【ISE328: Technology and Applications of Electronic Business Systems】
Resources from The Hong Kong Polytechnic University ISE328 Technology and Applications of Electronic Business Systems course
Content
- Lecture 1: Introduction to eBusiness and Application
-
- Idea of e-business
- Examples of e-business
- Analysis of e-banking
-
-
- Function of a bank
- E-banking example
- E-publication
- Music stores
- Reasons of driving e-Business
-
- 1. Customer-Oriented Trends
- 2. Service
- 3. Organizational
- 4. Enterprise technology
- 5. General technology
-
- Lecture 2: E-Business Design and Technologies
-
- The considerations during applying e-Business
-
- Designing e-Business
-
- 1. First-level strategy
- 2. Second-level strategy
- 3. Third-level strategy
- Electronic Business Technology
- Technology domains
-
- IoT
- ERP System Enterprise resource planning (ERP) is business process management software
-
- Four tiers of ERP
- Network Security
- Digital Money
- Virtual collaboration
- Lecture 4: Introduction to e-Commerce
-
- Difference between e-commerce and e-business
- Seven unique features of e-business Technology
- Introduction to m-commerce
- Lecture: Business System Development and Cases
Lecture 1: Introduction to eBusiness and Application
Idea of e-business
e-electronic (components)
-
e-Business was defined as “the transformation of key business process through the use of Internet Technologies”.
-
use Electronic Means to conduct business / any business processes.
Business means a company, a corporation, partnership, or have any such formal organization
Business is:
- the activity of making money
- producing or buying and selling products (goods and services)
- Shipping
- procurement
- Manufacturing
- ERP or management
e-commerce refers to buying and selling online, while e-business encompasses all business conducted online. E-commerce can be viewed as a subset of e-business.
Business categories:
Banking, retail, telecommunication, entertainment, tourism, public transport
Examples of e-business
e-Banking (HSBC, Hang Seng Bank)
Online Auction (e-Bay)
Online Book Seller (Amazon)
Online Game Providers
e-Government
e-Public Services
e-Health
e-Learning
Analysis of e-banking
-
Analyze the existing process e.g, Flow Chart.
-
Identify the advantages and disadvantages of the existing processes.
-
Determine what processes can be (to) improve.
Outcome, will be system. -
Identify how e-business is applied for the new approach.
Apply electronic means to replace existing process. -
Identify the advantages of new approach.
What processes have improved? -
Identify the disadvantages of new approach.
Any drawback?
Function of a bank
1.Banking
- Deposit money, Withdraw Cash, Money Transfer, Bill Payment, etc.
2.Investment - Securities, Foreign currency exchange, IPO, Investment Deposits, Gold Margin, etc.
3.Insurance - Travelsure, Home Care, Personal Accident, Term Life, etc.
4.Personal Credit - Loan, Tax Comforter, Overdraft Facility, etc.
5.Mortgage - Valuation, Mortgage Loan, etc.
6.Credit Card - Credit Card Application, Card Security Service, etc.
E-banking example
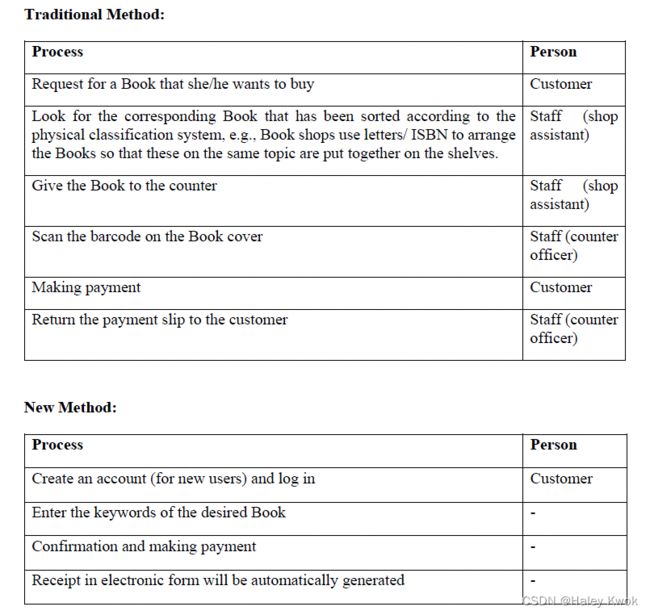
Tradition approach:
-Deposit Money
Step 1: Process-person-time = a table to make existing analysis
Step 2: pros and cons for company and customers of the existing process
Disadvantages for the company:
Cost
- Staffing cost
Types of staffs: Counter service officer, shop manager, security guards, etc. - Rent
Depends on the size of the shop. - Facilities cost
Decoration, electricity, etc. - Maintenance cost.
Repair/replacement, etc.
5.Various insurance costs.
Processing
6.Limited office hours.
7.Non-environmental friendly.
Wasting paper: various of documentation work, receipt, etc.
8.Risks of Human Error.
Miscalculation of money, input incorrect data, etc.
9.Time consuming.
Counting money, input data, etc.
Cost-detail-money= cost analysis
Disadvantages for the customers:
- Wasting time
-Go to the shop, Queuing, etc. - Inconvenience
-Office hours, etc.
Step 3: Determine what processes can be (to) improve.
- Save Cost, Reduce processing time.
Step 4: Identify how e-business is applied for the new approach.
Improved approach: (Quick Deposit Machine)
Step 5: advantages of new approach
-
Shop size smaller.
-
Decoration much lesser.
-
Staff number reduced.
-
Manual process reduced.
-
Risk of human error reduced.
-
Lead time of the process reduced.
-
No office hour limitation.
Step 6: disadvantages
-Machine costs.
-Installation fee.
-Maintenance costs.
