coco 数据集_手把手教你如何用SOLOV2训练自己的数据集
title: 手把手教你如何用SOLOV2训练自己的数据集
date: 2020-07-24 14:59:11
category: 默认分类
本文介绍 手把手教你如何用SOLOV2训练自己的数据集
手把手教你如何用SOLOV2训练自己的数据集
本文由林大佬原创,转载请注明出处,来自腾讯、阿里等一线AI算法工程师组成的QQ交流群欢迎你的加入: 1037662480
最近后台很多小伙伴跟我说能不能出一些实例分割训练的教程, 因为网上很多都是关于加速/部署的, 为了满足大家的愿望, 今天特意给大家带来了现在比较火的SOLO系列算法的训练教程. 确实现在关于实力分割的教程都比较复杂, 这篇文章可以让大家轻松地入门SOTA的实例分割方案, 感兴趣的同学也可以给本文点个赞, 转发一下, 你的支持是我们创作的原始动力!
这篇教程不需要任何神力会员权限, 直接从github clone代码, 先将代码准备好, 就可以开始了:
git clone https://github.com/WXinlong/SOLO现在网上有好几个不同版本的SOLO开源算法, 但是原作者的这个应该是比较权威的吧, 大家可以用这个版本, 笔者用下来, 这个版本具有几个优点:
- 它基于mmdetection, 模块化, 代码看起来也比较通熟易懂;
- 训练起来没什么坑, 对于没有8卡GPU的同学,用单卡或者两卡也是可以train的, 我们这篇文章会给出大家的具体指导;
但是也有一些缺点:
- 代码pytorch1.5跑不起来,更别说现在最新的pytorch1.7了, 需要我们修改过的代码 (兼容pytorch1.5和mmdetection2.0) 可以移步神力平台获取现成的代码;
- 代码注册新的dataset有点麻烦, 而且我发现(没有确认) 原始的dataset有bug, 相信很多同学在训练自己的数据集的时候会遇到第一个类别被自动忽略的bug, 当然这个bug已经被我们修复了, 详情也可以移步神力平台, 文末会放出我们的代码链接.
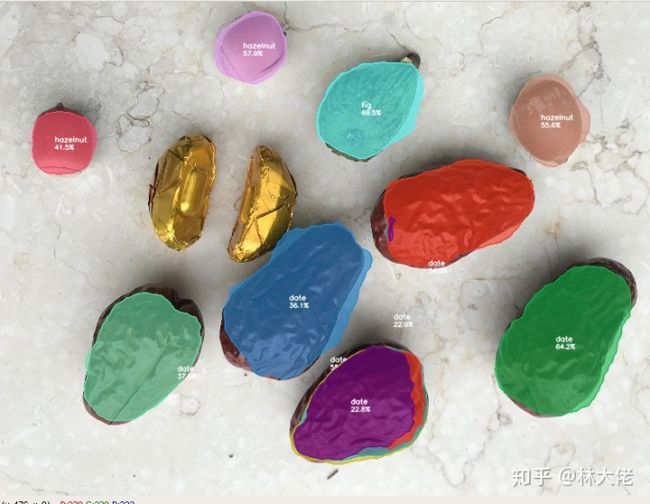
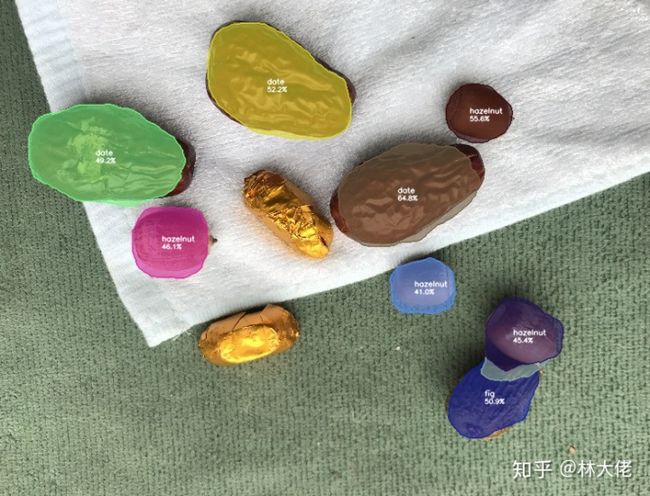
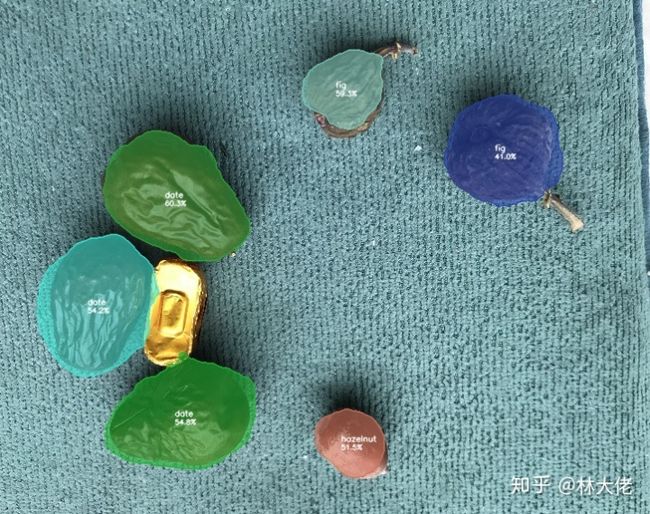
当然, 如果你只是训练我们今天的数据集, 那是足够了, 因为今天的数据集的主角很小很小很小, 但是麻雀虽小五脏俱全. 先来看看SOLOv2的分割效果:
这个数据集的名字叫做 坚果数据集.
因为它很小, 所以经常被我用来检测一个算法是不是work, 基本上两分钟就可以出结果. 我也强烈建议大家用起来, 关于数据集的下载, 推荐大家看这篇文章, 这篇文章的博主其实将的比较完全了:
https://www.jianshu.com/p/a94b1629f827www.jianshu.com这里也贴一下下载:
wget https://github.com/Tony607/detectron2_instance_segmentation_demo/releases/download/V0.1/data.zip数据集的版权credit@Tony607 , 感谢这位作者的工作.
材料都准备好了, 接下来按照步骤来教授大家如何训练吧.
01. SOLO注册自定义数据集
首先, 我们需要注册一个自己的自定义数据集, 在原始的SOLO项目里面, 具体的注册方式为:
a). 在 mmdet/dataset 文件下, 创建一个 coco_toy.py 的文件, 文件中就是我们要注册的数据类.
