Vue学习笔记(四)基于Vue2的学生信息增删查案例 | Vuex组件简介、工作原理 | Vuex的三层结构——store负责响应组件、mutations负责操作数据、state负责存储数据
文章目录
- 一、参考资料
- 二、运行环境
- 三、Vuex@3插件
-
- 3.1 状态管理模式
- 3.2 Vuex 核心概念和API
-
- 3.2.1 [state](https://v3.vuex.vuejs.org/zh/guide/state.html#state)
- 3.2.3 [actions](https://v3.vuex.vuejs.org/zh/guide/actions.html#action)
- 3.2.4 [mutations](https://v3.vuex.vuejs.org/zh/guide/mutations.html#mutation)
- 3.2.5 [getters](https://v3.vuex.vuejs.org/zh/guide/getters.html#getter)
- 3.3 Vuex 模块化开发
- 3.4 Vuex 简化的Map四件套
-
- 3.4.1 mapState
- 3.4.2 mapGetter
- 3.4.3 mapMutations
- 3.4.4 mapActions
- 3.4.5 总结
- 四、基于Vue2的学生信息管理案例
-
- 4.1 全局事件总线方法代码实现
-
- 4.1.1 Main.js
- 4.1.2 App.vue
- 4.1.3 Student.vue
- 4.1.4 Search.vue
- 4.2 Vuex 方式代码实现
-
- 4.2.1 main.js
- 4.2.2 store/index.js
- 4.2.3 store/student.js
- 4.2.4 store/search.js
- 4.2.5 App.vue
- 4.2.6 Student.vue
- 4.2.7 Search.vue
一、参考资料
视频资料
二、运行环境
- Windows11
- Visual Studio Code v2022
- Node.js v16.5.01
- Vue/cli v5.0.6
- Bootstrap 5.1.3
三、Vuex@3插件
注意:这里的Vuex知识是基于Vuex版本3的。
Vuex 是一个专为 Vue.js 应用程序开发的状态管理模式。对 vue 应用中多个组件的共享状态进行集中式的管理(读/写),也是一种组件间通信的方式,且适用于任意组件间通信。
Vuex插件的GitHub地址:点击查看
适用场景:
- 多个Vue组件依赖于同一状态
- 来自不同Vue组件的行为需要变更同一状态
3.1 状态管理模式
Vue官方提供的案例:计数
new Vue({
// state 驱动应用的数据源
data () {
return {
count: 0
}
},
// view 以声明方式将 state 映射到视图
template: `
{{ count }}
`,
// actions 响应在 view 上的用户输入导致的状态变化
methods: {
increment () {
this.count++
}
}
})
这个状态自管理应用包含以下三个部分:state、view、actions
以下是一个表示“单向数据流”理念的简单示意:
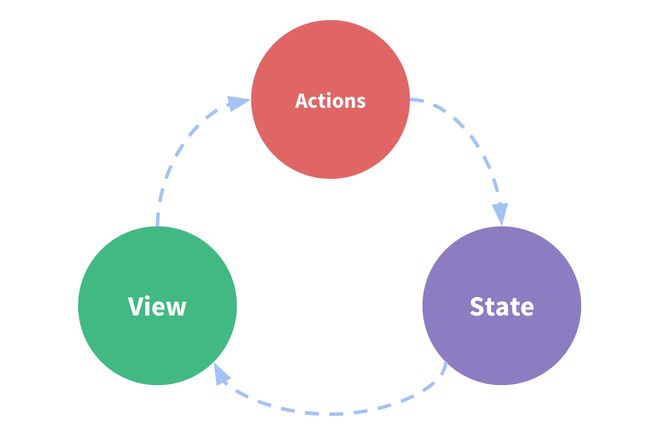
当应用遇到多个组件共享状态时,单向数据流的简洁性很容易被破坏。
Vuex设计思路:
将Vue组件的共享状态抽取出来,以一个全局 单例模式 管理。
在这种模式下,组件树就构成了一个巨大的“视图”,不管在树的哪个位置,任何组件都能获取状态或者触发行为。
据官方说明, Vuex的设计借鉴了 Flux、Redux 和 The Elm Architecture
Vuex结构图:
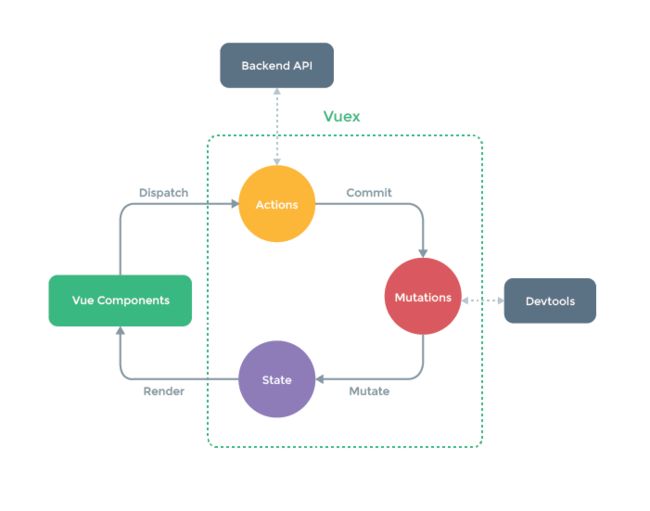
如果拿SpringMVC架构和这张图做对比,那么会发现它们有类似的地方,如下图:
- A c t i o n s Actions Actions层负责响应请求,同时执行一些业务逻辑,类似于后端的 C o n t r o l l e r + S e r v i c e Controller+Service Controller+Service ,在 A c t i o n s Actions Actions 层通常会适用
axios发送请求到后端获取数据,同时可以调用API获取数据。 - M u t a t i o n s Mutations Mutations层负责进行数据的处理,类似于后端的 D A O DAO DAO 层,它会根据 A c t i o n s Actions Actions 层传来的数据对存储在 s t a t e state state层的数据进行增删改查之类的操作。
- S t a t e State State 层负责存储数据,在Vue中通常用于渲染页面。
