【论文阅读】VIT——AN IMAGE IS WORTH 16X16 WORDS: TRANSFORMERS FOR IMAGE RECOGNITION AT SCALE
文章目录
-
-
- 论文阅读
- 代码实现
-
- vit_model.py
- train.py
- predict.py
- 实验结果
-
论文阅读
感谢P导
AN IMAGE IS WORTH 16X16 WORDS:TRANSFORMERS FOR IMAGE RECOGNITION AT SCALE
使用Transformer在全局方面提取特征,没有引入很多的归纳偏置,模型的上界高,没有相应的先验假设。数据量的要求和归纳偏置的引入成反比,归纳偏置的引入就是引入人为经验
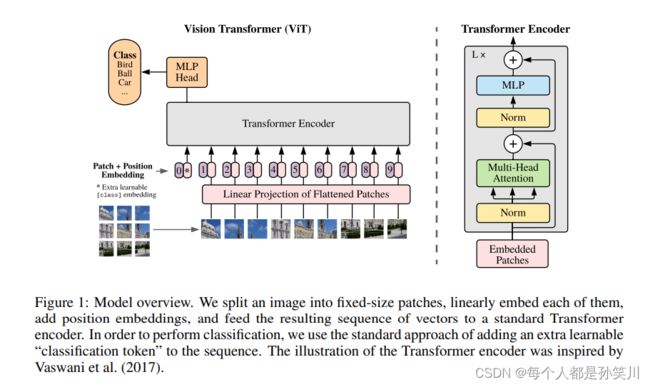
本文的工作非常简单,架构也是很Simple的,利用Transformer中的Encoder来做图像工作,将图像分成N个PXP的patch,拉长之后通过Linear将所得序列pad到固定长度,之后添加相应的position encoding ,并在这些patch序列之前添加一个pos为0的信息,当做最后的分类向量。
通过好多层Encoder之后直接将分类向量切片出来通过一个MLP层得到分类结果。
结构如下:
代码实现
vit_model.py
关于第一步预处理,本代码中使用的是卷积,stride=kernel_size,之后得到对应channel=dim,之后进行flatten,当然也有另外一种方法,将图片进行patch之后直接进行embeddings操作

"""
original code from rwightman:
https://github.com/rwightman/pytorch-image-models/blob/master/timm/models/vision_transformer.py
"""
from functools import partial
from collections import OrderedDict
from typing import Callable, Optional
from grpc import Call
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
def drop_path(x, drop_prob: float = 0., training: bool = False):
"""
Drop paths (Stochastic Depth) per sample (when applied in main path of residual blocks).
This is the same as the DropConnect impl I created for EfficientNet, etc networks, however,
the original name is misleading as 'Drop Connect' is a different form of dropout in a separate paper...
See discussion: https://github.com/tensorflow/tpu/issues/494#issuecomment-532968956 ... I've opted for
changing the layer and argument names to 'drop path' rather than mix DropConnect as a layer name and use
'survival rate' as the argument.
"""
if drop_prob == 0. or not training:
return x
keep_prob = 1 - drop_prob
# work with diff dim tensors, not just 2D ConvNets
shape = (x.shape[0],) + (1,) * (x.ndim - 1)
random_tensor = keep_prob + \
torch.rand(shape, dtype=x.dtype, device=x.device)
random_tensor.floor_() # binarize
output = x.div(keep_prob) * random_tensor
return output
class DropPath(nn.Module):
"""
Drop paths (Stochastic Depth) per sample (when applied in main path of residual blocks).
"""
def __init__(self, drop_prob=None):
super(DropPath, self).__init__()
self.drop_prob = drop_prob
def forward(self, x):
return drop_path(x, self.drop_prob, self.training)
class PatchEmbed(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,
img_size: int = 224,
patch_size: int = 16,
in_channels: int = 3,
embed_dim: int = 768,
norm_layer: Optional[Callable[..., nn.Module]] = None):
super(PatchEmbed, self).__init__()
img_size = (img_size, img_size)
patch_size = (patch_size, patch_size)
self.img_size = img_size
self.patch_size = patch_size
self.grid_size = (img_size[0] // patch_size[0],
img_size[1] // patch_size[1]) # base模型中224*224/16=14*14
self.num_patches = self.grid_size[0] * self.grid_size[1]
self.proj = nn.Conv2d(
in_channels, embed_dim, kernel_size=patch_size, stride=patch_size)
self.norm = norm_layer(embed_dim) if norm_layer else nn.Identity()
def forward(self, x):
# batch_size, channels, high,width
B, C, H, W = x.shape
assert H == self.img_size[0] and W == self.img_size[1], \
f"Input image size ({H}*{W}) doesn't match model ({self.img_size[0]}*{self.img_size[1]})."
