【中级算法】设计/数学/其他 (下)
目录
七、设计问题
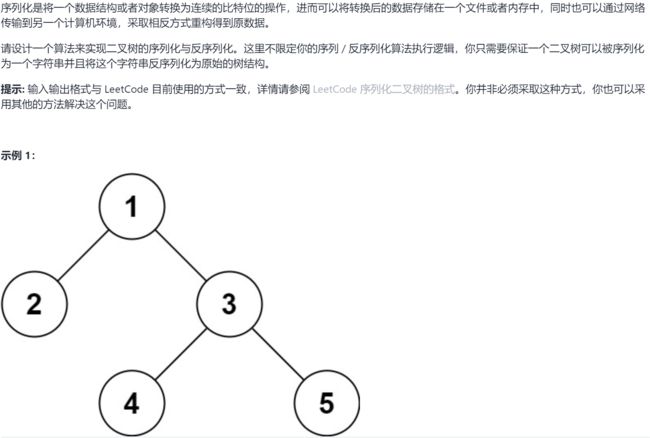
7.1 LC 二叉树的序列化与反序列化 ☆
7.1.1 题求
7.1.2 求解
7.2 LC 常数时间插入、删除和获取随机元素
7.2.1 题求
7.2.2 求解
八、数学
九、其他
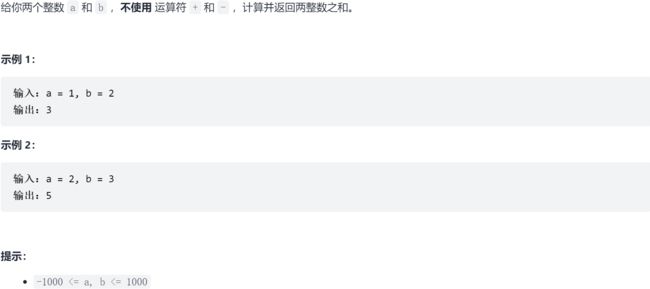
9.1 LC 两整数之和
9.1.1 题求
9.1.2 求解
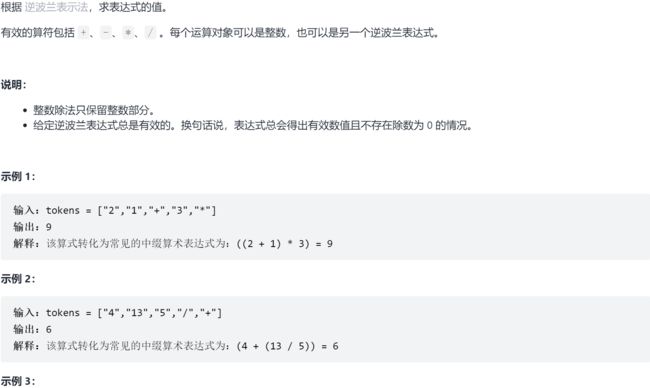
9.2 LC 逆波兰表达式求值 ☆
9.2.1 题求
9.2.2 求解
9.3 LC 多数元素 ☆
9.3.1 题求
9.3.2 求解
9.4 LC 任务调度器
9.4.1 题求
9.4.2 求解
七、设计问题
7.1 LC 二叉树的序列化与反序列化 ☆
7.1.1 题求
7.1.2 求解
法一:列表与奇偶索引记录二叉树
# 55.85% - 136ms
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode(object):
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Codec:
def serialize(self, root):
""" Encodes a tree to a single string. (recursion)
type root: TreeNode
rtype: str
"""
def encode_recur(node, index):
if not node:
return
record[index] = node.val # 当前节点索引为 index
encode_recur(node.left, index*2+1) # 当前节点左子节点索引为 index*2+1
encode_recur(node.right, index*2+2) # 当前节点右子节点索引为 index*2+2
record = {} # 仅记录有效节点的哈希表, {index:val}
encode_recur(root, 0)
return str(record)
def deserialize(self, data):
""" Decodes your encoded data to tree. (recursion)
type data: str
rtype: TreeNode
"""
def decode_recur(index):
if index not in record: # 索引不在哈希表中, 节点为 None
return None
root = TreeNode(record[index]) # 根据索引取得节点值, 创建当前节点
root.left = decode_recur(index*2+1) # 当前节点指向左子节点 index*2+1
root.right = decode_recur(index*2+2) # 当前节点指向右子节点 index*2+2
return root
record = eval(data) # str -> dict
return decode_recur(0)
# Your Codec object will be instantiated and called as such:
# ser = Codec()
# deser = Codec()
# ans = deser.deserialize(ser.serialize(root))参考资料:
力扣
7.2 LC 常数时间插入、删除和获取随机元素
7.2.1 题求
7.2.2 求解
法一:哈希表+列表
from random import choice
class RandomizedSet():
def __init__(self):
"""
Initialize your data structure here.