因为Vuex插件支持所有组件共享$store这个对象,所以每个组件都可以通过$sotre获取到 s t a t e state state 层里的数据。
而组件可以直接获取数据,另外还可以通过 计算属性 获取到state层的数据,例如:
computed: {
studentList(){
return this.$store.state.student.studentList || []
},
},
在使用Vuex3 时,我们需要按照其设计的流程来执行,其中 M u t a t i o n s Mutations Mutations层是必须要经过的,因为Devtools调试工具会监听这一层的变化而不会监听Actions的变化。
除此之外,适用Vuex3的调用流程通常有两种:
- a c t i o n s − > m u t a t i o n s − > s t a t e actions -> mutations -> state actions−>mutations−>state
- m u t a t i o n s − > s t a t e mutations -> state mutations−>state
我们可以忽略actions,这个就和后端的Controller和Service不同了,区别在于前端的actions层主要是负责请求获取数据的,如果无需请求数据,比如:根据当前state里的数据进行筛选查询,此时就不需要请求获取数据,那么Vuex支持直接执行mutations层的代码,直接处理state的数据即可。
3.2 Vuex 核心概念和API
3.2.1 state
概念与特点:
- vuex 管理的状态对象
- 唯一,不可重复
例如:
state: {
// 若有本地缓存就读缓存,否则设置为空
studentList: JSON.parse(localStorage.getItem('studentList')) || []
}
3.2.3 actions
注: Action是Vuex运行原理图中Vue组件使用Vuex的入口,Mutation也可以是入口。
概念与特点:
- 值为一个对象,包含多个响应用户动作的回调函数
- 通过 commit() 来触发 mutation 中函数的调用, 间接更新 state
- action 提交的是 mutation,而不是直接变更状态。
- action 可以包含任意异步操作。支持AJAX、定时器等异步操作。
重点:触发 actions 中的回调函数
在组件中使用:$store.dispatch('对应的 action 回调名') 触发,例如(查询学生信息):
// search.js
actions: {
searchStuById(context, info){
// 业务逻辑比较简单,这里可以发送axios请求获取数据
context.commit('getStuById',info)
},
...
}
// Search.Vue
this.$store.dispatch('search/searchStuById', [this.searchInfo, this.allStudent])
注意:actions中的回调函数第一个参数默认为应用上下文对象,第二个参数才是通过dispatch传递的值,应用上下文对象内容如下:
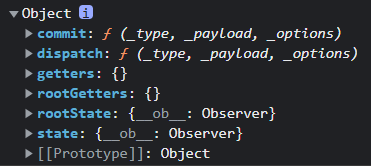
这表示我们可以通过这个应用上下文对象继续 dispatch 分发,也可以commit提交到mutation等。
3.2.4 mutations
概念与特点:
- 值是一个对象,包含多个直接更新 state 的方法
- 每个 mutation 都有一个字符串的 事件类型 (type) 和 一个 回调函数 (handler)。
- 有两种调用方式:1)在 action 中(由第一个参数)使用:commit(‘对应的 mutations 方法名’) 触发
- mutations 中方法的特点:1) 不能写异步代码;2) 只能单纯的操作 state
例如(根据ID查询学生信息):
mutations: {
// 根据ID查询学生
getStuById(state, info){
let id = info[0]
let studentList = info[1]
state.searchStudentList = studentList.filter((stu) => stu.id === id)
},
...
}
这里提一句,在mutation修改完数据后,state里的数据就发生改变了,那么页面里的数据是如何受到影响的呢?
因为Vuex支持所有组件共享同一个 $store ,所以最简单的做法就是可以写一个计算属性,去获取 $store 里state层的数据。例如:
computed: {
searchStudentList(){
return this.$store.state.search.searchStudentList || []
},
...
