【SpringBoot】第二章 SpringBoot入门
第二章 Spring Boot入门
2.1 介绍
SpringBoot是Spring大家族中的一个成员, 可以简化Spring、SpringMVC的使用。 核心还是IOC容器。
特点:
• Create stand-alone Spring applications:创建spring应用。
• Embed Tomcat, Jetty or Undertow directly (no need to deploy WAR files):内嵌服务器tomcat、jetty、Undertow 。
• Provide opinionated ‘starter’ dependencies to simplify your build configuration:提供starter起步依赖,简化应用的配置。 比如使用MyBatis框架 ,需要在Spring项目中配置MyBatis的对象 :SqlSessionFactory 、Dao的代理对象。
在SpringBoot项目中的pom.xml里面,加入一个 mybatis-spring-boot-starter依赖即可实现上述操作。
• Automatically configure Spring and 3rd party libraries whenever possible:尽可能去配置spring和第三方库自动配置(就是把spring中的第三方库中的对象都创建好,放到容器中, 开发人员可以直接使用)
• Provide production-ready features such as metrics, health checks, and externalized configuration:提供了健康检查、统计、外部化配置(例如properties文件)等功能。
• Absolutely no code generation and no requirement for XML configuration:不用生成代码, 不用使用xml,做配置
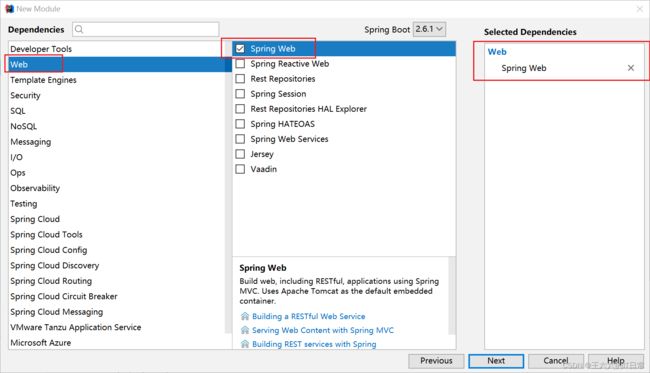
2.2 创建Spring Boot项目
看这个博客 【Spring boot】创建项目方式 也ok。
2.2.1 第一种方式
使用Spring提供的初始化器, 就是向导创建SpringBoot应用
Spring官网: https://start.spring.io

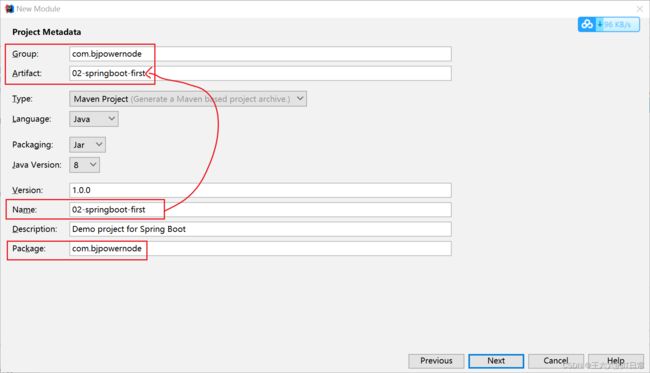
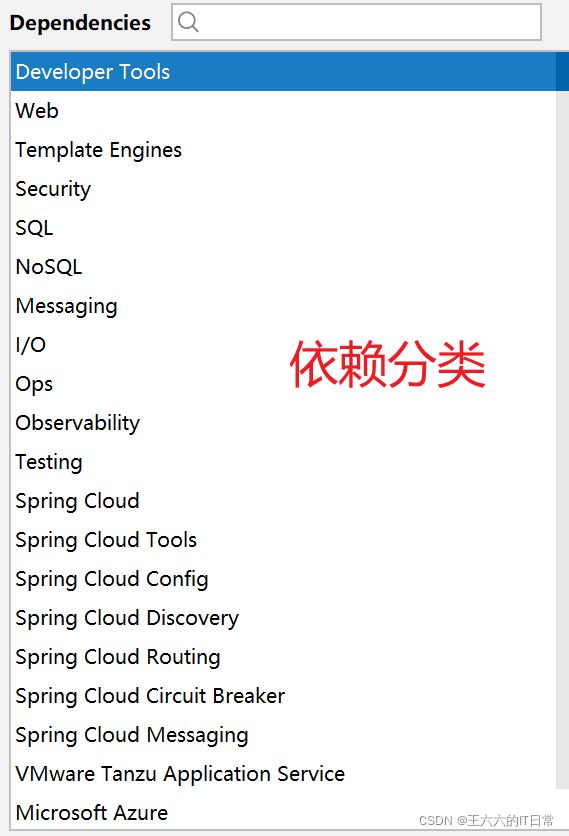
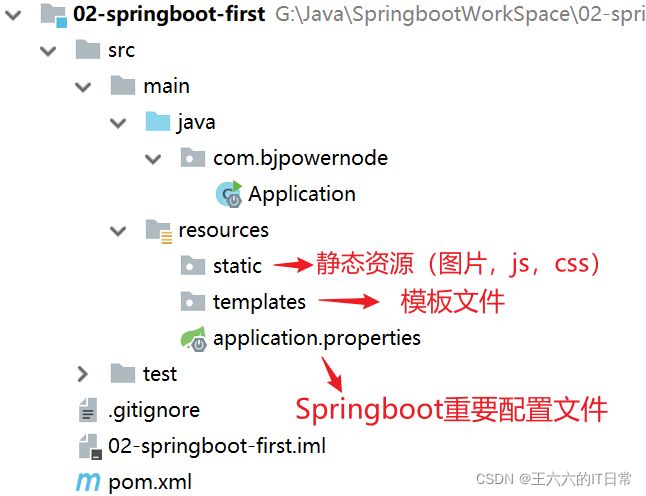
SpringBoot项目的结构:
2.2.1 第二种方式
使用国内的地址(访问比较快,稳定)
国内地址https://start.springboot.io

在浏览器中使用向导地址:
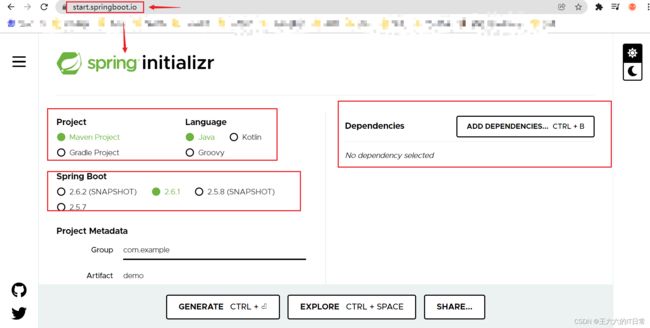

依赖项:

第三种方式
使用maven 向导创建项目。
跟Springboot相比,没啥加啥。
基于Springboot的web例子
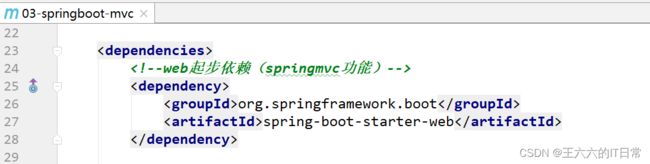
创建controller包处理请求并创建HelloSpringBoot类:
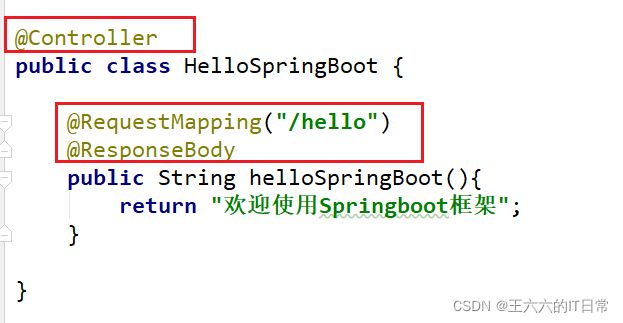
从主程序启动项目:
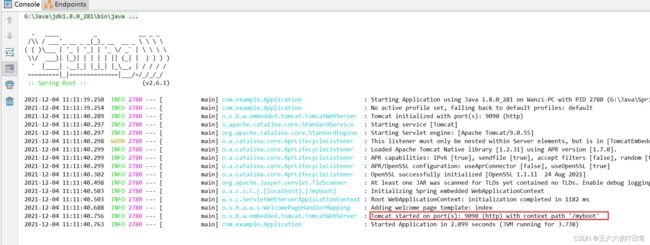
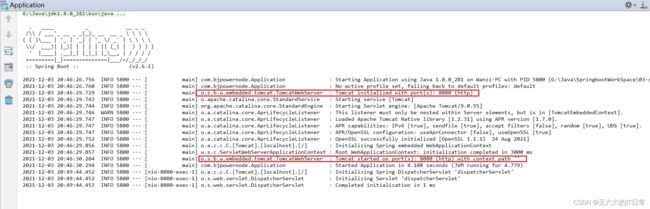
控制台输出了 Tomcat 访问的端口号:
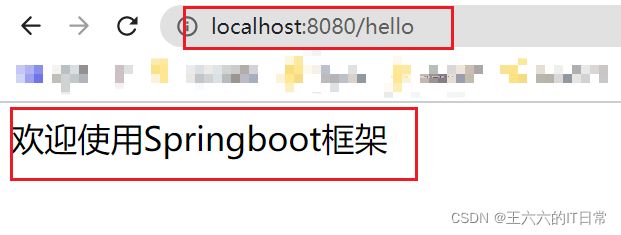
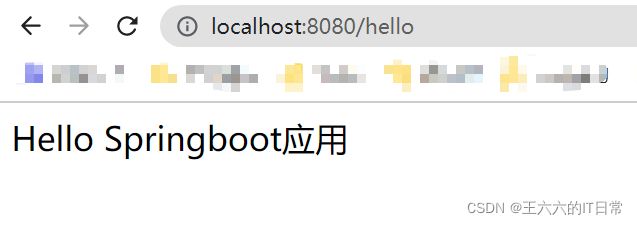