-Security.
-Inconvenience to elders
Tradition approach:
-Securities
Processes involved:
- Disadvantages for the company:
- Human mistakes.
- Listening to others spoken language.
“command”, “stock code”, “quantity”.
- Incorrect in Input data.
Mistakes lead to:
- Financial lost.
- Lost of customers.
- Damage in company reputation. - Staff.
- required many staff to receive calls.
- High cost in making records.
- voice recording.
Disadvantages for the customers:
- Hard for Real time transaction.
- Stock Prices changes every sec.
- Transaction must be quick.
- Can’t wasting time in queuing.
- Long lead time for customer identification/verification.
- Can’t wasting time in contacting servicing staff on call
-
Save Cost, Reduce processing time.
Improved approach: (Internet) -
Identify how e-business is applied for the new approach.
-
Advantages of company:
- Avoid human error made by staff.
- Customers become self servicing.
Advantages of customer: - Transaction faster.
- Response to the market faster.
- Wider Accessibility.
- More command support.
- Disadvantages of customer:
- Risk of inaccessible.
• E-book store example
- Disadvantages for the company:
High Fixed cost.- Wide space,
- High level decoration to provide
a leisure reading environment.
Risk of stock keeping.
- Stocks are “books”.
- Damage by customers.
High inventory holding cost.
- Keep humidity of the room temperature.
High/Distributed inventory level. - Each shop keeps certain inventory.
- e-bookstores
- Apply electronic means to replace existing process: internet.
5&6. advantages for company
Avoid high fixed cost.
Reduce the risk of book damaging.
Keeping low inventory cost. [physical shops distributed in different areas which need more considerations on how to deliver the book to different customers.]
Centralized warehouse. [online shops deliver the products from one place only, which is centralized and efficient]
Disadvantages of company:
- Relatively higher transportation cost. [need to transport to different customers point-by-point]
Advantages of customer: - Accessible 24 hrs.
- Easier to search for specify books.
E-publication
In tradition: (Publication)
- Printing out the manual script,
- Submit manual script to publisher,
- Editing,
- Send to the printer,
- Doing the printing and binding,
- Deliver to different book stores,
- Display.
Advantages to company.
- More unique books.
- Increase the diversity of collections.
Advantages to authors.
- Reduce the publication lead time.
Readers can come from world wide.
Music stores
In Tradition: (Music Store)
Disadvantages for the company:
- High Fixed cost.
- Wide space,
- Leisure environment,
- Numerous of high quality
music players / displayers.
- Risk of stock keeping.
- Distributed inventory.
Advantages for the company:
- Avoid High Fixed cost.
- Search function.
- Sample music / video.
- Keeping low inventory cost.
- Centralized warehouse.
- Availability of electronic version.
Disadvantages of company:
Relatively higher transportation cost.
Reasons of driving e-Business
1. Customer-Oriented Trends
◦ Service availability, Servicing time, Self-service,
More product choices, Integrated solutions. (through different platforms)
Service Availability (Ability to provide immediate service)
- first step to attract consumers to use your service.
- most customers count the speed of service as a key reason.
- they like to get the service as fast as possible.
- they hate waiting for service.
e.g. Choosing a bank service provider
Do you like waiting in line for 30mins in bank? If others don’t have to wait, which one will you prefer?
Servicing Time
- important factor to retain consumer.
- customers look for companies that provide faster service.
- to customers, time is money.
- companies are forced to reduce the number of steps it takes to serve customers.
- enhance the efficiency by technology.
e.g. Deposit money
How to reduce the number of processes, and time required for each process.
Reducing the processing time of counting, form filling, and data entry.
Self-service
- customers are looking for self-service solutions that not only save them time but also empower them.
- they can finish their transaction (buying what they want) without the help of sales personnel.
- they are able to shop at anytime, and if possible should be in anywhere.
Example: Online Shopping
Consumers are changing their buying habit from traditional face-to-face model to purchase online.
In the survey, 67% of the respondents said they had searched for the company name, product or service names, or advertising slogan that they saw in offline marketing or ads. And of those online searchers who started with an offline marketing message, 39% eventually made a purchase.
More product choices
-customers love one-stop locations that offer them everything under one roof.
-however, impossible in traditional retailer.
-because of the limited shelf space and inventory constraints, especially in Hong Kong
-online companies can offer more different merchandise than a physical company does.
Integrated solutions
- Consumers don’t like to go to many places to look for different services they want.
- They want integrated-service business that provide them one-stop shopping needs.
- In today’s business, customers usually have too many choices, products, and stores.
- To solve the “choice” problem, customers increasingly looking for integrated solutions that can make their decision process easier.
2. Service
◦ Integrated sales and service, Seamless support, Flexible fulfillment, and Convenient service delivery.
Integrated sales and service:
- Its idea is to narrow the gap between sales and services.
- Provide better customer relationship.
- Customers usually like to have some access about the information of product and the services they will have before they purchase the product.
What is Sales?
In economics, it is an exchange process between two parties.
It involved in selling products or services in return for money or other compensation.
What is Service?
It is a form of product that consist of activities, benefits, or satisfactions offered for sale that are essentially intangible and do not result in the ownership of anything.
Seamless support
- Provide user friendly and easy-to-use customer service
processes with single point of contact.
- Named “customer service easy” and “solution oriented” are the most important trends in today’s business. E.g., AI robot
Flexible fulfillment and convenient service delivery
- home delivery and other unique fulfillment services continue to gain importance.
- in old model, companies waiting for customer to come.
- in new model, companies bring their services to customers.
Increased process visibility
- Provide customers with access to accurate, timely information about order status, product pricing, and product availability.
- Famous example UPS, tracking system.