# flatten: [B, C, H, W] -> [B, C, HW]
# transpose: [B, C, HW] -> [B, HW, C]
# base中[B,768,14,14] -> [B,768,196]->[B,196,768]
x = self.proj(x).flatten(2).transpose(1, 2)
x = self.norm(x)
return x
class Attention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,
dim: int, # 输入token的dim
num_heads: int = 8, # head的个数
qkv_bias: bool = False, # 生成qkv时候是否使用bias
qk_scale=None,
attn_drop_ratio: float = 0.,
proj_drop_ratio: float = 0.):
super(Attention, self).__init__()
self.num_heads = num_heads
head_dim = dim // num_heads # 每个head的dim
self.scale = qk_scale or head_dim ** -0.5 # qk点积之后除的scale
# 要求是三个输出维度为dim的Linear得到QKV,但是使用dim*3直接输出,有助于并行化
self.qkv = nn.Linear(dim, dim * 3, bias=qkv_bias)
self.attn_drop = nn.Dropout(attn_drop_ratio)
self.proj = nn.Linear(dim, dim)
self.proj_drop = nn.Dropout(proj_drop_ratio)
def forward(self, x):
# num_patches指的是patch_size^2
# [batch_size, num_patches + 1, total_embed_dim]
# base 模型为[B,197,768]
B, N, C = x.shape
# qkv(): -> [batch_size, num_patches + 1, 3 * total_embed_dim]
# reshape: -> [batch_size, num_patches + 1, 3, num_heads, embed_dim_per_head]
# permute: -> [3, batch_size, num_heads, num_patches + 1, embed_dim_per_head]
qkv = self.qkv(x).reshape(B, N, 3, self.num_heads, C //
self.num_heads).permute(2, 0, 3, 1, 4)
# [batch_size, num_heads, num_patches + 1, embed_dim_per_head]
# make torchscript happy (cannot use tensor as tuple)
# [batch_size, num_heads, num_patches + 1, embed_dim_per_head]
q, k, v = qkv[0], qkv[1], qkv[2]
# transpose: -> [batch_size, num_heads, embed_dim_per_head, num_patches + 1]
# 多维的矩阵乘法的shape转换是针对最后两个维度
# @: multiply -> [batch_size, num_heads, num_patches + 1, num_patches + 1]
attn = (q @ k.transpose(-2, -1)) * self.scale
# 最后一维进行softmax
attn = attn.softmax(dim=-1)
attn = self.attn_drop(attn)
# @: multiply -> [batch_size, num_heads, num_patches + 1, embed_dim_per_head]
# transpose: -> [batch_size, num_patches + 1, num_heads, embed_dim_per_head]
# 通过reshape相当于把多个head的结果[num_heads, embed_dim_per_head]concate到了一起[total_embed_dim]
# reshape: -> [batch_size, num_patches + 1, total_embed_dim] base model为[B,197,768]
x = (attn @ v).transpose(1, 2).reshape(B, N, C)
x = self.proj(x)
x = self.proj_drop(x)
return x
class Mlp(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,
in_features, # 输入features
hidden_features=None, # MLPsize 一般为4倍
out_features=None, # 输出features
act_layer=nn.GELU,
drop: float = 0.):
super().__init__()
out_features = out_features or in_features
hidden_features = hidden_features or in_features
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(in_features, hidden_features)
self.act = act_layer()
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(hidden_features, out_features)
self.drop = nn.Dropout(drop)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.fc1(x)
x = self.act(x)
x = self.drop(x)
x = self.fc2(x)
x = self.drop(x)
return x
class Block(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,
dim: int, # dimension
num_heads: int, # attention中 headers个数
mlp_ratio: float = 4., # hidden dim跟输入dim的倍数
qkv_bias: bool = False, # 是否使用qkvbias
qk_scale: float = None, # scale
drop_ratio: float = 0., # atten之后proj的dropout ratio
attn_drop_ratio: float = 0., # attention的dropout ratio
drop_path_ratio: float = 0., # 原文中注意力块之后的dropout层,代码中为dropout path层
act_layer=nn.GELU,
norm_layer=nn.LayerNorm):
super(Block, self).__init__()
# 第一个layernorm
self.norm1 = norm_layer(dim)
# 多头注意力块
self.attn = Attention(dim, num_heads=num_heads, qkv_bias=qkv_bias, qk_scale=qk_scale,
attn_drop_ratio=attn_drop_ratio, proj_drop_ratio=drop_ratio)
# NOTE: drop path for stochastic depth, we shall see if this is better than dropout here
self.drop_path = DropPath(
drop_path_ratio) if drop_path_ratio > 0. else nn.Identity()
self.norm2 = norm_layer(dim)
self.mlp = Mlp(in_features=dim, hidden_features=int(dim * mlp_ratio),
act_layer=act_layer, drop=drop_ratio)
