编译原理实验三:预测分析法语法分析器的设计
编译原理实验三:预测分析法语法分析器的设计
一、实验目的
根据文法编制预测分析法语法分析程序,以便对输入的符号串进行语法分析。通过编写预测分析法语法分析程序掌握预测分析法的基本原理、FIRST和FOLLOW集的计算、预测分析表的构造方法以及语法分析法主控程序的设计。
二、实验内容
对于给定的上下文无关文法,编程完成以下功能:
- 消除左递归
- 计算非终结符的FIRST和FOLLOW集
- 构造预测分析表
- 判断消除了左递归后的文法是否为LL(1)文法
- 编写预测分析法语法分析程序,要求对输入的任意符号串进行语法分析,输出推导过程或语法分析树。
三、实验要求
1、 输入/输出格式
文法的输入示例参考cfg1.txt以及cfg2.txt。例如文法以以下形式给出:
E::=E + T
E::=E - T
E::=T
T::=T * F
T::=T / F
T::=F
F::=( E )
F::=id
文法只给出产生式列表,每个产生式占一行,产生式右边的文法符号串每个符号之间有一个空格,末尾没有空格。第一个产生式左边的非终结符为开始符号。如果某非终结符A的候选式为ε,则产生式直接表示为A::=ε。
输出的结果按照实验内容依次输出:
- 消除左递归后的文法✔️
- 非终结符的
FIRST和FOLLOW集✔️ - 预测分析表✔️
- 是否为LL(1)文法✔️
- 测试字符串利用预测分析法进行语法分析。✔️
2、上述要求仅为基本要求,可以在此基础上扩充。
例如:
- 能够处理间接左递归✔️
- 增加错误处理✔️
- 输出错误信息等✔️
- 进一步可以指出出错的位置。
- ……
3、编程语言:C++
4、实验报告要求:
(1) 实验报告的内容应该包括:实验目的、实验要求、测试方案及测试结果、实验小结、主要方法的源代码。
(2)编程时注意编程风格:空行的使用、注释的使用、缩进的使用等。
(3) 源代码及电子实验报告发送到课堂派(源代码如果有多个文件,压缩成一个文件),同时学号尾数为3、8的同学需要提交纸质实验报告。
四、测试方案
算法流程描述
LL(1)文法是一种自上而下的分析,使用最左推导,从左至右扫描输入串,且对每次最左推导只需向前看一个输入符号,便可确定当前所应当选择的算法规则。

-
输入文法
-
消除间接左递归
检测循环推导:S ——> A ——> B ——> S
解决:化为直接左递归,即B的候选式代入A,A的候选式代入B,……S ——>Sab…
-
消除直接左递归
A ——> Aa | b转换为:
A ——> bA’
A’ ——> aA’ | ε -
分别提取终结符VT和非终结符VN
-
计算每个非终结符的FIRST集合
每轮循环,扫描每一个产生式的每一个符号
1)是终结符,A ——> a形式,直接
FIRST[A] += {a};2)是非终结符,A ——> B形式,
FIRST[A] += (FIRST[B] - {ε}); 如果FIRST[B]是否有
ε,继续扫描产生式后面的符号。 如果FIRST[B]有
ε且 B 是该候选式的最后一个符号,则FIRST[A] += {ε}每轮循环中有FIRST集合发生变化,继续循环,否则退出循环。
-
计算每个非终结符的FOLLOW集合
每轮循环,扫描每一个产生式的每一个符号
若当前符号是
非终结符,看当前符号的后一个符号: 1)后面没有符号,
A->aB形式,则FOLLOW[B] += FOLLOW[A]; 2)后面为终结符,
A->aBc形式,则FOLLOW[B] += {c}; 3)后面为非终结符,
A->aBC形式,则FOLLOW[B] += (FIRST[C]-{ε}) 如果
C->...->ε,则同1)情况,则需FOLLOW(B) += FOLLOW(A) -
计算每个候选式的FIRST集合(为后续语法分析表的构建服务)
-
输出消除左递归后的产生式,FIRST与FOLLOW集合。
-
构建预测分析表
对于每个产生式
A-> ri,ri是右部整个候选式1)FIRST(ri) = a,M[A, a]处填入此产生式
2)FIRST(ri) = ε ,求FOLLOW[A] = b,则M[A, b]处填入此产生式
3)空白处,error
-
判断是否为LL(1)文法
对每个产生式
A ——> r1 | r2 | ... | ri,应有:
FIRST(ri) ∩ FIRST(rj) != ∅如果有候选式为
ε,则其余非空候选式应满足FIRST(ri) ∩ FOLLOW(A) != ∅ -
接收字串输入
-
对字串进行语法分析
构建语法分析栈,首先压入
#终止符和文法开始符。依次读取字串,如果当前字符与栈顶元素相同,即匹配成功,出栈;
否则查表
M[栈顶非终结符,待分析字符],如果为空,即为error报错,否则栈顶元素出栈,把分析表对应位置处的产生式压入栈。
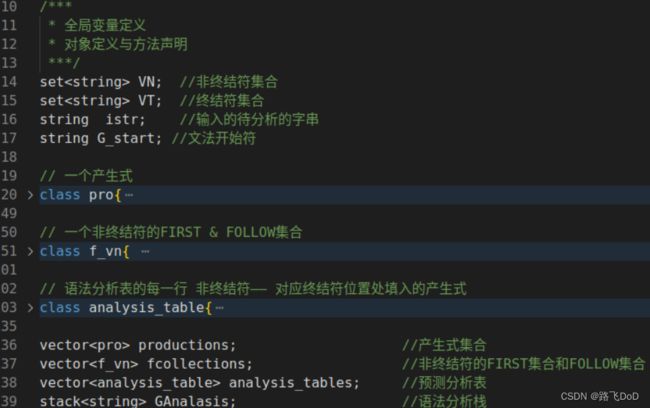
全局变量与函数声明
封装了三个类,pro类即代表产生式,包含属性有产生式的左部、一个候选式集合、该候选式的FIRST集合、该产生式的编号,包含插入与输出相关信息的操作;f_vb类即存放一个非终结符的FIRST集合和FOLLOW集合,包含插入与输出相关信息的操作;analysis_table类即存放语法分析表每一行的信息,非终结符,对应每个终结符处的产生式信息。
/***
* 全局变量定义
* 对象定义与方法声明
***/
set<string> VN; //非终结符集合
set<string> VT; //终结符集合
string istr; //输入的待分析的字串
string G_start; //文法开始符
// 一个产生式
class pro{
public:
string left; //产生式左部
vector<string> right; //产生式右部
set<string> rfirst; //产生式右部的first集合
int index; //产生式编号
pro(const string & str){
left=str;
right.clear();
rfirst.clear();
index=0;
}
void push(const string & str){
right.push_back(str);
}
void print(){
cout<<left<<"::=";
vector<string>::iterator it = right.begin();
for (;it!= right.end();it++ ){
cout<<(*it)<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
}
void insert(const string & str){
if(rfirst.count(str) < 1){
rfirst.insert(str);
}
}
};
// 一个非终结符的FIRST & FOLLOW集合
class f_vn{
public:
string vn; //非终结符
set<string> vfirst; //FIRST集合
set<string> vfollow; //FOLLOW集合
f_vn(const string & str){ // 构造函数
vn = str;
vfirst.clear();
vfollow.clear();
}
void insert1(string t){ // FIRST集合插入
if(vfirst.empty() == true || vfirst.count(t) < 1){
vfirst.insert(t);
}
}
void insert2(string t){ // FOLLOW集合插入
if(vfollow.empty() == true || vfollow.count(t) < 1){
vfollow.insert(t);
}
}
void print(){ // 输出FIRST、FOLLOW集合
if(vfirst.empty()){
cout<<"FIRST:NULL"<<endl;
}else{
cout<<"FIRST["<<vn<<"] = { ";
set<string>::iterator it1 = vfirst.begin();
cout<<(*it1);
it1++;
for(;it1!=vfirst.end();it1++){
cout<<", "<<(*it1);
}
cout<<" }\t\t\t";
}
if(vfollow.empty()){
cout<<"FOLLOW:NULL"<<endl;
}else{
cout<<"FOLLOW["<<vn<<"] = { ";
set<string>::iterator it2 = vfollow.begin();
cout<<(*it2);
it2++;
for(;it2!=vfollow.end();it2++){
cout<<", "<<(*it2);
}
cout<<"}"<<endl;
}
}
};
// 语法分析表的每一行 非终结符—— 对应终结符位置处填入的产生式
class analysis_table{
public:
string vn; // 非终结符
map<string, string> atlist; // <终结符,产生式>
map<string, int> atindex; // <终结符,产生式编号>
analysis_table(const string &str){
vn = str;
atlist.clear();
