LightGBM源码学习
知乎 - LightGBM 源码剖析
知乎 - LightGBM源码阅读(一)
知乎 - LightGBM源码阅读(二)
CSDN - LightGBM源码阅读+理论分析(处理特征类别,缺省值的实现细节)
简述FastDBT和LightGBM中GBDT的实现
文章目录
- 调试准备
- 从main到GBDT::Train
-
- 执行路径
- 重点看一下TrainOneIter
-
- GBDT::BoostFromAverage
- ObjectiveFunction::GetGradients
- 回顾迭代过程
- SerialTreeLearner::Train
-
- num_leaves次数的最佳叶子结点分裂过程
- EFB
调试准备
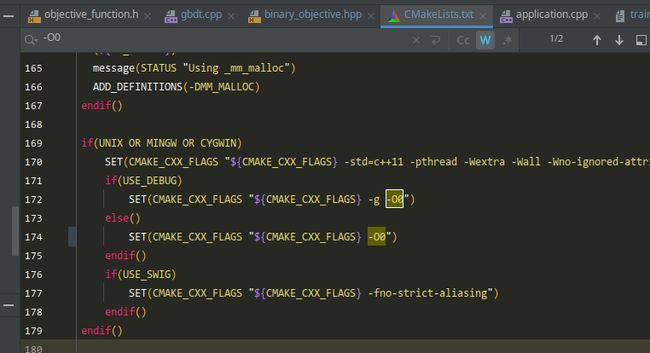
把-O3改为-O0,不然指令优化之后有些值调试不出来
代码里面有些带#pragma omp parallel for 的预处理语句可以注释掉,并行改串行,不然调试不进去
从main到GBDT::Train
执行路径
- main函数执行路径
Application::Train
src/application/application.cpp:200
boosting_->Train(config_.snapshot_freq, config_.output_model);
去看boosting
include/LightGBM/boosting.h
boosting是一个抽象类,派生出boosting_type对应的4个子类
有空画个继承关系图
src/boosting/gbdt.cpp:246
fun_timer应该是一个RAII对象
Common::FunctionTimer fun_timer("GBDT::Train", global_timer);
朴实无华的迭代过程,看TrainOneIter
注意上层调用方式是is_finished = TrainOneIter(nullptr, nullptr);,gradient和hessian都是空指针
GBDT有两个成员变量,维护每次迭代时的梯度和黑塞(用了自己写的内存分配器)
vector里面放智能指针比放指针靠谱(对比sLSM源码)
/*! \brief First order derivative of training data */
std::vector<score_t, Common::AlignmentAllocator<score_t, kAlignedSize>> gradients_;
/*! \brief Secend order derivative of training data */
std::vector<score_t, Common::AlignmentAllocator<score_t, kAlignedSize>> hessians_;
/*! \brief Trained models(trees) */
std::vector<std::unique_ptr<Tree>> models_;
/*! \brief Tree learner, will use this class to learn trees */
std::unique_ptr<TreeLearner> tree_learner_;
/*! \brief Objective function */
const ObjectiveFunction* objective_function_;
/*! \brief Pointer to training data */
const Dataset* train_data_;
重点看一下TrainOneIter
GBDT::BoostFromAverage
重点看一下初始值怎么设的
- BinaryLogLoss
double init_score = ObtainAutomaticInitialScore(objective_function_, class_id);
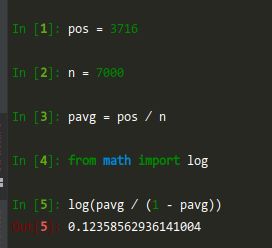
马上打印出:
[LightGBM] [Info] [binary:BoostFromScore]: pavg=0.530877 -> initscore=0.123666
去ObtainAutomaticInitialScore看看
跳到src/objective/binary_objective.hpp:134
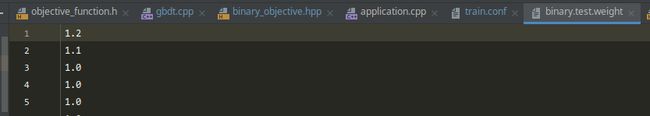
如图,总共7000全量样本,正样本3716,pavg=0.53
i n i t s c o r e = log ( p a v g 1 − p a v g ) initscore=\log(\frac{pavg}{1-pavg}) initscore=log(1−pavgpavg)
算出来的是logits
ObjectiveFunction::GetGradients
本小节主要阐述目标函数
1 2阶导数的求解,如果后期需要实现hinge loss或者focal loss可以用得上
init_scores看完了,我们看GBDT::Boosting → \rightarrow → ObjectiveFunction::GetGradients
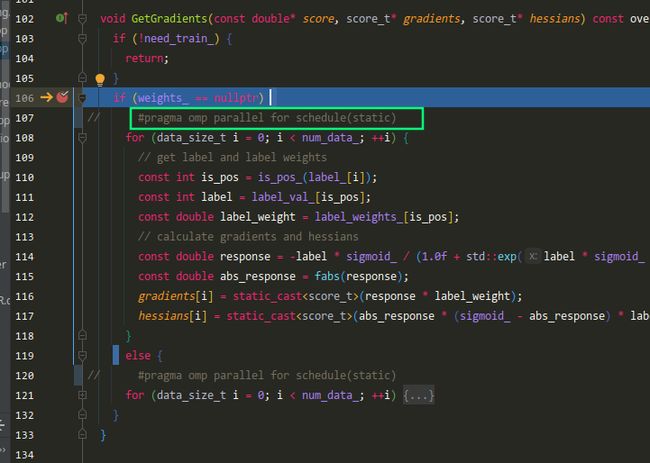
src/objective/binary_objective.hpp:101
为了方便调试,注释掉#pragma omp parallel for schedule(static)