def forward(self, x):
x = x + self.drop_path(self.attn(self.norm1(x)))
x = x + self.drop_path(self.mlp(self.norm2(x)))
return x
class VisionTransformer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,
img_size: int = 224, # input image size
patch_size: int = 16, # patch size
in_channels: int = 3, # number of input channels
num_classes: int = 1000, # number of classes for classification head
embed_dim: int = 768, # embedding dimension
depth: int = 12, # depth of transformer / number of encoders
num_heads: int = 12, # number of attention heads
mlp_ratio: float = 4.0, # ration of mlp hidden dim to embedding dim
qkv_bias: bool = True, # enable bias for qkv if True
qk_scale: float = None, # qk点积之后除的scale
# 最后一个MLP Head中是否有pre-Logits,
representation_size: Optional[int] = None,
# distilled: bool = False, 兼容搭建DeiT模型 VIT中用不到,就把相关代码都删了
drop_ratio: float = 0., # dropout rate
attn_drop_ratio: float = 0., # attention dropout ratio
drop_path_ratio: float = 0., # after attention proj dropout ratio
embed_layer: Optional[Callable[..., nn.Module]] = PatchEmbed,
# patch embedding layer
norm_layer: Optional[Callable[..., nn.Module]] = None,
# normalization layer
act_layer: Optional[Callable[..., nn.Module]] = None
):
super(VisionTransformer, self).__init__()
self.num_classes = num_classes
# num_features for consistency with other models
self.num_features = self.embed_dim = embed_dim
self.num_tokens = 1
norm_layer = norm_layer or partial(nn.LayerNorm, eps=1e-6)
act_layer = act_layer or nn.GELU
# patch embeding
self.patch_embed = embed_layer(
img_size=img_size, patch_size=patch_size, in_channels=in_channels, embed_dim=embed_dim)
num_patches = self.patch_embed.num_patches
self.cls_token = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(1, 1, embed_dim))
self.pos_embed = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(
1, num_patches + self.num_tokens, embed_dim))
# 添加pos之后的drop层
self.pos_drop = nn.Dropout(p=drop_ratio)
# 从0-drop_path_ratio 中的等差序列,一共有depth个元素
dpr = [x.item() for x in torch.linspace(0, drop_path_ratio, depth)]
self.blocks = nn.Sequential(*[
Block(dim=embed_dim, num_heads=num_heads, mlp_ratio=mlp_ratio,
qkv_bias=qkv_bias, qk_scale=qk_scale, drop_ratio=drop_ratio,
attn_drop_ratio=attn_drop_ratio, drop_path_ratio=dpr[i],
norm_layer=norm_layer, act_layer=act_layer)
for i in range(depth)
])
self.norm = norm_layer(embed_dim)
# Representation layer,判断是否有Logits层,如果没有的话,最后的MLP只有一个Linear
if representation_size:
self.has_logits = True
self.num_features = representation_size
self.pre_logits = nn.Sequential(OrderedDict([
("fc", nn.Linear(embed_dim, representation_size)),
("act", nn.Tanh())
]))
else:
self.has_logits = False
self.pre_logits = nn.Identity()
# Classifier head(s)
self.head = nn.Linear(
self.num_features, num_classes) if num_classes > 0 else nn.Identity()
# Weight init
nn.init.trunc_normal_(self.pos_embed, std=0.02)
nn.init.trunc_normal_(self.cls_token, std=0.02)
self.apply(_init_vit_weights)
def forward(self, x):
# [B, C, H, W] -> [B, num_patches, embed_dim]
x = self.patch_embed(x) # [B, 196, 768]
# [1, 1, 768] -> [B, 1, 768]
cls_token = self.cls_token.expand(x.shape[0], -1, -1)
x = torch.cat((cls_token, x), dim=1) # [B, 197, 768]
x = self.pos_drop(x + self.pos_embed)
x = self.blocks(x)
x = self.norm(x)
x = self.head(self.pre_logits(x[:, 0]))
return x
def _init_vit_weights(m):
if isinstance(m, nn.Linear):
nn.init.trunc_normal_(m.weight, std=.01)
if m.bias is not None:
nn.init.zeros_(m.bias)
elif isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode="fan_out")
if m.bias is not None:
nn.init.zeros_(m.bias)
elif isinstance(m, nn.LayerNorm):
nn.init.zeros_(m.bias)
nn.init.ones_(m.weight)
def vit_base_patch16_224_in21k(num_classes: int = 21843, has_logits: bool = True):
"""
ViT-Base model (ViT-B/16) from original paper (https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.11929).