浏览器发起请求,看页面返回:
2.3 注解的使用
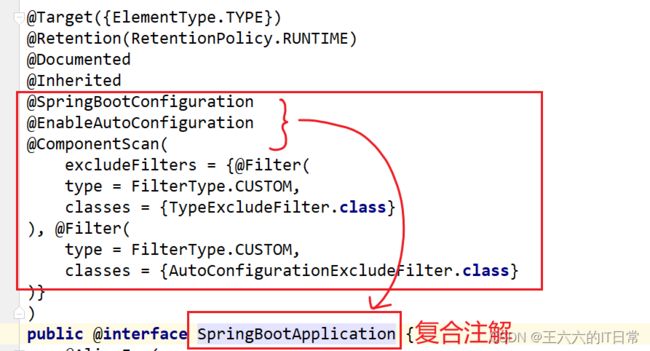
@SpringBootApplication是一个复合注解,由@SpringBootConfiguration、@EnableAutoConfiguration、@ComponentScan联合在一起组成的。
- @SpringBootConfiguration : 具有
@Configuration这 个 注 解 的 功 能 ,使用了@SpringBootConfiguration注解标注的类,可以作为配置文件使用,可以使用@Bean声明对象,注入到容器。
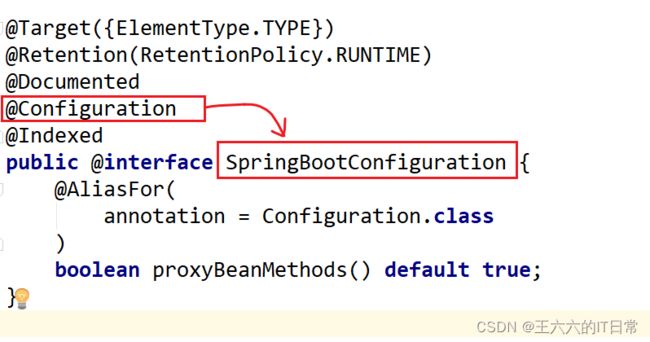
@EnableAutoConfiguration:启用自动配置, 把java对象配置好,注入到spring容器中。例如可以把mybatis的对象创建好,放入到容器中。@ComponentScan:组件扫描器, 找到注解,根据注解的功能,创建 java bean,给属性赋值等等。组件扫描器默认扫描的是@ComponentScan注解所在的类以及类所在的包和子包。
2.4 SpringBoot的配置文件
- properties( k=v) ;
- 主推
yml( k:(空格)v)
使用application.properties, application.yml
举例:
创建controller:

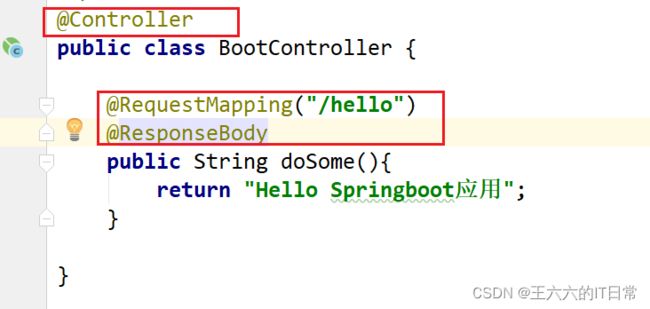
创建主启动类MyApplication:
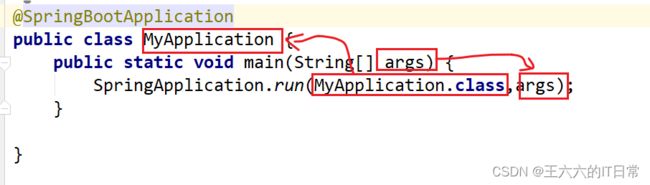
执行main函数,在浏览器输入地址:
添加外部属性配置文件:
运行MyApplication的main函数,在浏览器输入网址:
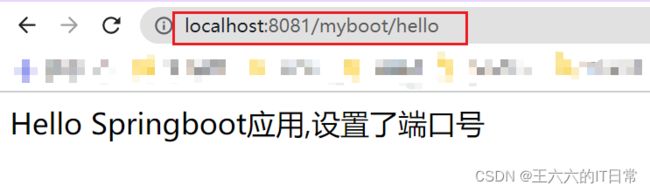