b). 给数据类添加代码:
import numpy as np
from pycocotools.coco import COCO
from .custom import CustomDataset
from .registry import DATASETS
@DATASETS.register_module
class CocoToyDataset(CustomDataset):
CLASSES = ('date', 'fig', 'hazelnut')
def load_annotations(self, ann_file):
self.coco = COCO(ann_file)
self.cat_ids = self.coco.get_cat_ids(cat_names=self.CLASSES)
self.cat2label = {cat_id: i for i, cat_id in enumerate(self.cat_ids)}
self.img_ids = self.coco.get_img_ids()
data_infos = []
for i in self.img_ids:
info = self.coco.load_imgs([i])[0]
info['filename'] = info['file_name']
data_infos.append(info)
return data_infos
def get_ann_info(self, idx):
img_id = self.data_infos[idx]['id']
ann_ids = self.coco.get_ann_ids(img_ids=[img_id])
ann_info = self.coco.load_anns(ann_ids)
return self._parse_ann_info(self.data_infos[idx], ann_info)
def get_cat_ids(self, idx):
img_id = self.data_infos[idx]['id']
ann_ids = self.coco.get_ann_ids(img_ids=[img_id])
ann_info = self.coco.load_anns(ann_ids)
return [ann['category_id'] for ann in ann_info]
def _filter_imgs(self, min_size=32):
"""Filter images too small or without ground truths."""
valid_inds = []
ids_with_ann = set(_['image_id'] for _ in self.coco.anns.values())
for i, img_info in enumerate(self.data_infos):
if self.filter_empty_gt and self.img_ids[i] not in ids_with_ann:
continue
if min(img_info['width'], img_info['height']) >= min_size:
valid_inds.append(i)
return valid_inds
def get_subset_by_classes(self):
"""Get img ids that contain any category in class_ids.