atindex.clear();
}
void initmap(){
string empty_str = " ";
for(auto i : VT){
atlist.insert(pair<string, string>(i, empty_str));
}
atlist.insert(pair<string, string>("#", empty_str)); // 补充#
}
void printrow(){ // 打印一行数据
cout<<setw(4)<<left<<vn;
cout<<"|";
map<string,string>::iterator it;
for(auto it:VT){
cout<<setw(15)<<left<<atlist.find(it)->second;
}
cout<<setw(15)<<left<<atlist.find("#")->second<<endl;
}
void insert(string vt, string p){ //产生式p放入M[vn, vt];
atlist.find(vt)->second = p;
}
};
vector<pro> productions; //产生式集合
vector<f_vn> fcollections; //非终结符的FIRST集合和FOLLOW集合
vector<analysis_table> analysis_tables; //预测分析表
stack<string> GAnalasis; //语法分析栈
函数声明:
//函数声明
void inputG(); // 文法输入处理函数
void eliminateILeftRecusive(); // 消除间接左递归
void eliminateDLeftRecusive(); // 消除直接左递归
void printProductions(); // 测试,打印存储的产生式集合
void printVNT(); // 测试,打印所有的非终结符,终结符
void calVN(); // 记录所有非终结符
void calVT(); // 记录所有终结符
void initFcollections(); // 初始化产生式集合(将所有非终结符加入进去)
void calFIRST(); // 计算FIRST集合
void calFOLLOW(); // 计算FOLLOW集合
void calRightFIRST(); // 计算每个候选式右部的FIRST集合
void printFirstFollow(); // 打印FIRST FOLLOW集合
void initAnalysisTable(); // 初始化预测分析表
void createAnalysisTable(); // 构建预测分析表
bool isVN(string str); // 判断是否为非终结符
string getpro(int j); // 得到productions[j]的产生式字符串
void printAnalysisTable(); // 打印预测分析表
bool isLL1(); // 判断是否为LL(1)文法
void judgeG(); // 评判该文法
void inputIstr(); // 输入待分析的字符串
string getStackStr(); // 获得语法分析栈中的所有内容
void analysisIstr(); // 语法分析输入的字符串
main函数
int main()
{
cout<<"Hello!"<<endl;
inputG(); //文法输入处理
eliminateILeftRecusive(); // 消除间接左递归
eliminateDLeftRecusive(); // 消除直接左递归
calVN(); // 记录所有非终结符
calVT(); // 记录所有终结符 包括ε
initFcollections(); // 初始化产生式集合(将所有非终结符加入进去)
calFIRST(); // 计算FIRST集合
calFOLLOW(); // 计算FOLLOW集合
calRightFIRST(); // 计算每个候选式右部的FIRST集合
printVNT(); // 测试,打印所有的非终结符,终结符
printProductions(); // 测试,打印存储的产生式集合
printFirstFollow(); // 打印FIRST FOLLOW集合
initAnalysisTable(); // 初始化预测分析表
createAnalysisTable(); // 构建预测分析表
printAnalysisTable(); // 打印预测分析表
judgeG(); // 评判该文法
void analysisIstr(); // 语法分析输入的字符串
return 0;
}
五、测试结果
测试样例一
E::=E + T
E::=E - T
E::=T
T::=T * F
T::=T / F
T::=F
F::=( E )
F::=id
输入文法:
消除左递归结果,FIRST和FOLLOW集合
语法分析表以及LL(1)文法判断:
输入:a+b*c-(1/f)#
输入:i*i-1+a)#
测试样例二
S::=( L )
S::=a
L::=L , S
L::=S
输入文法:
消除左递归结果,FIRST和FOLLOW集合
语法分析表以及LL(1)文法判断:
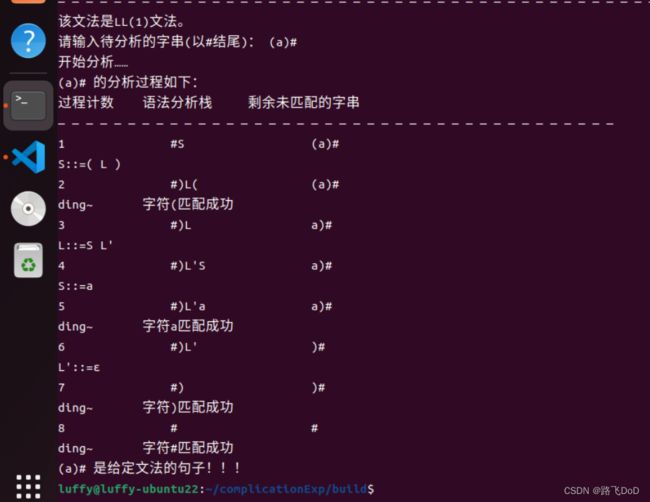
输入:(a)
输入:(a,a)
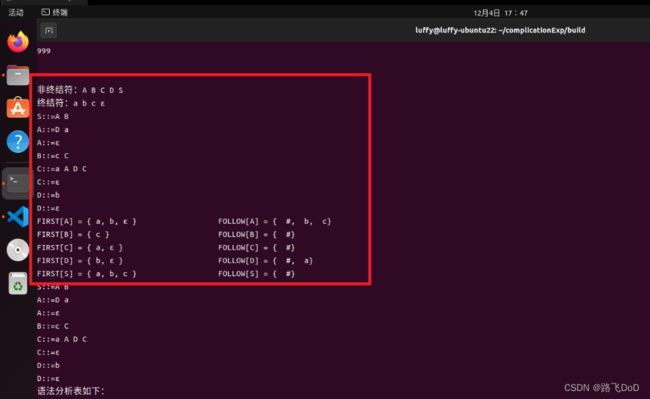
测试样例三
S::=A B
A::=D a
A::=ε
B::=c C
C::=a A D C
C::=ε
D::=b
D::=ε
输入文法:
消除左递归结果,FIRST和FOLLOW集合
语法分析表以及LL(1)文法判断:
测试样例四(存在间接左递归)
S::=Q c
S::=c
Q::=R b
Q::=b
R::=S a
R::=a
输入文法:
消除左递归结果:
语法分析表以及LL(1)文法判断:
输入
六、实验小结
本次实验还存在的缺陷:对输入的串只是逐个字符读取分析,没有结合上次实验的词法分析,仍存在许多有待优化完善的地方。
对自顶向下的文法分析的过程有了较为深入的理解,只是这个代码复现过程……要吐了。

从0开始一点一点敲起来,敲了1000行,这强度,实在顶不住。
七、主要方法源代码
消除间接左递归:eliminateDLeftRecusive()
void eliminateDLeftRecusive(){
string flag_E = "";
vector<string> temp; //存放要补充 E'->ε产生式子 的 E
vector<pro>::iterator it = productions.begin();
while(it!=productions.end()){
flag_E=(*it).left;
vector<pro>::iterator it2 = it;
int flagdi=0;
//判断是否存在直接左递归
while(it2 !=productions.end() && (*it2).left == flag_E)
{
if((*it2).left == (*it2).right[0]) // E->Ea
{
flagdi=1;
it2++;
continue;
}
if(flagdi==1 && (*it2).left != (*it2).right[0]) //E->b
{
flagdi=2;
break;
}
it2++;
}
//消除直接左递归
if(flagdi==2)
{
temp.push_back(flag_E);
while(it!=productions.end() && (*it).left==flag_E)
{
string tmp = (*it).left+'\'';
if((*it).left == (*it).right[0]){ //E->Ea
// 变成 E'->aE'
(*it).left = tmp;
(*it).right.erase((*it).right.begin());
(*it).push(tmp);
}else{
//E->b 变成 E->bE'
(*it).push(tmp);
}
it++;
}
}else{
it++;
}
}
for(int i=0; i<temp.size(); i++){
string str = temp[i]+'\'';
pro p1(str);
p1.push("ε");
productions.push_back(p1);
}
}
计算FIRST集:calFIRST()
void calFIRST(){
bool is_change = true; // 标记每轮扫瞄准是否更新FIRST集合
while(is_change)
{
is_change = false;
for(int i=0; i<productions.size(); i++)
{
int k=0;
//定出fcollections[k].vn = productions[i].left 即为当前分析的非终结符
for(k=0; k<fcollections.size(); k++)
{
if(fcollections[k].vn == productions[i].left)
{
break;
}
}
bool have_e=false; //标记能否一直推出ε
for(int ri=0; ri<productions[i].right.size(); ri++){