- Especially important in outsourced manufacturing.
- To let the customers know exactly what is happening, so that they feel more ease and controllable.
3. Organizational
◦ Outsourcing, Contract manufacturing,
Virtual distribution.
Outsourcing Management
- Today’s business climate demands companies to be flexible in order to survive.
- It forces companies to outsource specific business processes in order to improve the overall business performance, called Business process outsourcing (BPO).
- Traditionally, outsourcing is cost-control technique.
- Today, outsourcing is for quality improvement.
- Outsourcing always take about some parts that you are not strong/specialize on.
- Then you outsource it in order to improve the product quality.
Contract manufacturing
- Usually used by those companies, if their capital is very tight, or if they don’t want to spend much money in install the machines, building a factory, order too urgent, etc.
- Companies only focus on the designing the core/key component and subcontract other to suppliers.
- This can help them to increase their flexibility.
- To move them from capital/asset-intensive focus to knowledge-intensive one
e.g. Limit capacity
If a shoes manufacturer has to produce 1000 pair of shoes, but its production capacity can produce only 600 unit, then it can contract out to other manufacturers.
Virtual distribution
- A new intermediary, like a virtual company
- These companies aggregate buyers and sellers by using Web technology.
- They aggregate the marketing and product information content and establish efficient marketplaces.
e.g. e-Chemical
- A neutral online marketplace that allows registered buyers and sellers to select a product, get a price, and order or track small chemical shipments online through its web site.
4. Enterprise technology
◦ Integrated enterprise applications.
Integrated enterprise applications
Because of the popularity and maturity of ERP system…
-Each of them work as an Individual Unit, totally Independent, lacking or with little communication with others.
-Recently, companies recognize that if a chain of processes is to perform at a high level.
-The individual business functions (departments) and their applications, which supporting them must be tightly linked with each other.
Example: Systems Applications and Product (SAP)
- SAP is the world’s leading provider of e-business software solutions.
- Through the mySAP.com e-business platform, businesses are improving relationships with customers and partners, streamlining operations, and achieving efficiencies throughout their supply chains.
SAP system
It is an integrated ERP software including different functions such as Finance, Materials, Production, Quality, Maintenance & HR.
5. General technology
◦ Wireless Web applications, Portable computing and information appliances, Infrastructure convergence, Application service providers.
Wireless Web applications
-with the widespread rollout of wireless infrastructure, a new wave of consumer and business applications will begin.
-Wireless applications increase the efficiency of performing everyday tasks, such as organizing business, personal affairs, sending e-mail, making phone calls, etc.
Portable computing and information appliances
-The reduction in device size and cost, and the improvements in the functionality, storage and reliability stimulate the usage of portable appliances.
-Consumers are more demanding to have same productivity and communications capability everywhere as they are working on their desks.
Summary:
Analysing the new approach: existing flow [Person-process-time]- advantages/disadvantages [Cost-detail-money]- improvement- new approaches details (comparsion )- pros and cons
Common aspects to talk about the pros and cons:
Cost
- Staffing cost
Types of staffs: Counter service officer, shop manager, security guards, etc. - Rent
Depends on the size of the shop. - Facilities cost
Decoration, electricity, etc. - Maintenance cost.
Repair/replacement, etc.
5.Various insurance costs.
Processing
6.Limited office hours.
7.Non-environmental friendly.
Wasting paper: various of documentation work, receipt, etc.
8.Risks of Human Error.
Miscalculation of money, input incorrect data, etc.
9.Time consuming.
Counting money, input data, etc.
-reducing the risk of damage
-centralized warehouse/ low in inventory cost
-relatively higher in transportation cost.
5 reasons of e-business
Lecture 2: E-Business Design and Technologies
The considerations during applying e-Business
Basic questions:
- Which Parts/Departments?
- What is the motivation for the changes? 【Do some analysis listed in lecture 1, to know which part(s) need to make changes】
- What are the advantages and disadvantages? 【The pros and cons that the change made】
- What should convert? 【Consumer may need to transfer to your shop-> website】
- How to do it? 【Any technologies or methods?】
- When to implement? 【It will affect your original business, which time is the best time to change e.g., covid-19?】
-SMES
Can Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises (SMES) convert to e-Business?
• Excellent opportunity especially for SMEs.
• SMEs do not have to concern with fixing their old systems before adopting e- business like the large companies. (need to change the whole systems)
• SMEs are relatively more flexible, without too many departments/functional groups clearly separated.
-Business transplantation vs business transformation
e-Business is NOT about complete replacement of conventional ways of doing business
Transplantation
• to make the current ways of conducting business more efficient and reliable.
• transplanting existing business practices from traditional media to new media.
Transformation
• Opening up completely new ways of conducting business. (Changing from one business model to another business model)
For example: Operating a book store
Transplantation
• Applying POS system, central database
• Some parts of workflow are changed
Transformation
• Become an online bookstore like Amazion.com
• Whole of the business model is changed
Designing e-Business
3 Levels in e-business direction:
1. First-level strategy
Functions and features In designing your e-business, you have to take care of:
-Value Proposition(what you want to show?)
e.g. provide quality service, to be the pioneer ,……
-Customer Segments (who your customers are?)
e.g. teenagers, adults ,…… (facebook, ig)
-Customer Priorities (what your customers want?)
e.g. convenient, fast, cheap ,………
To create an innovative e-business design…… (new idea that not yet exist in the market)
Q1 . What business design can make your customer’s shopping and service experience unique and memorable?
- how you can impress your customers.
- how to use new technologies to surprise them.
- how to provide better services.
- how to meet your customer’s demand not only today but also in future.
Q2. What capabilities and competencies can create rich customer experiences?
- What features required to meet your customer’s need, after you understand/realize what they want.
