'}; %移动方向
%初始化一些进行路径的修正需要用到的变量
Parent_node=0; %Parent_node初始化,否则会报错
Expected_note=0;%Expected_note初始化,否则会报错
untext_ii=0; %未经过检验的新的ii
amend_count=0;% 记录修正的次数
% 这个函数用来随机生成环境,障碍物,起点,终点
axishandle = createFigure(field,costchart,startposind,goalposind); %将随机生成的方格及障碍物的数据生成图像
%%
% 这个while循环是本程序的核心,利用循环进行迭代来寻找终止点
while ~max(ismember(setOpen,goalposind)) && ~isempty(setOpen)
[temp, ii] = min(setOpenCosts +Weights*setOpenHeuristics); %寻找拓展出来的最小值
if ((setOpen(ii)~=startposind) && (Corner_amend==1))
[new_ii,amend_count_1]=Path_optimization(temp, ii,fieldpointers,setOpen,setOpenCosts,startposind,Weights,setOpenHeuristics,Parent_node,Expected_note,untext_ii,amend_count); %进行路径的修正,在保证不增加距离的基础上,使其减少转弯的次数
ii=new_ii;
amend_count=amend_count_1;
end
%这个函数的作用就是把输入的点作为父节点,然后进行拓展找到子节点,并且找到子节点的代价,并且把子节点距离终点的代价找到
[costs,heuristics,posinds] = findFValue(setOpen(ii),setOpenCosts(ii), field,goalposind,'euclidean');
setClosed = [setClosed; setOpen(ii)]; % 将找出来的拓展出来的点中代价最小的那个点串到矩阵setClosed 中
setClosedCosts = [setClosedCosts; setOpenCosts(ii)]; % 将拓展出来的点中代价最小的那个点的代价串到矩阵setClosedCosts 中
% 从setOpen中删除刚才放到矩阵setClosed中的那个点
%如果这个点位于矩阵的内部
if (ii > 1 && ii < length(setOpen))
setOpen = [setOpen(1:ii-1); setOpen(ii+1:end)];
setOpenCosts = [setOpenCosts(1:ii-1); setOpenCosts(ii+1:end)];
setOpenHeuristics = [setOpenHeuristics(1:ii-1); setOpenHeuristics(ii+1:end)];
%如果这个点位于矩阵第一行
elseif (ii == 1)
setOpen = setOpen(2:end);
setOpenCosts = setOpenCosts(2:end);
setOpenHeuristics = setOpenHeuristics(2:end);
%如果这个点位于矩阵的最后一行
else
setOpen = setOpen(1:end-1);
setOpenCosts = setOpenCosts(1:end-1);
setOpenHeuristics = setOpenHeuristics(1:end-1);
end
%%
% 把拓展出来的点中符合要求的点放到setOpen 矩阵中,作为待选点
for jj=1:length(posinds)
if ~isinf(costs(jj)) % 判断该点(方格)处没有障碍物
% 判断一下该点是否 已经存在于setOpen 矩阵或者setClosed 矩阵中
% 如果我们要处理的拓展点既不在setOpen 矩阵,也不在setClosed 矩阵中
if ~max([setClosed; setOpen] == posinds(jj))
fieldpointers(posinds(jj)) = movementdirections(jj);
costchart(posinds(jj)) = costs(jj);
setOpen = [setOpen; posinds(jj)];
setOpenCosts = [setOpenCosts; costs(jj)];
setOpenHeuristics = [setOpenHeuristics; heuristics(jj)];
% 如果我们要处理的拓展点已经在setOpen 矩阵中
elseif max(setOpen == posinds(jj))
I = find(setOpen == posinds(jj));
% 如果通过目前的方法找到的这个点,比之前的方法好(代价小)就更新这个点
if setOpenCosts(I) > costs(jj)
costchart(setOpen(I)) = costs(jj);
setOpenCosts(I) = costs(jj);
setOpenHeuristics(I) = heuristics(jj);
fieldpointers(setOpen(I)) = movementdirections(jj);
end
% 如果我们要处理的拓展点已经在setClosed 矩阵中
else
I = find(setClosed == posinds(jj));
% 如果通过目前的方法找到的这个点,比之前的方法好(代价小)就更新这个点
if setClosedCosts(I) > costs(jj)
costchart(setClosed(I)) = costs(jj);
setClosedCosts(I) = costs(jj);