}
前端页面渲染只需要遍历计算属性的名称即可:
<ul>
<li v-for="(stu) in searchStudentList" :key="stu.id">
{{stu.id}}, {{stu.name}}
li>
ul>
3.2.5 getters
概念与特点:
- 值为一个对象,包含多个用于返回数据的函数
- 调用方式 —— $store.getters.xxx
- 可以认为是 store 的计算属性
- 类似于计算属性,getter 的返回值会根据其依赖被 缓存 起来,且只有当其依赖值 发生了改变 才会被重新计算。
- 跟之前的state、action和mutation一样,可以在任意组件中访问,例如:
// student.js
getters: {
studentCount (state){
return state.studentList.lenth
}
}
// Student.vue
computed: {
studentCount () {
return this.$store.getters.studentCount
}
}
3.3 Vuex 模块化开发
modules
概念与特点:
- Vuex支持在modules里设置多个 module
- 一个 module 是一个 store 的配置对象
- 与每个组件(包含有共享数据)对应
如下图所示,Vuex通常可以分为不同的模块,比如这里比较简单的分为了学生模块和查询模块。
// 该文件用于创建 VueX 中最为核心的 Store
// 引入 Vue
import Vue from 'vue'
// 安装vuex@3 npm i vuex@3
import Vuex from 'vuex'
import search from './search'
import student from './student'
Vue.use(Vuex)
// 创建 Store并导出
export default new Vuex.Store({
modules: {search, student}
})
search.js
export default {
namespaced: true,
// Actions —— 用于响应组件中的动作
actions: { ... },
// Mutations —— 用于操作数据(state)
mutations: { ... },
// State —— 用于存储数据
state: { ... }
}
模块开发引入的js文件中必须有 namespaced: true 这一项,否则多个module之间会发生混淆。
注: 在使用模块开发后,手动调用dispatch,commit方法时候需要在函数名前加上对应的模块名。
例如:根据ID查询学生信息
this.$store.dispatch('search/searchStuById', [this.searchInfo, this.allStudent])
3.4 Vuex 简化的Map四件套
这四件套分别是:
- mapState
- mapGetters
- mapMutations
- mapActions
组件仍然保有局部状态
使用 Vuex 并不意味着你需要将所有的状态放入 Vuex。虽然将所有的状态放到 Vuex 会使状态变化更显式和易调试,但也会使代码变得冗长和不直观。如果有些状态严格属于单个组件,最好还是作为组件的局部状态。你应该根据你的应用开发需要进行权衡和确定。
上述的四个map函数主要是为了方便将 $store里的属性放到组件里的,接下来就是它们的原型与简化方式:
案例:
student.js
import { nanoid } from "nanoid"
export default {
namespaced:true,
// Actions —— 用于响应组件中的动作(若无Axios可不使用)
actions: {},
// Mutations —— 用于操作数据(state)
mutations: {
// 添加学生
addStudent(state, stuName){
state.studentList.unshift({
id: nanoid().substring(0, 5),
name: stuName,
})
},
// 根据ID删除学生
removeStuById(state, id){
state.studentList = state.studentList.filter(
(stu) => stu.id !== id
)
}
},
// State —— 用于存储数据
state: {
// 若有本地缓存就读缓存,否则就初始化三个学生数据
studentList:
JSON.parse(localStorage.getItem('studentList')) ||
[
{
'id': '1',
'name': '张三',
},
{
'id': '2',
'name': '李四',
},
{
'id':'3',
'name':'王五',
}
],
}
}
注意,接下来的案例将使用到ES6的拓展运算符:
let obj ={
name: 'uni',
age: '22'
}
let arr = [1,2,3]
console.log('@obj', {obj})
console.log('@arr', ...arr)
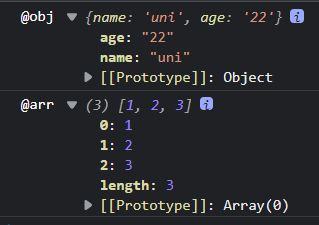
运行效果:
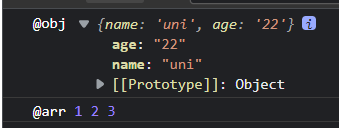
可理解为 ... 会将可迭代的对象(包括数组、Map、Set)拆分,拆分后的结果可以重新放到对应的类型中,比如 { …obj } 或 […arr] 。
通过这个方式再加上 ES6的解构赋值 可以用于多个可迭代对象的合并,例如:
var obj1 ={
name: 'uni',
}
var obj2 = {
age: '22'
}
var arr1 = [1,2]
var arr2 = [3]
