ResNet代码实现及原理——学习记录
引言
论文下载地址:
Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition
Pytorch版源代码下载地址:
https://github.com/pytorch/vision/blob/master/torchvision/models/resnet.py
ResNet
ResNet原理及具体细节不过多介绍,网上很多大佬总结的很好,我主要就是记录自己学习ResNet的过程,感觉是重点和难点的部分,话不多说进入正题。
一、ResNet核心
1、深度残差网络(Deep Residual Network)
刚看论文,就一系列问题:什么是深度残差网络?深度有多深?残差是什么?为什么用深度残差网络?能干什么?优点是什么?
深度残差网络就是它允许网络尽可能的加深。一般的网络,随着网络加深,训练集准确率会下降,但能够确定不是因为过拟合造成的(若是过拟合的情况,训练集应该准确率很高)。ResNet就是为了解决这个问题,克服由于网络深度加深而产生的学习效率变低与准确率无法有效提升的问题,让网络的性能不会随着深度增加而降低了。
2、残差结构
ResNet中使用了一种连接方式叫做"shortcut connection",顾名思义,就是抄近道的意思。
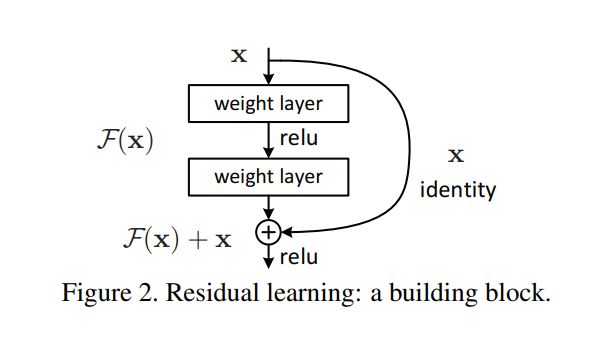
如上图,可以看到一个“弯弯的弧线“,这个就是所谓的”shortcut connection“,也是文中提到identity mapping。输入x直接从右边“抄近道”,输出是 H(x)=F(x)+x,所以残差指的就是F(x)部分 。
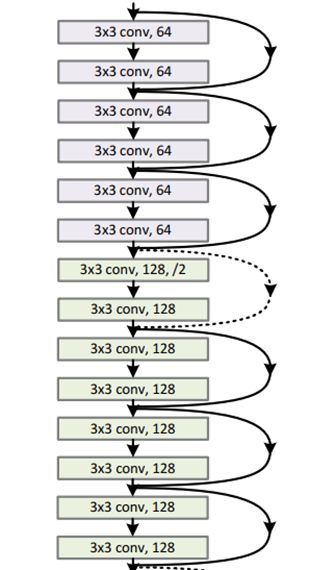
上图可见,有两种链接方式,实线的的connection部分(”第一个粉色矩形和第三个粉色矩形“)都是执行3x3x64的卷积,他们的channel数一致,所以采用计算方式:
y= F(x) + x
虚线的的connection部分(”第一个绿色矩形和第三个绿色矩形“)分别是3x3x64和3x3x128的卷积操作,他们的channel数不同(64和128),无法相加,那么就需要对 identity的通道数做一次修改。所以采用计算方式:
y=F(x)+Wx
实线connection对应代码中的:
out += identity
虚线connection对应代码中的:
if self.downsample is not None:
identity = self.downsample(x)
out += identity
3、两种残差块设计:
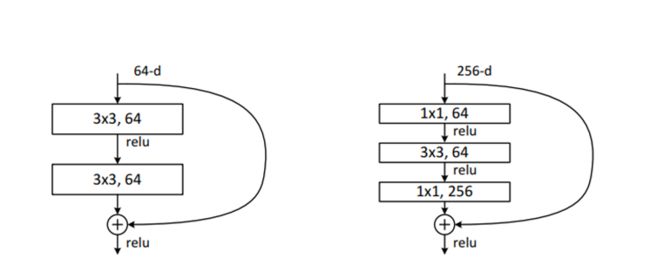
两种残差块结构分别针对ResNet18/34(左图)和ResNet50/101/152(右图),一般称整个结构为一个”building block“。
左图为基本的残差结构可以称为"basic block",右图为针对深层网络提出的block称为”bottleneck”。
basic block中包含两个卷积层,卷积核数量相同,卷积核均为3x3,输入输出均为64通道,可直接相加。该block主要使用在相对浅层网络,比如ResNet-34。
bottle neck的结构是前两组滤波核数量相同,第三层滤波核数量是前两组的4倍,第二层尺寸3x3,其余两层尺寸是1x1,主要目的就是为了降低参数的数目,第一个64通道数的1x1卷积把256维通道数(channel)降到64维通道,然后在最后通过一个256通道的1x1卷积恢复。
下面为两种block的代码:
# ResNet18、ResNet34:basic block
class BasicBlock(nn.Module):
expansion = 1
def __init__(
self,
inplanes,
planes,
stride=1,
downsample=None,
groups=1,
base_width=64,
dilation=1,
norm_layer=None):
super(BasicBlock, self).__init__()
if norm_layer is None:
norm_layer = nn.BatchNorm2d # Batch Normalization
if groups != 1 or base_width != 64:
raise ValueError('BasicBlock only supports groups=1 and base_width=64')
if dilation > 1:
raise NotImplementedError("Dilation > 1 not supported in BasicBlock")
# Both self.conv1 and self.downsample layers downsample the input when stride != 1
self.conv1 = conv3x3(inplanes, planes, stride)
self.bn1 = norm_layer(planes)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.conv2 = conv3x3(planes, planes)
self.bn2 = norm_layer(planes)
self.downsample = downsample
self.stride = stride
def forward(self, x):
identity = x
out = self.conv1(x)
out = self.bn1(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv2(out)
out = self.bn2(out)
if self.downsample is not None:
identity = self.downsample(x)
out += identity # F(x) + x
out = self.relu(out)
return out
# ResNet50、ResNet101 : bottleneck blcok
class Bottleneck(nn.Module):
expansion = 4
def __init__(
self,
inplanes,
planes,
stride=1,
downsample=None,
groups=1,
base_width=64,
dilation=1,
norm_layer=None):
super(Bottleneck, self).__init__()
if norm_layer is None:
norm_layer = nn.BatchNorm2d
width = int(planes * (base_width / 64.)) * groups
# Both self.conv2 and self.downsample layers downsample the input when stride != 1
self.conv1 = conv1x1(inplanes, width)
self.bn1 = norm_layer(width)
self.conv2 = conv3x3(width, width, stride, groups, dilation)
self.bn2 = norm_layer(width)
# 输出通道数由64变为256,故下面要乘self.expansion
self.conv3 = conv1x1(width, planes * self.expansion)