Different from the coco.getImgIds(), this function returns the id if
the img contains one of the categories rather than all.
Args:
class_ids (list[int]): list of category ids
Return:
ids (list[int]): integer list of img ids
"""
ids = set()
for i, class_id in enumerate(self.cat_ids):
ids |= set(self.coco.cat_img_map[class_id])
self.img_ids = list(ids)
data_infos = []
for i in self.img_ids:
info = self.coco.load_imgs([i])[0]
info['filename'] = info['file_name']
data_infos.append(info)
return data_infos
def _parse_ann_info(self, img_info, ann_info):
"""Parse bbox and mask annotation.
Args:
ann_info (list[dict]): Annotation info of an image.
with_mask (bool): Whether to parse mask annotations.
Returns:
dict: A dict containing the following keys: bboxes, bboxes_ignore,
labels, masks, seg_map. "masks" are raw annotations and not
decoded into binary masks.
"""
gt_bboxes = []
gt_labels = []
gt_bboxes_ignore = []
gt_masks_ann = []
for i, ann in enumerate(ann_info):
if ann.get('ignore', False):
continue
x1, y1, w, h = ann['bbox']
if ann['area'] <= 0 or w < 1 or h < 1:
continue
if ann['category_id'] not in self.cat_ids:
continue
bbox = [x1, y1, x1 + w, y1 + h]
if ann.get('iscrowd', False):
gt_bboxes_ignore.append(bbox)
else:
gt_bboxes.append(bbox)
# left 0 to be bk, all instance start from 1
gt_labels.append(self.cat2label[ann['category_id']]+1)
gt_masks_ann.append(ann['segmentation'])
if gt_bboxes:
gt_bboxes = np.array(gt_bboxes, dtype=np.float32)
gt_labels = np.array(gt_labels, dtype=np.int64)
else:
gt_bboxes = np.zeros((0, 4), dtype=np.float32)
gt_labels = np.array([], dtype=np.int64)
if gt_bboxes_ignore:
gt_bboxes_ignore = np.array(gt_bboxes_ignore, dtype=np.float32)
else:
gt_bboxes_ignore = np.zeros((0, 4), dtype=np.float32)
seg_map = img_info['filename'].replace('jpg', 'png')
ann = dict(
bboxes=gt_bboxes,
labels=gt_labels,
bboxes_ignore=gt_bboxes_ignore,
masks=gt_masks_ann,
seg_map=seg_map)
return ann
def xyxy2xywh(self, bbox):
_bbox = bbox.tolist()
return [
_bbox[0],
_bbox[1],
_bbox[2] - _bbox[0],
_bbox[3] - _bbox[1],
]
def _proposal2json(self, results):
json_results = []
for idx in range(len(self)):
img_id = self.img_ids[idx]
bboxes = results[idx]
for i in range(bboxes.shape[0]):
data = dict()
data['image_id'] = img_id
data['bbox'] = self.xyxy2xywh(bboxes[i])
data['score'] = float(bboxes[i][4])
data['category_id'] = 1
json_results.append(data)
return json_results
def _det2json(self, results):
json_results = []
for idx in range(len(self)):
img_id = self.img_ids[idx]
result = results[idx]
for label in range(len(result)):
bboxes = result[label]
for i in range(bboxes.shape[0]):
data = dict()
data['image_id'] = img_id
data['bbox'] = self.xyxy2xywh(bboxes[i])
data['score'] = float(bboxes[i][4])
data['category_id'] = self.cat_ids[label]
json_results.append(data)
return json_results
def _segm2json(self, results):
bbox_json_results = []
segm_json_results = []
for idx in range(len(self)):
img_id = self.img_ids[idx]
det, seg = results[idx]
for label in range(len(det)):
# bbox results
bboxes = det[label]
for i in range(bboxes.shape[0]):
data = dict()
data['image_id'] = img_id
data['bbox'] = self.xyxy2xywh(bboxes[i])
data['score'] = float(bboxes[i][4])
data['category_id'] = self.cat_ids[label]
bbox_json_results.append(data)
# segm results
# some detectors use different scores for bbox and mask
if isinstance(seg, tuple):
segms = seg[0][label]
mask_score = seg[1][label]
else:
segms = seg[label]
mask_score = [bbox[4] for bbox in bboxes]
for i in range(bboxes.shape[0]):
data = dict()
data['image_id'] = img_id
data['bbox'] = self.xyxy2xywh(bboxes[i])
data['score'] = float(mask_score[i])
data['category_id'] = self.cat_ids[label]
if isinstance(segms[i]['counts'], bytes):
segms[i]['counts'] = segms[i]['counts'].decode()
data['segmentation'] = segms[i]
segm_json_results.append(data)
return bbox_json_results, segm_json_results
def results2json(self, results, outfile_prefix):
"""Dump the detection results to a json file.