// 遍历该候选式的右部
have_e=false;
//是非终结符 E->A类型 FIRST[E] += ( FIRST[A] - {ε} );
if(productions[i].right[ri][0] >= 'A' && productions[i].right[ri][0]<='Z'){
//定fcollections[h].vn = productions[i].right[ri] 即右部要分析的非终结符 A
int h=0;
for(;h<fcollections.size();h++){
if(fcollections[h].vn == productions[i].right[ri]){
break;
}
}
//判断FIRST[A]非空
if(!(fcollections[h].vfirst.empty())){
//判断FIRST[A]中是否有相对FIRST[E]的新元素
for(auto it : fcollections[h].vfirst){
if(it != "ε"){
//更新FIRST[E]集合
if(fcollections[k].vfirst.count(it) < 1){
is_change = true;
}
fcollections[k].insert1(it);
}
}
}
else{
//FIRST[A]为空
//跳过本轮
break;
}
if(fcollections[h].vfirst.count("ε")){
//ε 属于 FIRST[A] 继续遍历右部
have_e = true;
}else{
// 否则,跳出循环
break;
}
}
//是终结符 或 ε
else{
// E->a类型 FIRST[E] += {a};
if(fcollections[k].vfirst.count(productions[i].right[ri]) < 1){
is_change = true;
}
fcollections[k].insert1(productions[i].right[ri]); //更新FIRST集合
//终结符 跳出循环
break;
}
}
if(have_e){
//能一直推出ε
// FIRST[E] += {ε}
fcollections[k].insert1("ε");
}
}
}
}
计算FOLLOW集:calFOLLOW()
void calFOLLOW(){
bool is_change = true; // 标记每轮扫瞄中是否更新FOLLOW集合
while(is_change){
is_change = false;
for(int i=0; i<productions.size(); i++)
{
for(int j=0; j<productions[i].right.size(); j++){
//判断是否为非终结符
if(productions[i].right[j][0] >= 'A' && productions[i].right[j][0] <= 'Z')
{
//1.形式为 A->aF follow(A)加入到follow(F)
if(j+1 == productions[i].right.size()){
int k=0, m=0,fg=0;
//定出fcollections[k].vn=A
// fcollections[m].vn=F
for(int nn=0; nn<fcollections.size(); nn++)
{
if(fcollections[nn].vn == productions[i].left)
{
k=nn;
fg++;
}
if(fcollections[nn].vn == productions[i].right[j])
{
m=nn;
fg++;
}
if(fg==2){
break;
}
}
//判断FOLLOW[A]是否为空
if(!(fcollections[k].vfollow.empty())){
//判断FOLLOW[A]中是否有新元素
for(auto it : fcollections[k].vfollow){
if(fcollections[m].vfollow.count(it) < 1){
fcollections[m].insert2(it); //更新FOLLOW集合
is_change = true;
}
}
}
}
//2.形式为 A->aFB FIRST(B)-ε 加入到follow(F)
else if(productions[i].right[j+1][0] >= 'A' && productions[i].right[j+1][0] <= 'Z')
{
int k=0, m=0, fg=0;
//定出fcollections[k].vn=F
// fcollections[m].vn=B
for(int nn=0; nn<fcollections.size(); nn++)
{
if(fcollections[nn].vn == productions[i].right[j])
{
k=nn;
fg++;
}
if(fcollections[nn].vn == productions[i].right[j+1])
{
m=nn;
fg++;
}
if(fg==2){
break;
}
}
int flag_e=0;
for(auto it : fcollections[m].vfirst){
if(it == "ε"){
flag_e = 1;
}
if(it != "ε") //除去ε
{
if(fcollections[k].vfollow.count(it) < 1){
fcollections[k].insert2(it); //更新FOLLOW集合
is_change = true;
}
}
}
// 2.2 B->...->ε follow(A)加入到follow(F)
if(flag_e){
// fcollections[k].vn=F
// 定出fcollections[m].vn=A
for(m=0;m<fcollections.size();m++)
{
if(fcollections[m].vn == productions[i].left)
{
break;
}
}
//判断FOLLOW[A]是否为空
if(!(fcollections[m].vfollow.empty()))
{
//判断FOLLOW[A]中是否有新元素
for(auto it : fcollections[m].vfollow)
{
if(fcollections[k].vfollow.count(it) < 1)
{
fcollections[k].insert2(it); //更新FOLLOW集合
is_change = true;
}
}
}
}
}
//3.形式为 A->aFb {b}加入到follow(F)
else
{
int k=0;
//定出fcollections[k].vn=F
for(k=0; k<fcollections.size(); k++)
{
if(fcollections[k].vn == productions[i].right[j])
{
break;
}
}
//判断是否要更新follow集合
if(fcollections[k].vfollow.count(productions[i].right[j+1]) < 1){
fcollections[k].insert2(productions[i].right[j+1]); //更新FOLLOW集合
is_change = true;
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
创建语法分析表:createAnalysisTable()
void createAnalysisTable(){
for(int i=0; i<productions.size(); i++){
// cout<<"分析产生式(进行中。。。):";
productions[i].print();
// 对于一个产生式 A->ri
string A = productions[i].left;
int h=0, k=0;
//定位analysis_tables[h].vn=A;
//fcollections[k].vn = A;
for(;h<analysis_tables.size();h++){
if(analysis_tables[h].vn == A){
break;
}
}
for(;k<fcollections.size();k++){
if(fcollections[k].vn == A){
break;
}
}
if(productions[i].rfirst.count("ε")){
// 末尾可导出ε,求得FOLLOW[A]={c}, 则M[A,c]填入此产生式
for(auto jj : fcollections[k].vfollow){
string s1 = getpro(i);
analysis_tables[h].insert(jj, s1);
analysis_tables[h].atindex.insert(pair<string,int>(jj,productions[i].index));
}
}
for(auto t:productions[i].rfirst){
if(t!="ε"){
string s1 = getpro(i);