self.bn3 = norm_layer(planes * self.expansion)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.downsample = downsample
self.stride = stride
def forward(self, x):
identity = x
out = self.conv1(x)
out = self.bn1(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv2(out)
out = self.bn2(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv3(out)
out = self.bn3(out)
if self.downsample is not None:
identity = self.downsample(x)
out += identity
out = self.relu(out)
return out
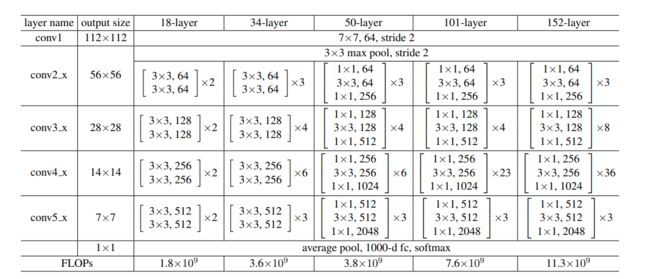
4、ResNet整体网络结构
上面一共提出了5中深度的ResNet,分别是18,34,50,101和152,首先看表2最左侧,我们发现所有的网络都分成5部分,分别是:conv1,conv2_x,conv3_x,conv4_x,conv5_x。
拿101-layer举例:首先有个输入7x7x64的卷积,然后经过3 + 4 + 23 + 3 = 33个building block,每个block为3层,所以有33 x 3 = 99层,最后有个fc层(用于分类),所以1 + 99 + 1 = 101层。101层网络仅仅指卷积或者全连接层,而激活层或者Pooling层并没有计算在内。
二、代码复现
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
__all__ = ['ResNet', 'resnet18', 'resnet34', 'resnet50', 'resnet101',
'resnet152', 'resnext50_32x4d', 'resnext101_32x8d',
'wide_resnet50_2', 'wide_resnet101_2']
model_urls = {
'resnet18': 'https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnet18-5c106cde.pth',
'resnet34': 'https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnet34-333f7ec4.pth',
'resnet50': 'https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnet50-19c8e357.pth',
'resnet101': 'https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnet101-5d3b4d8f.pth',
'resnet152': 'https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnet152-b121ed2d.pth',
'resnext50_32x4d': 'https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnext50_32x4d-7cdf4587.pth',
'resnext101_32x8d': 'https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnext101_32x8d-8ba56ff5.pth',
'wide_resnet50_2': 'https://download.pytorch.org/models/wide_resnet50_2-95faca4d.pth',
'wide_resnet101_2': 'https://download.pytorch.org/models/wide_resnet101_2-32ee1156.pth',
}
def conv3x3(in_planes, out_planes, stride=1, groups=1, dilation=1):
"""3x3 convolution with padding"""
return nn.Conv2d(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=3, stride=stride,
padding=dilation, groups=groups, bias=False, dilation=dilation)
def conv1x1(in_planes, out_planes, stride=1):
"""1x1 convolution"""
return nn.Conv2d(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=False)
class BasicBlock(nn.Module): # 一个BasicBlock对应于图1中的【】 【】后面乘几 就是说这种BasicBlock调用几次
expansion = 1
def __init__(self, inplanes, planes, stride=1, downsample=None, groups=1,
base_width=64, dilation=1, norm_layer=None):
super(BasicBlock, self).__init__()
if norm_layer is None:
norm_layer = nn.BatchNorm2d
if groups != 1 or base_width != 64:
raise ValueError('BasicBlock only supports groups=1 and base_width=64')
if dilation > 1:
raise NotImplementedError("Dilation > 1 not supported in BasicBlock")
# Both self.conv1 and self.downsample layers downsample the input when stride != 1
self.conv1 = conv3x3(inplanes, planes, stride)
self.bn1 = norm_layer(planes)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.conv2 = conv3x3(planes, planes)
self.bn2 = norm_layer(planes)
self.downsample = downsample
self.stride = stride
def forward(self, x):
identity = x # x 给自己先备份一份
out = self.conv1(x) # 对x做卷积
out = self.bn1(out) # 对x归一化
out = self.relu(out) # 对x用激活函数
out = self.conv2(out) # 对x做卷积
out = self.bn2(out) # 归一化
if self.downsample is not None:
identity = self.downsample(x)