There are 3 types of results: proposals, bbox predictions, mask
predictions, and they have different data types. This method will
automatically recognize the type, and dump them to json files.
Args:
results (list[list | tuple | ndarray]): Testing results of the
dataset.
outfile_prefix (str): The filename prefix of the json files. If the
prefix is "somepath/xxx", the json files will be named
"somepath/xxx.bbox.json", "somepath/xxx.segm.json",
"somepath/xxx.proposal.json".
Returns:
dict[str: str]: Possible keys are "bbox", "segm", "proposal", and
values are corresponding filenames.
"""
result_files = dict()
if isinstance(results[0], list):
json_results = self._det2json(results)
result_files['bbox'] = f'{outfile_prefix}.bbox.json'
result_files['proposal'] = f'{outfile_prefix}.bbox.json'
mmcv.dump(json_results, result_files['bbox'])
elif isinstance(results[0], tuple):
json_results = self._segm2json(results)
result_files['bbox'] = f'{outfile_prefix}.bbox.json'
result_files['proposal'] = f'{outfile_prefix}.bbox.json'
result_files['segm'] = f'{outfile_prefix}.segm.json'
mmcv.dump(json_results[0], result_files['bbox'])
mmcv.dump(json_results[1], result_files['segm'])
elif isinstance(results[0], np.ndarray):
json_results = self._proposal2json(results)
result_files['proposal'] = f'{outfile_prefix}.proposal.json'
mmcv.dump(json_results, result_files['proposal'])
else:
raise TypeError('invalid type of results')
return result_files
def fast_eval_recall(self, results, proposal_nums, iou_thrs, logger=None):
gt_bboxes = []
for i in range(len(self.img_ids)):
ann_ids = self.coco.get_ann_ids(img_ids=self.img_ids[i])
ann_info = self.coco.load_anns(ann_ids)
if len(ann_info) == 0:
gt_bboxes.append(np.zeros((0, 4)))
continue
bboxes = []
for ann in ann_info:
if ann.get('ignore', False) or ann['iscrowd']:
continue
x1, y1, w, h = ann['bbox']
bboxes.append([x1, y1, x1 + w, y1 + h])
bboxes = np.array(bboxes, dtype=np.float32)
if bboxes.shape[0] == 0:
bboxes = np.zeros((0, 4))
gt_bboxes.append(bboxes)
recalls = eval_recalls(
gt_bboxes, results, proposal_nums, iou_thrs, logger=logger)
ar = recalls.mean(axis=1)
return ar
def format_results(self, results, jsonfile_prefix=None, **kwargs):
"""Format the results to json (standard format for COCO evaluation).
Args:
results (list): Testing results of the dataset.
jsonfile_prefix (str | None): The prefix of json files. It includes
the file path and the prefix of filename, e.g., "a/b/prefix".
If not specified, a temp file will be created. Default: None.
Returns:
tuple: (result_files, tmp_dir), result_files is a dict containing
the json filepaths, tmp_dir is the temporal directory created
for saving json files when jsonfile_prefix is not specified.
"""
assert isinstance(results, list), 'results must be a list'
assert len(results) == len(self), (
'The length of results is not equal to the dataset len: {} != {}'.
format(len(results), len(self)))
if jsonfile_prefix is None:
tmp_dir = tempfile.TemporaryDirectory()
jsonfile_prefix = osp.join(tmp_dir.name, 'results')
else:
tmp_dir = None
result_files = self.results2json(results, jsonfile_prefix)
return result_files, tmp_dir
def evaluate(self,
results,
metric='bbox',
logger=None,
jsonfile_prefix=None,
classwise=False,
proposal_nums=(100, 300, 1000),
iou_thrs=np.arange(0.5, 0.96, 0.05)):
"""Evaluation in COCO protocol.