analysis_tables[h].insert(t, s1);
analysis_tables[h].atindex.insert(pair<string,int>(t,productions[i].index));
}
}
}
}
判断是否为LL1文法:isLL1()
bool isLL1(){
bool is_cross = false; //标记是否有集合相交
for(int i=0; i<productions.size(); i++){
string A = productions[i].left;
int index_e = -1; //记录FIRST[ri] = {ε}的候选式
for(int j=i;j<productions.size();j++){
if(productions[j].left != A){
continue;
}
if(productions[j].rfirst.count("ε")){
index_e = j;
break;
}
}
if(index_e != -1){
//有候选式为ε,要求其余候选式FIRST 交 FOLLOW[A] = 空
for(int k=0;k<productions.size();k++){
if(productions[k].left == A && k!=index_e){
//定fcollections[mm].vn = A
int mm=0;
for(;mm<fcollections.size();mm++){
if(fcollections[mm].vn == A){
break;
}
}
for(auto af:fcollections[mm].vfollow){
if(productions[k].rfirst.count(af)){
// 有交集
is_cross=true;
// 指出错误
string f1 = getpro(k);
cout<<f1<<"的产生式右部FIRST集合 ∩ FOLLOW["<<A<<"] = {"<<af<<"}"<<endl;
cout<<"ERROR: 交集非空"<<endl;
return (!is_cross);
}
}
}
}
}
for(int j=i+1; j<productions.size();j++){
if(productions[j].left != A || j==index_e){
continue;
}
//判断productions[i].vfirst和productions[j].vfirst的交集
for(auto it:productions[i].rfirst){
for(auto jt:productions[j].rfirst){
if(it == jt){
// 有交集
is_cross=true;
string f1 = getpro(i);
string f2 = getpro(j);
cout<<f1<<"的产生式右部FIRST集合 ∩"<<f2<<"的产生式右部FIRST集合 = {"<<it<<"}"<<endl;
cout<<"ERROR: 交集非空"<<endl;
return(!is_cross);
}
}
}
}
}
return (!is_cross);
}
附件
cfg1.txt
E::=E + T
E::=E - T
E::=T
T::=T * F
T::=T / F
T::=F
F::=( E )
F::=id
cfg2.txt
S::=( L )
S::=a
L::=L , S
L::=S
cfg3.txt
S::=A B
A::=D a
A::=ε
B::=c C
C::=a A D C
C::=ε
D::=b
D::=ε
源码
#include "iostream"
#include "string"
#include "stack"
#include "vector"
#include "map"
#include "set"
#include "iomanip"
using namespace std;
/***
* 全局变量定义
* 对象定义与方法声明
***/
set<string> VN; //非终结符集合
set<string> VT; //终结符集合
string istr; //输入的待分析的字串
string G_start; //文法开始符
// 一个产生式
class pro{
public:
string left; //产生式左部
vector<string> right; //产生式右部
set<string> rfirst; //产生式右部的first集合
int index; //产生式编号
pro(const string & str){
left=str;
right.clear();
rfirst.clear();
index=0;
}
void push(const string & str){
right.push_back(str);
}
void print(){
cout<<left<<"::=";
vector<string>::iterator it = right.begin();
for (;it!= right.end();it++ ){
cout<<(*it)<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
}
void insert(const string & str){
if(rfirst.count(str) < 1){
rfirst.insert(str);
}
}
};
// 一个非终结符的FIRST & FOLLOW集合
class f_vn{
public:
string vn; //非终结符
set<string> vfirst; //FIRST集合
set<string> vfollow; //FOLLOW集合
f_vn(const string & str){ // 构造函数
vn = str;
vfirst.clear();
vfollow.clear();
}
void insert1(string t){ // FIRST集合插入
if(vfirst.empty() == true || vfirst.count(t) < 1){
vfirst.insert(t);
}
}
void insert2(string t){ // FOLLOW集合插入
if(vfollow.empty() == true || vfollow.count(t) < 1){
vfollow.insert(t);
}
}
void print(){ // 输出FIRST、FOLLOW集合
if(vfirst.empty()){
cout<<"FIRST:NULL"<<endl;
}else{
cout<<"FIRST["<<vn<<"] = { ";
set<string>::iterator it1 = vfirst.begin();
cout<<(*it1);
it1++;
for(;it1!=vfirst.end();it1++){
cout<<", "<<(*it1);
}
cout<<" }\t\t\t";
}
if(vfollow.empty()){
cout<<"FOLLOW:NULL"<<endl;
}else{
cout<<"FOLLOW["<<vn<<"] = { ";
set<string>::iterator it2 = vfollow.begin();
cout<<(*it2);
it2++;
for(;it2!=vfollow.end();it2++){
cout<<", "<<(*it2);
}
cout<<"}"<<endl;
}
}
};
// 语法分析表的每一行 非终结符—— 对应终结符位置处填入的产生式
class analysis_table{
public:
string vn; // 非终结符
map<string, string> atlist; // <终结符,产生式>
map<string, int> atindex; // <终结符,产生式编号>
analysis_table(const string &str){
vn = str;
atlist.clear();
atindex.clear();
}
void initmap(){
string empty_str = " ";
for(auto i : VT){
atlist.insert(pair<string, string>(i, empty_str));
}
atlist.insert(pair<string, string>("#", empty_str)); // 补充#
}
void printrow(){ // 打印一行数据
cout<<setw(4)<<left<<vn;
cout<<"|";
map<string,string>::iterator it;
for(auto it:VT){
cout<<setw(15)<<left<<atlist.find(it)->second;
}
cout<<setw(15)<<left<<atlist.find("#")->second<<endl;
}
void insert(string vt, string p){ //产生式p放入M[vn, vt];
atlist.find(vt)->second = p;
}
};
vector<pro> productions; //产生式集合
vector<f_vn> fcollections; //非终结符的FIRST集合和FOLLOW集合