out += identity # 这个是 对应图2中的弯曲的箭头连接
out = self.relu(out)
# 上面这些对应图1中的【】中括号里面的操作
return out
class Bottleneck(nn.Module):
# Bottleneck in torchvision places the stride for downsampling at 3x3 convolution(self.conv2)
# while original implementation places the stride at the first 1x1 convolution(self.conv1)
# according to "Deep residual learning for image recognition"https://arxiv.org/abs/1512.03385.
# This variant is also known as ResNet V1.5 and improves accuracy according to
# https://ngc.nvidia.com/catalog/model-scripts/nvidia:resnet_50_v1_5_for_pytorch.
expansion = 4
def __init__(self, inplanes, planes, stride=1, downsample=None, groups=1,
base_width=64, dilation=1, norm_layer=None):
super(Bottleneck, self).__init__()
if norm_layer is None:
norm_layer = nn.BatchNorm2d
width = int(planes * (base_width / 64.)) * groups
# Both self.conv2 and self.downsample layers downsample the input when stride != 1
self.conv1 = conv1x1(inplanes, width)
self.bn1 = norm_layer(width)
self.conv2 = conv3x3(width, width, stride, groups, dilation)
self.bn2 = norm_layer(width)
self.conv3 = conv1x1(width, planes * self.expansion)
self.bn3 = norm_layer(planes * self.expansion)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.downsample = downsample
self.stride = stride
def forward(self, x):
identity = x
out = self.conv1(x)
out = self.bn1(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv2(out)
out = self.bn2(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv3(out)
out = self.bn3(out)
if self.downsample is not None:
identity = self.downsample(x)
out += identity
out = self.relu(out)
return out
class ResNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, block, layers, num_classes=6, zero_init_residual=False,
groups=1, width_per_group=64, replace_stride_with_dilation=None,
norm_layer=None):
super(ResNet, self).__init__()
if norm_layer is None:
norm_layer = nn.BatchNorm2d
self._norm_layer = norm_layer
self.inplanes = 64
self.dilation = 1
if replace_stride_with_dilation is None:
# each element in the tuple indicates if we should replace
# the 2x2 stride with a dilated convolution instead
replace_stride_with_dilation = [False, False, False]
if len(replace_stride_with_dilation) != 3:
raise ValueError("replace_stride_with_dilation should be None "
"or a 3-element tuple, got {}".format(replace_stride_with_dilation))
self.groups = groups
self.base_width = width_per_group
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, self.inplanes, kernel_size=7, stride=2, padding=3,
bias=False)
self.bn1 = norm_layer(self.inplanes)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.maxpool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1)
self.layer1 = self._make_layer(block, 64, layers[0]) # 对应着con2_x
self.layer2 = self._make_layer(block, 128, layers[1], stride=2,
dilate=replace_stride_with_dilation[0]) # 对应着con3_x
self.layer3 = self._make_layer(block, 256, layers[2], stride=2,
dilate=replace_stride_with_dilation[1]) # 对应着con4_x
self.layer4 = self._make_layer(block, 512, layers[3], stride=2,
dilate=replace_stride_with_dilation[2]) # 对应着con5_x
self.avgpool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, 1))
self.fc = nn.Linear(512 * block.expansion, num_classes)
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out', nonlinearity='relu')
elif isinstance(m, (nn.BatchNorm2d, nn.GroupNorm)):
nn.init.constant_(m.weight, 1)