注意到BinaryLogloss初始化的时候*weights_=1.2
发现是配置文件指定了weight
我们康康gradient和hessian是怎么算的
初次计算时,score就是init_scores,用label avg算的

// calculate gradients and hessians
const double response = -label * sigmoid_ / (1.0f + std::exp(label * sigmoid_ * score[i]));
const double abs_response = fabs(response);
gradients[i] = static_cast<score_t>(response * label_weight * weights_[i]);
hessians[i] = static_cast<score_t>(abs_response * (sigmoid_ - abs_response) * label_weight * weights_[i]);
忽略样本权重,可以归纳为这两个式子(注意,label已经变换为{-1, 1},即 y ∈ { − 1 , 1 } y\in\{-1, 1\} y∈{−1,1}):
g = − y 1 + e x p ( y × y ^ ) g=-\frac{y}{1+exp(y\times \hat{y})} g=−1+exp(y×y^)y
h = ∣ g ∣ × ( 1 − ∣ g ∣ ) h=|g|\times (1-|g|) h=∣g∣×(1−∣g∣)
好,我们来推一下这两个公式怎么来的
知乎 - 逻辑回归损失函数的两种形式
根据上述知乎文章,可知在 y ∈ { − 1 , 1 } y\in\{-1, 1\} y∈{−1,1}条件下,负对数似然函数为
N L L = log ( 1 + e x p ( − y ⋅ y ^ ) ) NLL=\log(1+exp(-y \cdot \hat{y})) NLL=log(1+exp(−y⋅y^))
NLL对 y ^ \hat{y} y^求导,可得
∂ N L L ∂ y ^ = − y 1 + e x p ( y ⋅ y ^ ) = − σ ( − y ⋅ y ^ ) ⋅ y \Large{ \begin{array}{ll} \frac{\partial{NLL}}{\partial{\hat{y}}} &=-\frac{y}{1+exp(y\cdot \hat{y})} \\ \\ &=-\sigma(-y\cdot \hat{y}) \cdot y \end{array} } ∂y^∂NLL=−1+exp(y⋅y^)y=−σ(−y⋅y^)⋅y
h = ∣ g ∣ × ( 1 − ∣ g ∣ ) h=|g|\times (1-|g|) h=∣g∣×(1−∣g∣)
回顾迭代过程
SerialTreeLearner::Train
TreeLearner派生了很多Learner,这里以SerialTreeLearner为例进行学习
启动过程:
GBDT::Init
train_data_是const Dataset*类型,Dataset包含EFB之后的结果
tree_learner_->Init(train_data_, is_constant_hessian_);
在SerialTreeLearner::Init中:
这些变量全部被初始化为长度num_leaves的vector
在HistogramPool::DynamicChangeSize方法中,会将pool_和data_设为num_leaves,将feature_metas_设为num_features
(gdb) p num_data_
$2 = 5626
原本在GBDT::Init中调用SerialTreeLearner::Init的时候,不应该是7000个数据吗,怎么变成5626了呢?我回去看了下,是在GBDT::Train中调用了GBDT::Bagging导致的
num_leaves次数的最佳叶子结点分裂过程
- 遍历所有可分裂的叶子
for (int split = init_splits; split < config_->num_leaves - 1; ++split) {- SerialTreeLearner::BeforeFindBestSplit
histogram_pool_相关处理
- SerialTreeLearner::FindBestSplits
- ConstructHistograms(is_feature_used, use_subtract);
- FindBestSplitsFromHistograms(is_feature_used, use_subtract);
for (int feature_index = 0; feature_index < num_features_; ++feature_index) {- SerialTreeLearner::ComputeBestSplitForFeature
- FeatureHistogram::FindBestThreshold
- find_best_threshold_fun_(仿函数对象)
- FeatureHistogram::FindBestThresholdSequentially
- find_best_threshold_fun_(仿函数对象)
- FeatureHistogram::FindBestThreshold
- SerialTreeLearner::ComputeBestSplitForFeature
- 根据成员变量