vector<analysis_table> analysis_tables; //预测分析表
stack<string> GAnalasis; //语法分析栈
//函数声明
void inputG(); // 文法输入处理函数
void eliminateILeftRecusive(); // 消除间接左递归
void eliminateDLeftRecusive(); // 消除直接左递归
void printProductions(); // 测试,打印存储的产生式集合
void printVNT(); // 测试,打印所有的非终结符,终结符
void calVN(); // 记录所有非终结符
void calVT(); // 记录所有终结符
void initFcollections(); // 初始化产生式集合(将所有非终结符加入进去)
void calFIRST(); // 计算FIRST集合
void calFOLLOW(); // 计算FOLLOW集合
void calRightFIRST(); // 计算每个候选式右部的FIRST集合
void printFirstFollow(); // 打印FIRST FOLLOW集合
void initAnalysisTable(); // 初始化预测分析表
void createAnalysisTable(); // 构建预测分析表
bool isVN(string str); // 判断是否为非终结符
string getpro(int j); // 得到productions[j]的产生式字符串
void printAnalysisTable(); // 打印预测分析表
bool isLL1(); // 判断是否为LL(1)文法
void judgeG(); // 评判该文法
void inputIstr(); // 输入待分析的字符串
string getStackStr(); // 获得语法分析栈中的所有内容
void analysisIstr(); // 语法分析输入的字符串
int main()
{
cout<<"Hello!"<<endl;
inputG(); //文法输入处理
eliminateILeftRecusive(); // 消除间接左递归
eliminateDLeftRecusive(); // 消除直接左递归
calVN(); // 记录所有非终结符
calVT(); // 记录所有终结符 包括ε
initFcollections(); // 初始化产生式集合(将所有非终结符加入进去)
calFIRST(); // 计算FIRST集合
calFOLLOW(); // 计算FOLLOW集合
calRightFIRST(); // 计算每个候选式右部的FIRST集合
printVNT(); // 测试,打印所有的非终结符,终结符
printProductions(); // 测试,打印存储的产生式集合
printFirstFollow(); // 打印FIRST FOLLOW集合
initAnalysisTable(); // 初始化预测分析表
createAnalysisTable(); // 构建预测分析表
printAnalysisTable(); // 打印预测分析表
judgeG(); // 评判该文法
void analysisIstr(); // 语法分析输入的字符串
return 0;
}
void inputG(){
string input_str;
int xixi=0;
while(getline(cin, input_str)){
if(!(input_str[0]>='A' && input_str[0]<='Z')){
break;
}
if(xixi==0){
//输入的第一个非终结符标记为文法的开始符
G_start = input_str[0];
xixi=1;
}
int i = 0;
string tmp1 = "";
while(input_str[i] != ':'){
tmp1 += input_str[i++];
}
i+=3;
pro pro1(tmp1);
// cout<<"input_str.length(): "<
while(true){
string tmp2 = "";
while(input_str[i] != ' '){
tmp2 += input_str[i];
i++;
if(i>=input_str.length()){
break;
}
}
pro1.push(tmp2);
if(i<input_str.size()){
i++;
}else{
break;
}
}
productions.push_back(pro1);
}
}
void eliminateILeftRecusive(){
int cnt=0;
bool flag1=true;
while(flag1){
flag1 = false;
for(int i=0;i<productions.size();i++){
if(!(productions[i].right[0] >= "A" && productions[i].right[0] <= "Z")){
//候选式首个为终结符,跳过
continue;
}
vector<string> circle; //记录存在循环的非终结符
circle.clear();
circle.push_back(productions[i].left);
circle.push_back(productions[i].right[0]);
for(int j=i+1; j<productions.size(); j++){
if(!(productions[j].right[0] >= "A" && productions[j].right[0] <= "Z")){
//候选式首个为终结符,跳过
continue;
}
if(productions[j].left == circle[circle.size()-1]){
circle.push_back(productions[j].right[0]);
if(circle[0] == circle[circle.size() - 1]){
// S-A-B-S循环闭合
break;
}
}
}
// cout<<"circle: ";
// for(auto cc:circle){
// cout<
// }
cout<<endl;
int flagi=1;
for(;flagi<circle.size(); flagi++){
if(circle[0] != circle[flagi]){
break;
}
}
if(flagi < circle.size() && circle[0] == circle[circle.size() - 1]){
// S-A-B-S循环闭合
flag1=true;
cnt++;
//打印该条信息
cout<<"存在间接左递归"<<endl;
for(auto t:circle){
cout<<t<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
vector<pro> tmp1; //暂存替换后的所有产生式
vector<vector<string>> rightB; //暂存要去替换的B的所有候选式
//消除左递归
for(int k=circle.size()-2; k>0; k--){
rightB.clear();
//先保存B的产生式
if(tmp1.size() == 0){
for(int l=0;l<productions.size();l++){
if(productions[l].left == circle[k]){
rightB.push_back(productions[l].right);
}
}
}
else{
for(int l=0; l<tmp1.size(); l++){
if(tmp1[l].left == circle[k]){
rightB.push_back(tmp1[l].right);
}
}
}
//保存的B->ab 替换为 A->Bc -- A->abc
for(int l=0; l<productions.size(); l++){
if(productions[l].left == circle[k-1]){
if(productions[l].right[0] == circle[k]){
for(int jj=0; jj<rightB.size(); jj++){
pro pp(circle[k-1]);
pp.right = rightB[jj];
for(int kk=1; kk<productions[l].right.size(); kk++){
pp.right.push_back(productions[l].right[kk]);
}
tmp1.push_back(pp);
}
}else{
// 不需要替换,直接存
pro pp(circle[k-1]);
pp.right = productions[l].right;
tmp1.push_back(pp);
}
}
}
}
vector<pro> tmp2; //保存新的产生式集合
for(int gg=0;gg<tmp1.size();gg++){
//存在循环的产生式集合 合并后的收进来
if(tmp1[gg].left == circle[0]){