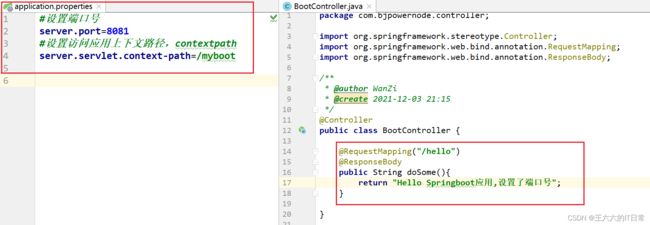
例1:application.properties设置 端口和上下文
#设置端口号
server.port=8082
#设置访问应用上下文路径, contextpath
server.servlet.context-path=/myboot
例2: application.yml(推荐)
:后必须有空格
server:
port: 8083
servlet:
context-path: /myboot2
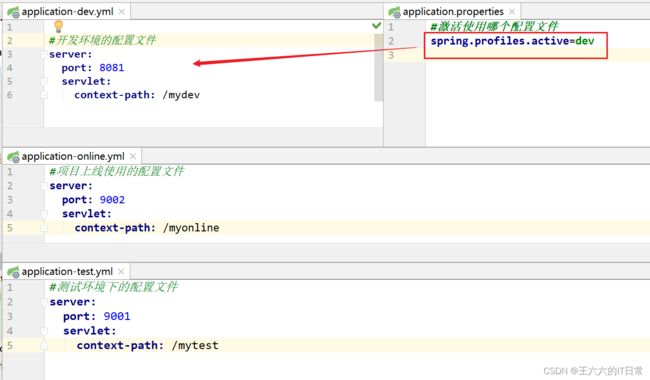
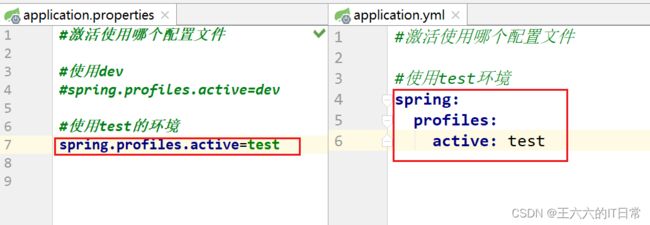
2.5 多环境配置
有开发环境, 测试环境, 上线的环境。
每个环境有不同的配置信息, 例如端口、上下文件、数据库url、用户名、密码等等。
使用多环境配置文件,可以方便的切换不同的配置。
使用方式: 创建多个配置文件, 名称规则: application-环境名称.properties(yml)
创建开发环境的配置文件: application-dev.properties( application-dev.yml )
创建测试者使用的配置: application-test.properties
2.6 Spring Boot 自定义配置
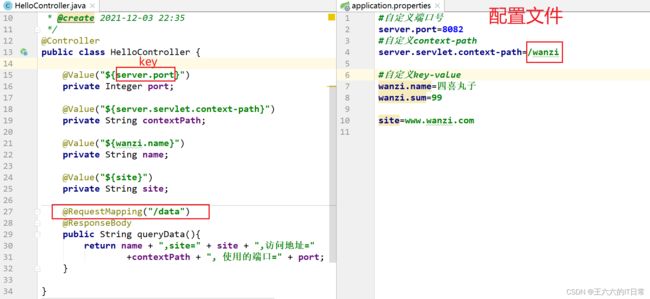
SpringBoot 的核心配置文件中,除了使用内置的配置项之外,我们还可以在自定义配置,然后采用如下注解去读取配置的属性值
使用@Value注解读取数据
@Value("${key}") , key 来自 application.properties(yml)
@ConfigurationProperties 注解
把配置文件的数据映射为java对象
属性:prefix 配置文件中的某些key的开头的内容。