console.log('@obj', {...obj1, ...obj2})
console.log('@arr', [...arr1, ...arr2])
运行效果:
在了解到ES6拓展运算符和解构赋值的特点后,接下来就是Vuex提供的map函数的运用了。
3.4.1 mapState
// 使用前,按需在对应的组件里引入。
import {mapState} from 'vuex'
// 手动写法
computed:{
studentList(){
return this.$store.state.student.studentList
}
}
// 使用mapState
computed:{
//借助mapState生成计算属性,从state中读取数据。(对象写法)
// ...mapState('student', {studentList:'studentList'}),
// ...mapState('student', {studentList}), (简写)
//借助mapState生成计算属性,从state中读取数据。(数组写法)
...mapState('student', ['studentList'])
}
3.4.2 mapGetter
// 使用前,按需在对应的组件里引入。
import {mapGetter} from 'vuex'
// 手动写法
computed:{
studenCount(){
return this.$store.getters['student/studentCount']
}
}
// 使用mapGetter
computed:{
//借助mapGetters生成计算属性,从getters中读取数据。(对象写法)
// ...mapGetters({studentCount:'studentCount'})
// ...mapGetters({studentCount}) (简写)
//借助mapGetters生成计算属性,从getters中读取数据。(数组写法)
...mapGetters(['studentCount'])
}
3.4.3 mapMutations
mapMutations简写了commit方法,和之前的mapState和mapGetter不同,它是放在methods里的,在调用方法时需要传参,个人感觉这种简写比较鸡肋,容易和组件里的其他methods弄混。
// 使用前,按需在对应的组件里引入。
import {mapMutations} from 'vuex'
// 手动写法
methods: {
// 添加学生
addStudent(){
if(this.newStudentName === '')
return alert('学生名字不能为空~')
this.$store.commit('student/addStudent', this.newStudentName)
this.newStudentName = ''
},
// 删除学生
removeStuById(id){
this.$store.commit('student/removeStuById', id)
}
}
// 使用 mapMutations
methods: {
//借助mapMutations生成对应的方法,方法中会调用commit去联系mutations(对象写法)
...mapMutations('student',{removeStuById:'removeStuById'}),
}
3.4.4 mapActions
这个和之前的mapMutations一样,放在方法里的,不过它简写的是dispatch方法
// 使用前,按需在对应的组件里引入。
import {mapActions} from 'vuex'
// 手动写法
methods: {
search(){
// 筛选学生信息
if(this.searchType === 'id'){ // 根据ID查询
this.$store.dispatch('search/searchStuById', [this.searchInfo, this.allStudent])
} else if (this.searchType === 'name'){ // 根据学生名字查询
this.$store.dispatch('search/searchStuByName', [this.searchInfo, this.allStudent])
}
// 显示结果条数
if(this.searchStudentList.length)
this.searchResultText = this.searchStudentList.length + ' 条'
else
this.searchResultText = '没有查询到数据'
}
}
// 使用 mapMutations
methods: {
...mapActions('search',['searchStuById', 'searchStuByName']),
search(){
// 筛选学生信息
if(this.searchType === 'id'){ // 根据ID查询
this.searchStuById([this.searchInfo, this.allStudent])
} else if (this.searchType === 'name'){ // 根据学生名字查询
this.searchStuByName([this.searchInfo, this.allStudent])
}
// 显示结果条数
if(this.searchStudentList.length)
this.searchResultText = this.searchStudentList.length + ' 条'
else
this.searchResultText = '没有查询到数据'
}
}
3.4.5 总结
共同点:
- 都支持数组和对象两种写法。
- 都可以被任意组件通过$store里的属性调用
简写的区别:
