fast rcnn 代码解析(一)
 、
、
输入为一张图像和2000个候选框,conv5的特征和2000个候选框同时输入到Roi Pooling层中,将不同大小的框映射到conv5特征图,并统一为相同的尺寸,其实就是将大小不同的矩形框映射成大小相同的矩形框,Roi Pooling层如下所示:
由于2000个矩形框中的坐标对应的是原始图像,首先坐标映射到conv5的feature map上,就是把各个坐标除以输入图片与feature map的大小的比值,得到了feature map上的box坐标后,我们使用pooling得到输出;由于输入的图片大小不一,所以这里我们使用的spp pooling,spp pooling在pooling的过程中需要计算pooling后的结果对应的两个像素点反映社到feature map上所占的范围,然后在那个范围中进行取max或者取average。
在\caffe-fast-rcnn\src\caffe\layers\roi_pooling_layer.cu中查看具体实现过程如下
// LayerSetUp
template
void ROIPoolingLayer::LayerSetUp(const vector*>& bottom,
const vector*>& top) {
ROIPoolingParameter roi_pool_param = this->layer_param_.roi_pooling_param();
//经过Pooling后的feature map的高
pooled_height_ = roi_pool_param.pooled_h();
//经过Pooling后的feature map的宽
pooled_width_ = roi_pool_param.pooled_w();
//输入图片与feature map之前的比值,这个feature map指roi pooling层的输入
spatial_scale_ = roi_pool_param.spatial_scale();
}
//Reshape
template
void ROIPoolingLayer::Reshape(const vector*>& bottom,
const vector*>& top) {
//输入的feature map的channel数
channels_ = bottom[0]->channels();
//输入的feature map的高
height_ = bottom[0]->height();
//输入的feature map的宽
width_ = bottom[0]->width();
//设置输出的形状NCHW,N=ROI的个数,C=channels_,H=pooled_height_,W=pooled_width_
top[0]->Reshape(bottom[1]->num(), channels_, pooled_height_,
pooled_width_);
//max_idx_的形状与top一致
max_idx_.Reshape(bottom[1]->num(), channels_, pooled_height_,
pooled_width_);
}
//Forward
template
void ROIPoolingLayer::Forward_cpu(const vector*>& bottom,
const vector*>& top) {
//输入有两部分组成,data和rois
const Dtype* bottom_data = bottom[0]->cpu_data();
const Dtype* bottom_rois = bottom[1]->cpu_data();
// Number of ROIs
int num_rois = bottom[1]->num();
int batch_size = bottom[0]->num();
int top_count = top[0]->count();
Dtype* top_data = top[0]->mutable_cpu_data();
caffe_set(top_count, Dtype(-FLT_MAX), top_data);
int* argmax_data = max_idx_.mutable_cpu_data();
caffe_set(top_count, -1, argmax_data);
// For each ROI R = [batch_index x1 y1 x2 y2]: max pool over R
for (int n = 0; n < num_rois; ++n) {
int roi_batch_ind = bottom_rois[0];
//把原图的坐标映射到feature map上面
int roi_start_w = round(bottom_rois[1] * spatial_scale_);
int roi_start_h = round(bottom_rois[2] * spatial_scale_);
int roi_end_w = round(bottom_rois[3] * spatial_scale_);
int roi_end_h = round(bottom_rois[4] * spatial_scale_);
//计算每个roi在feature map上面的大小
int roi_height = max(roi_end_h - roi_start_h + 1, 1);
int roi_width = max(roi_end_w - roi_start_w + 1, 1);
//pooling之后的feature map的一个值对应于pooling之前的feature map上的大小
//注:由于roi的大小不一致,所以每次都需要计算一次
const Dtype bin_size_h = static_cast(roi_height)
/ static_cast(pooled_height_);
const Dtype bin_size_w = static_cast(roi_width)
/ static_cast(pooled_width_);
//找到对应的roi的feature map,如果input data的batch size为1
//那么roi_batch_ind=0
const Dtype* batch_data = bottom_data + bottom[0]->offset(roi_batch_ind);
//pooling的过程是针对每一个channel的,所以需要循环遍历
for (int c = 0; c < channels_; ++c) {
//计算output的每一个值,所以需要遍历一遍output,然后求出所有值
for (int ph = 0; ph < pooled_height_; ++ph) {
for (int pw = 0; pw < pooled_width_; ++pw) {
// Compute pooling region for this output unit:
// start (included) = floor(ph * roi_height / pooled_height_)
// end (excluded) = ceil((ph + 1) * roi_height / pooled_height_)
// 计算output上的一点对应于input上面区域的大小[hstart, wstart, hend, wend]
int hstart = static_cast(floor(static_cast(ph)
* bin_size_h));
int hend = static_cast(ceil(static_cast(ph + 1)