ImageNet-21k weights @ 224x224, source https://github.com/google-research/vision_transformer.
weights ported from official Google JAX impl:
https://github.com/rwightman/pytorch-image-models/releases/download/v0.1-vitjx/jx_vit_base_patch16_224_in21k-e5005f0a.pth
"""
model = VisionTransformer(img_size=224,
patch_size=16,
embed_dim=768,
depth=12,
num_heads=12,
representation_size=768 if has_logits else None,
num_classes=num_classes)
return model
def vit_base_patch32_224_in21k(num_classes: int = 21843, has_logits: bool = True):
"""
ViT-Base model (ViT-B/32) from original paper (https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.11929).
ImageNet-21k weights @ 224x224, source https://github.com/google-research/vision_transformer.
weights ported from official Google JAX impl:
https://github.com/rwightman/pytorch-image-models/releases/download/v0.1-vitjx/jx_vit_base_patch32_224_in21k-8db57226.pth
"""
model = VisionTransformer(img_size=224,
patch_size=32,
embed_dim=768,
depth=12,
num_heads=12,
representation_size=768 if has_logits else None,
num_classes=num_classes)
return model
def vit_large_patch16_224_in21k(num_classes: int = 21843, has_logits: bool = True):
"""
ViT-Large model (ViT-L/16) from original paper (https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.11929).
ImageNet-21k weights @ 224x224, source https://github.com/google-research/vision_transformer.
weights ported from official Google JAX impl:
https://github.com/rwightman/pytorch-image-models/releases/download/v0.1-vitjx/jx_vit_large_patch16_224_in21k-606da67d.pth
"""
model = VisionTransformer(img_size=224,
patch_size=16,
embed_dim=1024,
depth=24,
num_heads=16,
representation_size=1024 if has_logits else None,
num_classes=num_classes)
return model
def vit_large_patch32_224_in21k(num_classes: int = 21843, has_logits: bool = True):
"""
ViT-Large model (ViT-L/32) from original paper (https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.11929).
ImageNet-21k weights @ 224x224, source https://github.com/google-research/vision_transformer.
weights ported from official Google JAX impl:
https://github.com/rwightman/pytorch-image-models/releases/download/v0.1-vitjx/jx_vit_large_patch32_224_in21k-9046d2e7.pth
"""
model = VisionTransformer(img_size=224,
patch_size=32,
embed_dim=1024,
depth=24,
num_heads=16,
representation_size=1024 if has_logits else None,
num_classes=num_classes)
return model
def vit_huge_patch14_224_in21k(num_classes: int = 21843, has_logits: bool = True):
"""
ViT-Huge model (ViT-H/14) from original paper (https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.11929).
ImageNet-21k weights @ 224x224, source https://github.com/google-research/vision_transformer.
NOTE: converted weights not currently available, too large for github release hosting.
