NNDL 作业5:卷积
目录
作业一
作业二
一、概念
二、探究不同卷积核的作用
三、编程实现
总结
作业一
编程实现
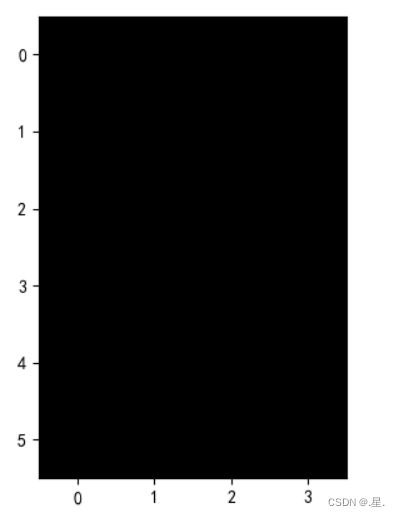
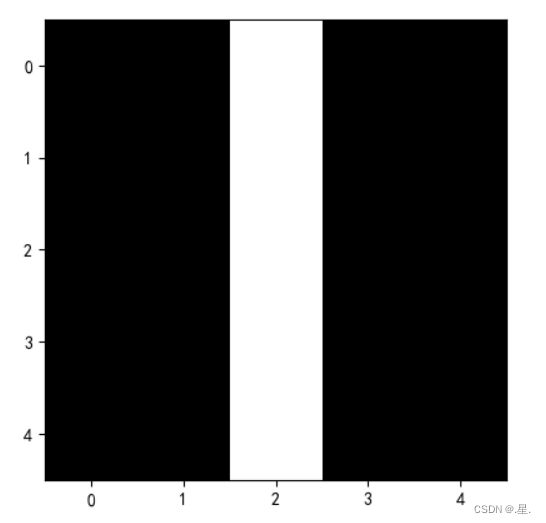
1. 图1使用卷积核![]() ,输出特征图
,输出特征图
import torch
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import torch.nn.functional as F
import numpy as np
#生成图片
def create_pic():
picture = torch.Tensor([[0,0,0,255,255,255],
[0,0,0,255,255,255],
[0,0,0,255,255,255],
[0,0,0,255,255,255],
[0,0,0,255,255,255]])
return picture
#确定卷积网络
class MyNet(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self,kernel,kshape):
super(MyNet, self).__init__()
kernel = torch.reshape(kernel,kshape)
self.weight = torch.nn.Parameter(data=kernel, requires_grad=False)
def forward(self, picture):
picture = F.conv2d(picture,self.weight,stride=1,padding=0)
return picture
#确定卷积层
kernel = torch.tensor([-1.0,1.0])
#更改卷积层的形状适应卷积函数
kshape = (1,1,1,2)
#生成模型
model = MyNet(kernel=kernel,kshape=kshape)
#生成图片
picture = create_pic()
#更改图片的形状适应卷积层
picture = torch.reshape(picture,(1,1,5,6))
output = model(picture)
output = torch.reshape(output,(5,5))
plt.imshow(output,cmap='gray')
plt.show()
运行结果:
2. 图1使用卷积核![]() ,输出特征图
,输出特征图
import torch
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import torch.nn.functional as F
import numpy as np
#生成图片
def create_pic():
picture = torch.Tensor([[0,0,0,255,255,255],
[0,0,0,255,255,255],
[0,0,0,255,255,255],
[0,0,0,255,255,255],
[0,0,0,255,255,255]])
return picture
#确定卷积网络
class MyNet(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self,kernel,kshape):
super(MyNet, self).__init__()
kernel = torch.reshape(kernel,kshape)
self.weight = torch.nn.Parameter(data=kernel, requires_grad=False)
def forward(self, picture):
picture = F.conv2d(picture,self.weight,stride=1,padding=0)
return picture
#确定卷积层
kernel = torch.tensor([-1.0,1.0])
#更改卷积和的形状为转置
kshape = (1,1,2,1)
model = MyNet(kernel=kernel,kshape=kshape)
picture = create_pic()
picture = torch.reshape(picture,(1,1,5,6))
output = model(picture)
output = torch.reshape(output,(6,4))
plt.imshow(output,cmap='gray')
plt.show()
运行结果:
3. 图2使用卷积核![]() ,输出特征图
,输出特征图
import torch
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import torch.nn.functional as F
import numpy as np
#生成图像
def create_pic():
picture = torch.Tensor([[0,0,0,255,255,255],
[0,0,0,255,255,255],
[0,0,0,255,255,255],
[255,255,255,0,0,0],
[255,255,255,0,0,0],
[255,255,255,0,0,0]])
return picture
#确定卷积核
kernel = torch.tensor([-1.0,1.0])
kshape = (1,1,1,2)
#生成模型
model = MyNet(kernel=kernel,kshape=kshape)
picture = create_pic()
picture = torch.reshape(picture,(1,1,6,6))
print(picture)
output = model(picture)