pro pp(circle[0]);
pp.right = tmp1[gg].right;
tmp2.push_back(pp);
}
}
for(int gg=0; gg<productions.size(); gg++){
bool ff=true;
for(auto hh:circle){
if(productions[gg].left == hh){
ff=false;
break;
}
}
if(ff){
//原产生式集合中不存在循环的收进来
pro pp(productions[gg].left);
pp.right = productions[gg].right;
tmp2.push_back(pp);
}
}
productions.clear();
for(auto t:tmp2){
productions.push_back(t);
}
break;
}
else{
//不存在间接左递归
flag1=false;
}
}
}
if(cnt > 0){
cout<<"消除间接左递归完成:"<<endl;
printProductions();
}
}
void eliminateDLeftRecusive(){
string flag_E = "";
vector<string> temp; //存放要补充 E'->ε产生式子 的 E
vector<pro>::iterator it = productions.begin();
while(it!=productions.end()){
flag_E=(*it).left;
vector<pro>::iterator it2 = it;
int flagdi=0;
//判断是否存在直接左递归
while(it2 !=productions.end() && (*it2).left == flag_E)
{
if((*it2).left == (*it2).right[0]) // E->Ea
{
flagdi=1;
it2++;
continue;
}
if(flagdi==1 && (*it2).left != (*it2).right[0]) //E->b
{
flagdi=2;
break;
}
it2++;
}
//消除直接左递归
if(flagdi==2)
{
temp.push_back(flag_E);
while(it!=productions.end() && (*it).left==flag_E)
{
string tmp = (*it).left+'\'';
if((*it).left == (*it).right[0]){ //E->Ea
// 变成 E'->aE'
(*it).left = tmp;
(*it).right.erase((*it).right.begin());
(*it).push(tmp);
}else{
//E->b 变成 E->bE'
(*it).push(tmp);
}
it++;
}
}else{
it++;
}
}
for(int i=0; i<temp.size(); i++){
string str = temp[i]+'\'';
pro p1(str);
p1.push("ε");
productions.push_back(p1);
}
}
void printProductions(){
//产生式编号
int j=1;
for(int i=0; i<productions.size(); i++){
productions[i].print();
productions[i].index = j;
j++;
}
}
void calVN(){
vector<pro>::iterator it = productions.begin();
for(;it!=productions.end();it++){
if(VN.count((*it).left) <= 1){
VN.insert((*it).left);
}
for(int i=0; i<(*it).right.size(); i++){
if((*it).right[i][0] >= 'A' && (*it).right[i][0] <= 'Z'){
if(VN.count((*it).right[i]) < 1){
VN.insert((*it).right[i]);
}
}
}
}
}
void calVT(){
vector<pro>::iterator it = productions.begin();
for(;it!=productions.end();it++){
for(int i=0; i<(*it).right.size(); i++){
if(VN.count((*it).right[i]) < 1 && VT.count((*it).right[i]) < 1){
VT.insert((*it).right[i]);
}
}
}
}
void printVNT(){
cout<<"非终结符:";
for(auto it : VN){
cout<<it<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
cout<<"终结符:";
for(auto it: VT){
cout<<it<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
}
void initFcollections(){
for(auto it : VN){
f_vn f1(it);
if(it==G_start){
//文法开始符 #插入FOLLOW集
f1.insert2("#");
}
fcollections.push_back(f1);
}
}
void calFIRST(){
bool is_change = true; // 标记每轮扫瞄准是否更新FIRST集合
while(is_change)
{
is_change = false;
for(int i=0; i<productions.size(); i++)
{
int k=0;
//定出fcollections[k].vn = productions[i].left 即为当前分析的非终结符
for(k=0; k<fcollections.size(); k++)
{
if(fcollections[k].vn == productions[i].left)
{
break;
}
}
bool have_e=false; //标记能否一直推出ε
for(int ri=0; ri<productions[i].right.size(); ri++){
// 遍历该候选式的右部
have_e=false;
//是非终结符 E->A类型 FIRST[E] += ( FIRST[A] - {ε} );
if(productions[i].right[ri][0] >= 'A' && productions[i].right[ri][0]<='Z'){
//定fcollections[h].vn = productions[i].right[ri] 即右部要分析的非终结符 A
int h=0;
for(;h<fcollections.size();h++){
if(fcollections[h].vn == productions[i].right[ri]){
break;
}
}
//判断FIRST[A]非空
if(!(fcollections[h].vfirst.empty())){
//判断FIRST[A]中是否有相对FIRST[E]的新元素
for(auto it : fcollections[h].vfirst){
if(it != "ε"){
//更新FIRST[E]集合
if(fcollections[k].vfirst.count(it) < 1){
is_change = true;
}
fcollections[k].insert1(it);
}
}
}
else{
//FIRST[A]为空
//跳过本轮
break;
}
if(fcollections[h].vfirst.count("ε")){
//ε 属于 FIRST[A] 继续遍历右部
have_e = true;
}else{
// 否则,跳出循环
break;
}
}
//是终结符 或 ε
else{
// E->a类型 FIRST[E] += {a};
if(fcollections[k].vfirst.count(productions[i].right[ri]) < 1){
is_change = true;
}
fcollections[k].insert1(productions[i].right[ri]); //更新FIRST集合
//终结符 跳出循环
break;
}
}
if(have_e){
//能一直推出ε
// FIRST[E] += {ε}
fcollections[k].insert1("ε");
}
}
}
}
void calFOLLOW(){
bool is_change = true; // 标记每轮扫瞄中是否更新FOLLOW集合
while(is_change){
is_change = false;
for(int i=0; i<productions.size(); i++)
{
for(int j=0; j<productions[i].right.size(); j++){
//判断是否为非终结符
if(productions[i].right[j][0] >= 'A' && productions[i].right[j][0] <= 'Z')
{
//1.形式为 A->aF follow(A)加入到follow(F)
if(j+1 == productions[i].right.size()){
int k=0, m=0,fg=0;
//定出fcollections[k].vn=A
// fcollections[m].vn=F
for(int nn=0; nn<fcollections.size(); nn++)
{
if(fcollections[nn].vn == productions[i].left)
{
k=nn;
fg++;
}
if(fcollections[nn].vn == productions[i].right[j])
{
m=nn;
fg++;
}
if(fg==2){
break;
}
}
//判断FOLLOW[A]是否为空
if(!(fcollections[k].vfollow.empty())){
//判断FOLLOW[A]中是否有新元素
for(auto it : fcollections[k].vfollow){
if(fcollections[m].vfollow.count(it) < 1){
fcollections[m].insert2(it); //更新FOLLOW集合
is_change = true;
}
}
}
}
//2.形式为 A->aFB FIRST(B)-ε 加入到follow(F)
else if(productions[i].right[j+1][0] >= 'A' && productions[i].right[j+1][0] <= 'Z')
{
int k=0, m=0, fg=0;
//定出fcollections[k].vn=F
// fcollections[m].vn=B
for(int nn=0; nn<fcollections.size(); nn++)
{
if(fcollections[nn].vn == productions[i].right[j])
{
k=nn;
fg++;
}
if(fcollections[nn].vn == productions[i].right[j+1])
{
m=nn;
fg++;
}
if(fg==2){
break;
}
}
int flag_e=0;
for(auto it : fcollections[m].vfirst){
if(it == "ε"){
flag_e = 1;
}
if(it != "ε") //除去ε
{
if(fcollections[k].vfollow.count(it) < 1){
fcollections[k].insert2(it); //更新FOLLOW集合
is_change = true;
}
}
}
// 2.2 B->...->ε follow(A)加入到follow(F)
if(flag_e){
// fcollections[k].vn=F
// 定出fcollections[m].vn=A
for(m=0;m<fcollections.size();m++)
{
if(fcollections[m].vn == productions[i].left)
{
break;
}
}
//判断FOLLOW[A]是否为空
if(!(fcollections[m].vfollow.empty()))
{
//判断FOLLOW[A]中是否有新元素
for(auto it : fcollections[m].vfollow)
{
if(fcollections[k].vfollow.count(it) < 1)
{
fcollections[k].insert2(it); //更新FOLLOW集合
is_change = true;
}
}
}
}
}
//3.形式为 A->aFb {b}加入到follow(F)
else
{
int k=0;
//定出fcollections[k].vn=F
for(k=0; k<fcollections.size(); k++)
{
if(fcollections[k].vn == productions[i].right[j])
{
break;
}
}
//判断是否要更新follow集合
if(fcollections[k].vfollow.count(productions[i].right[j+1]) < 1){
fcollections[k].insert2(productions[i].right[j+1]); //更新FOLLOW集合
is_change = true;
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
void calRightFIRST(){
for(int i=0; i<productions.size(); i++){
//遍历产生式的右部
bool have_e=false;
for(auto t:productions[i].right){
have_e=false;
if(isVN(t)){
//是非终结符
//定位fcollections[j].vn = t
int j=0;
for(;j<fcollections.size();j++){
if(fcollections[j].vn == t){
break;
}
}
for(auto u:fcollections[j].vfirst){
if(u=="ε"){
have_e=true;
}else{
productions[i].insert(u);
}
}
if(have_e == false){
break;
}
}else{
//是终结符
productions[i].insert(t);
break;
}
}
if(have_e){
productions[i].insert("ε");
}
}
}
void printFirstFollow(){
for(int i=0; i<fcollections.size(); i++){
fcollections[i].print();
}
}
void initAnalysisTable(){
for(auto it : VN){
analysis_table at(it);
at.initmap();
analysis_tables.push_back(at);
}
}
bool isVN(string str){
return (VN.count(str) > 0);
}
string getpro(int j){
string res="";
res += productions[j].left;
res += "->";
for(auto it:productions[j].right){
res += it;
res += " ";
}
return res;
}
void createAnalysisTable(){
for(int i=0; i<productions.size(); i++){
// cout<<"分析产生式(进行中。。。):";
productions[i].print();
// 对于一个产生式 A->ri
string A = productions[i].left;
int h=0, k=0;
//定位analysis_tables[h].vn=A;
//fcollections[k].vn = A;
for(;h<analysis_tables.size();h++){
if(analysis_tables[h].vn == A){
break;
}
}
for(;k<fcollections.size();k++){
if(fcollections[k].vn == A){
break;
}
}
if(productions[i].rfirst.count("ε")){
// 末尾可导出ε,求得FOLLOW[A]={c}, 则M[A,c]填入此产生式
for(auto jj : fcollections[k].vfollow){
string s1 = getpro(i);
analysis_tables[h].insert(jj, s1);
analysis_tables[h].atindex.insert(pair<string,int>(jj,productions[i].index));
}
}
for(auto t:productions[i].rfirst){
if(t!="ε"){
string s1 = getpro(i);
analysis_tables[h].insert(t, s1);
analysis_tables[h].atindex.insert(pair<string,int>(t,productions[i].index));
}
}
}
}
void printAnalysisTable(){
//打印表头
cout<<"语法分析表如下:"<<endl;
cout<<setw(4)<<left<<" ";
cout<<"|";
for(auto it:VT){
if(it != "ε"){
cout<<setw(15)<<left<<it;
}
}
cout<<setw(15)<<left<<"#"<<endl;
for(int i=0;i<VT.size()*5;i++){
cout<<"— — ";
}
cout<<endl;
for(int i=0; i<analysis_tables.size(); i++){