- mapState简写了
$store.state.Vuex模块名.state变量名 - mapGetter简写了
$store.getters['Vuex模块名/getter函数名'] - mapMutation 简写了
$store.commit('Vuex模块名/函数名', 数据) - mapActions 简写了
$sotre.dispath('Vuex模块名/函数名', 数据)
位置的区别
- 写在 computed的:mapState、mapGetters
- 写在 methods的:mapMutations、mapActions
四、基于Vue2的学生信息管理案例
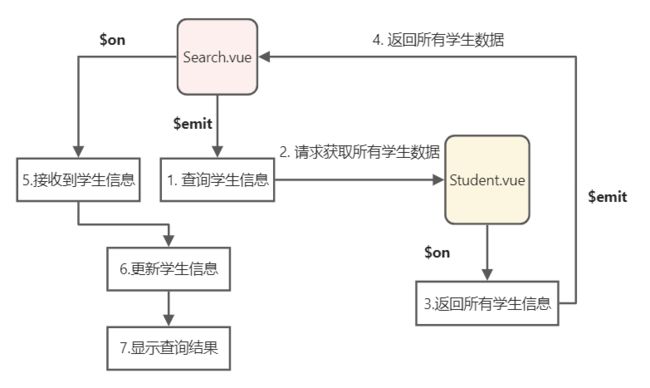
如下图所示,主要使用App组件引入自定义的Search.vue 和 Student.vue两个组件,分别用于搜索学生和学生管理。
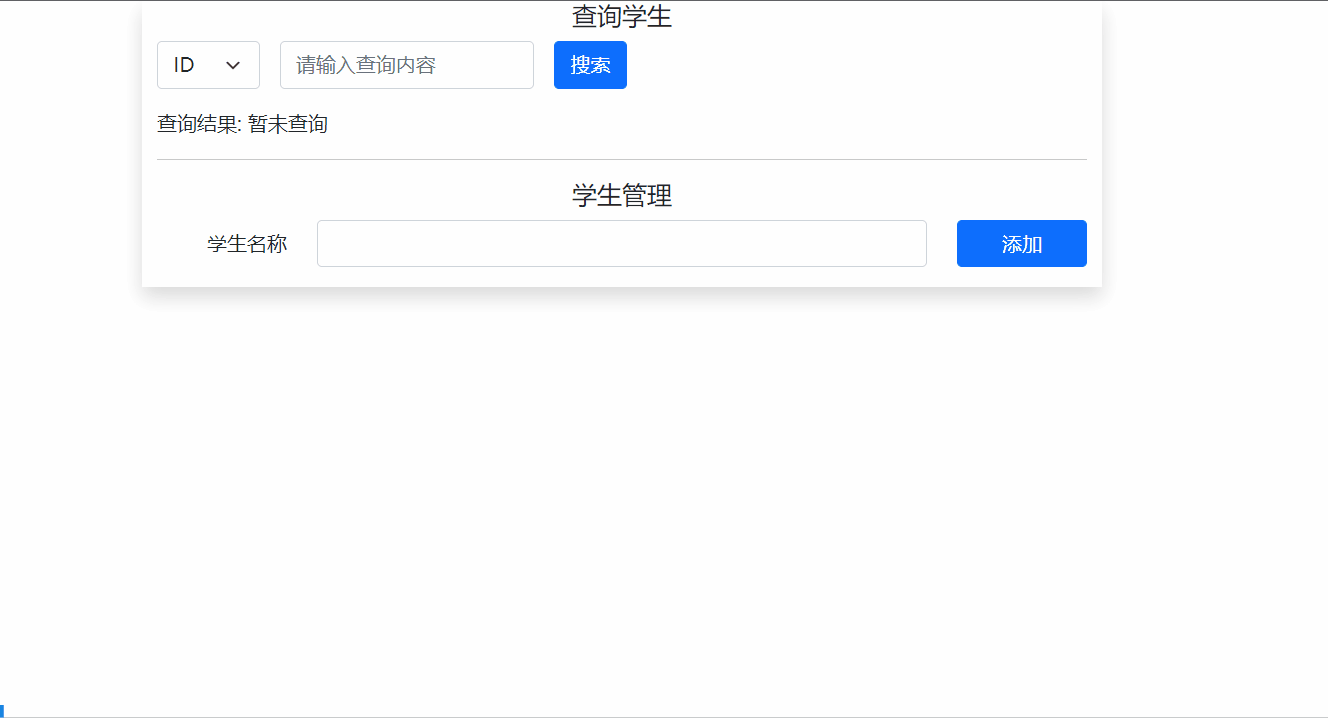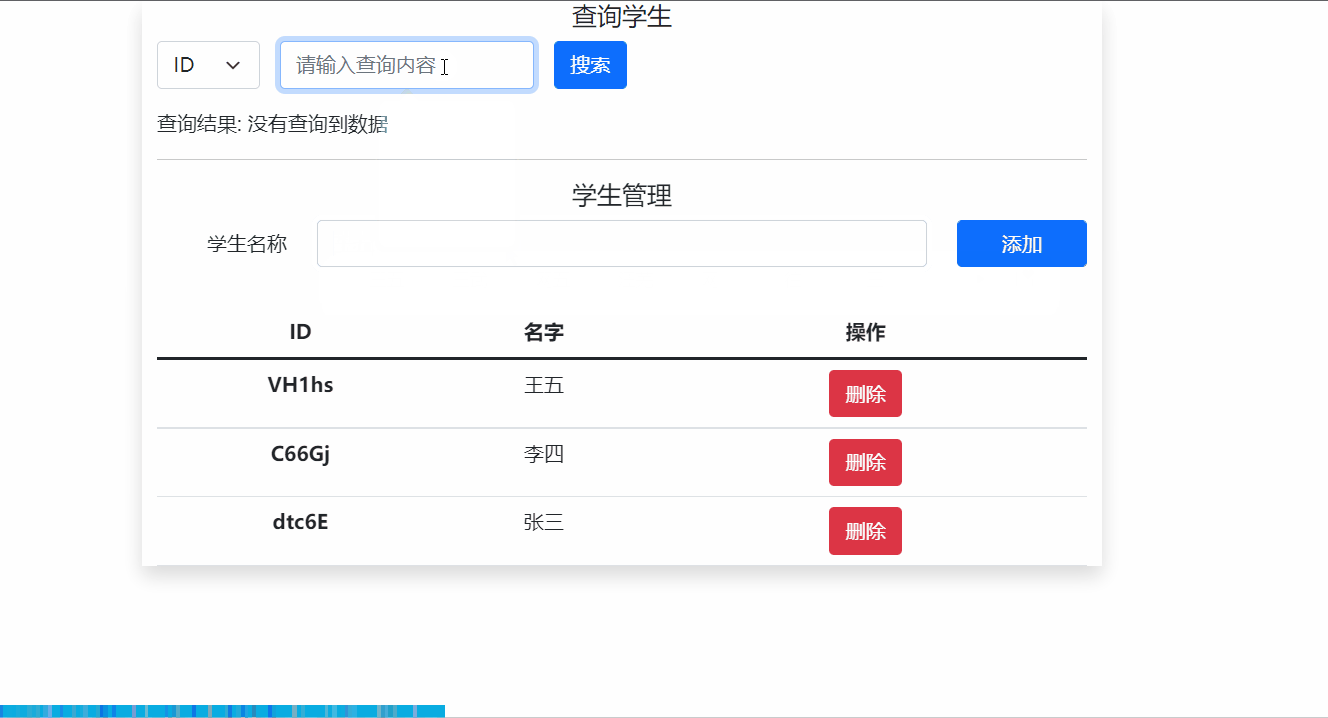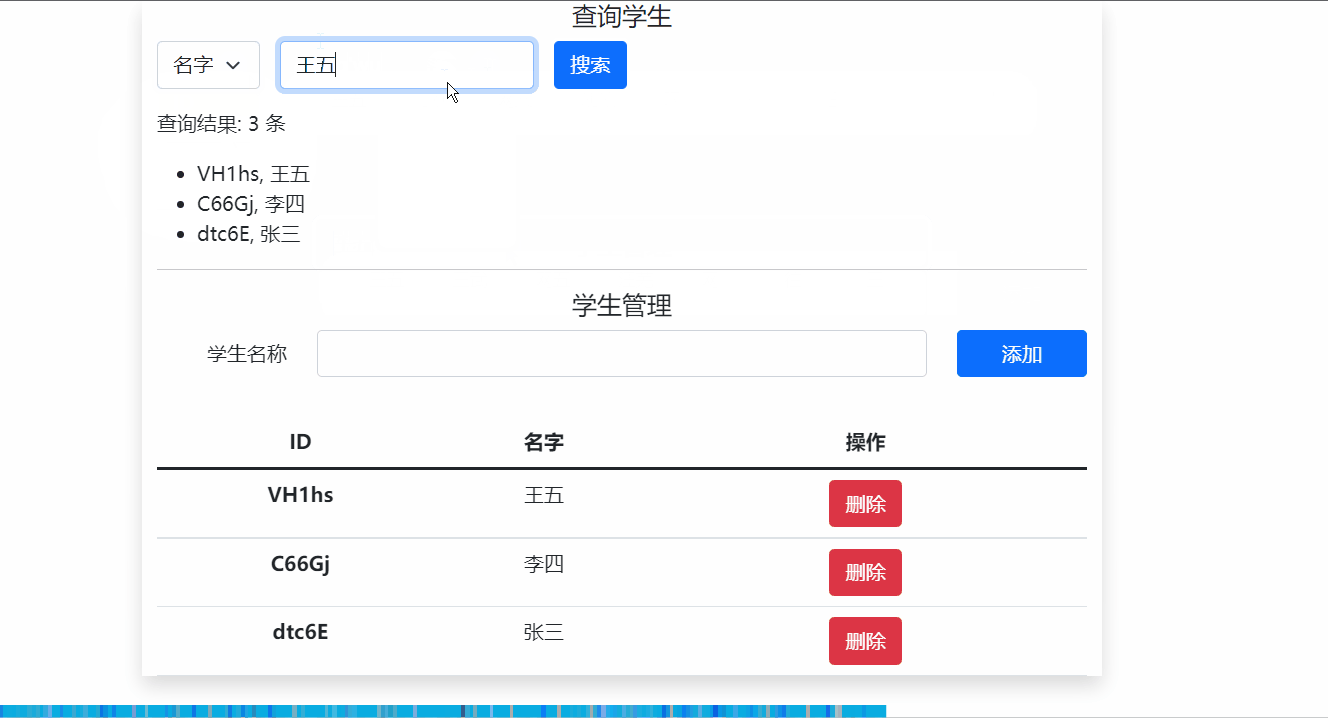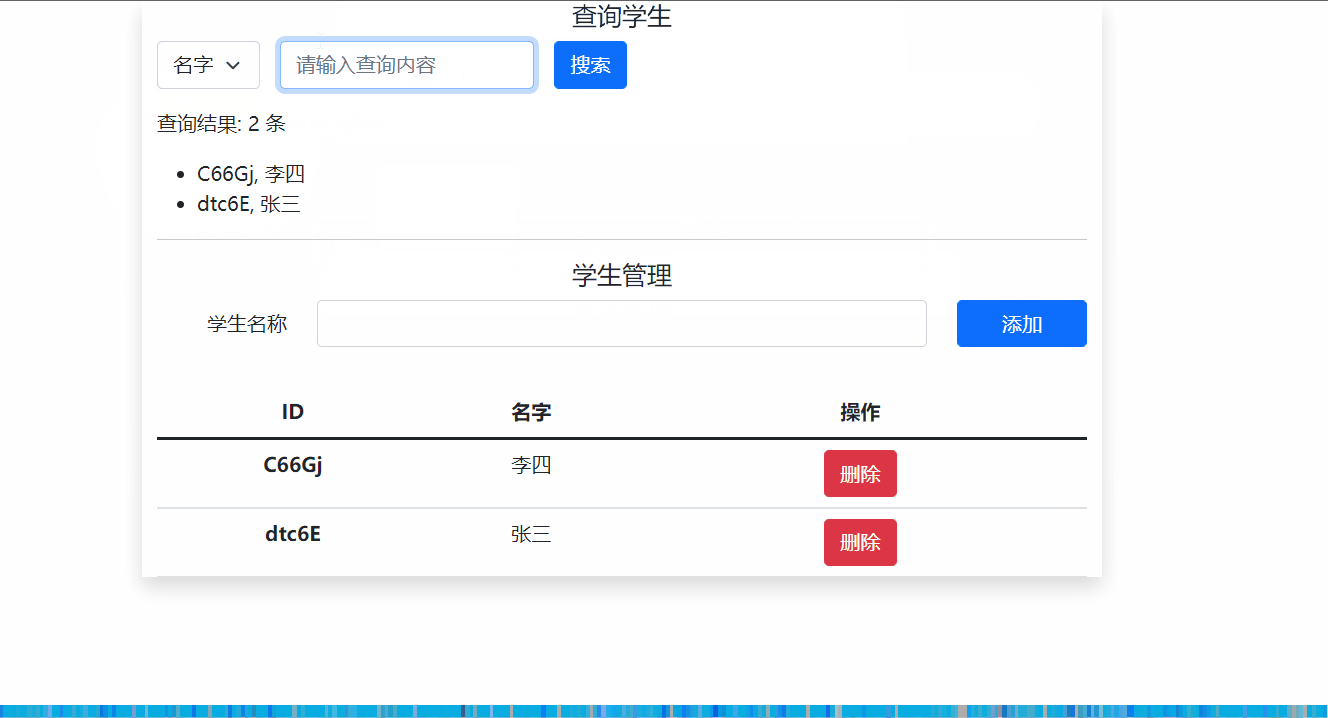
4.1 全局事件总线方法代码实现
在全局事件总线的方法下,数据主要是通过$emit 发送出来,通过 $on 进行接收,上述组件的数据交互主要在搜索用户的时候,在Search.vue中搜索用户,然后Student.vue需要返回用户,查询一次的示意图如下:
4.1.1 Main.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
// // 引入 store
// import store from './store/index'
// 关闭Vue的生产提示
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
render: h => h(App),
beforeCreate(){
Vue.prototype.$bus = this
}
// store
}).$mount('#app')
4.1.2 App.vue
<template>
<div class="container shadow col-md-6">
<div class="col-md-12">
<Search>
<h5>查询学生h5>
Search>
div>
<div class="col-md-12">
<Student>
<h5>学生管理h5>
Student>
div>
div>
template>
<script>
import Student from './components/Student.vue'
import Search from './components/Search.vue'
// npm i bootstrap
import 'bootstrap/dist/js/bootstrap'
import 'bootstrap/dist/css/bootstrap.min.css'
export default {
name: 'App',
components: {Student, Search},
mounted(){
}
}
script>
<style scoped>
div{
text-align: center;
}
style>
4.1.3 Student.vue
<template>
<div>
<slot>slot>
<div class="mb-3 row">
<label for="student-input" class="col-sm-2 col-form-label text-end">学生名称label>
<div class="col-sm-8">
<input v-model="newStudentName" @keydown.enter="addStudent" class="form-control" id="student-input">
div>
<div class="col-sm-2">
<button @click="addStudent" class="btn btn-primary w-100 mb-3">添加button>
div>
div>
<table class="table" v-show="studentList.length > 0">
<thead>
<tr>
<th scope="col">IDth>
<th scope="col">名字th>
<th scope="col">操作th>
tr>
thead>
<tbody>
<tr v-for="(stu) in studentList" :key="stu.id">
<th scope="row">{{ stu.id }}th>
<td>{{ stu.name }}td>
<td>
<button @click="removeStuById(stu.id)" class="btn btn-danger mx-3">删除button>
td>
tr>
tbody>
table>
div>
template>
<script>
import { nanoid } from 'nanoid'
export default {
name: 'Student',
data(){
return {
// 若有本地缓存就读缓存,否则就初始化三个学生数据
studentList:
JSON.parse(localStorage.getItem('studentList')) ||
[
{
'id': 1,
'name': '张三',
},
{
'id': 2,
'name': '李四',
},
{
'id':3,
'name':'王五',
}
],
newStudentName: ''
}
},
methods: {
// 添加学生
addStudent(){