output = torch.reshape(output,(6,5))
print(output)
plt.imshow(output,cmap='gray')
plt.show()
运行结果:
4. 图2使用卷积核![]() ,输出特征图
,输出特征图
import torch
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import torch.nn.functional as F
import numpy as np
#生成图像
def create_pic():
picture = torch.Tensor([[0,0,0,255,255,255],
[0,0,0,255,255,255],
[0,0,0,255,255,255],
[255,255,255,0,0,0],
[255,255,255,0,0,0],
[255,255,255,0,0,0]])
return picture
#确定卷积核
kernel = torch.tensor([-1.0,1.0])
kshape = (1,1,2,1)
model = MyNet(kernel=kernel,kshape=kshape)
picture = create_pic()
picture = torch.reshape(picture,(1,1,6,6))
print(picture)
output = model(picture)
output = torch.reshape(output,(5,6))
print(output)
plt.imshow(output,cmap='gray')
plt.show()
运行结果:
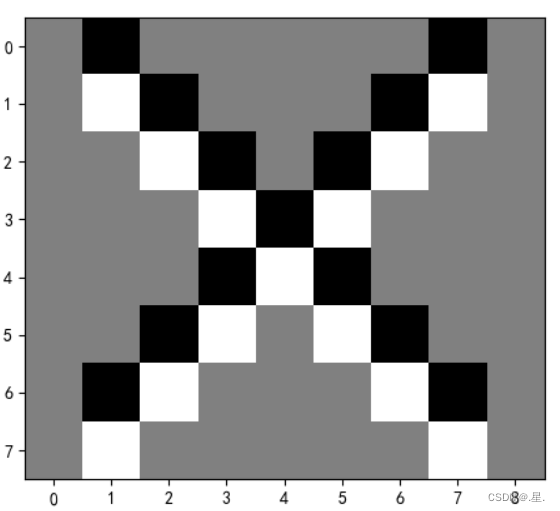
5. 图3使用卷积核![]() ,
,![]() ,
,![]() ,输出特征图
,输出特征图
![]()
import torch
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import torch.nn.functional as F
import numpy as np
#生成图像
def create_pic():
picture = torch.Tensor(
[[255,255,255,255,255,255,255,255,255],
[255,0 ,255,255,255,255,255,0 ,255],
[255,255,0 ,255,255,255,0 ,255,255],
[255,255,255,0 ,255,0 ,255,255,255],
[255,255,255,255,0 ,255,255,255,255],
[255,255,255,0 ,255,0 ,255,255,255],
[255,255,0 ,255,255,255,0 ,255,255],
[255,0 ,255,255,255,255,255,0 ,255],
[255,255,255,255,255,255,255,255,255],])
return picture
#生成卷积核
kernel = torch.tensor([-1.0,1.0])
#更改卷积核的形状适应卷积函数
kshape = (1,1,1,2)
model = MyNet(kernel=kernel,kshape=kshape)
picture = create_pic()
picture = torch.reshape(picture,(1,1,9,9))
print(picture)
output = model(picture)
output = torch.reshape(output,(9,8))
print(output)
plt.imshow(output,cmap='gray')
plt.show()
运行结果:
![]()
import torch
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import torch.nn.functional as F
import numpy as np
#生成图像
def create_pic():
picture = torch.Tensor(
[[255,255,255,255,255,255,255,255,255],
[255,0 ,255,255,255,255,255,0 ,255],
[255,255,0 ,255,255,255,0 ,255,255],
[255,255,255,0 ,255,0 ,255,255,255],
[255,255,255,255,0 ,255,255,255,255],
[255,255,255,0 ,255,0 ,255,255,255],
[255,255,0 ,255,255,255,0 ,255,255],
[255,0 ,255,255,255,255,255,0 ,255],
[255,255,255,255,255,255,255,255,255],])
return picture
#生成卷积核
kernel = torch.tensor([-1.0,1.0])
kshape = (1,1,2,1)
model = MyNet(kernel=kernel,kshape=kshape)
picture = create_pic()
picture = torch.reshape(picture,(1,1,9,9))
print(picture)
output = model(picture)
output = torch.reshape(output,(8,9))
print(output)
plt.imshow(output,cmap='gray')
plt.show()
运行结果:
![]()
import torch
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import torch.nn.functional as F