* bin_size_h));
int wstart = static_cast(floor(static_cast(pw)
* bin_size_w));
int wend = static_cast(ceil(static_cast(pw + 1)
* bin_size_w));
//将映射后的区域平动到对应的位置[hstart, wstart, hend, wend]
hstart = min(max(hstart + roi_start_h, 0), height_);
hend = min(max(hend + roi_start_h, 0), height_);
wstart = min(max(wstart + roi_start_w, 0), width_);
wend = min(max(wend + roi_start_w, 0), width_);
//如果映射后的矩形框不符合
bool is_empty = (hend <= hstart) || (wend <= wstart);
//pool_index指的是此时计算的output的值对应于output的位置
const int pool_index = ph * pooled_width_ + pw;
//如果矩形不符合,此处output的值设为0,此处的对应于输入区域的最大值为-1
if (is_empty) {
top_data[pool_index] = 0;
argmax_data[pool_index] = -1;
}
//遍历output的值对应于input的区域块
for (int h = hstart; h < hend; ++h) {
for (int w = wstart; w < wend; ++w) {
// 对应于input上的位置
const int index = h * width_ + w;
//计算区域块的最大值,保存在output对应的位置上
//同时记录最大值的索引
if (batch_data[index] > top_data[pool_index]) {
top_data[pool_index] = batch_data[index];
argmax_data[pool_index] = index;
}
}
}
}
}
// Increment all data pointers by one channel
batch_data += bottom[0]->offset(0, 1);
top_data += top[0]->offset(0, 1);
argmax_data += max_idx_.offset(0, 1);
}
// Increment ROI data pointer
bottom_rois += bottom[1]->offset(1);
}
} 
如上图所示,输入层一共有5个输出,该层是一个python层,源代码在fast-rcnn-master\lib\roi_data_layer\layer.py中:
def setup(self, bottom, top):
"""Setup the RoIDataLayer."""
# parse the layer parameter string, which must be valid YAML
# 将五个输出,reshape为对应的大小
layer_params = yaml.load(self.param_str_)
self._num_classes = layer_params['num_classes']
self._name_to_top_map = {
'data': 0,
'rois': 1,
'labels': 2}
# data blob: holds a batch of N images, each with 3 channels
# The height and width (100 x 100) are dummy values
top[0].reshape(1, 3, 100, 100)
# rois blob: holds R regions of interest, each is a 5-tuple
# (n, x1, y1, x2, y2) specifying an image batch index n and a
# rectangle (x1, y1, x2, y2)
top[1].reshape(1, 5)
# labels blob: R categorical labels in [0, ..., K] for K foreground
# classes plus background
top[2].reshape(1)
if cfg.TRAIN.BBOX_REG:
self._name_to_top_map['bbox_targets'] = 3
self._name_to_top_map['bbox_loss_weights'] = 4
# bbox_targets blob: R bounding-box regression targets with 4
# targets per class
top[3].reshape(1, self._num_classes * 4)
# bbox_loss_weights blob: At most 4 targets per roi are active;
# thisbinary vector sepcifies the subset of active targets
top[4].reshape(1, self._num_classes * 4)
def forward(self, bottom, top):
"""Get blobs and copy them into this layer's top blob vector."""
# 进入下一个minibatch
blobs = self._get_next_minibatch()
for blob_name, blob in blobs.iteritems():
top_ind = self._name_to_top_map[blob_name]
# Reshape net's input blobs
top[top_ind].reshape(*(blob.shape))
# Copy data into net's input blobs
top[top_ind].data[...] = blob.astype(np.float32, copy=False)
def backward(self, top, propagate_down, bottom):
"""This layer does not propagate gradients."""
pass
def reshape(self, bottom, top):
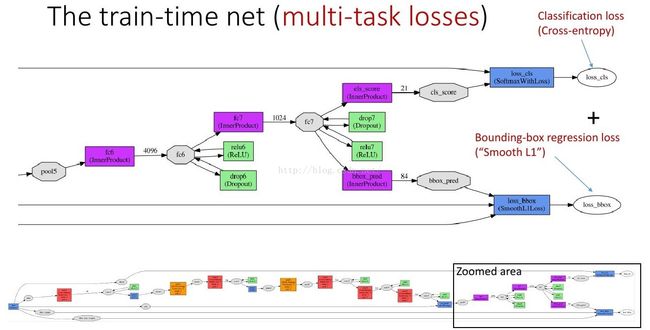
pass联合的损失函数,分类层为互熵损失,回归层为平滑的L1损失
两个输出层,一个对每个RoI输出离散概率分布,类别k=21:
一个输出bounding box回归的位移:
k表示类别的索引,前两个参数是指相对于object proposal尺度不变的平移,后两个参数是指对数空间中相对于object proposal的高与宽。把这两个输出的损失写到一起:
k*是真实类别,式中第一项是分类损失,第二项是定位损失,L由R个输出取均值而来.对于分类loss,是一个N+1路的softmax输出,其中的N是类别个数,1是背景。对于回归loss,是一个4xN路输出的regressor,也就是说对于每个类别都会训练一个单独的regressor,这里regressor的loss不是L2的,而是一个平滑的L1,形式如下: