MySQL____高级查询、联合查询
文章目录
- 一. 聚合查询
-
- 1. count查询(总数统计)
-
- 1.1count 用法1
- 1.2 count 用法2
- 1.3count 用法3
- 1.4 注意事项:
- 2. SUM函数(总和统计)
- 3.AVG函数
- 4. MAX函数
- 5.MIN函数
- 二. ifnull 函数
-
- 示例1
- 示例2
- 示例3
- 示例4(解决总成绩为null的查询)
- 三. 分组查询 GROUP BY
-
- 3.1 语法
- 3.2分组条件查询 HAVING
- 四. 联合查询(多表查询)
-
- 4.1前置知识----笛卡尔积
- 4.2 内连接
-
- 4.2.1 内连接使用语法
- 4.2.2 内连接实战1
- 4.3 外连接
-
-
- 4.3.2 外连接实战1
- 4.3.3 on 和 where 的区别
-
- 4.4 自连接
-
- 4.4.1 自连接语法
- 4.4.2 内连接实战1
- 4.5 子查询(嵌套查询)
-
- 4.5.1 子查询实战练习1
- 4.5.2 in和 = 区别
- 4.6 合并查询
一. 聚合查询
1. count查询(总数统计)
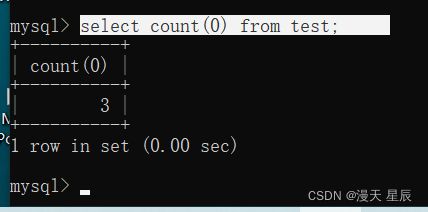
1.1count 用法1

推荐使用,最标准的,可以查询出所有 null 和非null的数据
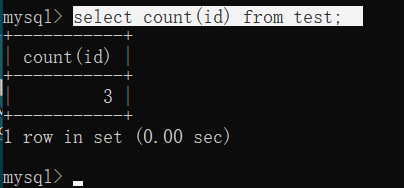
1.2 count 用法2
1.3count 用法3
1.4 注意事项:
在不同的count统计场景下,要使用不同的count查询,比如要查询所有的数据数量(null和非null) -> count()
特殊场景的统计考虑使用 count() from table_name+where 条件查询
不推荐使用 count(字段名) 不稳定
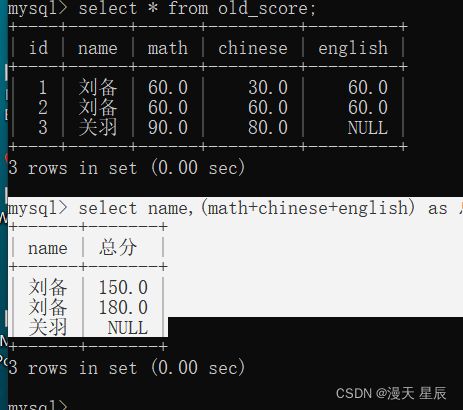
2. SUM函数(总和统计)

和统计,如果有null,或者是统计非整数值,那么它的结果是只会统计有效的整数值
3.AVG函数
返回查询到的数据的平均值,不是数字没有意义

avg计算平均值时,如果有不符合规范的数据 如(null)就会把此行数据直接舍弃掉
4. MAX函数
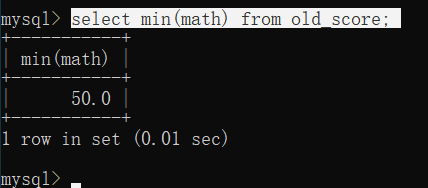
5.MIN函数
二. ifnull 函数
判断是否为null的函数 如果第一个参数不为null,则返回第一个参数,否则,返回第二个参数
示例1
示例2
空
示例3
示例4(解决总成绩为null的查询)
三. 分组查询 GROUP BY
3.1 语法
select colum1,sum(colum2),..from table group by colum2;
3.2分组条件查询 HAVING
having查询:过滤group by中的数据
语法:having 是在group by 之后条件,它的执行顺序也是在group by 之后
四. 联合查询(多表查询)
4.1前置知识----笛卡尔积
笛卡尔积又又称直积,表示为XY,比如A表中的数据为m行,B表中的数据有n行,那么A和B做笛卡尔积,结果为mn行。
准备:
建表
-- 创建数据库
drop database if exists java33;
create database java33 default character set 'utf8mb4';
-- 切换数据库
use java33;
-- 创建班级表
drop table if exists class;
create table class(
id int primary key auto_increment comment '班级编号',
classname varchar(250) not null comment '班级名称'
);
-- 创建学生表
drop table if exists student;
create table student(
id int primary key auto_increment comment '学生编号',
sn varchar(50) comment '学号',
username varchar(250) not null comment '学生名称',
`mail` varchar(250) comment '邮箱',
class_id int,
foreign key (class_id) references class(id)
);
-- 创建课程表
drop table if exists course;
create table course(
id int primary key auto_increment comment '课程编号',
name varchar(250) not null
);
-- 成绩表
drop table if exists score_table;
create table score_table(
id int primary key auto_increment comment '成绩编号',
score decimal(4,1),
student_id int not null,
course_id int not null,
foreign key (student_id) references student(id),
foreign key (course_id) references course(id)
);
-- 班级表添加数据
insert into class(id,classname) values(1,'Java班级'),(2,'C++班级');
-- 课程表添加数据
insert into course(id,name) values(1,'计算机'),(2,'英语');
-- 学生表添加数据
insert into student(id,sn,username,mail,class_id) values(1,'CN001','张三','[email protected]',1),(2,'CN002','李四','[email protected]',2),(3,'CN003','王五','[email protected]',1);
-- 成绩表添加数据
insert into score_table(id,score,student_id,course_id) values(1,90,1,1),(2,59,1,2),(3,65,2,1),(4,NULL,2,2);
4.2 内连接
内连接侧重于两个表之间的共性,它的作用是使用联接,比较两个(或多个)表之间的共有数据
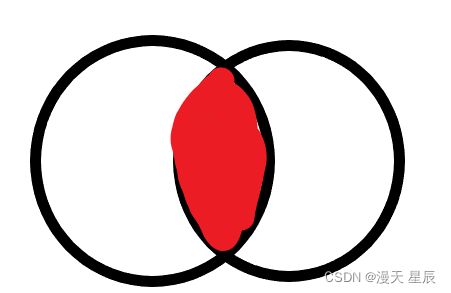
4.2.1 内连接使用语法
select * from t1 [inner|cross] join t2 [on 过滤条件] [where 过滤条件]
on ------从语法上来说可以省略,但如果省略它,将查询的是多表的笛卡尔积
两种常见语法:
select * from t1 join t2 [on 过滤条件] [where 过滤条件]
select * from t1,t2[where 过滤条件]
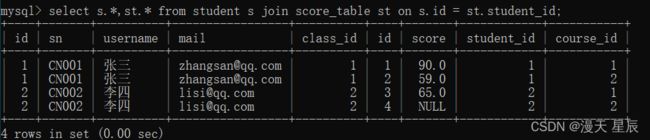
4.2.2 内连接实战1
查询张三的成绩:
- 进行内连接查询(做笛卡尔积)
select s.*,st.* from student s join score_table st;
- 去掉无效的成绩 (on 过滤条件)
select s.*,st.* from student s join score_table st on s.id = st.student_id;
- 查询张三的成绩(where 过滤条件)
方法1
select s.*,st.* from student s join score_table st on s.id = st.student_id where s.username = '张三';
select s.*,st.* from student s cross join score_table st on s.id = st.student_id where s.username = '张三';
方法3
select s.*,st.* from student s inner join score_table st on s.id = st.student_id where s.username = '张三';
方法4
select s.*,st.* from student s,score_table st where s.id = st.student_id and s.username = '张三';
4.3 外连接
select * from t1 left join t2 on连接条件 [where 条件查询]
右连接语法如下:
select * from t1 right join t2 on连接条件 [where 查询条件]