import numpy as np
#生成图像
def create_pic():
picture = torch.Tensor(
[[255,255,255,255,255,255,255,255,255],
[255,0 ,255,255,255,255,255,0 ,255],
[255,255,0 ,255,255,255,0 ,255,255],
[255,255,255,0 ,255,0 ,255,255,255],
[255,255,255,255,0 ,255,255,255,255],
[255,255,255,0 ,255,0 ,255,255,255],
[255,255,0 ,255,255,255,0 ,255,255],
[255,0 ,255,255,255,255,255,0 ,255],
[255,255,255,255,255,255,255,255,255],])
return picture
#生成卷积核
import torch
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import torch.nn.functional as F
import numpy as np
#生成图像
def create_pic():
picture = torch.Tensor(
[[0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0],
[0,255 ,0,0,0,0,0,255 ,0],
[0,0,255 ,0,0,0,255 ,0,0],
[0,0,0,255 ,0,255 ,0,0,0],
[0,0,0,0,255 ,0,0,0,0],
[0,0,0,255 ,0,255 ,0,0,0],
[0,0,255 ,0,0,0,255 ,0,0],
[0,255 ,0,0,0,0,0,255 ,0],
[0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0],])
return picture
#生成卷积核
#确定卷积核
kernel = torch.tensor([[1.0,-1.0],
[-1.0,1.0]])
#更改卷积核的大小适配卷积函数
kshape = (1,1,2,2)
#生成网络模型
model = MyNet(kernel=kernel,kshape=kshape)
picture = create_pic()
picture = torch.reshape(picture,(1,1,9,9))
print(picture)
output = model(picture)
output = torch.reshape(output,(8,8))
print(output)
plt.imshow(output,cmap='gray')
plt.show()
运行结果:
作业二
一、概念
用自己的语言描述“卷积、卷积核、特征图、特征选择、步长、填充、感受野”。
卷积:卷积是一种运算,类似于乘法,是原像素与卷积核的相乘再相加
卷积核:在由原像素变为新像素时,需要与一个定义的权重相乘再相加,这个权重函数就是卷积核
特征图:图像经过卷积操作后的内容就是特征图
特征选择:特征选择指从原始特征中挑选出某些对算法学习最有利特征。
步长:每进行一次卷积操作卷积核需要横向或纵向移动的长度
填充:在进行卷积操作时,输入图像的边缘处不会位于卷积核的中心,从而会丢失部分信息,所以在矩阵的边界上填充一些值增加矩阵的大小,解决这个问题
感受野:指特征图上的一个点对应的卷积前输入图上的区域。
二、探究不同卷积核的作用
1.锐化
内核
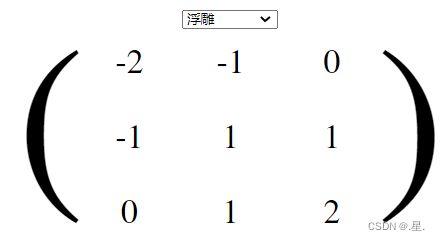
2.浮雕
内核
3. 模糊
内核
4.边缘检测
内核
三、编程实现
原图
1.实现灰度图的边缘检测、锐化、模糊。
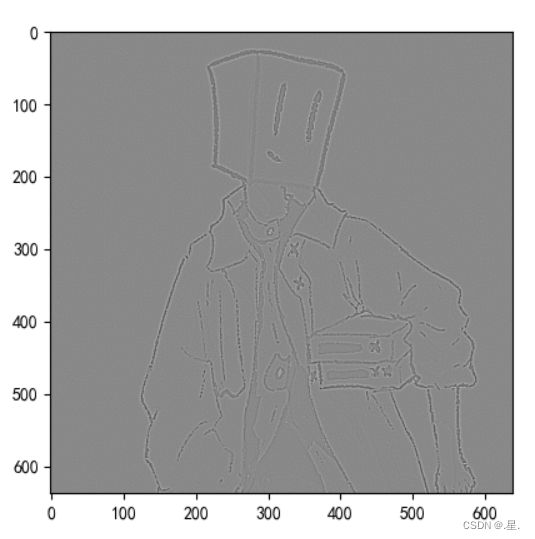
边缘检测
import numpy as np
import torch
from torch import nn
from torch.autograd import Variable
from PIL import Image
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei'] # 用来正常显示中文标签
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False # 用来正常显示负号 #有中文出现的情况,需要u'内容
file_path = 'touxiang.jpg'
im = Image.open(file_path).convert('L') # 读入一张灰度图的图片
im = np.array(im, dtype='float32') # 将其转换为一个矩阵
print(im.shape[0], im.shape[1])
plt.imshow(im.astype('uint8'), cmap='gray') # 可视化图片
plt.title('原图')
plt.show()
im = torch.from_numpy(im.reshape((1, 1, im.shape[0], im.shape[1])))
conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 1, 3, bias=False) # 定义卷积
sobel_kernel = np.array([[-1, -1, -1],
[-1, 8, -1],
[-1, -1, -1]], dtype='float32') # 定义轮廓检测算子
sobel_kernel = sobel_kernel.reshape((1, 1, 3, 3)) # 适配卷积的输入输出