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
# Zero-initialize the last BN in each residual branch,
# so that the residual branch starts with zeros, and each residual block behaves like an identity.
# This improves the model by 0.2~0.3% according to https://arxiv.org/abs/1706.02677
if zero_init_residual:
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, Bottleneck):
nn.init.constant_(m.bn3.weight, 0)
elif isinstance(m, BasicBlock):
nn.init.constant_(m.bn2.weight, 0)
# blocks对应着表1中的 [2, 2, 2, 2]之 中的2 这个数 。它由resnet类型决定 block 对应于Bottleneck还是BasicBlock残差块
def _make_layer(self, block, planes, blocks, stride=1, dilate=False):
norm_layer = self._norm_layer
downsample = None
previous_dilation = self.dilation
if dilate:
self.dilation *= stride
stride = 1
if stride != 1 or self.inplanes != planes * block.expansion:
downsample = nn.Sequential(
conv1x1(self.inplanes, planes * block.expansion, stride),
norm_layer(planes * block.expansion),
)
layers = []
layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes, stride, downsample, self.groups,
self.base_width, previous_dilation, norm_layer))
self.inplanes = planes * block.expansion
for _ in range(1, blocks):
layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes, groups=self.groups,
base_width=self.base_width, dilation=self.dilation,
norm_layer=norm_layer))
return nn.Sequential(*layers)
def _forward_impl(self, x):
# See note [TorchScript super()]
x = self.conv1(x) # 第一次做卷积 对应图1中conv1 x shape [1 64 112 112]
x = self.bn1(x) # 归一化处理了 x shape [1 64 112 112]
x = self.relu(x) # 归一化处理了 x shape [1 64 112 112]
x = self.maxpool(x) # 对应图1中的 conv2_x的3x3 maxpool x shape [1 64 56 56]
x = self.layer1(x)
x = self.layer2(x)
x = self.layer3(x)
x = self.layer4(x)
x = self.avgpool(x)
x = torch.flatten(x, 1)
x = self.fc(x)
return x
def forward(self, x):
return self._forward_impl(x) # resnet处理的主函数。x是输入的图像,待处理数据
def _resnet(arch, block, layers, pretrained, progress, **kwargs):
model = ResNet(block, layers, **kwargs)
return model
def resnet18(pretrained=False, progress=True, **kwargs):
r"""ResNet-18 model from
`"Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition" `_
Args:
pretrained (bool): If True, returns a model pre-trained on ImageNet
progress (bool): If True, displays a progress bar of the download to stderr
"""
return _resnet('resnet18', BasicBlock, [2, 2, 2, 2], pretrained, progress,
**kwargs)
def resnet34(pretrained=False, progress=True, **kwargs):
r"""ResNet-34 model from
`"Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition" `_
Args:
pretrained (bool): If True, returns a model pre-trained on ImageNet
progress (bool): If True, displays a progress bar of the download to stderr
"""
return _resnet('resnet34', BasicBlock, [3, 4, 6, 3], pretrained, progress,
**kwargs)
def resnet50(pretrained=False, progress=True, **kwargs):
r"""ResNet-50 model from
`"Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition" `_
Args:
pretrained (bool): If True, returns a model pre-trained on ImageNet
progress (bool): If True, displays a progress bar of the download to stderr
"""
return _resnet('resnet50', Bottleneck, [3, 4, 6, 3], pretrained, progress,
**kwargs)
def resnet101(pretrained=False, progress=True, **kwargs):
r"""ResNet-101 model from
`"Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition" `_
Args:
pretrained (bool): If True, returns a model pre-trained on ImageNet
progress (bool): If True, displays a progress bar of the download to stderr
"""
return _resnet('resnet101', Bottleneck, [3, 4, 23, 3], pretrained, progress,
**kwargs)
def resnet152(pretrained=False, progress=True, **kwargs):
r"""ResNet-152 model from
`"Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition" `_