Args:
results (list): Testing results of the dataset.
metric (str | list[str]): Metrics to be evaluated.
logger (logging.Logger | str | None): Logger used for printing
related information during evaluation. Default: None.
jsonfile_prefix (str | None): The prefix of json files. It includes
the file path and the prefix of filename, e.g., "a/b/prefix".
If not specified, a temp file will be created. Default: None.
classwise (bool): Whether to evaluating the AP for each class.
proposal_nums (Sequence[int]): Proposal number used for evaluating
recalls, such as recall@100, recall@1000.
Default: (100, 300, 1000).
iou_thrs (Sequence[float]): IoU threshold used for evaluating
recalls. If set to a list, the average recall of all IoUs will
also be computed. Default: 0.5.
Returns:
dict[str: float]
"""
metrics = metric if isinstance(metric, list) else [metric]
allowed_metrics = ['bbox', 'segm', 'proposal', 'proposal_fast']
for metric in metrics:
if metric not in allowed_metrics:
raise KeyError(f'metric {metric} is not supported')
result_files, tmp_dir = self.format_results(results, jsonfile_prefix)
eval_results = {}
cocoGt = self.coco
for metric in metrics:
msg = f'Evaluating {metric}...'
if logger is None:
msg = 'n' + msg
print_log(msg, logger=logger)
if metric == 'proposal_fast':
ar = self.fast_eval_recall(
results, proposal_nums, iou_thrs, logger='silent')
log_msg = []
for i, num in enumerate(proposal_nums):
eval_results[f'AR@{num}'] = ar[i]
log_msg.append(f'nAR@{num}t{ar[i]:.4f}')
log_msg = ''.join(log_msg)
print_log(log_msg, logger=logger)
continue
if metric not in result_files:
raise KeyError(f'{metric} is not in results')
try:
cocoDt = cocoGt.loadRes(result_files[metric])
except IndexError:
print_log(
'The testing results of the whole dataset is empty.',
logger=logger,
level=logging.ERROR)
break
iou_type = 'bbox' if metric == 'proposal' else metric
cocoEval = COCOeval(cocoGt, cocoDt, iou_type)
cocoEval.params.catIds = self.cat_ids
cocoEval.params.imgIds = self.img_ids
if metric == 'proposal':
cocoEval.params.useCats = 0
cocoEval.params.maxDets = list(proposal_nums)
cocoEval.evaluate()
cocoEval.accumulate()
cocoEval.summarize()
metric_items = [
'AR@100', 'AR@300', 'AR@1000', 'AR_s@1000', 'AR_m@1000',
'AR_l@1000'
]
for i, item in enumerate(metric_items):
val = float(f'{cocoEval.stats[i + 6]:.3f}')
eval_results[item] = val
else:
cocoEval.evaluate()
cocoEval.accumulate()
cocoEval.summarize()
if classwise: # Compute per-category AP
# Compute per-category AP
# from https://github.com/facebookresearch/detectron2/
precisions = cocoEval.eval['precision']
# precision: (iou, recall, cls, area range, max dets)
assert len(self.cat_ids) == precisions.shape[2]
results_per_category = []
for idx, catId in enumerate(self.cat_ids):
# area range index 0: all area ranges
# max dets index -1: typically 100 per image
nm = self.coco.loadCats(catId)[0]
precision = precisions[:, :, idx, 0, -1]
precision = precision[precision > -1]
if precision.size:
ap = np.mean(precision)