- These decisions determine what your customer will see and encounter when interacting your e-business design.
- So, what techniques should be involved?
2. Second-level strategy
e-Business Infra-Structure How do you structure your organization for efficiency?
- How to reduce the time of business process by using electronic equipment?
- How to improve the communication efficiency between departments?
- How to increase the data exchange efficiency between companies.
e.g., RFID tag to improve Inaccurate counting, Time-consuming, E-business hardware and software
You have to analyze your company’s structure.
How many departments there, and their relationship. What functions each department want to have.
Based on the software functionality/applications required to design your e-business.
- CRM
- ERP
- e-Procurement
- Financial Control
- Supply Chain Management
3. Third-level strategy
e-Business Info-Structure This is regarded as the structural foundation supporting the application layer.
- Web Servers, Database, ASP, etc.
Ensure the applications are working, accessible and available. - Reliability, security, etc.
Electronic Business Technology
Business technology is a strategy for organizing and coordinating technology management across the entire enterprise.
It is a set of management practices, tools, organizational structures and technology governance
It is designed to optimize across the enterprise Aim of satisfying customer needs and expectations
Three dimensions:
Business capabilities and transformation Innovation and data leadership
Emerging technologies are accelerating digital transformation, requiring business and process development and a forward-looking governance
-Business capabilities are the sum of all processes and assets (systems and data), including any supporting functions within the organisation.
Business capabilities are the key for developing the business and for utilising technology in the best possible way.
-Transformation comprises of the parts and processes of an organisation that are engaged in improving business capabilities
Digital frontline
Customer experience and loyalty leadership
Digitalisation provides new business opportunities and requires consistent design thinking on how to face customers, partners and employees in a networked multi-channel world.
-The digital frontline can be defined as any digital means that connects the company to the user and is visible to the user, whether the user is a customer or a partner, or whether the customer is internal or external.
-Customer experience is at the heart of all digital frontline activities.
-Digital frontline is a crucial area as it is the key area where the emerging business focus and growth possibilities reside and where digital transformation happens through speed and agility.
-Digital apps and web, as well as digital enterprises, enable the creation of new business possibilities around customer experience, digital business and internet of things (IoT) services.
Technology backbone
Cost quality and performance leadership
Traditional information technology management function (or IT) needs to become the technology backbone that is responsible for development, and management of digital and administrative solutions in a professional way.
-The technology backbone consists of all information technology systems and processes that support the running of the businesses operations, through the management of end-user services, plus enterprise and business applications.
-It is where the essential business asset of a company resides, and the purpose is to provide operational efficiency to the company through reliability, security and scalability.
Technology domains
- Operational efficiency
- Product quality
- Customer experience
- Data security
- Business process
IoT
- The Internet of things (IoT) describes the network of physical objects—“things”—that are embedded with sensors, software, and other technologies for the purpose of connecting and exchanging data with other devices and systems over the internet.
- The internet of things, or IoT, is a system of interrelated computing devices, mechanical and digital machines, objects, animals or people that are provided with unique identifiers and the ability to transfer data over a network without requiring human-to-human or human-to-computer interaction.
e.g., Air conditioner
Internet: use some apps to control it
Sensor: whether the temperature is in a certain degree
Unique: remote-control a particular one
Three paradigm
e.g., industrial automation
Challenges and issues of IoT
Ethical issues
Data security: will data dispose to another people?
Data privacy: personal information
Standardization: code to code communicate
Interoperability: interconnect
Unique addressing: IPv6 has more storage numbers, otherwise you cannot detect particular devices
ERP System Enterprise resource planning (ERP) is business process management software
Allows an organization to use a system of integrated applications to manage the business
Automate many back-office functions related to technology, services and human resources
ERP intergration
- EAM (Enterprise Asset Management). This module governs asset management, as well as planning and scheduling maintenance procedures.
- CRM (Customer Relationship Management). This ERP module forms and controls the database of customers and contracts in all stages of fulfilment.
- BI (Business Information). This module creates different reports based on data generated by other ERP software components. [trend, decide marketing strategy…]
- ECM (Enterprise Content Management). This module stores and governs different documents among the enterprise.
- HR (Human Resources). This solution automates operations with enterprise personnel and provides necessary links between the database of employees and other ERP modules.
- FA (Financial Analytics). Users can control finances and accounts that belong to an enterprise by using this module, as well as optimizing costs and expenses.
- WMS (Inventory). The extended warehouse management system is a key for successful operations of other enterprise resource planning systems.
- SCM (Supply Chain Management). By using this module, employees automate contacts with vendors and logistic operations.
Benefits of ERP
Disadvantages
- cost of ERP
- ERP success depending on software experience
- not purchasing a customizable system
- ERP resistance
https://www.workwisellc.com/blog/15-benefits-implementing-erp-software/
improving company productivity, collaboration and communication because all the information is integrated in one system.
Four tiers of ERP
ERP System Selection
Step 1. Form a project team and conduct the business process re- engineering (BPR).
Step 2. Collect all possible information about ERP vendors and systems. Filter out unqualified vendors.
Step 3. Establish the attribute hierarchy and assign weights to the attributes.
Step 4. Interview vendors and collect detailed information.
Step 5. Analyze the data obtained from the external professional reports to obtain the objective ERP suitability.
Step 6. Assign subjective ratings to the ERP projects on the basis of data acquired in interviews to calculate the subjective ERP suitability.
Step 7. Combine the evaluations of both data sources and aggregate the decision-making assessments to determine the final fuzzy ERP suitability.
Step 8. Utilize the fuzzy integral value ranking method to obtain the rank of each ERP project
Step 9. Analyze the results. Observe the change in the final ERP suitability and the final ranking value.