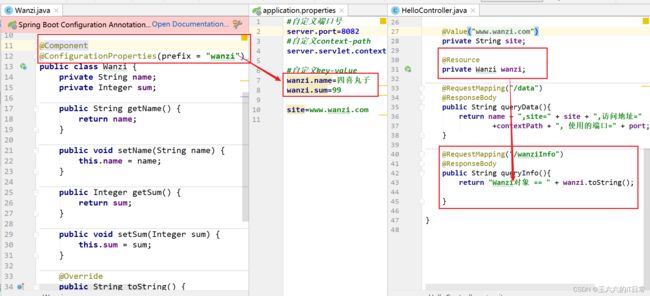
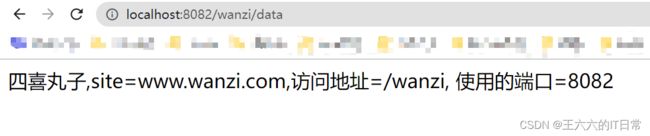
执行 Application , 访问浏览器查看数据
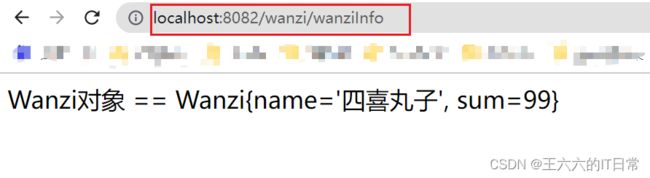
出现:
![]()
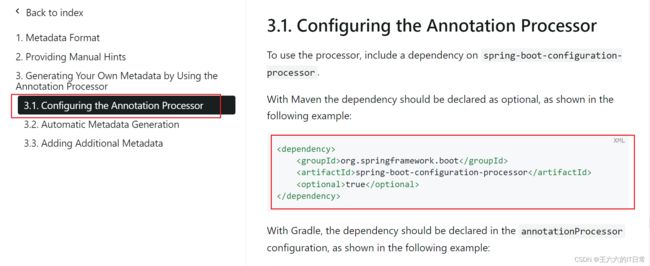
将此依赖项添加到pom.xml中即可:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processorartifactId>
<optional>trueoptional>
dependency>
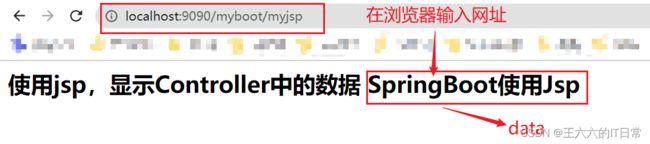
2.7 使用jsp
SpringBoot不推荐使用jsp ,而是使用模板技术代替jsp
使用jsp需要配置:
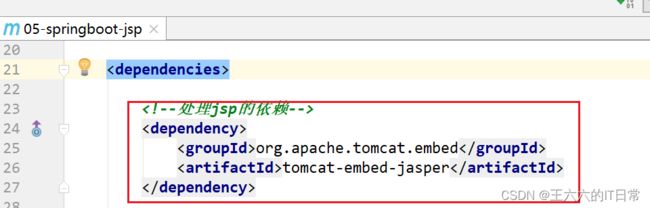
1) 加入一个处理jsp的依赖。 负责编译jsp文件
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.tomcat.embedgroupId>
<artifactId>tomcat-embed-jasperartifactId>
dependency>
2)如果需要使用servlet, jsp,jstl的功能
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servletgroupId>
<artifactId>jstlartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servletgroupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-apiartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet.jspgroupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet.jsp-apiartifactId>
<version>2.3.1version>
dependency>
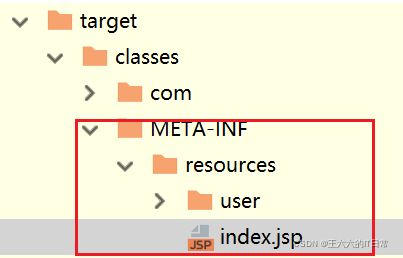
3)创建一个存放jsp的目录,一般叫做webapp
例如:index.jsp
4)需要在pom.xml指定jsp文件编译后的存放目录META-INF/resources
5)创建Controller访问jsp
6)在application.propertis文件中配置视图解析器

此时webapp不能作为web应用文件夹使用,需要进行设置:
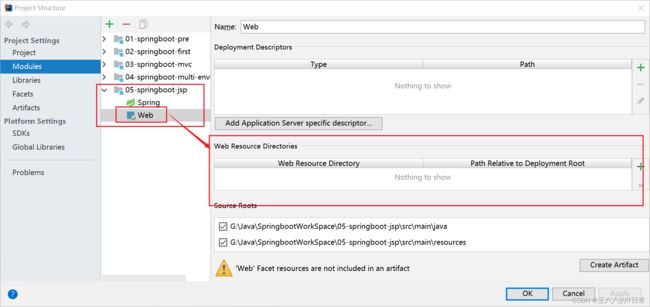
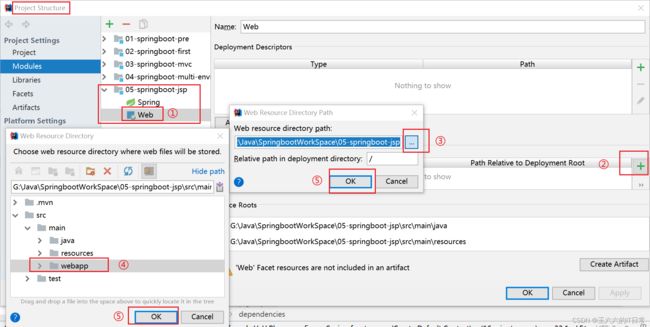
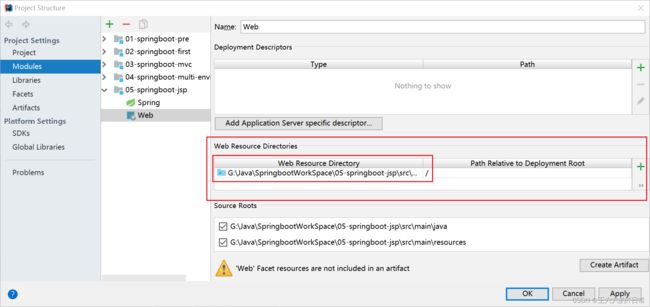

可以新建jsp了:



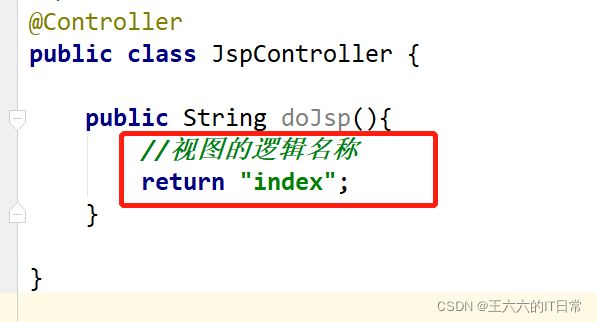
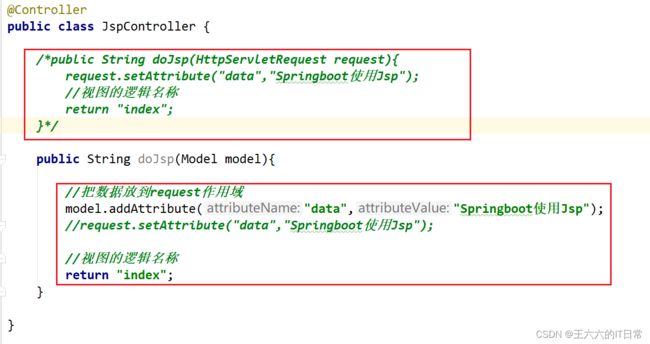
String返回一个视图,因此需要配置视图解析器以及端口号:

需要在pom.xml指定jsp文件编译后的存放目录META-INF/resources
在
<resources>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/webappdirectory>
<targetPath>META-INF/resourcestargetPath>
<includes>
<include>**/*.*include>
includes>
resource>