else:
ap = float('nan')
results_per_category.append(
(f'{nm["name"]}', f'{float(ap):0.3f}'))
num_columns = min(6, len(results_per_category) * 2)
results_flatten = list(
itertools.chain(*results_per_category))
headers = ['category', 'AP'] * (num_columns // 2)
results_2d = itertools.zip_longest(*[
results_flatten[i::num_columns]
for i in range(num_columns)
])
table_data = [headers]
table_data += [result for result in results_2d]
table = AsciiTable(table_data)
print_log('n' + table.table, logger=logger)
metric_items = [
'mAP', 'mAP_50', 'mAP_75', 'mAP_s', 'mAP_m', 'mAP_l'
]
for i in range(len(metric_items)):
key = f'{metric}_{metric_items[i]}'
val = float(f'{cocoEval.stats[i]:.3f}')
eval_results[key] = val
ap = cocoEval.stats[:6]
eval_results[f'{metric}_mAP_copypaste'] = (
f'{ap[0]:.3f} {ap[1]:.3f} {ap[2]:.3f} {ap[3]:.3f} '
f'{ap[4]:.3f} {ap[5]:.3f}')
if tmp_dir is not None:
tmp_dir.cleanup()
return eval_results
然后只需要在同级目录下的 __init__.py 里面, 用这个替换掉原来的:
from .builder import build_dataset
from .cityscapes import CityscapesDataset
from .coco import CocoDataset
from .coco_toy import CocoToyDataset
from .custom import CustomDataset
from .dataset_wrappers import ConcatDataset, RepeatDataset
from .loader import DistributedGroupSampler, GroupSampler, build_dataloader
from .registry import DATASETS
from .voc import VOCDataset
from .wider_face import WIDERFaceDataset
from .xml_style import XMLDataset
__all__ = [
'CustomDataset', 'XMLDataset', 'CocoDataset', 'VOCDataset', 'CocoToyDataset',
'CityscapesDataset', 'GroupSampler', 'DistributedGroupSampler',
'build_dataloader', 'ConcatDataset', 'RepeatDataset', 'WIDERFaceDataset',
'DATASETS', 'build_dataset'
]这样, 我们自定义的数据集就注册好了.
02. 接着修改配置文件
这一步, 有必要强调一下, 原始配置文件, num_classes 是81, 因为coco里面有80类, 加了1, 所以是81类. 但是我们的数据集是3类, 因此类别数目这里我们用4类.
主要修改的地方就这么几个:
num_classes; 你的类别数目加1;- lr 以及 多少块GPU
我们这边修改了一个两卡的配置供大家参考:
# model settings
model = dict(
type='SOLOv2',
pretrained='torchvision://resnet50',
backbone=dict(
type='ResNet',
depth=50,
num_stages=4,
out_indices=(0, 1, 2, 3), # C2, C3, C4, C5
frozen_stages=1,
style='pytorch'),
neck=dict(
type='FPN',
in_channels=[256, 512, 1024, 2048],
out_channels=256,
start_level=0,
num_outs=5),
bbox_head=dict(
type='SOLOv2Head',
# cityscapes have 8 classes
num_classes=4,
in_channels=256,
stacked_convs=2,
seg_feat_channels=256,
strides=[8, 8, 16, 32, 32],
scale_ranges=((1, 56), (28, 112), (56, 224), (112, 448), (224, 896)),
sigma=0.2,
num_grids=[40, 36, 24, 16, 12],
ins_out_channels=128,
loss_ins=dict(
type='DiceLoss',
use_sigmoid=True,
loss_weight=3.0),
loss_cate=dict(
type='FocalLoss',
use_sigmoid=True,
gamma=2.0,
alpha=0.25,
loss_weight=1.0)),
mask_feat_head=dict(
type='MaskFeatHead',
in_channels=256,
out_channels=128,
start_level=0,
end_level=3,
# hxwxs^2
num_classes=128,
norm_cfg=dict(type='GN', num_groups=32, requires_grad=True)),
)
# training and testing settings
train_cfg = dict()
test_cfg = dict(
nms_pre=500,
score_thr=0.1,
mask_thr=0.5,
update_thr=0.05,