Step 10. Select the ERP project with the maximum ranking value.
Step 11. Implement the selected ERP project.
Network Security
-Network security consists of the policies and practices adopted to prevent and monitor unauthorized access, misuse, modification, or denial of a computer network and network-accessible resources.
-Network security involves the authorization of access to data in a network, which is controlled by the network administrator. Users choose or are assigned an ID and password or other authenticating information that allows them access to information and programs within their authority.
Coverage
-Network security covers a variety of computer networks, both public and private, that are used in everyday jobs: conducting transactions and communications among businesses, government agencies and individuals. Networks can be private, such as within a company, and others which might be open to public access.
-Network security is involved in organizations, enterprises, and other types of institutions. It does as its title explains: it secures the network, as well as protecting and overseeing operations being done. The most common and simple way of protecting a network resource is by assigning it a unique name and a corresponding password.
Benefits
Protecting Our sensitive data,
Personally Identifiable Information (PII),
Protected Health Information (PHI),
Personal information,
Intellectual property data
-
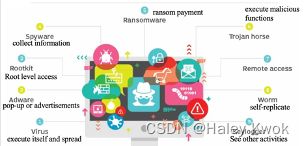
Malware
Malicious Software” is developed by a cyber-attacker with the purpose of invading the target’s computer and taking some or full control.
Usually, Malware can infect the system or network with the initial unintentional and unknowing help from a human and continue to self- replicate automatically. Once security is breached and the Malware is in the system, it can do serious damage. -
Phishing
A cyber-attack that aims to obtain sensitive information by cheating targets into believing fake messages.
Phishing attackers disguise themselves as a trustworthy source and send lures usually through email, social media, or other electronic media. -
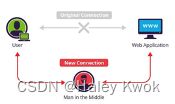
Man in the Middle Attack(MITM)
attempts to secretly intercept and listen to the legitimate communication between two hosts.
Most Common Types:
• Email Hijacking
• Wireless LAN Eavesdrop
• Session Hijacking
-
DoS and DDoS
Denial-of-service attack (DoS attack) is a cyber-attack in which the perpetrator seeks to make a machine or network resource unavailable to its intended users by temporarily or indefinitely disrupting services of a host connected to the Internet. Denial of service is typically accomplished by flooding the targeted machine or resource with superfluous requests in an attempt to overload systems and prevent some or all legitimate requests from being fulfilled.
In a distributed denial-of-service attack (DDoS attack), the incoming traffic flooding the victim originates from many different sources. This effectively makes it impossible to stop the attack simply by blocking a single source. (HTTP Flood is the variation of DDoS) -
Cross Site Scripting
This attack aims to insert malicious code into a website which targets a visitor’s browser.
Cross Site Scripting, also knowns as XSS targets trusted web applications. The attacker uses the web app to inject the code such as a browser or client-side scripts that is viewed by other users of the same application. -
SQL Injection
An SQL injection attack interferes with the queries that a web application makes to the database. An attacker inserts crafted SQL (Structured Query Language) code lines that allow data to be reveals.
Solutions
-Zero-day Exploits
the term “zero-day” refers to the day when a new vulnerability is discovered by a software vendor. From that moment, of zero-day detection, the clock is ticking for the software vendor to produce a patch as quickly as possible. Once a patch is produced, the software’s end users must install and verify the patch and security vendors must update their attack detection signatures and push those updates to their tools.
-Security monitoring system
§ SolarWinds Log and Event Manager
§ Splunk
§ RSA NetWitness Suite
§ ManageEngine Log360
Digital Money
-Electronic money is money which exists only in banking computer systems and is not held in any physical form.
-Electronic money, or e-money, is the money balance recorded electronically on a stored-value card. E.g., 點數卡
-It may refers to several systems which enable a buyer to pay electronically by transmitting a unique number (called digital certificate) similar to a banknote number.
-In economic terms electronic money is monetary value provided by the issuer on demand, expressed in government or private monetary units stored in electronic form on an electronic device.
-Both virtual currencies and cryptocurrencies are types of digital currencies, but the converse is incorrect.
History
In 2009, The first decentralized cryptocurrency, bitcoin, was created
Cryptocurrencies
Four different systems
- Centralized Systems
Many systems—such as PayPal, eCash, WebMoney, Payoneer, cashU, and Hub Culture’s Ven will sell their electronic currency directly to the end user.
Other systems only sell through third party digital currency exchangers - Decentralized Systems
Decentralized e-money is stored and flows through a peer-to- peer computer network that directly links users, much like a chat room. No single user controls the network.
Some decentralized types:
-
Bitcoin
• Bitcoin is a digital asset and a payment system invented by Satoshi Nakamoto, who published the invention in 2008 and released it as open-source software in 2009.
• The system is peer-to-peer; users can transact directly without needing an intermediary.
• Transactions are verified by network nodes and recorded in a public distributed ledger called the block chain.
• The ledger uses bitcoin as its unit of account. The system works without a central repository or single administrator, which has led the U.S. Treasury to categorize bitcoin as a decentralized virtual currency.
• Bitcoin is often called the first cryptocurrency
e.g., NFT: non-fungible token [create your own picture]
Identify
Use Ethereum as a transaction platform -
Monero
-
Litecoin
-
Ripple Monetary System
-
Dogecoin
-
Nxt
-
Mobile sub-systems/Digital Wallets
• A number of electronic money systems use contactless payment transfer in order to facilitate easy payment and give the payee more confidence in not letting go of their electronic wallet during the transaction.
• On September 9th, 2014 Apple Pay was announced at the iPhone 6 event. In October 2014 it was released as an update to work on iPhone 6 and Apple Watch. It is very similar to Google Wallet, but for Apple devices only.
e.g., GNU Taler is an anonymous, open source electronic payment system currently (September 2015) in development
BKasH is the leading payment system in Bangladesh -
Offline anonymous system
It can be done ‘offline’.