resources>
将webapp目录下的以及任意子目录中的文件都需要编译到指定的目录之中:
<includes>
<include>**/*.*include>
includes>
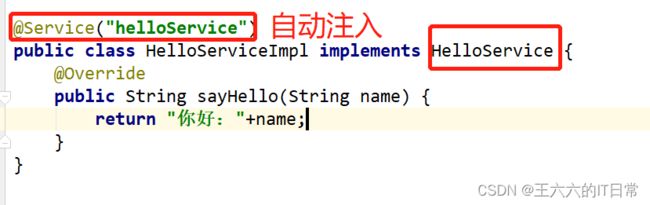
2.8 使用容器
通过代码从容器中获取对象:
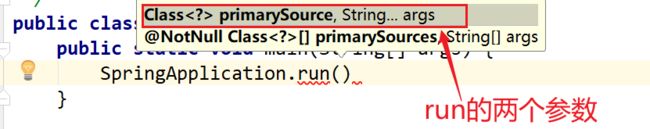
在 main 方法中 SpringApplication.run()方法获取返回的 Spring 容器对象,再获取业务 bean进行调用。即通过SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args); 返回值获取容器对象。

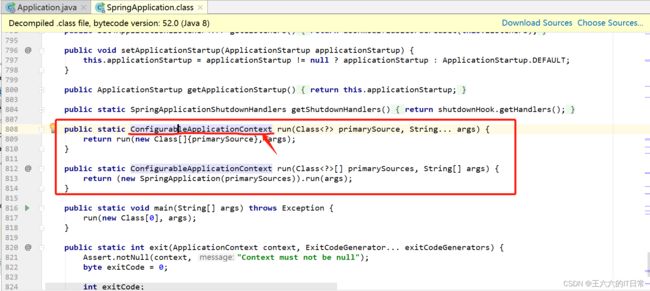
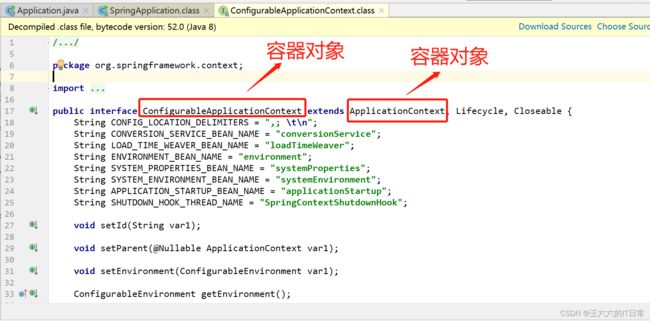
ConfigurableApplicationContext : 接口是ApplicationContext的子接口
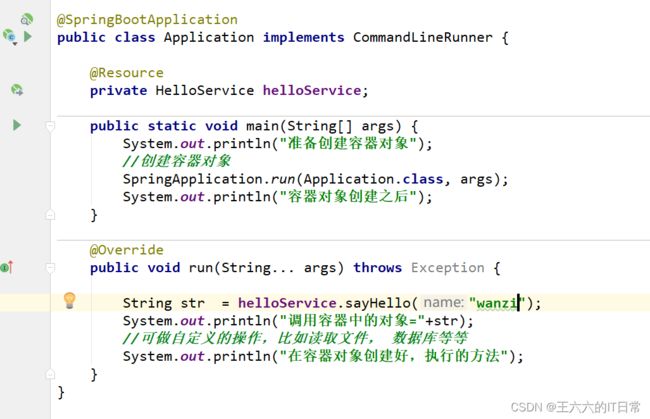
2.9 ComnandLineRunner 接口 , ApplcationRunner接口
这两个接口都 有一个run方法。 执行时间在容器对象创建好后, 自动执行run()方法。
可以完成自定义的在容器对象创建好的一些操作。
@FunctionalInterface
public interface CommandLineRunner {
void run(String... args) throws Exception;
}
@FunctionalInterface
public interface ApplicationRunner {
void run(ApplicationArguments args) throws Exception;
}