左连接和右连接只需掌握一种语法即可,因为使用左连接可以实现“右连接”,只需要将表的查询顺序调换一下就可以实现左连接/右连接
4.3.2 外连接实战1
查询所有人的个人信息+课程名+分数信息
先分析需求:
(1) 需要哪些表———学生表 课程表 成绩表
(2)所有——使用外连接 主表——student表
select s.sn,s.username,s.mail,c.name,st.score from student s left join score_table st on s.id = st.student_id left join course c on c.id = st.course_id;
4.3.3 on 和 where 的区别
- 内连接 on 是可以省略的 , 在左连接和右连接中 on 是不能省略的,
- 其次 on 在左/右连内中的作用是不一样的,并且在 左/右连接中 on 和 where 的作用也是不一样的
- left join 不加on 会报错
- 注意:
在外连接查询时,如果有多个查询条件,咱们正确的写法,是将查询条件的表达式全部写在where表达式中,而非on中,在on中咱们一般情况下只需要写一个笛卡尔积无效数据的过滤条件即可。
4.4 自连接
是指同一张表连接自身进行查询
4.4.1 自连接语法
select * from table_name as t1, table_name as t2 where t1.id = t2.id[...];
4.4.2 内连接实战1
查询英语成绩> 计算机成绩
分析问题:成绩表 成绩表 score_name(自己和自己进行连表查询)
- 去除笛卡尔积中的无意义数据
有效数据:主键相同,学生id相同
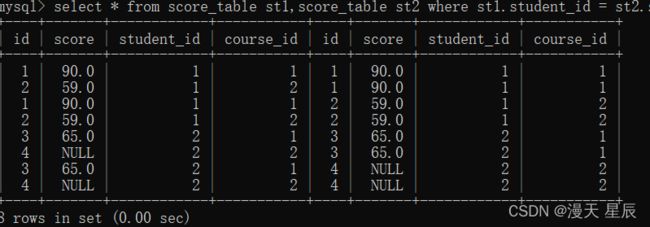
select * from score_table st1,score_table st2 where st1.student_id = st2.student_id;
- 设置where查询条件,让表一只查询英语成绩,让表二查询计算机成绩
select * from score_table st1,score_table st2 where st1.student_id = st2.student_id and st1.course_id = 2 and st2.course_id = 1;
- 设置where多条件查询,让英语成绩>计算机成绩
select * from score_table st1,score_table st2 where st1.student_id = st2.student_id and st1.course_id = 2 and st2.course_id = 1 and st1.score < st2.score;
select st1.score'英语成绩',st2.score'计算机成绩' from score_table st1,score_table st2 where st1.student_id = st2.student_id and st1.course_id = 2 and st2.course_id = 1 and st1.score < st2.score;
4.5 子查询(嵌套查询)
子查询是指嵌入在其他sql语句中的select语句,也叫嵌套查询。
4.5.1 子查询实战练习1
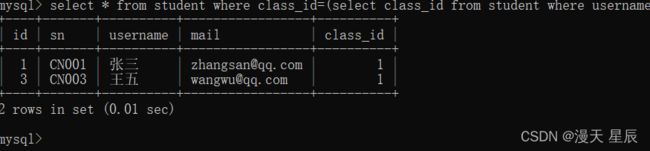
2.根据上一条查询的班级id查询出所有列表
select * from student where class_id=(select class_id from student where username = '张三');
4.5.2 in和 = 区别
= 查询需要一个具体确定的值
in 查询,可以是一个或多个值,并且满足任意一个将返回true。