fieldpointers(setClosed(I)) = movementdirections(jj);
end
end
end
end
%%
if isempty(setOpen) break; end
set(axishandle,'CData',[costchart costchart(:,end); costchart(end,:) costchart(end,end)]);
set(gca,'CLim',[0 1.1*max(costchart(find(costchart < Inf)))]);
drawnow;
end
%%
%调用findWayBack函数进行路径回溯,并绘制出路径曲线
if max(ismember(setOpen,goalposind))
disp('Solution found!');
p = findWayBack(goalposind,fieldpointers); % 调用findWayBack函数进行路径回溯,将回溯结果放于矩阵P中
plot(p(:,2)+0.5,p(:,1)+0.5,'Color',0.2*ones(3,1),'LineWidth',4); %用 plot函数绘制路径曲线
drawnow;
drawnow;
clear sound
[y,Fs] = audioread('002.wav'); sound(y,Fs); % 播放名为000的音乐,注意该文件需要跟matlab文件位于同一文件夹下
elseif isempty(setOpen)
disp('No Solution!');
clear sound
[y,Fs] = audioread('000.wav');
sound(y,Fs);
end
%%
%findWayBack函数用来进行路径回溯,这个函数的输入参数是终止点goalposind和矩阵fieldpointers,输出参数是P
function p = findWayBack(goalposind,fieldpointers)
n = length(fieldpointers); % 获取环境的长度也就是n
posind = goalposind;
[py,px] = ind2sub([n,n],posind); % 将索引值posind转换为坐标值 [py,px]
p = [py px];
%利用while循环进行回溯,当我们回溯到起始点的时候停止,也就是在矩阵fieldpointers中找到S时停止
while ~strcmp(fieldpointers{posind},'S')
switch fieldpointers{posind}
case 'L' % ’L’ 表示当前的点是由左边的点拓展出来的
px = px - 1;
case 'R' % ’R’ 表示当前的点是由右边的点拓展出来的
px = px + 1;
case 'U' % ’U’ 表示当前的点是由上面的点拓展出来的
py = py - 1;
case 'D' % ’D’ 表示当前的点是由下边的点拓展出来的
py = py + 1;
end
p = [p; py px];
posind = sub2ind([n n],py,px);% 将坐标值转换为索引值
end
end
%%
%这个函数的作用就是把输入的点作为父节点,然后进行拓展找到子节点,并且找到子节点的代价,并且把子节点距离终点的代价找到。
%函数的输出量中costs表示拓展的子节点到起始点的代价,heuristics表示拓展出来的点到终止点的距离大约是多少,posinds表示拓展出来的子节点
function [cost,heuristic,posinds] = findFValue(posind,costsofar,field,goalind,heuristicmethod)
n = length(field); % 获取矩阵的长度
[currentpos(1) currentpos(2)] = ind2sub([n n],posind); %将要进行拓展的点(也就是父节点)的索引值拓展成坐标值
[goalpos(1) goalpos(2)] = ind2sub([n n],goalind); %将终止点的索引值拓展成坐标值
cost = Inf*ones(4,1); heuristic = Inf*ones(4,1); pos = ones(4,2); %将矩阵cost和heuristic初始化为4x1的无穷大值的矩阵,pos初始化为4x2的值为1的矩阵
% 拓展方向一
newx = currentpos(2) - 1; newy = currentpos(1);
if newx > 0
pos(1,:) = [newy newx];
switch lower(heuristicmethod)
case 'euclidean'
heuristic(1) = 10*abs(goalpos(2)-newx) + 10*abs(goalpos(1)-newy);
case 'taxicab'
heuristic(1) = 10*abs(goalpos(2)-newx) +10*abs(goalpos(1)-newy);
end
cost(1) = costsofar + field(newy,newx);
end
% 拓展方向二
newx = currentpos(2) + 1; newy = currentpos(1);
if newx <= n
pos(2,:) = [newy newx];
switch lower(heuristicmethod)
case 'euclidean'
heuristic(2) = 10*abs(goalpos(2)-newx) +10*abs(goalpos(1)-newy);
case 'taxicab'
heuristic(2) = 10*abs(goalpos(2)-newx) + 10*abs(goalpos(1)-newy);
end
cost(2) = costsofar + field(newy,newx);
end
% 拓展方向三
newx = currentpos(2); newy = currentpos(1)-1;
if newy > 0