In this electronic money system, the merchants do not need to have interaction with banks before receiving currency from the users. Instead of that, the merchants can collect spent money by users and deposits the money later to the bank.
The merchant can deliver his storage media in bank for exchanging the electronic money to cash.
Virtual collaboration
Virtual collaboration is the method of collaboration between virtual team members that is carried out via technology-mediated communication.
Virtual collaboration follows the same process as collaboration, but the parties involved in virtual collaboration do not physically interact and communicate exclusively through technological channels.
Distributed teams use virtual collaboration to simulate the information transfer present in face-to-face meetings, communicating virtually through verbal, visual, written, and digital means.
Three Characteristics
Sharing of information: Virtual collaboration is meant to enable the sharing of knowledge between parties who cannot exchange information due to physical separation. Virtual collaboration platforms allow the transfer of different types of information between collaborators to work towards a common goal.
Dispersed Collaborators: Collaborators within virtual collaboration are
physically separated from each other and can only interact virtually. Being able to physically interact with a team member affords many benefits that virtual collaboration cannot provide, and eliminates any need for virtual meetings (sharing of context, interpersonal relationships, etc.).
Technology-mediated: Because virtual collaborators cannot interact physically they use technology to share information over several mediums. Most virtual collaboration platforms are carried out via the internet, for example email, video conferencing, and virtual workspaces.
Two types
Synchronous collaboration occurs when team members are able to share information and ideas instantaneously.
Examples: instant messaging, chat rooms, and video or audio conferencing .
Asynchronous collaboration occurs when team members communicate without the ability to instantly respond to messages or ideas.
Examples: e-mail, discussion boards, application-specific groupware, or shared databases
Advantages
- Pooling of expertise:
Virtual collaboration provides more opportunities for experts to join project groups where their knowledge can be best used, and be complemented with other experts whose knowledge contributes to a common goal.
Virtual collaboration allows teams to be formed based on subject and expertise, without the restriction of physical proximity of collaborators. The pool of expertise is much greater abroad than in most local team settings, meaning that virtual collaboration gives teams an opportunity to add a quality expert that fits the needs of the team.
This can be proved by the fact that dispersed teams with recruited experts tend to have higher net earnings than local teams with a local expert. - Cost effective:
Compared to face-to-face meetings of distributed group members, virtual collaboration is much less costly. The time and costs associated with transportation to physically bring together team members from different geographic locations can be substantially higher than the cost of a virtual collaborative application.
Software used to connect distributed teams can be found for free on the internet, with more feature-loaded and specialized applications having a one-time cost or a paid subscription.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Virtual_collaboration#Advantages
Disadvantages
• Lower Group Potency: ineffective discussion
• Reduced Cohesiveness
• Poor Satisfaction
• Technological limits
• Reliance on Technology
• Asynchronous and lagged communication
• Means of exclusion: choose to receive certain information
Challenges
- Technology-related challenges
The team needs to have knowledge of both the nature of their work and the virtual collaboration media they choose, and select the best suited media to deal with the most suitable situation. The team also need the skill to deal with the media to overcome issues coming from the media. - Cultural diversity-related challenges
The team members need to have good knowledge on cultural differences between members and the knowledge of choosing the proper media to smooth these differences. The members are expected to have the skill to adjust their communication behavior and the language proficiency to achieve cultural adaption. - Trust-related challenges
Trust between members of virtual teams affects the quality and amount of shared information. When virtual teams meet face-to- face, it creates trust and cohesion and ensures knowledge sharing . Knowledge sharing in virtual teams influences the formation of trust and contributes to the effectiveness of the team. In written communication one cannot be sure about other members’ commitment and it is difficult to recognize others’ emotions - Geographic dispersion-related challenges [time difference]
The team member should clearly understand pros and cons of choosing synchronous and asynchronous medias to avoid issues resulted from dispersed workplaces. The skill of time and self- management of team members are also emphasized to overcome this challenge. - Time-related challenges [responding]
If a virtual project is only a small part of the team members’ job, members may not have enough time for the virtual project. Thus, for example, they have to process information fast. A particular challenge in virtual teams is following- through and responding at a right time because not responding could be interpreted as a lack of competence or commitment.
–
Lecture 4: Introduction to e-Commerce
Difference between e-commerce and e-business
Rayport and Jaworksi (2003)
“e-commerce includes the entire world of electronically based organizational activities that support a firm’s market exchanges – including a firm’s entire Information System’s infrastructure”.
Kalakota and Robinson (2003)
“e-business encompasses the entire world of internal and external electronically based activities, including e-commerce”.
Laudon and Traver (2007)
e-business (1)
It refers primarily to the digital enablement of activities and processes within a company.
e.g. Information systems under the control of the company.
e-business (2)
It does not include commercial transactions across the company’s boundaries.
It will not directly generate revenue for the company from outside the company’s boundaries.
e.g. a company’s online inventory control system is a component of e- business, you will not generate revenue from it.
e-commerce
Includes commercial transactions across the company’s boundaries.
It will directly generate revenue for the company from outside the company’s boundaries.
Which services are regarded as e-commerce?
Providing Information
- Simply providing information to customer alone is NOT e-commerce.
e.g. Checking balance, request e-statement, etc.
e-Commerce - Generate revenue for company.
e.g. Buying stock, money transfer (with service charges), etc.
Seven unique features of e-business Technology
-
Ubiquity
It means just available everywhere, at all times.
e-Business technology moves the marketplace from traditional physical space to your desktop / mobile / etc.