best_split_per_leaf_找到最佳叶子索引(int)best_leaf - 如果
best_leaf_SplitInfo.gain <= 0.0,break - 调用
Split(tree_prt, best_leaf, &left_leaf, &right_leaf);进行叶子分裂
- SerialTreeLearner::BeforeFindBestSplit
real_feature_idx_
(gdb) p train_data_->real_feature_idx_
$8 = std::vector of length 28, capacity 28 = {2, 6, 3, 22, 24, 27, 0, 9, 5, 10, 4, 7, 18, 11, 17, 26, 13, 1, 14, 16, 23, 8, 19, 12, 20, 25, 15, 21}
- SerialTreeLearner
/*! \brief number of data */
data_size_t num_data_;
/*! \brief number of features */
int num_features_;
/*! \brief training data */
const Dataset* train_data_;
/*! \brief gradients of current iteration */
const score_t* gradients_;
/*! \brief hessians of current iteration */
const score_t* hessians_;
/*! \brief training data partition on leaves */
std::unique_ptr<DataPartition> data_partition_;
/*! \brief pointer to histograms array of parent of current leaves */
FeatureHistogram* parent_leaf_histogram_array_;
/*! \brief pointer to histograms array of smaller leaf */
FeatureHistogram* smaller_leaf_histogram_array_;
/*! \brief pointer to histograms array of larger leaf */
FeatureHistogram* larger_leaf_histogram_array_;
/*! \brief store best split points for all leaves */
std::vector<SplitInfo> best_split_per_leaf_;
/*! \brief store best split per feature for all leaves */
std::vector<SplitInfo> splits_per_leaf_;
/*! \brief stores minimum and maximum constraints for each leaf */
std::unique_ptr<LeafConstraintsBase> constraints_;
/*! \brief stores best thresholds for all feature for smaller leaf */
std::unique_ptr<LeafSplits> smaller_leaf_splits_;
/*! \brief stores best thresholds for all feature for larger leaf */
std::unique_ptr<LeafSplits> larger_leaf_splits_;
/*! \brief gradients of current iteration, ordered for cache optimized */
std::vector<score_t, Common::AlignmentAllocator<score_t, kAlignedSize>> ordered_gradients_;
/*! \brief hessians of current iteration, ordered for cache optimized */
std::vector<score_t, Common::AlignmentAllocator<score_t, kAlignedSize>> ordered_hessians_;
/*! \brief used to cache historical histogram to speed up*/
HistogramPool histogram_pool_;
/*! \brief config of tree learner*/
const Config* config_;
ColSampler col_sampler_;
const Json* forced_split_json_;
std::unique_ptr<TrainingShareStates> share_state_;
std::unique_ptr<CostEfficientGradientBoosting> cegb_;
EFB
src/io/dataset.cpp:338
hist_t是double的别名
meta_维护了num_bin,config 等
const FeatureMetainfo* meta_;
hist_t* data_;