analysis_tables[i].printrow();
}
for(int i=0;i<VT.size()*5;i++){
cout<<"— — ";
}
cout<<endl;
}
bool isLL1(){
bool is_cross = false; //标记是否有集合相交
for(int i=0; i<productions.size(); i++){
string A = productions[i].left;
int index_e = -1; //记录FIRST[ri] = {ε}的候选式
for(int j=i;j<productions.size();j++){
if(productions[j].left != A){
continue;
}
if(productions[j].rfirst.count("ε")){
index_e = j;
break;
}
}
if(index_e != -1){
//有候选式为ε,要求其余候选式FIRST 交 FOLLOW[A] = 空
for(int k=0;k<productions.size();k++){
if(productions[k].left == A && k!=index_e){
//定fcollections[mm].vn = A
int mm=0;
for(;mm<fcollections.size();mm++){
if(fcollections[mm].vn == A){
break;
}
}
for(auto af:fcollections[mm].vfollow){
if(productions[k].rfirst.count(af)){
// 有交集
is_cross=true;
// 指出错误
string f1 = getpro(k);
cout<<f1<<"的产生式右部FIRST集合 ∩ FOLLOW["<<A<<"] = {"<<af<<"}"<<endl;
cout<<"ERROR: 交集非空"<<endl;
return (!is_cross);
}
}
}
}
}
for(int j=i+1; j<productions.size();j++){
if(productions[j].left != A || j==index_e){
continue;
}
//判断productions[i].vfirst和productions[j].vfirst的交集
for(auto it:productions[i].rfirst){
for(auto jt:productions[j].rfirst){
if(it == jt){
// 有交集
is_cross=true;
string f1 = getpro(i);
string f2 = getpro(j);
cout<<f1<<"的产生式右部FIRST集合 ∩"<<f2<<"的产生式右部FIRST集合 = {"<<it<<"}"<<endl;
cout<<"ERROR: 交集非空"<<endl;
return(!is_cross);
}
}
}
}
}
return (!is_cross);
}
void judgeG(){
if(isLL1()){
cout<<"该文法是LL(1)文法。"<<endl;
analysisIstr();
}
else{
cout<<"该文法不是LL(1)文法!!!"<<endl;
}
}
void inputIstr(){
cout<<"请输入待分析的字串(以#结尾): ";
cin>>istr;
cout<<"开始分析……"<<endl;
}
string getStackStr(){
stack<string> s1;
vector<string> ss1;
string res="";
s1 = GAnalasis;
while(!s1.empty()){
ss1.push_back(s1.top());
s1.pop();
}
for(int i=ss1.size()-1; i>=0; i--){
res += ss1[i];
}
return res;
}
void analysisIstr(){
inputIstr();
//压入终止符号和文法的开始符合
GAnalasis.push("#");
GAnalasis.push(G_start);
int i=0, steps=0;
cout<<istr<<" 的分析过程如下:"<<endl;
cout<<setw(16)<<left<<"过程计数";
cout<<setw(20)<<left<<"语法分析栈";
cout<<setw(30)<<left<<"剩余未匹配的字串"<<endl;
for(int ppp=0; ppp<20;ppp++)cout<<"— — ";
cout<<endl;
while(i<istr.length()){
steps++;
cout<<setw(16)<<left<<steps;
string tmp = getStackStr();
cout<<setw(20)<<left<<tmp;
string tmp2="";
for(int j=i;j<istr.length();j++){
tmp2+=istr[j];
}
cout<<setw(30)<<left<<tmp2<<endl;
char cur_c = istr[i]; //当前指示字符
//取栈顶元素
if(GAnalasis.empty()){
cout<<"栈为空!!!"<<endl;
return;
}
string top_str=GAnalasis.top(); //栈顶符号
if(top_str == "id"){
//id类型单独判断
if((cur_c >= 'a' && cur_c <= 'z') || (cur_c >= '0' && cur_c <= '9')){
//匹配成功
i++;
//栈顶元素出栈
if(GAnalasis.empty()){
cout<<"ERROR:栈为空,出栈操作失败"<<endl;
return;
}
GAnalasis.pop();
cout<<setw(12)<<left<<"ding~";
cout<<"字符"<<cur_c<<"匹配成功"<<endl;
}
}else if(isVN(top_str)){
//非终结符
//查预测分析表
string tp="";
if(VT.count("id") > 0){
if((cur_c >= 'a' && cur_c <= 'z') || (cur_c >= '0' && cur_c <= '9')){
tp+="id";
}else{
tp+=cur_c;
}
}
else{
tp+=cur_c;
}
//定analysis_tables[h].vn == top_str
int h=0;
for(;h<analysis_tables.size();h++){
if(analysis_tables[h].vn == top_str){
break;
}
}
if(analysis_tables[h].atlist.find(tp)->second == " "){
//分析表对应位置为空;
//ERROR
cout<<"ERROR!"<<endl;
cout<<"匹配失败,该串不是给定文法的句子!"<<endl;
return;
}else{
//栈顶元素出栈
if(GAnalasis.empty()){
cout<<"ERROR:栈为空,出栈操作失败"<<endl;
return;
}
GAnalasis.pop();
//锁定对应产生式的序号
if(analysis_tables[h].atindex.count(tp) < 1){
//对应语法分析表处为空
cout<<"ERROR:对应语法分析表处为空,分析失败!!!"<<endl;
return;
}
int k = analysis_tables[h].atindex.find(tp)->second;
int pp=0;
//定productions[pp].index == k
//匹配对应的文法产生式
for(;pp<productions.size();pp++){
if(productions[pp].index == k){
break;
}
}
if(productions[pp].right[0] == "ε"){
//推出ε产生式,直接过,不用压栈
productions[pp].print();
}else{
for(int l=productions[pp].right.size()-1; l>=0 ; l--){
GAnalasis.push(productions[pp].right[l]);
}
productions[pp].print();
}
}
}else{
//终结符
if(cur_c == top_str[0]){
//匹配成功
i++;
//栈顶元素出栈
if(GAnalasis.empty()){
cout<<"ERROR:栈为空,出栈操作失败"<<endl;
return;
}
GAnalasis.pop();
cout<<setw(12)<<left<<"ding~";
cout<<"字符"<<cur_c<<"匹配成功"<<endl;
}else{
//两个终结符不相同 报错
cout<<"ERROR:匹配失败"<<endl;
return;
}
}
}
cout<<istr<<" 是给定文法的句子!!!"<<endl;
}