Ubiquity reduces the transaction costs, mainly in the cost of participating in a market.
e.g. Think about the ways of checking the balance of your bank account. -
Global reach
e-Business technology permits commercial transactions to cross cultural and national boundaries far more conveniently and cost effectively.
The potential market size for e-commerce merchants is roughly equal to the size of the world’s online population.
e.g. As we mentioned before, whoever has a computer and can access Internet can be your customer.
In contrast, most traditional commerce is local or regional. -
Universal standards (common platform)
It refers to the technical standards of the Internet.
The universal technical standards of Internet and e-commerce greatly lower market entry cost, meaning the cost just to bring their goods to market.
It also reduces the search costs that the effort required to find the suitable products.
Airdrop -> different technical standards
WhatsApp -> both android and iOS -
Information Richness
refers to the complexity and content of a message.
refers to the personal, face-to-face service provided when making a sale. traditional markets makes good use of them to increase their selling power.
e.g. Buying digital camera
-When you go to buy a digital camera in some shop in person, the salesperson in the shop will usually “nicely” explain the features and functions of the product, letting you play around with different camera models. You can ask questions and their opinions about camera.
However, since the larger the audience reached, the less rich the message. a trade-off between richness and reach should be made.
e.g. Buying digital camera
If you buy it online, no salesperson will come to service you.
-This is one of the disadvantages in doing e-commerce.
When you do business, you have to realize that whether you customers can purchase the product online or not. If your products can also be purchased online, then you have to provide much better customer services to attract them to shop.
- Interactivity
Interactivity allows an online merchant to engage a consumer in ways similar to face-to-
face experience.
-Internet conferencing, internet phone, e-mail, etc
However, this information richness still may not be as good as traditional approach. - Information Density
e-business technologies reduce cost in information collection, storage, processing, and communication.
in the mean time it also increases the currency, accuracy and timeliness of information.
e.g. The old way to share information……e.g. papers, mail, voice
making information more useful and important than ever.
In e-commerce market, therefore, prices and costs become more transparent.
e.g. Comparing Prices
-Strictly speaking, this fast spreading of information feature is because of the advantage of the Internet.
- Getting the idea of the price of a iPod Nano.
- Personalization/Customization
e-Business technologies permit personalization.
Merchants can target their marketing messages to specific individuals by adjusting the message to a person’s name, interests, and past purchases record.
e.g. Nike enables consumers to design their own pair of personalized shoes by allowing consumers to specify the colors for the various shoe parts.
e.g. More example:
For customers:
You can set your preference to include the things or news that you are interested in.
For companies:
They can categorize their customers according to their buying habits, age groups, academic background, etc.
and delivery some special or tailor-made promotion to them.
For customization, user’s preferences or behavior can be changed as desired.
Advantages:
- Save time & money on repetitive searches
- e.g. find movies by the same director
- Better information
e.g. filter out the advertisements that we don’t want - Tailor a product to a customer’s taste
e.g. able to offer unique combination - Create a feeling of “ownership” of one’s web experience
Disadvantages:
- Anonymity preferred
- e.g. some people may not want to be identified
- Lack of relevance
e.g. I don’t want customized earrings - Impossible
e.g. I can’t watch American TV shows on Hulu.com, if I am out of the country.
Introduction to m-commerce
“m” refers to Mobile
- Idea of m-commerce is to conduct commerce using mobile device.
e.g. mobile phone, PDA, etc.
Other definitions: - “next generation e-commerce” (Rana Tassabehji, 2003)
- “a subset of e-commerce” (C. Coursaris & K. Hassanein, 2002)
- “at least one side uses mobile communication techniques.” (N Kreyer, K Pousttchi, K Turowski, 2002)
- “any transaction with monetary value that is conducted via a mobile network” (I. Clarke III, 2001)
Survey In 2005:
- There are many people using mobile phone than there are in using Internet.
- An estimated 1 billion people having a mobile phone.
Applications of m-commerce technologies
- Mobile Ticketing
- Idea is to make use of the Mobile phone to buy and obtain the tickets from any location and at any time.
e.g.
It can be used in buying Mass transit ticket, Sports ticket, and Cinema ticket
Advantages and Disadvantages of m-Ticketing
Advantages:
- Reduce cost of ticket printing and mailing.
- Reduce staffing costs.
- Improve customer convenience.
- Increase the accessibility to tickets.
Indeed, this feature is even more convenient than using Internet because all you need is just a mobile phone.
Disadvantage: - No battery !!
- Mobile Coupons
- Mobile ticketing technology can be used for the distribution of coupons to the mobile phone users.
- Then the customers can present the coupons in their mobile phones to shop when they use them.
Advantages of m-Coupons:
- Its cost effective, again companies can save money in doing the printing, and distributions.
The coupons are stored in the mobile phone, so that customers can have the coupons with them all the time whenever they have their mobile phone with them.
Quick and easy to deliver.
Compatible with the needs of target customers.
Feature Paper Coupon Mobile Coupon
Logo Support Yes Yes
Preparation and Distribution 7 to 14 days Less than 24 hours
Controlled time distribution (e.g. distribution at 13:00) No Yes
Ability to modify after published No Yes
Real time tracking No Yes
Automatic expiration No Yes
Distribution based on customer’s interest No Yes
Environment friendly No Yes
- Provide Information Services
- A wide variety of information services can be delivered to mobile phone users in much the same way as it is delivered to PCs.
e.g. - Map/Locations
- News services
- Stock Information
- Sports results
- Financial records
- Traffic data
Advantages:
- Increase music, animation, video and reading experiences
- Tell the specific location of the user’s mobile
- Search for internet content in search engine conveniently
- Get real-time information in everywhere at anytime
So that, you can …… - Prevent traffic jam with real-time traffic data
- Identify your location, destination and route in a map
- Make a quick decision in stock market
- Receive latest news in the world
- Mobile Banking
Many banks and some financial institutions enable their customer not only to access their account’s information, But also to make transactions.
e.g.
- Purchasing stocks
- Money transfer
Advantages of m-Banking:
-increase customer satisfaction and loyalty by providing anywhere, anytime banking
-lower administrative costs / handling charges
-lesser number of branches
-inform customers better, e.g. reminder of repayment
-save papers, e.g. receipts & forms
Technologies Behind m-Banking:
-
IVR (Interactive Voice Response)
Customer makes a call at the IVR number and choose options by pressing the corresponding number in their keypads.
The corresponding information will be read out. Major limitation: only provides Enquiry-based service -
SMS (Short Messaging Service)
Customer requests for information by sending an SMS containing a service command to pre-specified number.
the bank responds with a reply SMS containing the specific information. Main advantage: almost all mobile phone are SMS enabled -
WAP (Wireless Access Protocol)
Similar to internet banking.
Customers use WAP compatible browser on their mobile phones and access the bank’s site. -
Standalone Mobile Application
They can access all enquiry and transaction based services and also more complex transaction like trade in securities through their phone.- Mobile Marketing
Many companies are now using m-commerce to do marketing and advertisement.
e.g. Some company using the automatic dial-up program to make a call to you, and play the voice message that introduces their companies, products, and services.
Another way is done by sending you some messages.
- Mobile Marketing
Advantages of m-Marketing:
Mobiles are attractive medium for marketers because:
- People are always reachable
- Phones give the user’s location
- Relatively high response rate
- Cost-effective
- High-speed message delivery
- Targeted
- Interactivity
- Mobile Payment
This is often referring to m-Payment
At least one part of the transaction is conducted using a mobile device through a mobile telecommunication network, or via various wireless technologies.
Advantages of m-Payment:
- Queue avoidance
- Enhanced payment instrument availability
- Complement to cash
- Digital content and services, e.g. ticketing
- Small value purchases at point of sale, e.g. vending
- Being use for suddenly need for payments
Case Study: Container Terminal
Mathematically, more tractors can be handled with the same parking capacity.
Lecture: Business System Development and Cases
§ E-business System Development Process/Analysis
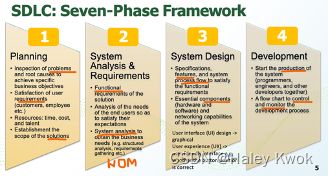
System Development Life Cycle (SDLC) refers to the entire process of formal, logical steps taken to develop a software product/system. The concept generally refers to computer or information systems.
Make comparison:
- Main features comparison (user reviews, dropshipping (units stored in warehouse , people just have to create their business website) , login, SKU(stock of units-> same model, different colours), SSL and check out (HHTPS… protect your exchange information) )
- Extra features (app stores)
- Ease of use
- Templates and flexibility
- Payment options
- Support
§ e-Commerce Types:
• B2B
B2B e-Commerce is defined as the sales of goods or services between businesses via online channels, instead of traditional ways, such as telephone and mail.
Transactions are carried out digitally, which helps reduce a great amount of overhead costs. E.g. semiconductor companies
• B2C
Business-to-consumer refers to the process of businesses selling products and services directly to consumers, with no middleperson.
B2C is typically used to refer to online retailers who sell products and services to consumers through the Internet. E.g. Amazon
• B2B2C
B2B2C is an e-commerce model that combines business to business (B2B) and business to consumer (B2C) for a complete product or service transaction in a mutually beneficial manner. E.g. during peak month
• C2B
C2B allows customers to provide a business with a service, from which the consumer makes a profit.
This is the reverse of the typical business-to-consumer model (or B2C), in which a company provides a service to customers through the sale of goods and services.
e.g. C2B (Customer to Business),比較本土的說法是要約,由客戶發佈自己要些什麼東西,要求的價格是什麼,然後由商家來決定是否接受客戶的要約。假如商家接受客戶 的要約,那麼交易成功;假如商家不接受客戶的要約,那麼就是交易失敗。C2B模式的核心,是通過聚合分散分佈但數量龐大的用戶形成一個強大的採購集團,以此來改變B2C模式中用戶一對一出價的弱勢地位,使之享受到以大批發商的價格買單件商品的利益。例子:U-deals、當家物業聯盟。
• C2C
Customer to customer (C2C) is a business model that enables customers to
trade with each other, frequently in an online environment. E.g. eBay
B2C 是business to consumer 是商家對個人, 這個就很多了卓越噹噹京東等等都是。
B2C C2C 很重要的一點是都運用了物流。
O2O 是 online to offline 就是你在線上消費,在線下享受服務,比如團購。O2O是不需要物流的, 你購買的東西必須要在線下去獲得。所以像聚美這種雖然是團購但不是O2O。
B2B 是business to business 是企業間的, 比如阿里巴巴。
原文網址:https://kknews.cc/finance/4mng3zx.html
§ Cross-border e-Commerce Logistics
Various e-commerce business types may influence logistics operations, tax values, and management strategies etc.
“Incoterms” is an acronym standing for international commercial terms. A trademark of the International Chamber of Commerce, registered in several countries.
Harmonized System (HS) Code
Among industry classification systems, Harmonized System (HS) Codes are commonly used throughout the export process for goods.
§ Three Real Cases in e-Commerce business
Elements for Development O2O Business
- Quality Product Strategy
- Intellectual Property Marketing Strategy
- Retail Technology Strategy *
• iBeacon technology / AI / AR / social media platform data analytics - Customer Relationship Management Strategy*
• STAR CARD MEMBER