if(this.newStudentName === '') return alert('学生名字不能为空~')
this.studentList.unshift({
id: nanoid().substring(0, 5),
name: this.newStudentName,
})
this.newStudentName = ''
},
// 删除学生
removeStuById(id){
if(!confirm('确认要删除吗?')) return
this.studentList = this.studentList.filter(
(stu) => stu.id !== id
)
}
},
mounted(){
// 响应其他组件获取学生列表
this.$bus.$on('sendStudentListRequest', () => {
// 发布学生列表数据
this.$bus.$emit('getStudentList', this.studentList)
}
)
},
beforeDestroy(){
this.$bus.$off('sendStudentListRequest')
},
// 监视属性值, 若有修改则将其放到本地缓存
watch: {
studentList: {
deep: true,
handler(value){
localStorage.setItem('studentList', JSON.stringify(value))
}
}
}
}
script>
4.1.4 Search.vue
<template>
<div>
<slot>slot>
<div class="mb-3 row">
<label for="student-input" class="col-sm-2 col-form-label text-end">学生名称label>
<div class="col-sm-8">
<input v-model="newStudentName" @keydown.enter="addStudent" class="form-control" id="student-input">
div>
<div class="col-sm-2">
<button @click="addStudent" class="btn btn-primary w-100 mb-3">添加button>
div>
div>
<table class="table" v-show="studentList.length > 0">
<thead>
<tr>
<th scope="col">IDth>
<th scope="col">名字th>
<th scope="col">操作th>
tr>
thead>
<tbody>
<tr v-for="(stu) in studentList" :key="stu.id">
<th scope="row">{{ stu.id }}th>
<td>{{ stu.name }}td>
<td>
<button @click="removeStuById(stu.id)" class="btn btn-danger mx-3">删除button>
td>
tr>
tbody>
table>
div>
template>
<script>
import { nanoid } from 'nanoid'
export default {
name: 'Student',
data(){
return {
// 若有本地缓存就读缓存,否则就初始化三个学生数据
studentList:
JSON.parse(localStorage.getItem('studentList')) ||
[
{
'id': 1,
'name': '张三',
},
{
'id': 2,
'name': '李四',
},
{
'id':3,
'name':'王五',
}
],
newStudentName: ''
}
},
methods: {
// 添加学生
addStudent(){
if(this.newStudentName === '') return alert('学生名字不能为空~')
this.studentList.unshift({
id: nanoid().substring(0, 5),
name: this.newStudentName,
})
this.newStudentName = ''
},
// 删除学生
removeStuById(id){
if(!confirm('确认要删除吗?')) return
this.studentList = this.studentList.filter(
(stu) => stu.id !== id
)
}
},
mounted(){
// 响应其他组件获取学生列表
this.$bus.$on('sendStudentListRequest', () => {
// 发布学生列表数据
this.$bus.$emit('getStudentList', this.studentList)
}
)
},
beforeDestroy(){
this.$bus.$off('sendStudentListRequest')
},
// 监视属性值, 若有修改则将其放到本地缓存
watch: {
studentList: {
deep: true,
handler(value){
localStorage.setItem('studentList', JSON.stringify(value))
}
}
}
}
script>
4.2 Vuex 方式代码实现
运行效果:
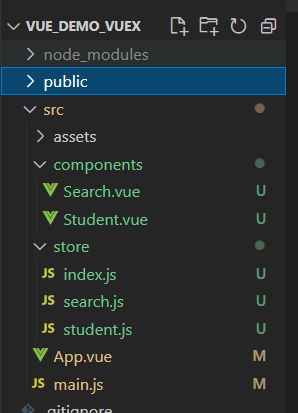
项目结构:
4.2.1 main.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
// // 引入 store
import store from './store'
// 关闭Vue的生产提示