"""
model = VisionTransformer(img_size=224,
patch_size=14,
embed_dim=1280,
depth=32,
num_heads=16,
representation_size=1280 if has_logits else None,
num_classes=num_classes)
return model
train.py
这里使用的为cifar100数据集进行训练
import os
import math
import argparse
import sys
from tqdm import tqdm
import torch
import torch.optim as optim
import torch.optim.lr_scheduler as lr_scheduler
from torch.utils.tensorboard import SummaryWriter
from torchvision import transforms, datasets
from vit_model import vit_base_patch16_224_in21k as create_model
def main(args):
print(args)
device = torch.device(args.device if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
batch_size = args.batch_size
# number of workers
nw = min([os.cpu_count(), batch_size if batch_size > 1 else 0, 8])
print('Using {} dataloader workers every process'.format(nw))
if os.path.exists("./weights") is False:
os.makedirs("./weights")
tb_writer = SummaryWriter()
data_transform = {
"train": transforms.Compose([transforms.RandomResizedCrop(224),
transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize([0.5, 0.5, 0.5], [0.5, 0.5, 0.5])]),
"val": transforms.Compose([transforms.Resize(256),
transforms.CenterCrop(224),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize([0.5, 0.5, 0.5], [0.5, 0.5, 0.5])])}
train_dataset = datasets.CIFAR100(root=args.data_path, train=True,
download=True, transform=data_transform['train'])
train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(train_dataset,
batch_size=batch_size,
shuffle=True,
pin_memory=True,
num_workers=nw)
val_dataset = datasets.CIFAR100(root=args.data_path, train=False,
download=True, transform=data_transform['val'])
val_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(val_dataset,
batch_size=batch_size,
shuffle=False,
pin_memory=True,
num_workers=nw)
model = create_model(num_classes=args.num_classes, has_logits=False).to(device)
if args.weights != "":
assert os.path.exists(
args.weights), "weights file: '{}' not exist.".format(args.weights)
weights_dict = torch.load(args.weights, map_location=device)
# 删除不需要的权重
del_keys = ['head.weight', 'head.bias'] if model.has_logits \
else ['pre_logits.fc.weight', 'pre_logits.fc.bias', 'head.weight', 'head.bias']
for k in del_keys:
del weights_dict[k]
print(model.load_state_dict(weights_dict, strict=False))
if args.freeze_layers:
for name, para in model.named_parameters():
# 除head, pre_logits外,其他权重全部冻结
if "head" not in name and "pre_logits" not in name:
para.requires_grad_(False)
else:
print("training {}".format(name))
pg = [p for p in model.parameters() if p.requires_grad]
optimizer = optim.SGD(pg, lr=args.lr, momentum=0.9, weight_decay=5E-5)
# Scheduler https://arxiv.org/pdf/1812.01187.pdf
def lf(x): return ((1 + math.cos(x * math.pi / args.epochs)) / 2) * \
(1 - args.lrf) + args.lrf # cosine
scheduler = lr_scheduler.LambdaLR(optimizer, lr_lambda=lf)
loss_function = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
for epoch in range(args.epochs):
# train
model.train()
accu_loss = torch.zeros(1).to(device) # 累计损失
accu_num = torch.zeros(1).to(device) # 累计预测正确的样本数
sample_num = 0
data_loader = tqdm(train_loader)
for step, data in enumerate(data_loader):
optimizer.zero_grad()
images, labels = data
sample_num += images.shape[0]
pred = model(images.to(device))
pred_classes = torch.max(pred, dim=1)[1]
accu_num += torch.eq(pred_classes, labels.to(device)).sum()
loss = loss_function(pred, labels.to(device))
loss.backward()
accu_loss += loss.detach()
data_loader.desc = "[train epoch {}] loss: {:.3f}, acc: {:.3f}".format(epoch,
accu_loss.item() / (step + 1),
accu_num.item() / sample_num)
if not torch.isfinite(loss):
print('WARNING: non-finite loss, ending training ', loss)
sys.exit(1)
optimizer.step()
train_loss = accu_loss.item() / (step + 1)
train_acc = accu_num.item() / sample_num
scheduler.step()
# validate
model.eval()
accu_num = torch.zeros(1).to(device) # 累计预测正确的样本数
accu_loss = torch.zeros(1).to(device) # 累计损失
sample_num = 0
data_loader = tqdm(val_loader)
for step, data in enumerate(data_loader):
images, labels = data
sample_num += images.shape[0]
pred = model(images.to(device))
pred_classes = torch.max(pred, dim=1)[1]
accu_num += torch.eq(pred_classes, labels.to(device)).sum()
loss = loss_function(pred, labels.to(device))
accu_loss += loss