"""
self.dict = {} # key: val = num: len(list)=idx
self.list = [] # idx -> val
def insert(self, val: int) -> bool:
"""
Inserts a value to the set. Returns true if the set did not already contain the specified element.
"""
if val in self.dict:
return False
self.dict[val] = len(self.list)
self.list.append(val)
return True
def remove(self, val: int) -> bool:
"""
Removes a value from the set. Returns true if the set contained the specified element.
"""
if val in self.dict:
# 待删除元素 val 及其在 list 中的索引 idx=self.dict[val]
# list 最后一个元素 last_element=self.list[-1]
last_element, idx = self.list[-1], self.dict[val]
# 二者交换 self.dict[last_element]=idx, self.list[idx]=last_element
self.list[idx], self.dict[last_element] = last_element, idx
# 直接删除最后一个元素 即 删除 val
self.list.pop()
del self.dict[val]
return True
return False
def getRandom(self) -> int:
"""
Get a random element from the set.
"""
# 随机选择 list 中的元素
return choice(self.list)参考资料:
力扣
八、数学
九、其他
9.1 LC 两整数之和 ☆
9.1.1 题求
9.1.2 求解
# https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/sum-of-two-integers/solution/liang-zheng-shu-zhi-he-by-leetcode-solut-c1s3/
MASK1 = 4294967296 # 2^32
MASK2 = 2147483648 # 2^31
MASK3 = 2147483647 # 2^31-1
class Solution:
def getSum(self, a: int, b: int) -> int:
a %= MASK1
b %= MASK1
while b != 0:
carry = ((a & b) << 1) % MASK1 # 当前进位结果
a = (a ^ b) % MASK1 # 当前无进位加法结果
b = carry # 进位
if a & MASK2: # 负数
return ~((a ^ MASK2) ^ MASK3)
else: # 正数
return a参考资料:
力扣
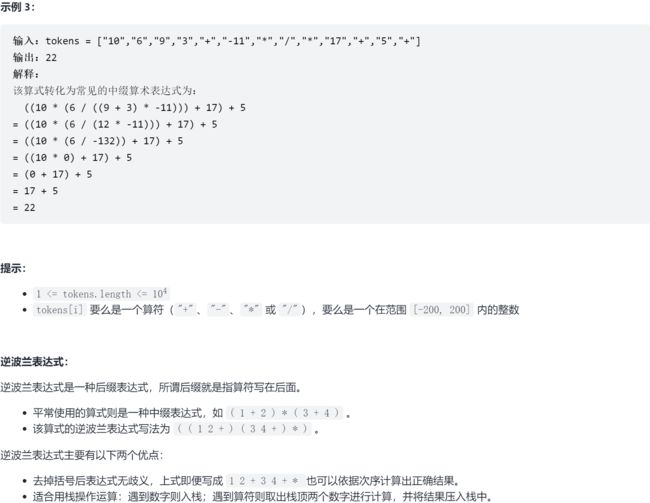
9.2 LC 逆波兰表达式求值 ☆
9.2.1 题求
9.2.2 求解
法一:栈
class Solution:
def evalRPN(self, tokens: List[str]) -> int:
# ["2","1","+","3","*"] -> ((2 + 1) * 3) = 9
stack = []
for i in tokens:
if i == '+':
num = stack.pop()
stack[-1] += num
elif i == '-':
num = stack.pop()
stack[-1] -= num
elif i == '/':
num = stack.pop()
stack[-1] = int(stack[-1] / num)
elif i == '*':
num = stack.pop()
stack[-1] *= num
else:
stack.append(int(i))
return stack[0]参考资料:
力扣
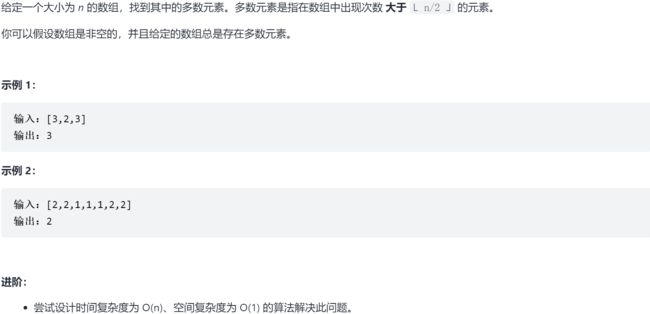
9.3 LC 多数元素 ☆
9.3.1 题求
9.3.2 求解
法一:摩尔投票法
class Solution:
def majorityElement(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
count = candidate = 0
for num in nums:
if count == 0:
candidate = num
count += (1 if num == candidate else -1)
return candidate参考资料:
力扣
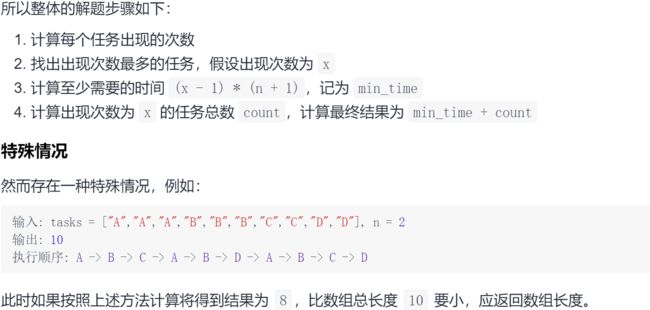
9.4 LC 任务调度器
9.4.1 题求
9.4.2 求解
来源:力扣
法一:模拟
# https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/task-scheduler/solution/python-xiang-jie-by-jalan/
class Solution(object):
def leastInterval(self, tasks, n):
# 任务总数
length = len(tasks)
if length <= 1:
return length
# 用于记录每个任务出现次数
task_map = collections.defaultdict(int)
for task in tasks:
task_map[task] += 1
# 按任务出现次数从大到小排序
task_sort = sorted(task_map.items(), key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)
# 出现最多次任务的次数
max_task_count = task_sort[0][1]
# 至少需要的最短时间
res = (max_task_count - 1) * (n + 1)
# 其余出现最多次的任务个数
for sort in task_sort:
if sort[1] != max_task_count:
break
res += 1
# 如果结果比任务数量少,则返回总任务数
return res if res >= length else length法二:构造
# https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/task-scheduler/solution/ren-wu-diao-du-qi-by-leetcode-solution-ur9w/
class Solution:
def leastInterval(self, tasks: List[str], n: int) -> int:
freq = collections.Counter(tasks)
# 最多的执行次数
maxExec = max(freq.values())
# 具有最多执行次数的任务数量
maxCount = sum(1 for v in freq.values() if v == maxExec)
return max((maxExec - 1) * (n + 1) + maxCount, len(tasks))参考资料:
力扣