conv1.weight.data = torch.from_numpy(sobel_kernel) # 给卷积的 kernel 赋值
edge1 = conv1(Variable(im)) # 作用在图片上
x = edge1.data.squeeze().numpy()
print(x.shape) # 输出大小
plt.imshow(x, cmap='gray')
plt.show()锐化
import numpy as np
import torch
from torch import nn
from torch.autograd import Variable
from PIL import Image
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei'] # 用来正常显示中文标签
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False # 用来正常显示负号 #有中文出现的情况,需要u'内容
file_path = 'touxiang.jpg'
im = Image.open(file_path).convert('L') # 读入一张灰度图的图片
im = np.array(im, dtype='float32') # 将其转换为一个矩阵
print(im.shape[0], im.shape[1])
plt.imshow(im.astype('uint8'), cmap='gray') # 可视化图片
plt.title('原图')
plt.show()
im = torch.from_numpy(im.reshape((1, 1, im.shape[0], im.shape[1])))
conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 1, 3, bias=False) # 定义卷积
sobel_kernel = np.array([[0, -1, 0],
[-1, 5, -1],
[0, -1, 0]], dtype='float32') # 定义轮廓检测算子
sobel_kernel = sobel_kernel.reshape((1, 1, 3, 3)) # 适配卷积的输入输出
conv1.weight.data = torch.from_numpy(sobel_kernel) # 给卷积的 kernel 赋值
edge1 = conv1(Variable(im)) # 作用在图片上
x = edge1.data.squeeze().numpy()
print(x.shape) # 输出大小
plt.imshow(x, cmap='gray')
plt.show()模糊
import numpy as np
import torch
from torch import nn
from torch.autograd import Variable
from PIL import Image
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei'] # 用来正常显示中文标签
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False # 用来正常显示负号 #有中文出现的情况,需要u'内容
file_path = 'touxiang.jpg'
im = Image.open(file_path).convert('L') # 读入一张灰度图的图片
im = np.array(im, dtype='float32') # 将其转换为一个矩阵
print(im.shape[0], im.shape[1])
plt.imshow(im.astype('uint8'), cmap='gray') # 可视化图片
plt.title('原图')
plt.show()
im = torch.from_numpy(im.reshape((1, 1, im.shape[0], im.shape[1])))
conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 1, 3, bias=False) # 定义卷积
sobel_kernel = np.array([[0.0625, 0.125, 0.0625],
[0.125, 0.25, 0.125],
[0.0625, 0.125, 0.0625]], dtype='float32') # 定义轮廓检测算子
sobel_kernel = sobel_kernel.reshape((1, 1, 3, 3)) # 适配卷积的输入输出
conv1.weight.data = torch.from_numpy(sobel_kernel) # 给卷积的 kernel 赋值
edge1 = conv1(Variable(im)) # 作用在图片上
x = edge1.data.squeeze().numpy()
print(x.shape) # 输出大小
plt.imshow(x, cmap='gray')
plt.show()2.调整卷积核参数,测试并总结
调整卷积核参数,设置步长为2
调整卷积核参数,设置步长为5
可以发现,步长越大,图像越模糊
3.使用不同尺寸图片,测试并总结
上一个图片大小为640*640,这次用一个1920*1080大小的图片
可以看出分辨率高的图片特征提取后越清晰
总结
本次实验进行了卷积和图像的特征提取,对于特征提取的原理,我感觉特征提取的卷积核起了很重要的作用。每一个特征提取的卷积核就像激活函数一样,把原来的图像的每个像素点激活为你想要的那个特征的像素点,从而做到提取特征。
参考
NNDL 作业5:卷积
Image Kernels explained visually (setosa.io)
【2021-2022 春学期】人工智能-作业4:CNN - 卷积_HBU_David的博客-CSDN博客