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
el: '#app',
render: h => h(App),
store,
beforeCreate(){
Vue.prototype.$bus = this
}
})
4.2.2 store/index.js
// 该文件用于创建 VueX 中最为核心的 Store
// 引入 Vue
import Vue from 'vue'
// 安装vuex@3 npm i vuex@3
import Vuex from 'vuex'
import search from './search'
import student from './student'
Vue.use(Vuex)
// 创建 Store并导出
export default new Vuex.Store({
modules: {search, student}
})
4.2.3 store/student.js
import { nanoid } from "nanoid"
export default {
namespaced:true,
// Actions —— 用于响应组件中的动作(若无Axios可不使用)
actions: {},
// Mutations —— 用于操作数据(state)
mutations: {
// 添加学生
addStudent(state, stuName){
state.studentList.unshift({
id: nanoid().substring(0, 5),
name: stuName,
})
},
// 根据ID删除学生
removeStuById(state, id){
state.studentList = state.studentList.filter(
(stu) => stu.id !== id
)
}
},
// State —— 用于存储数据
state: {
// 若有本地缓存就读缓存,否则就初始化三个学生数据
studentList:
JSON.parse(localStorage.getItem('studentList')) ||
[
{
'id': '1',
'name': '张三',
},
{
'id': '2',
'name': '李四',
},
{
'id':'3',
'name':'王五',
}
],
}
}
4.2.4 store/search.js
export default {
namespaced: true,
// Actions —— 用于响应组件中的动作
actions: {
searchStuById(context, info){
context.commit('getStuById',info)
},
searchStuByName(context, info){
context.commit('getStuByName', info)
}
},
// Mutations —— 用于操作数据(state)
mutations: {
// 根据ID查询学生
getStuById(state, info){
let id = info[0]
let studentList = info[1]
state.searchStudentList = studentList.filter((stu) => stu.id === id)
},
// 根据名字查询学生
getStuByName(state, info){
let name = info[0]
let studentList = info[1]
state.searchStudentList = studentList.filter((stu) => stu.name.indexOf(name) > -1 )
}
},
// State —— 用于存储数据
state: {
searchStudentList: [],
}
}
4.2.5 App.vue
<template>
<div class="container shadow col-md-6">
<div class="col-md-12">
<Search>
<h5>查询学生h5>
Search>
div>
<div class="col-md-12">
<Student>
<h5>学生管理h5>
Student>
div>
div>
template>
<script>
import Student from './components/Student.vue'
import Search from './components/Search.vue'
// npm i bootstrap
import 'bootstrap/dist/js/bootstrap'
import 'bootstrap/dist/css/bootstrap.min.css'
export default {
name: 'App',
components: {Student, Search},
}
script>
<style scoped>
div{
text-align: center;
}
style>
4.2.6 Student.vue
<template>
<div>
<slot>slot>
<div class="mb-3 row">
<label for="student-input" class="col-sm-2 col-form-label text-end">学生名称label>
<div class="col-sm-8">
<input v-model="newStudentName" @keydown.enter="addStudent" class="form-control" id="student-input">
div>
<div class="col-sm-2">
<button @click="addStudent" class="btn btn-primary w-100 mb-3">添加button>