kernel='gaussian', # gaussian/linear
sigma=2.0,
max_per_img=100)
# dataset settings
dataset_type = 'CocoToyDataset'
data_root = 'data/toy_ins/'
img_norm_cfg = dict(
mean=[123.675, 116.28, 103.53], std=[58.395, 57.12, 57.375], to_rgb=True)
train_pipeline = [
dict(type='LoadImageFromFile'),
dict(type='LoadAnnotations', with_bbox=True, with_mask=True),
dict(type='Resize',
img_scale=[(768, 512), (768, 480), (768, 448),
(768, 416), (768, 384), (768, 352)],
multiscale_mode='value',
keep_ratio=True),
dict(type='RandomFlip', flip_ratio=0.5),
dict(type='Normalize', **img_norm_cfg),
dict(type='Pad', size_divisor=32),
dict(type='DefaultFormatBundle'),
dict(type='Collect', keys=['img', 'gt_bboxes', 'gt_labels', 'gt_masks']),
]
test_pipeline = [
dict(type='LoadImageFromFile'),
dict(
type='MultiScaleFlipAug',
img_scale=(768, 448),
flip=False,
transforms=[
dict(type='Resize', keep_ratio=True),
dict(type='RandomFlip'),
dict(type='Normalize', **img_norm_cfg),
dict(type='Pad', size_divisor=32),
dict(type='ImageToTensor', keys=['img']),
dict(type='Collect', keys=['img']),
])
]
data = dict(
imgs_per_gpu=2,
workers_per_gpu=2,
train=dict(
type=dataset_type,
ann_file=data_root + 'data/trainval.json',
img_prefix=data_root + 'data/images/',
pipeline=train_pipeline),
val=dict(
type=dataset_type,
ann_file=data_root + 'data/trainval.json',
img_prefix=data_root + 'data/images/',
pipeline=test_pipeline),
test=dict(
type=dataset_type,
ann_file=data_root + 'data/trainval.json',
img_prefix=data_root + 'data/images/',
pipeline=test_pipeline))
# optimizer
optimizer = dict(type='SGD', lr=0.0025, momentum=0.9, weight_decay=0.0001)
optimizer_config = dict(grad_clip=dict(max_norm=35, norm_type=2))
# learning policy
lr_config = dict(
policy='step',
warmup='linear',
warmup_iters=500,
warmup_ratio=0.01,
step=[27, 33])
checkpoint_config = dict(interval=1)
# yapf:disable
log_config = dict(
interval=5,
hooks=[
dict(type='TextLoggerHook'),
dict(type='TensorboardLoggerHook')
])
# yapf:enable
# runtime settings
total_epochs = 72
device_ids = range(2)
dist_params = dict(backend='nccl')
log_level = 'INFO'
work_dir = './work_dirs/toy/solov2_light_release_r50_fpn_2gpu_3x'
load_from = None
resume_from = None
workflow = [('train', 1)]由于我们是2个GPU, 因此这里的学习速率可以改为 0.0025
03. 训练
准备好以后 训练就非常简单了:
python tools/train.py ./configs/solov2/toy/solov2_light_448_r50_fpn_2gpu_3x.py --gpus 2这样, 我们就开始了训练一个SOLOv2的light版本.
跑起来之后.
最后预测的结果, 我们来看看:
我个人觉得效果还是非常不错的.
另外如果大家有什么数据集想要我们帮忙训练的, 欢迎添加 微信 jintianandmerry 我们可以帮你训练.
本文的所有代码都是来自于github的原作者的训练框架, 我们有一个自己的fork版本, 本文用到的pytorch1.5支持, 可视化后处理等代码都是我们自己写并完善的, 所有代码可以参见神力平台:
神力AI(MANA)-国内最大的AI代码平台manaai.cn如果你想学习人工智能,对前沿的AI技术比较感兴趣,可以加入我们的知识星球,获取第一时间资讯,前沿学术动态,业界新闻等等!你的支持将会鼓励我们更频繁的创作,我们也会帮助你开启更深入的深度学习之旅!
往期文章
林大佬:YoloV5的TensorRT加速实现49FPS,mAP40+!zhuanlan.zhihu.com 林大佬:使用mmdetection2.0实现SOLOV2-全新的实例分割框架zhuanlan.zhihu.com 林大佬:PolyYolo开源!Yolo也能做实例分割,检测mAP提升40%!zhuanlan.zhihu.comReference
本文参考的论文以代码:
[1]. SOLOv2: Dynamic, Faster and Stronger
[2]. https://github.com/WXinlong/SOLO