data_loader.desc = "[valid epoch {}] loss: {:.3f}, acc: {:.3f}".format(epoch,
accu_loss.item() / (step + 1),
accu_num.item() / sample_num)
val_loss = accu_loss.item() / (step + 1)
val_acc = accu_num.item() / sample_num
tags = ["train_loss", "train_acc",
"val_loss", "val_acc", "learning_rate"]
tb_writer.add_scalar(tags[0], train_loss, epoch)
tb_writer.add_scalar(tags[1], train_acc, epoch)
tb_writer.add_scalar(tags[2], val_loss, epoch)
tb_writer.add_scalar(tags[3], val_acc, epoch)
tb_writer.add_scalar(tags[4], optimizer.param_groups[0]["lr"], epoch)
torch.save(model.state_dict(), "./weights/model-{}.pth".format(epoch))
if __name__ == '__main__':
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument('--num_classes', type=int, default=100)
parser.add_argument('--epochs', type=int, default=20)
parser.add_argument('--batch-size', type=int, default=64)
parser.add_argument('--lr', type=float, default=0.001)
parser.add_argument('--lrf', type=float, default=0.01)
# 数据集所在根目录
parser.add_argument('--data-path', type=str,
default="D:\dataset\cifar")
# 没用上
parser.add_argument('--model-name', default='', help='create model name')
# 预训练权重路径,如果不想载入就设置为空字符
# parser.add_argument('--weights', type=str, default='./vit_base_patch16_224_in21k.pth',
# help='initial weights path')
parser.add_argument('--weights', type=str, default='',
help='initial weights path')
# 是否冻结权重
parser.add_argument('--freeze-layers', type=bool, default=True)
parser.add_argument('--device', default='cuda:0',
help='device id (i.e. 0 or 0,1 or cpu)')
opt = parser.parse_args()
main(opt)
predict.py
import os
import json
import torch
from PIL import Image
from torchvision import transforms
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from vit_model import vit_base_patch16_224_in21k as create_model
def main():
device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
data_transform = transforms.Compose(
[transforms.Resize(256),
transforms.CenterCrop(224),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize([0.5, 0.5, 0.5], [0.5, 0.5, 0.5])])
# load image
img_path = "../tulip.jpg"
assert os.path.exists(img_path), "file: '{}' dose not exist.".format(img_path)
img = Image.open(img_path)
plt.imshow(img)
# [N, C, H, W]
img = data_transform(img)
# expand batch dimension
img = torch.unsqueeze(img, dim=0)
# read class_indict
json_path = './class_indices.json'
assert os.path.exists(json_path), "file: '{}' dose not exist.".format(json_path)
json_file = open(json_path, "r")
class_indict = json.load(json_file)
# create model
model = create_model(num_classes=5, has_logits=False).to(device)
# load model weights
model_weight_path = "./weights/model-9.pth"
model.load_state_dict(torch.load(model_weight_path, map_location=device))
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
# predict class
output = torch.squeeze(model(img.to(device))).cpu()
predict = torch.softmax(output, dim=0)
predict_cla = torch.argmax(predict).numpy()
print_res = "class: {} prob: {:.3}".format(class_indict[str(predict_cla)],
predict[predict_cla].numpy())
plt.title(print_res)
print(print_res)
plt.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
实验结果
本文中没有使用迁移学习,然后效果确实差,也就没有放相应的效果图,使用两个函数输出了对应的flops和params
# params
from vit_model import vit_base_patch32_224_in21k
model=vit_base_patch32_224_in21k(num_classes=5, has_logits=False)
total_params = sum(p.numel() for p in model.parameters())
print(f'{total_params:,} total parameters.')
total_trainable_params = sum(
p.numel() for p in model.parameters() if p.requires_grad)
print(f'{total_trainable_params:,} training parameters.')
# flops
import torch
from fvcore.nn import FlopCountAnalysis
from vit_model import Attention,vit_base_patch32_224_in21k
def main():
# Self-Attention
a1 = Attention(dim=512, num_heads=1)
a1.proj = torch.nn.Identity() # remove Wo
a3=vit_base_patch32_224_in21k(num_classes=5, has_logits=False)
t2=(torch.rand(32,3,224,224),)
# Multi-Head Attention
a2 = Attention(dim=512, num_heads=8)
# [batch_size, num_tokens, total_embed_dim]
t = (torch.rand(32, 1024, 512),)
flops1 = FlopCountAnalysis(a1, t)
print("Self-Attention FLOPs:", flops1.total())
flops2 = FlopCountAnalysis(a2, t)
print("Multi-Head Attention FLOPs:", flops2.total())
flops3 = FlopCountAnalysis(a3, t2)
print("Multi-Head Attention FLOPs:", flops3.total())
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()