pos(3,:) = [newy newx];
switch lower(heuristicmethod)
case 'euclidean'
heuristic(3) = 10*abs(goalpos(2)-newx) + 10*abs(goalpos(1)-newy);
case 'taxicab'
heuristic(3) = 10*abs(goalpos(2)-newx) + 10*abs(goalpos(1)-newy);
end
cost(3) = costsofar + field(newy,newx);
end
% 拓展方向四
newx = currentpos(2); newy = currentpos(1)+1;
if newy <= n
pos(4,:) = [newy newx];
switch lower(heuristicmethod)
case 'euclidean'
heuristic(4) = 10*abs(goalpos(2)-newx) + 10*abs(goalpos(1)-newy);
case 'taxicab'
heuristic(4) = 10*abs(goalpos(2)-newx) + 10*abs(goalpos(1)-newy);
end
cost(4) = costsofar + field(newy,newx);
end
posinds = sub2ind([n n],pos(:,1),pos(:,2)); % 将拓展出来的子节点的坐标值转换为索引值
end
%%
%这个矩阵的作用就是随机生成环境,障碍物,起始点,终止点等
function [field, startposind, goalposind, costchart, fieldpointers] = initializeField(n,wallpercent)
field = 10*ones(n,n);%设置任意两方格间的距离为10
field(ind2sub([n n],ceil(n^2.*rand(n*n*wallpercent,1)))) = Inf;%向上取整
% 随机生成起始点和终止点
startposind = sub2ind([n,n],ceil(n.*rand),ceil(n.*rand)); %随机生成起始点的索引值
goalposind = sub2ind([n,n],ceil(n.*rand),ceil(n.*rand)); %随机生成终止点的索引值
field(startposind) = 0; field(goalposind) = 0; %把矩阵中起始点和终止点处的值设为0
costchart = NaN*ones(n,n);%生成一个nxn的矩阵costchart,每个元素都设为NaN。就是矩阵初始NaN无效数据
costchart(startposind) = 0;%在矩阵costchart中将起始点位置处的值设为0
% 生成元胞数组
fieldpointers = cell(n,n);%生成元胞数组n*n
fieldpointers(:)= {'1'};
fieldpointers{startposind} = 'S'; fieldpointers{goalposind} = 'G'; %将元胞数组的起始点的位置处设为 'S',终止点处设为'G'
fieldpointers(field==inf)={'0'};
end
% end of this function
%%
%利用随机生成的环境数据来进行环境的绘制
function axishandle = createFigure(field,costchart,startposind,goalposind)
% 这个if..else结构的作用是判断如果没有打开的figure图,则按照相关设置创建一个figure图
if isempty(gcbf) %gcbf是当前返回图像的句柄,isempty(gcbf)假如gcbf为空的话,返回的值是1,假如gcbf为非空的话,返回的值是0
figure('Position',[560 70 700 700], 'MenuBar','none'); %对创建的figure图像进行设置,设置其距离屏幕左侧的距离为450,距离屏幕下方的距离为50,长度和宽度都为700,并且关闭图像的菜单栏
axes('position', [0.01 0.01 0.99 0.99]); %设置坐标轴的位置,左下角的坐标设为0.01,0.01 右上角的坐标设为0.99 0.99 (可以认为figure图的左下角坐标为0 0 ,右上角坐标为1 1 )
else
gcf; cla; %gcf 返回当前 Figure 对象的句柄值,然后利用cla语句来清除它
end
n = length(field); %获取矩阵的长度,并赋值给变量n
field(field < Inf) = 0; %将fieid矩阵中的随机数(也就是没有障碍物的位置处)设为0
pcolor(1:n+1,1:n+1,[field field(:,end); field(end,:) field(end,end)]);%多加了一个重复的(由n X n变为 n+1 X n+1 )
cmap = flipud(colormap('jet')); %生成的cmap是一个256X3的矩阵,每一行的3个值都为0-1之间数,分别代表颜色组成的rgb值
cmap(1,:) = zeros(3,1); cmap(end,:) = ones(3,1); %将矩阵cmap的第一行设为0 ,最后一行设为1
colormap(flipud(cmap)); %进行颜色的倒转
hold on;
axishandle = pcolor([1:n+1],[1:n+1],[costchart costchart(:,end); costchart(end,:) costchart(end,end)]); %将矩阵costchart进行拓展,插值着色后赋给axishandle
[goalposy,goalposx] = ind2sub([n,n],goalposind);
[startposy,startposx] = ind2sub([n,n],startposind);
plot(goalposx+0.5,goalposy+0.5,'ys','MarkerSize',10,'LineWidth',6);
plot(startposx+0.5,startposy+0.5,'go','MarkerSize',10,'LineWidth',6);
%uicontrol('Style','pushbutton','String','RE-DO', 'FontSize',12, 'Position', [1 1 60 40], 'Callback','astardemo');
end
%%
function [new_ii,amend_count_1] = Path_optimization(temp, ii,fieldpointers,setOpen,setOpenCosts,startposind,Weights,setOpenHeuristics,Parent_node,Expected_note,untext_ii,amend_count)
n = length(fieldpointers); %获取矩阵的长度,并赋值给变量n
%获取其父节点的索引值
switch fieldpointers {setOpen(ii)}
case 'L' % ’L’ 表示当前的点是由左边的点拓展出来的
Parent_node = setOpen(ii) - n;
case 'R' % ’R’ 表示当前的点是由右边的点拓展出来的
Parent_node = setOpen(ii) + n;
case 'U' % ’U’ 表示当前的点是由上面的点拓展出来的
Parent_node = setOpen(ii) -1;
case 'D' % ’D’ 表示当前的点是由下边的点拓展出来的
Parent_node = setOpen(ii) + 1;
end
if Parent_node==startposind %如果这个点的父节点是起始点的话,跳过修正
new_ii=ii;
amend_count_1=amend_count;
else
%获取期望下一步要走的点的索引值
switch fieldpointers{Parent_node}
case 'L' % ’L’ 表示当前的点是由左边的点拓展出来的,走直线的话,我们期望要走的下一个点为此点右边的点
Expected_note = Parent_node + n;
case 'R' % ’R’ 表示当前的点是由右边的点拓展出来的,走直线的话,我们期望要走的下一个点为此点左边的点
Expected_note = Parent_node - n;
case 'U' % ’U’ 表示当前的点是由上面的点拓展出来的,走直线的话,我们期望要走的下一个点为此点下面的点
Expected_note = Parent_node +1;
case 'D' % ’D’ 表示当前的点是由下边的点拓展出来的,走直线的话,我们期望要走的下一个点为此点上面的点
Expected_note = Parent_node - 1;
end
if ((Expected_note<=0)||(Expected_note>n*n)) %如果我们期望的点不在待选点矩阵setOpen中,或者超出边界,跳过修正
new_ii=ii;
amend_count_1=amend_count;
else
%计算新的要进行拓展的点在setOPen中的索引值
if fieldpointers{setOpen(ii)}==fieldpointers{Parent_node} %如果修正之前要走的点就是我们期望的构成直线的点,跳出修正
new_ii=ii;
amend_count_1=amend_count;
elseif find(setOpen == Expected_note) %如果我们期望要走的点在待选点矩阵setOpen中
untext_ii=find(setOpen == Expected_note);
now_cost=setOpenCosts(untext_ii) +Weights*setOpenHeuristics(untext_ii); %计算期望点要花费的代价
if temp==now_cost %如果我们期望的点要花费的代价等于修正之前要走的点花费的代价,就进行修正(因为之前要走的点,是待选点矩阵setOPen中代价最小的一个点之一,所以期望的点的代价不可能小于该点)
new_ii=untext_ii; %将新的setOPen矩阵的索引值赋值给new_ii输出
amend_count=amend_count+1;
amend_count_1=amend_count; %amend_count_1中记录了我们进行修正的次数,为了查看这个函数是否有发挥作用
else
new_ii=ii; %如果我们期望的点要花费的代价大于修正之前要走的点花费的代价,就跳过修正(A星算法要保证进行拓展的点是待选点中代价最小的,这也是导致远离终止点的哪一类拐角无法得到修正的原因)
amend_count_1=amend_count;
end
else
new_ii=ii; %如果我们期望的点不在待选点矩阵setOpen中(也就是这个点是障碍物或者超出边界了),则跳过修正
amend_count_1=amend_count;
end
end
end
end
本篇文章到这里就结束了,本系列文章到这里也就告一段落了,本文介绍的内容的完整代码的MATLAB文件我会放到附件里,听说在上传的时候设为粉丝可下载是不需要花费积分的,大家看一下需不需要积分,若还是需要积分,在评论区留言,我直接传给你
本篇文章内容的附件链接:
①matlab文件链接:动态衡量式A星算法及拐角优化matlab文件(https://download.csdn.net/download/qq_44339029/12903557)
②涉及的音乐文件链接:动态衡量式A星算法代码涉及的音乐文件(https://download.csdn.net/download/qq_44339029/12905811)
欢迎大家积极交流,本文未经允许谢绝转载