div>
div>
<table class="table" v-show="studentList.length > 0">
<thead>
<tr>
<th scope="col">IDth>
<th scope="col">名字th>
<th scope="col">操作th>
tr>
thead>
<tbody>
<tr v-for="(stu) in studentList" :key="stu.id">
<th scope="row">{{ stu.id }}th>
<td>{{ stu.name }}td>
<td>
<button @click="removeStuById(stu.id)" class="btn btn-danger mx-3">删除button>
td>
tr>
tbody>
table>
div>
template>
<script>
import { nanoid } from 'nanoid'
export default {
name: 'Student',
data(){
return {
newStudentName: ''
}
},
methods: {
// 添加学生
addStudent(){
if(this.newStudentName === '')
return alert('学生名字不能为空~')
this.$store.commit('student/addStudent', this.newStudentName)
this.newStudentName = ''
},
// 删除学生
removeStuById(id){
if(!confirm('确认要删除吗?')) return
this.$store.commit('student/removeStuById', id)
}
},
computed: {
// 计算属性: 获取store里的值
studentList(){
return this.$store.state.student.studentList
}
},
// 监视studentList属性值, 若有修改则将其放到本地缓存
watch: {
studentList:{
deep: true,
handler(value){
localStorage.setItem('studentList', JSON.stringify(value))
}
}
}
}
script>
4.2.7 Search.vue
<template>
<div>
<slot>slot>
<div class="row g-3">
<div class="col-auto">
<label for="staticEmail2" class="visually-hidden">学生名称label>
<select class="form-select" v-model="searchType">
<option value="id">IDoption>
<option value="name">名字option>
select>
div>
<div class="col-auto">
<label for="input-search" class="visually-hidden">学生名字label>
<input v-model="searchInfo" @keydown.enter="search" class="form-control" id="input-search" placeholder="请输入查询内容">
div>
<div class="col-auto">
<button @click="search" class="btn btn-primary mb-3">搜索button>
div>
div>
<div class="text-start">
<p>查询结果: {{ searchResultText }} p>
<ul>
<li v-for="(stu) in searchStudentList" :key="stu.id">
{{stu.id}}, {{stu.name}}
li>
ul>
div>
<hr>
div>
template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'Score',
data(){
return {
searchType: 'id',
searchInfo: '',
searchResultText: '暂未查询',
}
},
mounted(){
console.log(this.$store)
},
computed: {
searchStudentList(){
return this.$store.state.search.searchStudentList || []
},
allStudent(){
return this.$store.state.student.studentList || []
}
},
methods: {
search(){
// 筛选学生信息
if(this.searchType === 'id'){ // 根据ID查询
this.$store.dispatch('search/searchStuById', [this.searchInfo, this.allStudent])
} else if (this.searchType === 'name'){ // 根据学生名字查询
this.$store.dispatch('search/searchStuByName', [this.searchInfo, this.allStudent])
}
// 显示结果条数
if(this.searchStudentList.length)
this.searchResultText = this.searchStudentList.length + ' 条'
else
this.searchResultText = '没有查询到数据'
}
},
}
script>