Args:
pretrained (bool): If True, returns a model pre-trained on ImageNet
progress (bool): If True, displays a progress bar of the download to stderr
"""
return _resnet('resnet152', Bottleneck, [3, 8, 36, 3], pretrained, progress,
**kwargs)
def resnext50_32x4d(pretrained=False, progress=True, **kwargs):
r"""ResNeXt-50 32x4d model from
`"Aggregated Residual Transformation for Deep Neural Networks" `_
Args:
pretrained (bool): If True, returns a model pre-trained on ImageNet
progress (bool): If True, displays a progress bar of the download to stderr
"""
kwargs['groups'] = 32
kwargs['width_per_group'] = 4
return _resnet('resnext50_32x4d', Bottleneck, [3, 4, 6, 3],
pretrained, progress, **kwargs)
def resnext101_32x8d(pretrained=False, progress=True, **kwargs):
r"""ResNeXt-101 32x8d model from
`"Aggregated Residual Transformation for Deep Neural Networks" `_
Args:
pretrained (bool): If True, returns a model pre-trained on ImageNet
progress (bool): If True, displays a progress bar of the download to stderr
"""
kwargs['groups'] = 32
kwargs['width_per_group'] = 8
return _resnet('resnext101_32x8d', Bottleneck, [3, 4, 23, 3],
pretrained, progress, **kwargs)
def wide_resnet50_2(pretrained=False, progress=True, **kwargs):
r"""Wide ResNet-50-2 model from
`"Wide Residual Networks" `_
The model is the same as ResNet except for the bottleneck number of channels
which is twice larger in every block. The number of channels in outer 1x1
convolutions is the same, e.g. last block in ResNet-50 has 2048-512-2048
channels, and in Wide ResNet-50-2 has 2048-1024-2048.
Args:
pretrained (bool): If True, returns a model pre-trained on ImageNet
progress (bool): If True, displays a progress bar of the download to stderr
"""
kwargs['width_per_group'] = 64 * 2
return _resnet('wide_resnet50_2', Bottleneck, [3, 4, 6, 3],
pretrained, progress, **kwargs)
def wide_resnet101_2(pretrained=False, progress=True, **kwargs):
r"""Wide ResNet-101-2 model from
`"Wide Residual Networks" `_
The model is the same as ResNet except for the bottleneck number of channels
which is twice larger in every block. The number of channels in outer 1x1
convolutions is the same, e.g. last block in ResNet-50 has 2048-512-2048
channels, and in Wide ResNet-50-2 has 2048-1024-2048.
Args:
pretrained (bool): If True, returns a model pre-trained on ImageNet
progress (bool): If True, displays a progress bar of the download to stderr
"""
kwargs['width_per_group'] = 64 * 2
return _resnet('wide_resnet101_2', Bottleneck, [3, 4, 23, 3],
pretrained, progress, **kwargs)
# 测试运行代码
def test():
net = resnet34()
img = torch.randn(1, 3, 224, 224)
y = net(img)
print(y.size())
if __name__ == '__main__':
test()
三、参考链接
1、https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/263526658
2、https://note.youdao.com/ynoteshare/index.html?id=5a7dbe1a71713c317062ddeedd97d98e&type=note&_time=1647396402400?auto
3、https://blog.csdn.net/lanran2/article/details/79057994
4、https://blog.csdn.net/beautiful77moon/article/details/107144874?ops_request_misc=&request_id=&biz_id=102&utm_term=resnet%E4%BB%A3%E7%A0%81&utm_medium=distribute.pc_search_result.none-task-blog-2allsobaiduweb~default-6-107144874.142v2pc_search_result_control_group,143v4register&spm=1018.2226.3001.4187
5、https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_44791964/article/details/102790260?ops_request_misc=%257B%2522request%255Fid%2522%253A%2522164752205016781685357535%2522%252C%2522scm%2522%253A%252220140713.130102334.pc%255Fblog.%2522%257D&request_id=164752205016781685357535&biz_id=0&utm_medium=distribute.pc_search_result.none-task-blog-2blogfirst_rank_ecpm_v1~rank_v31_ecpm-1-102790260.nonecase&utm_term=resnet&spm=1018.2226.3001.4450